1. Ajax asynchronous interaction
1.1 basic configuration
1.1.1 Maven configuration
-
By default, spring MVC uses MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter to convert json data, which needs to be added
jackson's bag; Use < MVC: annotation driven / >
-
maven configuration
<dependencies> <!--springMVC coordinate--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!--servlet coordinate--> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!--jsp coordinate--> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.8</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId> <version>2.9.8</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
1.1.2 jquery
-
Download jquery: Jquery download address
-
Configure static resource access: in spring MVC XML configuration
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--Configure annotation scanning--> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.knightzz"/> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!-- Used to resolve the view name, /pages/success.jsp => Direct use success that will do--> <property name="prefix" value="/pages/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> <!-- Processor adapter, Enhanced functionality, support json Reading and writing--> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> <!--stay springmvc Open in configuration file DefaultServlet Processing static resources--> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> </beans>
1.2 @RequestBody
1.2.1 basic introduction
-
This annotation is used for the formal parameter declaration of the Controller's method. When ajax is used to submit and specify the contentType as json, the
The HttpMessageConverter interface is converted to the corresponding POJO object.
1.2.2 code case
-
ajap.jsp
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: knightzz98 Date: 2022/2/2 Time: 16:57 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>test Ajax</title> </head> <body> <script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/js/jquery-3.5.1.js"></script> <%--ajax Asynchronous interaction--%> <button id="btn1">ajax Asynchronous commit</button> <script> $("#btn1").click(function () { let url = '${pageContext.request.contextPath}/ajaxRequest'; let data = '[{"id":1,"username":"Zhang San"},{"id":2,"username":"Li Si"}]'; $.ajax({ type: 'POST', url: url, data : data, contentType : 'application/json;charset=utf-8', success: function (resp) { alert(JSON.stringify(resp)); } }) }) </script> </body> </html> -
AjaxController
package cn.knightzz.controller; import cn.knightzz.entity.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import java.util.List; /** * @author Wang Tianci * @title: AjaxController * @projectName springmvc-apply-02 * @description: * @website http://knightzz.cn/ * @github https://github.com/knightzz1998 * @date 2022/2/2 16:55 */ @Controller public class AjaxController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajaxRequest") public String ajaxRequest(@RequestBody List<User> list) { System.out.println(list); return "success"; } }
1.3 @ResponseBody
-
This annotation is used to convert the object returned by the Controller method into a number in the specified format through the HttpMessageConverter interface
For example, json,xml, etc., respond to the client through Response.
-
AjaxController
package cn.knightzz.controller; import cn.knightzz.entity.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.util.List; @Controller public class AjaxController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajaxRequest") @ResponseBody public List<User> ajaxRequest(@RequestBody List<User> list) { System.out.println(list); return list; } }
2. Restful
2.1 basic introduction
-
Restful provides an architecture, a set of design criteria, not a set of constraints. Mainly used
For the interactive software between client and server, the software designed based on this style can be simpler, more hierarchical and easier to implement the cache machine
System, etc. -
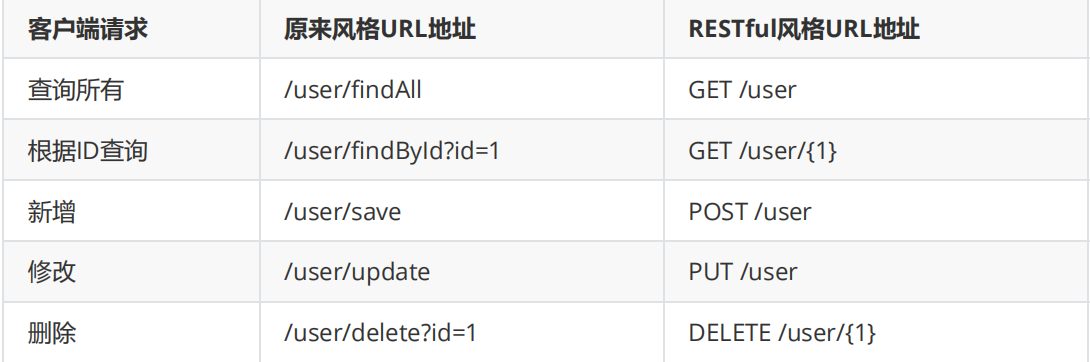
Restful style requests use "url + request method" to represent the purpose of a request. Four actions in the HTTP protocol represent the operation mode
The words are as follows:- GET: Read
- POST: Create
- PUT: Update
- Delete: delete
-
Comparison of different styles
2.2 code implementation
-
@PathVariable is used to receive the value of placeholder in RESTful style request address
-
@RestController Restful style is mostly used for front-end and back-end separated project development. The front end interacts asynchronously with the server through ajax. Our processor usually returns json data, so @ RestController is used to replace the two annotations @ Controller and @ ResponseBody.
-
Code case
package cn.knightzz.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; /** * @author Wang Tianci * @title: RestFulController * @projectName springmvc-apply-02 * @description: * @website http://knightzz.cn/ * @github https://github.com/knightzz1998 * @date 2022/2/2 20:32 */ @RestController public class RestFulController { @GetMapping(value = "/user/{id}") public String get(@PathVariable Integer id){ return "get : " + id; } @PostMapping(value = "/user") public String post(){ return "post"; } @PutMapping(value = "/user") public String put() { return "put"; } @DeleteMapping(value = "/user/{id}") public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) { return "delete: "+ id; } }
3. File upload
3.1 overview of file upload
-
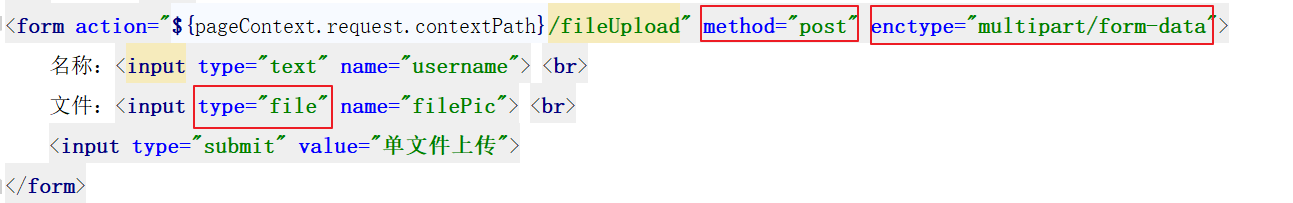
Form item type = "file"
-
Submission method of form method = "POST"
-
The enctype attribute of a form is a multipart form, enctype = "multipart / form data"“
3.2 file upload principle
- When the form is modified to a multi part form, request Getparameter() will fail.
- When the enctype value of the form is application/x-www-form-urlencoded,
- The format of the body content of the form is: name = value & name = value. When the enctype value of the form is mutilpart / form data, the body content of the request becomes a multi part form:
3.3 single file upload
3.3.1 maven configuration
<!-- File upload -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
3.3.2 configuration file upload parser
-
In spring context XML add the following configuration
<!--File upload parser--> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <!-- Set the maximum value of file upload to 5 MB,5*1024*1024 --> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="5242880"></property> <!-- Set the maximum value to be written into memory during file upload. If it is less than this parameter, no temporary file will be generated. The default value is 10240 --> <property name="maxInMemorySize" value="40960"></property> </bean>
3.3.3 writing file upload code
-
upload.jsp
<h3>Single file upload</h3> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/fileUpload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> name:<input type="text" name="username"> <br> File:<input type="file" name="filePic"> <br> <input type="submit" value="Single file upload"> </form> -
UploadController
package cn.knightzz.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; @Controller public class UploadController { /** * Upload document * @param username * @param filePic It needs to be consistent with the name of the front end of the uploaded file * @return * @throws IOException */ @RequestMapping("/fileUpload") public String upload(String username, MultipartFile filePic) throws IOException { System.out.println("username = " + username); String originalFilename = filePic.getOriginalFilename(); System.out.println(originalFilename); // Save file filePic.transferTo(new File("k://" + originalFilename)); return "success"; } }
3.4 multi file upload
-
upload.jsp
<h3>Multi file upload</h3> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/fileUpload2" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> name:<input type="text" name="username"> <br> Document 1:<input type="file" name="filePic"> <br> Document 2:<input type="file" name="filePic"> <br> <input type="submit" value="Multi file upload"> </form> -
UploadController
@RequestMapping("/fileUpload2") public String upload2(String username, MultipartFile[] filePic) throws IOException { System.out.println("username = " + username); for (MultipartFile multipartFile : filePic) { String originalFilename = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename(); System.out.println(originalFilename); // Save file multipartFile.transferTo(new File("k://" + originalFilename)); } return "success"; }
4. Exception handling
4.1 basic methods
-
In Java, there are generally two ways to handle exceptions:
- One is the current method capture processing (try catch), which will cause the coupling of business code and exception handling code.
- The other is not to handle it, but to throw it to the caller, who then throws it to its caller, that is, always
Throw it up.
-
Based on this method, the exception handling mechanism of spring MVC is derived.
-
The dao, service and controller of the system are thrown upward through the throw exception, and finally controlled by the spring MVC front end
The controller is handed over to the exception handler for exception handling, as shown in the following figure: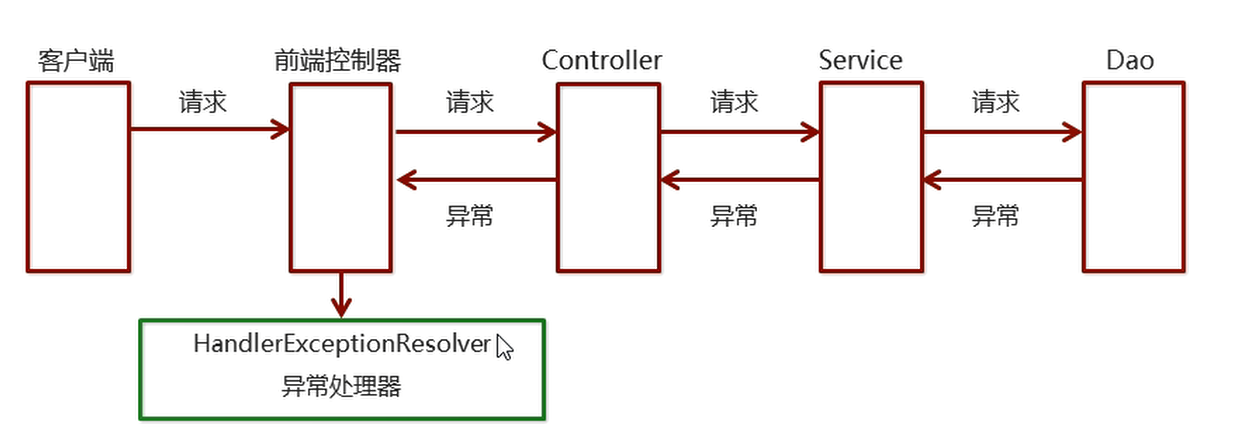
4.2 custom exception handler
4.2.1 basic steps
- Create an exception handler class to implement HandlerExceptionResolver
- Configure exception handler
- Write exception page
- Test abnormal jump
4.2.2 create exception handler
-
GlobalExceptionResolver
package cn.knightzz.exception; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class GlobalExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver { @Override public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object handler, Exception ex) { ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("error", ex.getMessage()); modelAndView.setViewName("error"); return modelAndView; } }
4.2.3 configuring exception handlers
-
annotation
@Component public class GlobalExecptionResovler implements HandlerExceptionResolver {} -
Or in spring MVC XML configuration
<!-- Exception global handler class --> <bean id="globalExceptionResolver" class="cn.knightzz.exception.GlobalExceptionResolver" />
4.2.4 configuration exception page
-
Configure exception page
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: knightzz98 Date: 2022/2/2 Time: 21:44 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Exception page</title> </head> <body> <h3>This is a final exception display page</h3> <p>${error}</p> </body> </html>
4.2.5 writing test code
-
TestController
package cn.knightzz.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/testException") public String testException() { int i = 1 / 0; return "success"; } }
4.2.6 web exception configuration
- On the web XML configuration add
<!--Handling 500 exceptions-->
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/500.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<!--Handling 404 exceptions-->
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/404.jsp</location>
</error-page>
5. Interceptor
5.1 interceptor overview
- The interceptor of Spring MVC is similar to the Filter in Servlet development, which is used to preprocess and post process the processor.
The interceptors are connected into a chain in a certain order, which is called interceptor chain. - When accessing the intercepted method or field, the interceptors in the interceptor chain will be called in the order they were previously defined. Interceptor is also the concrete implementation of AOP idea.
5.2 interceptors and filters
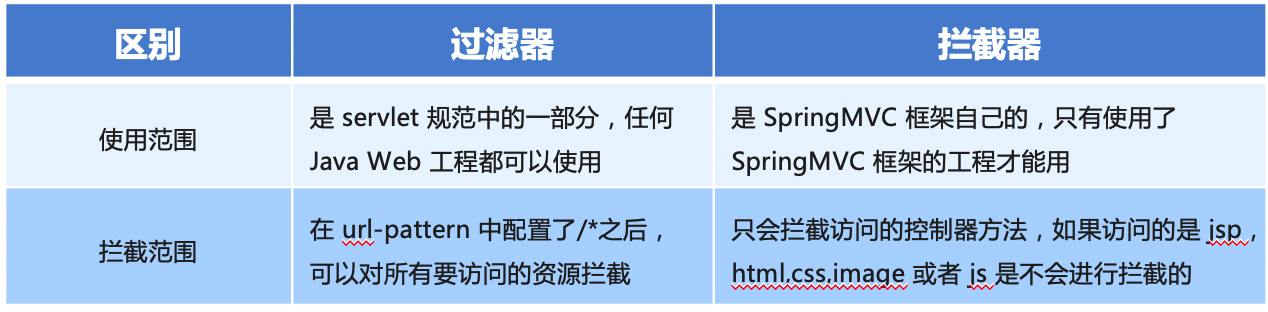
-
The difference between interceptor and filter is shown in the figure:
5.3 use of interceptors
5.3.1 creating interceptors
-
MyHandlerInterceptor
package cn.knightzz.interceptor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class MyHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { /** * Intercept before target method * @param request * @param response * @param handler * @return * @throws Exception */ @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("preHandle...."); return true; } /** * After the target method is executed, it is executed before the view object returns * @param request * @param response * @param handler * @param modelAndView * @throws Exception */ @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor.super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView); System.out.println("postHandle ... "); } /** * Execute after all processes are executed * @param request * @param response * @param handler * @param ex * @throws Exception */ @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor.super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex); System.out.println("afterCompletion ... "); } }
5.3.2 configure interceptors
-
In spring MVC XML file add
<!--Configuring Interceptors --> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <!--Which resources are intercepted--> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <bean class="cn.knightzz.interceptor.MyHandlerInterceptor"/> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
5.3.3 test code
-
TargetController
package cn.knightzz.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class TargetController { @RequestMapping("/target") public String targetMethod() { System.out.println("target implement..."); return "success"; } }
5.4 interceptor chain
-
In development, interceptors can be used alone or multiple interceptors can be used at the same time to form an interceptor chain. Development steps and individual interceptors
It's the same, except that more than one is registered during registration. Note that the registration order here represents the execution order of the interceptor.
-
In spring MVC Add filter chain to XML
<!--Configuring Interceptors --> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <!--Which resources are intercepted--> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <bean class="cn.knightzz.interceptor.MyHandlerInterceptor"/> </mvc:interceptor> <mvc:interceptor> <!--Which resources are intercepted--> <mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <bean class="cn.knightzz.interceptor.MyHandlerInterceptorX"/> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
5.5 method analysis
-
HandlerInterceptor interface method

6. Other issues
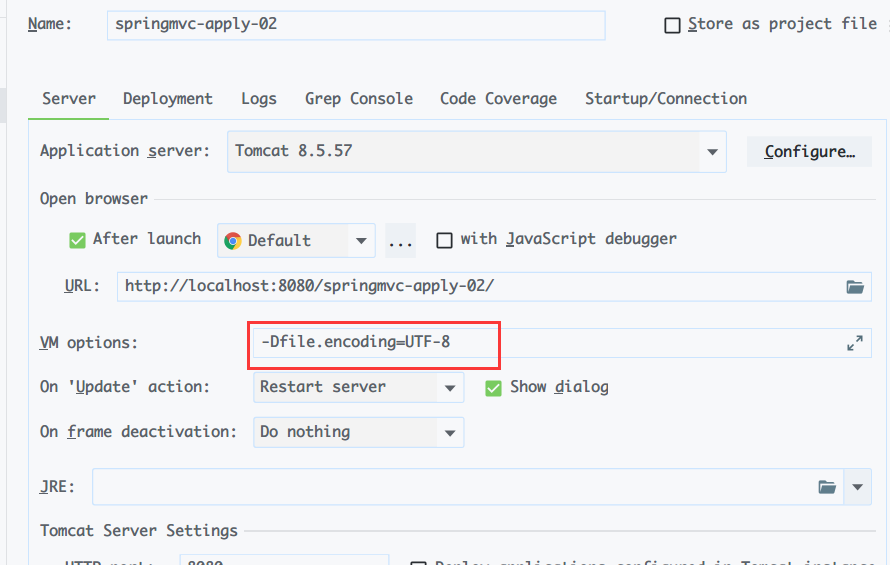
6.1 console garbled code
-
Solution: add - dfile encoding=UTF-8