topic
C + + MFC based laboratory room management system
Catalogue
2. Introduction to development technology
2.1 introduction to VC + + 6.0 development platform
2.2 introduction to database system
3. System requirements analysis
3.2 analysis of design objectives
3.3 security requirements analysis
3.4 development and operation environment
3.5 system feasibility analysis
4.1.1 master control end planning
4.2 design of functional module structure
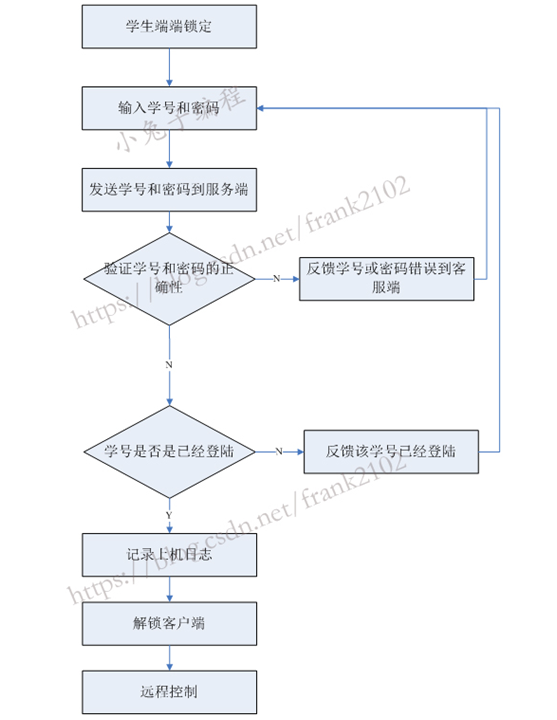
4.3 system operation flow chart
5.1.2 program related code analysis
5.2 design of student side full screen transparent login window
5.2.2 program related code analysis
5.3.2 program related code analysis
5.4 background thread design of student monitoring server
5.4.2 program related code analysis
5.5 system restoration failure detection
5.5.2 program related code analysis
5.6 design of multithreaded master
5.6.2 program related code analysis
5.7 implementation of Excel table import and export
5.7.2 program related code analysis
5.8 implementation of single program example
5.7.2 program related code analysis
5.9 implementation of host list
5.10 implementation of Remote Desktop
5.11 implementation of configuration information registry storage
5.12 realization of progress bar under status bar
6. System test and performance analysis
Thousands of words are omitted here
Outline design
Laboratory room management system is a typical C/S mode application, including student terminal and master terminal.
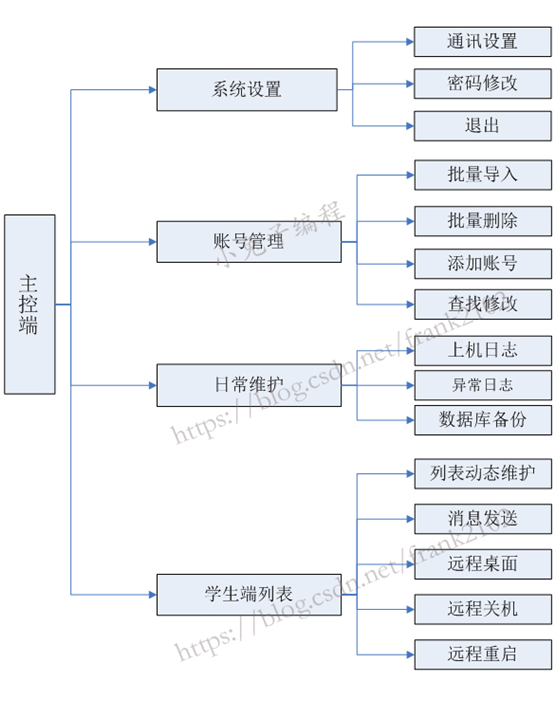
Master planning
The main control terminal is responsible for the verification of the login of the student terminal and the remote control of the student terminal. The specific functional modules are as follows:
(1) System setting module
1) Communication setting: the communication port setting between the main control end and the controlled end.
2) Password modification: modify the unlocking password of the master control terminal.
(2) Account management:
1) Add account: the required fields are: student number, name, class and password.
2) Account modification: modify the specified account. If the student forgets the password, the administrator can modify the password.
3) Batch import: you can import Excel table data containing account information into the database.
4) Batch delete: you can batch delete the queried account numbers.
(3) Routine maintenance:
1) Computer log: record the log of each login and logout of students.
2) Exception log: record the exception log of the student side, such as the failure of the restore card.
3) Database backup: the administrator can backup data regularly
(4) Student side list:
1) List dynamic maintenance: manage student connections and dynamically update them on the list.
2) Message sending: Send a message to the selected student terminal.
3) Remote desktop: Remote Desktop Control for a single student terminal.
4) Remote shutdown: issue shutdown command to the selected student terminal.
5) Remote restart: Send a shutdown command to the selected student terminal.
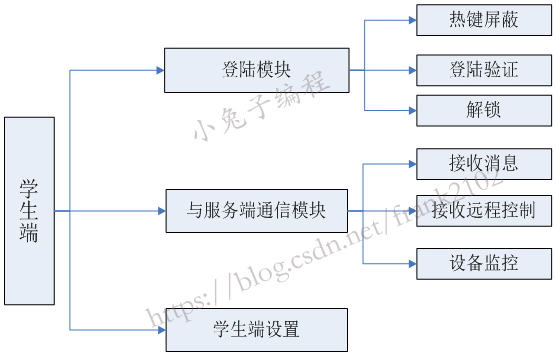
Student end planning
The student terminal is responsible for locking the screen of the student computer and executing the commands of the main control terminal. The specific functional modules are as follows:
(1) Login module:
1) Hot key shielding: shield the relevant hot keys when the system starts, lock the screen and display the login box.
2) Login verification: send the student number and password to the server. If the verification is successful, it will be unlocked automatically.
3) Administrator unlocking: the administrator can unlock the student terminal by using the unlocking password.
(2) Communication module with server:
1) Receive message: receive the message from the server and automatically prompt on the desktop.
2) Receive remote control: respond to various controls required by the server.
3) Exception monitoring: send the exceptions on the student side to the server.
4) Change Password: students change their login password.
(3) Student side setting: it can only be used in the management mode. Set the communication mode and unlock password.
Functional module structure design
System operation flow chart
System database design
Data sheet design (part)
For the laboratory room management system, the main function is to control the computer on the student side, and the database design is relatively simple. The system adopts SQL 2000 database, and the name of the system database is db_LabMS, database db_LabMS includes 3 data sheets. The following is a brief description of the database and the structure of the data table.
(1) User data sheet
The user saves the account information of the system user. The data table is named "student", and the structure is shown in table 4-1.
Table 4-1 user table (student)
| Serial number | Listing | data type | length | identification | Primary key | Allow null | Default value | explain |
| 1 | s_id | int | 4 | yes |
| no |
| Automatic numbering ID |
| 2 | s_xh | nvarchar | 12 |
| yes | no |
| Student number |
| 3 | s_name | nvarchar | 8 |
|
| no |
| name |
| 4 | s_pwd | nvarchar | 12 |
|
| no |
| password |
| 5 | s_class | nvarchar | 30 |
|
| no |
| class |
(2) Data sheet of computer operation record
It is used to save the data recorded by students on the computer. The data table is named "log", and the structure is shown in Table 4-2.
Table 4-2 data sheet of computer log
| Serial number | Listing | data type | length | identification | Primary key | Allow null | Default value | explain |
| 1 | l_id | int | 4 | yes | yes | no |
| Automatic numbering ID |
| 2 | s_xh | nvarchar | 12 |
|
| no |
| Student number |
| 3 | l_type | nvarchar | 8 |
|
| no |
| type |
| 4 | l_time | datetime | 8 |
|
| no | (getdate()) | time |
| 5 | l_pc | nvarchar | 20 |
|
| no |
| Pc name |
(3) Exception data sheet
It is used to save the abnormal information of the student machine. The data table is named "exception", and the structure is shown in table 4-3.
Table 4-3: exception
| Serial number | Listing | data type | length | identification | Primary key | Allow null | Default value | explain |
| 1 | e_id | int | 4 | yes | yes | no |
| Automatic numbering ID |
| 2 | e_type | nvarchar | 50 |
|
| yes |
| Exception type |
| 3 | e_state | nvarchar | 8 |
|
| yes | (N 'not processed') | state |
| 4 | e_pc | nvarchar | 20 |
|
| yes |
| Pc name |
| 5 | e_time | datetime | 8 |
|
| yes | (getdate()) | Abnormal occurrence time |
(4) Host list data sheet
It is used to save the list of currently logged in student computers. The data table is named "list", and the structure is shown in table 4-4.
Table 4-4 list of hosts
| Serial number | Listing | data type | length | identification | Primary key | Allow null | Default value | explain |
| 1 | l_xh | nvarchar | 12 |
|
| yes |
| Student number |
| 2 | l_mac | nvarchar | 12 |
|
| yes |
| MAC address |
| 3 | l_pc | nvarchar | 20 |
|
| yes |
| PC name |
| 4 | l_time | datetime | 8 |
|
| yes | (getdate()) | Landing time |
View design (part)
From the perspective of users, a view is to view the data in the database from a specific perspective. From the inside of the database system, the view is composed of data in one or more tables. From the outside of the database system, the view is like a table. The general operations that can be performed on the table can be applied to the view, such as query, insert, modify, delete, etc. [3]
The logview view creation statement of the system is as follows:
CREATE VIEW dbo.logview AS SELECT dbo.[log].l_time, dbo.[log].s_xh, dbo.student.s_name, dbo.[log].l_type, dbo.[log].l_pc, dbo.student.s_class FROM dbo.[log] INNER JOIN dbo.student ON dbo.[log].s_xh = dbo.student.s_xh
Trigger design (part)
A trigger is a special stored procedure , its execution is not called by the program or started manually, but triggered by events. For example, when a table is operated (insert, delete, update), it will be activated for execution. [4] When inserting into the log table, it will trigger the update of the list table, which saves the current host list.
Trigger trig_ The updatelist creation statement is as follows:
CREATE TRIGGER trig_updatelist ON dbo.[log] FOR insert AS if exists(select l_mac from inserted where l_mac not in (select l_mac from [list])) begin insert into [list](l_pc,l_mac,l_xh) select l_pc,l_mac,s_xh from inserted end else begin delete [list] where l_mac=(select l_mac from inserted) end
System implementation (part)
HOOK message HOOK design
5.1.1 general
When the student terminal starts up, it is necessary to lock the screen, shield the system hotkeys, and protect the lock screen program from being closed. To shield the system hotkey, HOOK technology needs to be used. HOOK is a platform of Windows message processing mechanism. The application program can set subroutines on it to monitor some messages of the specified Window, and the monitored Window can be created by other processes. [5] When the message arrives, it is processed before the target Window processing function. The HOOK mechanism allows the application to intercept and process Window messages or specific events. Through HOOK technology, some hot keys such as ALT+F4 and ALT+ESC can be shielded, which can effectively protect the screen lock program.
5.1.2 program related code analysis
Generally speaking, the system level hook must be a DLL. The following is a code fragment of a keyboard hook DLL (TaskKeyHook.dll):
//Header file
//TaskKeyHook.h
//
#define DLLIMPORT __declspec(dllimport)
DLLIMPORT BOOL DisableTaskKeys(BOOL bEnable, BOOL bBeep);
DLLIMPORT BOOL AreTaskKeysDisabled();
//Implementation file
// TaskKeyHook.cpp
//
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0500 // for KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT
#include <afxwin.h> // MFC core and standard components
#define DLLEXPORT __declspec(dllexport)
//
// App (DLL) object
//
class CTaskKeyHookDll : public CWinApp {
public:
CTaskKeyHookDll() { }
~CTaskKeyHookDll() { }
} MyDll;
// The following code indicates that this part is shared among all instances of this DLL
// Low level keyboard hooks must be system level hooks
//
#pragma data_seg (".mydata")
HHOOK g_hHookKbdLL = NULL; // Hook handle
BOOL g_bBeep = FALSE; // Beep when illegal key is pressed
#pragma data_seg ()
#pragma comment(linker, "/SECTION:.mydata,RWS") / / tell the linker: create a data sharing segment
//
// Low level keyboard hook
// Intercepting task conversion key: return directly without passing
//
LRESULT CALLBACK MyTaskKeyHookLL(int nCode, WPARAM wp, LPARAM lp)
{
KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT *pkh = (KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT *) lp;
if (nCode==HC_ACTION) {
BOOL bCtrlKeyDown =
GetAsyncKeyState(VK_CONTROL)>>((sizeof(SHORT) * 8) - 1);
if ((pkh->vkCode==VK_ESCAPE && bCtrlKeyDown) || // Ctrl+Esc
// Alt+TAB
(pkh->vkCode==VK_TAB && pkh->flags & LLKHF_ALTDOWN) ||
// Alt+Esc
(pkh->vkCode==VK_ESCAPE && pkh->flags & LLKHF_ALTDOWN)||
(pkh->vkCode==VK_LWIN || pkh->vkCode==VK_RWIN)) { // opening menu
if (g_bBeep && (wp==WM_SYSKEYDOWN||wp==WM_KEYDOWN))
MessageBeep(0); // Beep
return 1; // No longer pass to CallNextHookEx, return directly
}
}
return CallNextHookEx(g_hHookKbdLL, nCode, wp, lp);
}
// Is the task key sequence masked - that is, is the keyboard hook installed?
// Note: it is assumed that no other hook does the same thing
//
DLLEXPORT BOOL AreTaskKeysDisabled()
{
return g_hHookKbdLL != NULL;
}
// Mask task key: install low-level keyboard mechanism
// Returns the current mask flag (TRUE/FALSE)
//
DLLEXPORT BOOL DisableTaskKeys(BOOL bDisable, BOOL bBeep)
{
if (bDisable) {
if (!g_hHookKbdLL) {
g_hHookKbdLL = SetWindowsHookEx(WH_KEYBOARD_LL,
MyTaskKeyHookLL, MyDll.m_hInstance, 0);
}
} else if (g_hHookKbdLL != NULL) {
UnhookWindowsHookEx(g_hHookKbdLL);
g_hHookKbdLL = NULL;
}
g_bBeep = bBeep;
return AreTaskKeysDisabled();
} TaskKeyHook outputs two functions: DisableTaskKeys and aretaskkeys disabled. The former is installed with WH_KEYBOARD_LL hook; The latter determines whether the hook is installed. The processing idea of this keyboard hook is to intercept hotkeys such as Alt+Tab, Ctrl+Esc, Alt+Esc and Windows key.
Design of full screen transparent login form for students
5.2.1 general
Once the student terminal is started, it will automatically lock the student machine in full screen. The login interface of student end lock screen is shown in Figure 5-1. Its implementation principle is realized through two dialog boxes. The parent dialog box realizes the full screen transparent form, and then the sub dialog box (login box) pops up. The login box hides the border and fills the background with a brush.
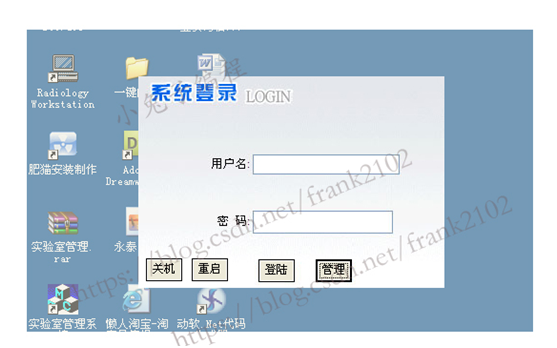
Figure 5-1 main window of laboratory room management system
5.2.2 program related code analysis
Main code fragments of full screen transparent login form:
// ClientDlg.cpp : implementation file
void CClientDlg::OnFullScreen()
{
LONG style = GetWindowLong(m_hWnd, GWL_STYLE); //Get window style
::ShowWindow(m_hWnd, SW_MAXIMIZE);
style = GetWindowLong(m_hWnd, GWL_STYLE);
style &= ~(WS_DLGFRAME | WS_THICKFRAME);
SetWindowLong(m_hWnd, GWL_STYLE, style); //Set window style
int cx = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXSCREEN);
int cy = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYSCREEN);
::SetWindowPos(m_hWnd, HWND_TOPMOST, -1, -1, cx+3, cy+3, SWP_FRAMECHANGED);//Full screen display
::InvalidateRect(m_hWnd,NULL,TRUE); //Window background to be erased
SetWindowLong(this->GetSafeHwnd(),GWL_EXSTYLE,
GetWindowLong(this->GetSafeHwnd(),GWL_EXSTYLE)^0x80000); //Windows join WS_EX_LAYERED extended attribute
HINSTANCE hInst = LoadLibrary("User32.DLL");
if (hInst)
{
typedef BOOL (WINAPI *MYFUNC)(HWND,COLORREF,BYTE,DWORD);
MYFUNC fun = NULL;
fun = (MYFUNC)GetProcAddress(hInst,"SetLayeredWindowAttributes"); //Gets the pointer to the SetLayeredWindowAttributes function
if (fun)
fun(this->GetSafeHwnd(),0,125,2); //Set the window to translucent
FreeLibrary(hInst);
}
CTaskKeyMgr::Disable(CTaskKeyMgr::ALL, TRUE); //Using Hook tool class to realize hot key shielding
CLoginDlg dlg=new CLoginDlg();
dlg.DoModal(); //Pop up the Mode dialog box and wait for the user to output
CTaskKeyMgr::Disable(CTaskKeyMgr::ALL, FALSE); //Restore all prohibited things
}Main code snippet of login box:
// LoginDlg.cpp : implementation file
//
//Fill background
void CLoginDlg::OnPaint()
{
CPaintDC dc(this); // device context for painting
CRect rect;
GetClientRect(&rect);
CDC dcMem;
dcMem.CreateCompatibleDC(&dc);
CBitmap bmpBackground;
bmpBackground.LoadBitmap(IDB_BITMAP1);
BITMAP bitmap;
bmpBackground.GetBitmap(&bitmap);
CBitmap *pbmpOld=dcMem.SelectObject(&bmpBackground);
dc.StretchBlt(0,0,rect.Width(),rect.Height(),&dcMem,0,0,
bitmap.bmWidth,bitmap.bmHeight,SRCCOPY);
}
void CLoginDlg::OnLogin()
{
// TODO: Add your control notification handler code here
UpdateData(true);
if ((m_uid == "")||(m_pwd == "")) //If the user name is empty
{
MessageBoxA("User name or password cannot be empty");
GetDlgItem(IDC_UID)->SetFocus();
return;
}
else
{
if (m_uid.Find(" ")!=-1)
{
MessageBoxA("The user name cannot contain spaces");
GetDlgItem(IDC_UID)->SetFocus();
return;
}else
if (m_pwd.Find(" ")!=-1)
{
MessageBoxA("The password cannot contain spaces");
GetDlgItem(IDC_PWD)->SetFocus();
return;
}
}
//Send the user name and password to the server for authentication
if (CScoketMgr::SendLogin(m_uid,m_pwd))
{
CDialog::OnCancel();
}
}
BOOL CLoginDlg::PreTranslateMessage(MSG* pMsg)
{
// Shield the RETURN, PAUSE and ESCAPE keys to prevent the login box from being closed
if (pMsg->message==WM_KEYDOWN&&pMsg->wParam==VK_RETURN)
{
return TRUE;
}
if (pMsg->message==WM_KEYDOWN&&pMsg->wParam==VK_PAUSE)
{
return TRUE;
}
if (pMsg->message==WM_KEYDOWN&&pMsg->wParam==VK_ESCAPE)
{
return TRUE;
}
return CDialog::PreTranslateMessage(pMsg);
}
void CLoginDlg::OnClose()
{
// Prevent the login box from being closed
return;
}
void CLoginDlg::OnUnlock()
{
// Unlock
UpdateData(true);
CMD5 md5T;
if (md5T.MD5(m_pwd)==theApp.unlockpwd) //Verify unlock password
OnCancel();
}
Thousands of words are omitted here
Resource download
Complete source program + database + paper + instructions for use download: https://download.csdn.net/download/frank2102/19414729