The previous Blog introduced in detail why Docker appeared and what problems it appeared to solve; The basic components and architecture of Docker. This Blog will learn more about how to install and uninstall Docker and what are the common operation commands. Because Docker can be installed on any physical machine, virtual machine, public cloud and private cloud, and the Tencent cloud server I purchased is already a windows system and running services, so I'd better use the virtual machine installed on my PC to operate. The virtual machine I installed is Centos7. Previously, I have two blogs detailing how to install a virtual machine cluster through VMWare: [distributed cluster construction I] virtual machine configuration (VMware+Centos7+SecureCRT+AppNode) and [Distributed Cluster Construction II] clone virtual machines and configure clusters , if necessary, you can install the virtual machine locally according to my previous steps, so you don't need to buy ECs.
Docker installation
Next, install Docker on Centos7 and use SecureCRT for virtual host control. Of course, you can also use AppNode for visual remote control.
1 Environmental preparation
First, check the kernel version of Centos7 and confirm that Docker is supported. First, open VMWARE and start a virtual machine host:
Click to open the virtual host CentOS-7-TML1:
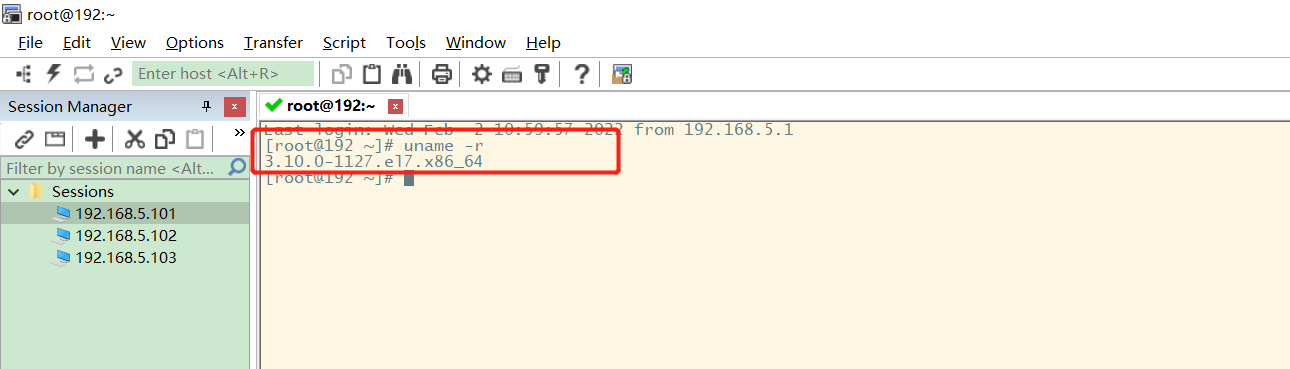
After opening the CentOS-7-TML1 host, remote control the virtual host through SecureCRT: check the kernel version: uname -r, and you can see that the kernel version is greater than 3.10
View the system configuration: cat / etc / OS release
NAME="CentOS Linux" VERSION="7 (Core)" ID="centos" ID_LIKE="rhel fedora" VERSION_ID="7" PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:centos:centos:7" HOME_URL="https://www.centos.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.centos.org/" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT="CentOS-7" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="7" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="centos" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="7"
2. Docker installation
Visit the official website of Docker and follow the steps to install: https://docs.docker.com/
Since the operation is carried out under Linux, you can directly choose Linux system installation:
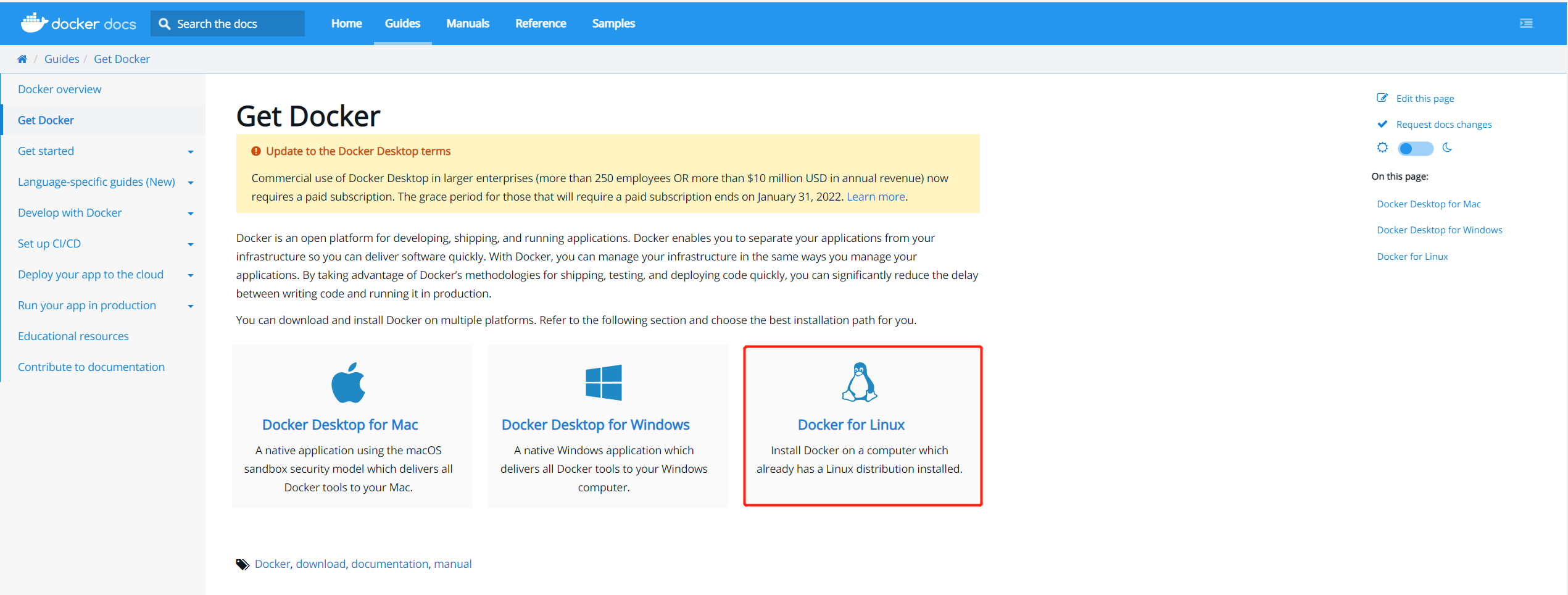
1 uninstall old version
Find the CentOS installation documentation. The first step in installing Docker is to uninstall the old version:
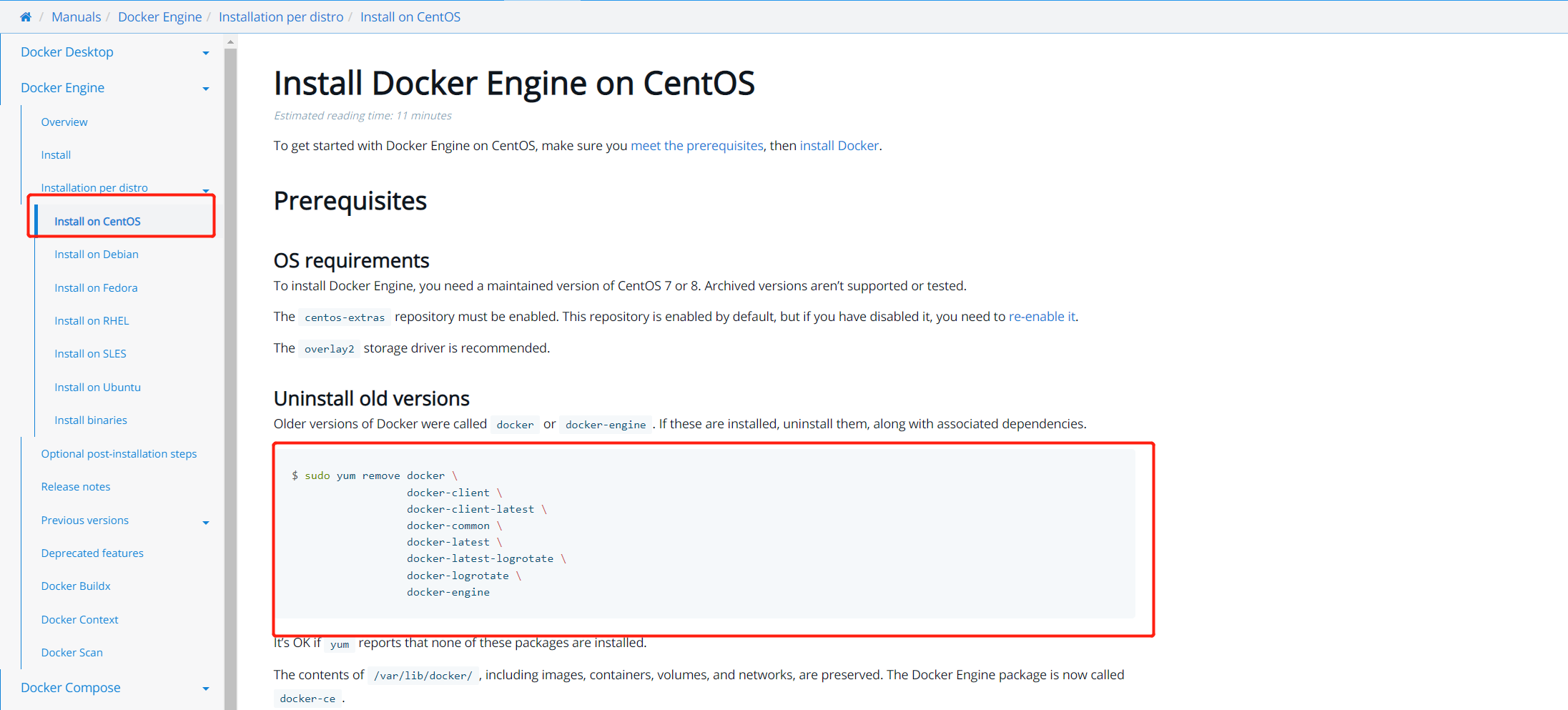
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
Because Docker has not been installed on my computer before, I will be prompted as follows:
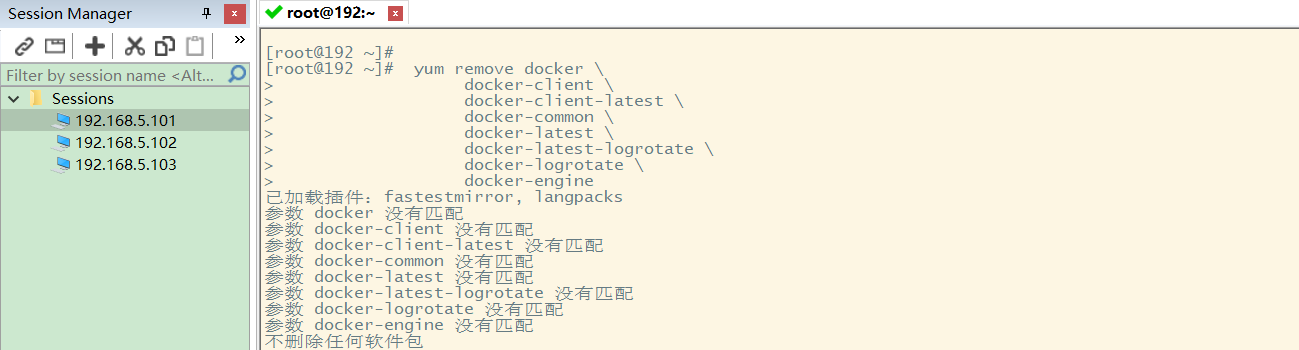
2 download the required installation package
Install the package of the running environment through the following command: Yum install - y Yum utils

3. Set Docker image warehouse
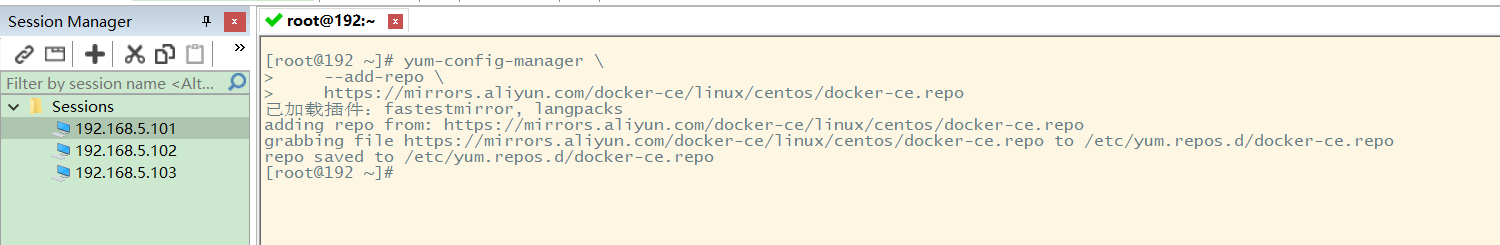
The default download address is foreign, and the domestic image warehouse can be used:
#Foreign address
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# Set up Alibaba cloud Docker image warehouse
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
The configuration results are as follows:
4 update the yum package index
Update the yum package before installing Docker engine: yum makecache fast
5. Install Docker engine
The command to install Docker engine is as follows: Yum install Docker CE Docker CE cli containerd io:
1. If the image cannot be found during the process, use this command to clean up the yum package: yum clean all.
2. If the installation result indicates that [no secret key has been installed], follow the following steps:
- View the system version information cat / etc / RedHat release: CentOS Linux release 7.8.2003 (Core)
- From the open source site: http://mirrors.163.com/centos/ , find the corresponding secret key of the system and install it: rpm --import http://mirrors.163.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
After completing the above two steps, execute the Docker installation command again:
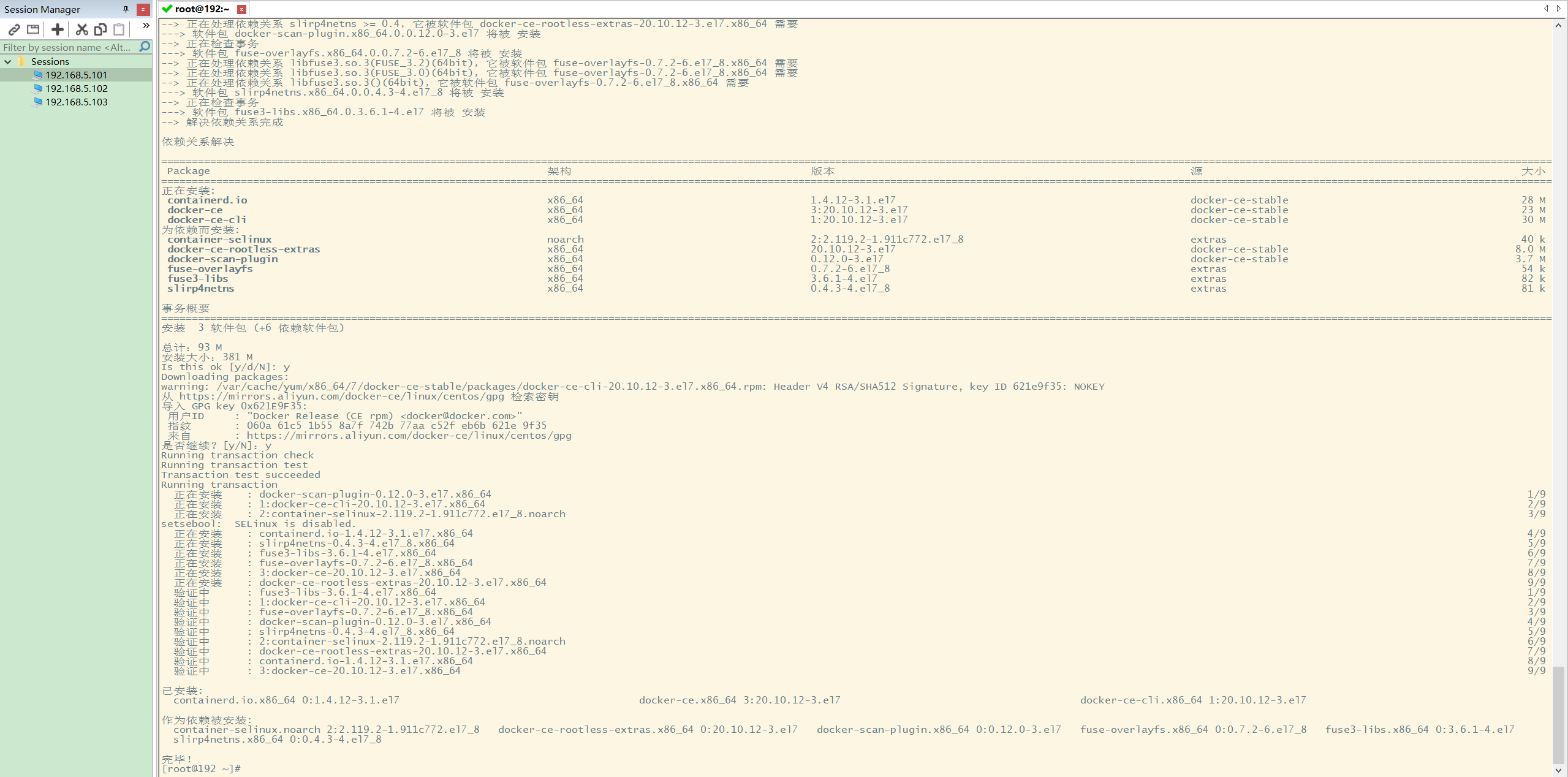
6 start Docker
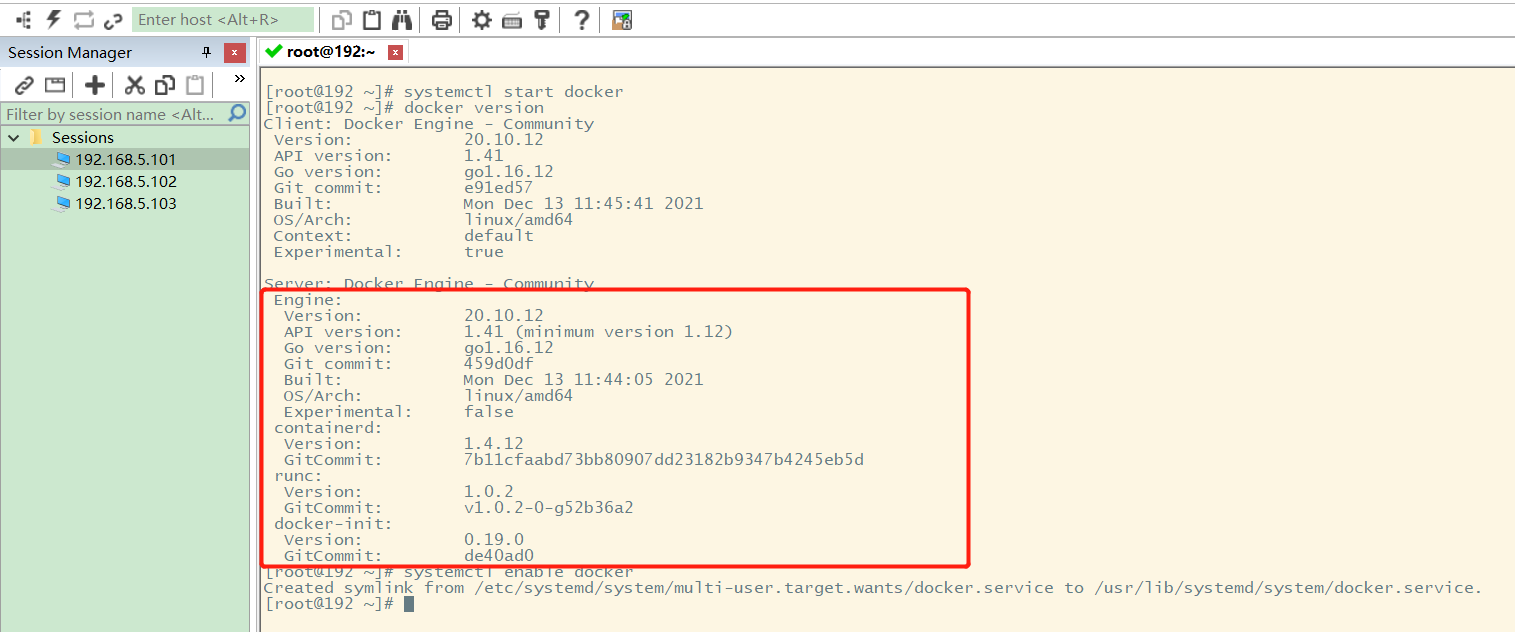
Start Docker through the following command, check the Docker version and set the automatic startup of Docker:
systemctl start docker # Check the current version number to see if it is started successfully docker version # Set startup and self startup systemctl enable docker
The results are as follows:
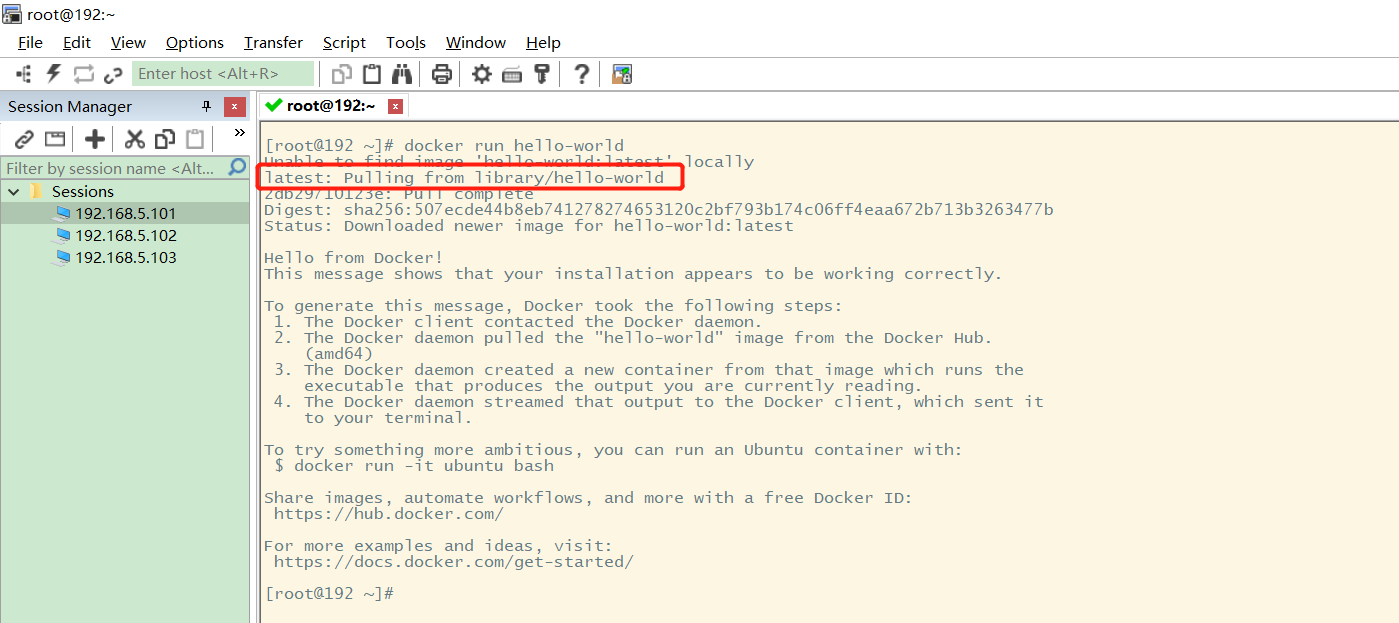
7 testing the Hello world program
After installation, we can download the Hello world image for testing: docker run Hello World
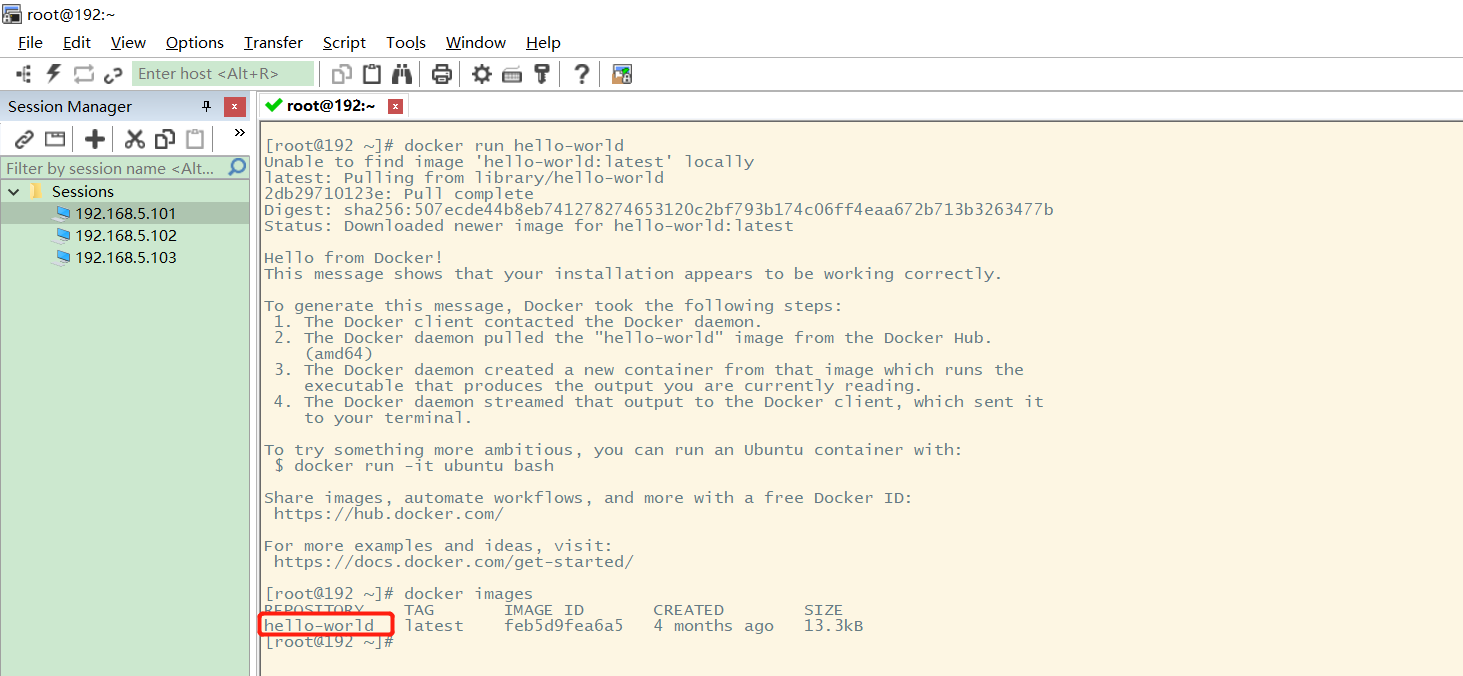
View the downloaded Hello world image: docker images
3. Docker unloading
The uninstallation command of Docker is as follows:
# 1. Uninstall dependency yum remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io # 2. Delete resources/ var/lib/docker is the default working path of docker rm -rf /var/lib/docker
4. Configure Alibaba cloud image acceleration
Enter Alibaba cloud's official website and search container image service: https://cr.console.aliyun.com/cn-hangzhou/instances/mirrors
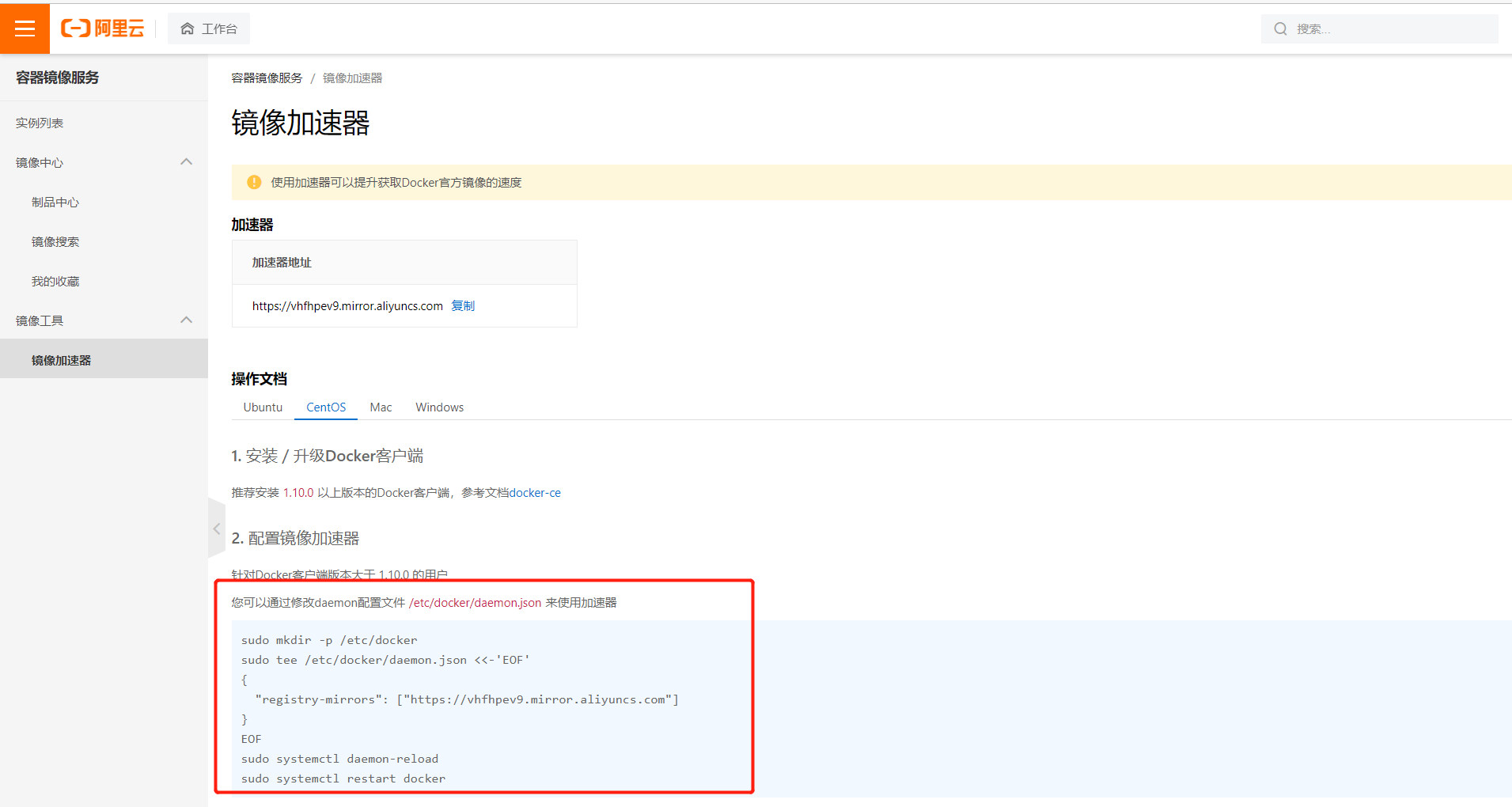
Use the following commands to configure the image. Each person has his own unique accelerator
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://vhfhpev9.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
Just follow the above command:
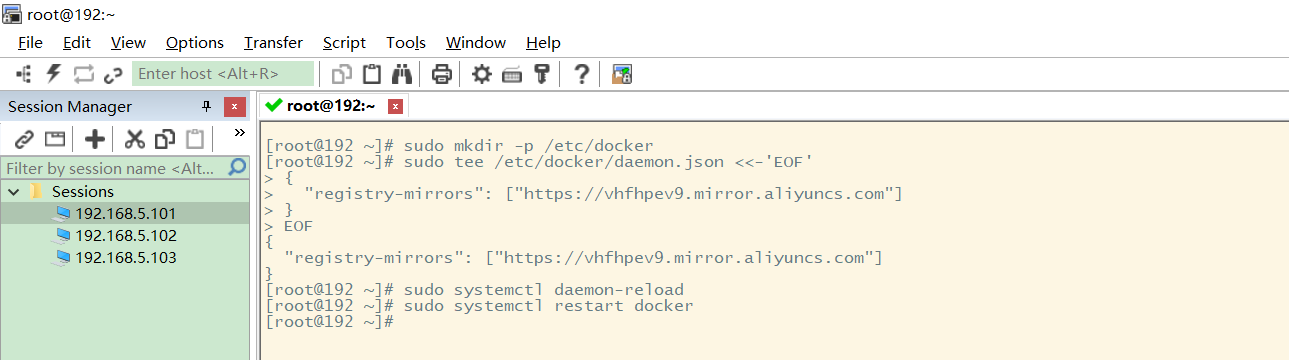
Docker operation process
Refer to the previous Hello world image pulling process:
[root@192 ~]# docker run hello-world Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/hello-world 2db29710123e: Pull complete Digest: sha256:507ecde44b8eb741278274653120c2bf793b174c06ff4eaa672b713b3263477b Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
You can know the execution process of docker run command, start and run a hello world container.
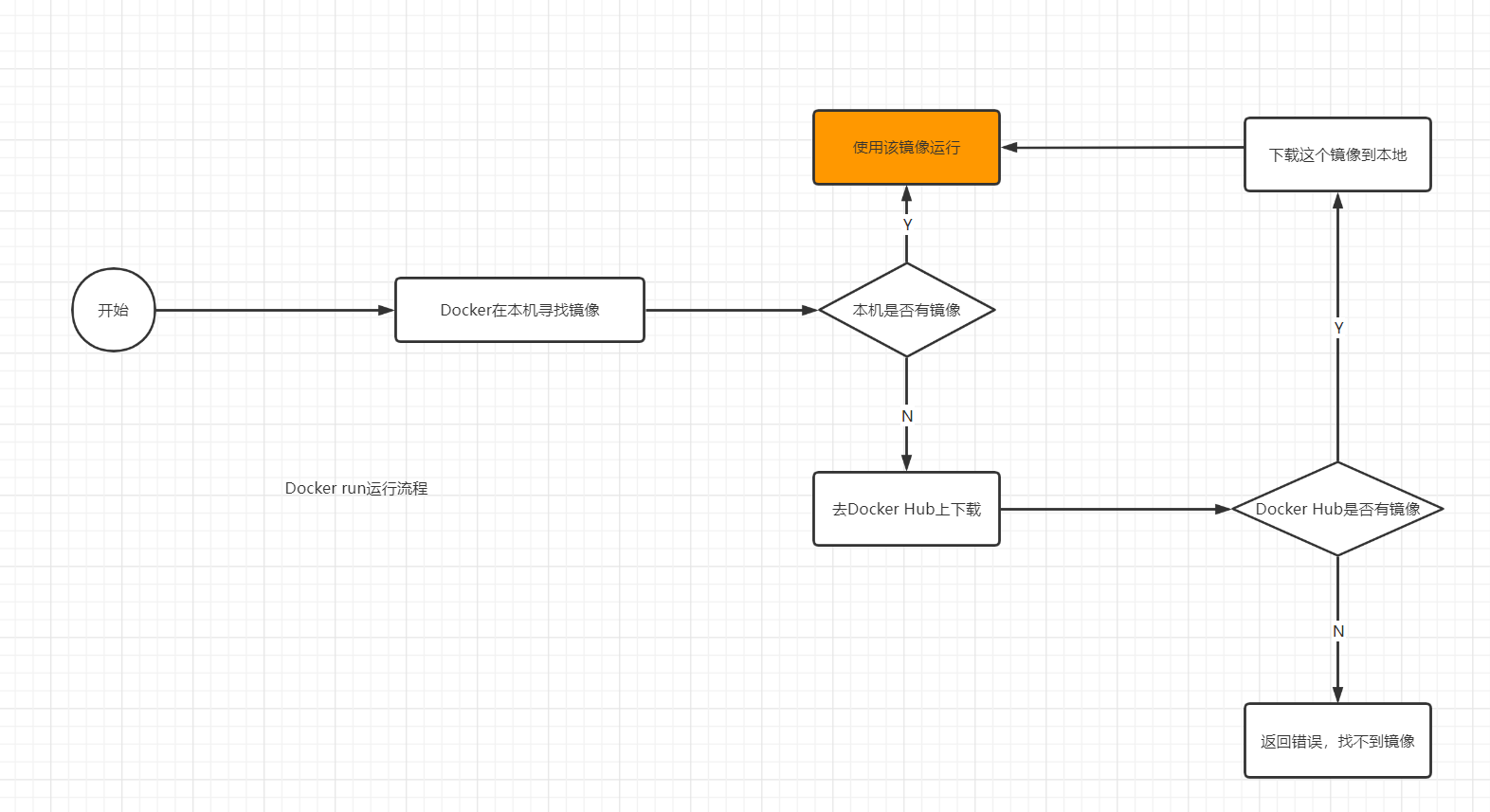
Docker is a system with client server structure. The daemon of docker runs on the host and is accessed from the client through Socker! When Docker Server receives the docker client instruction, it will execute this instruction!
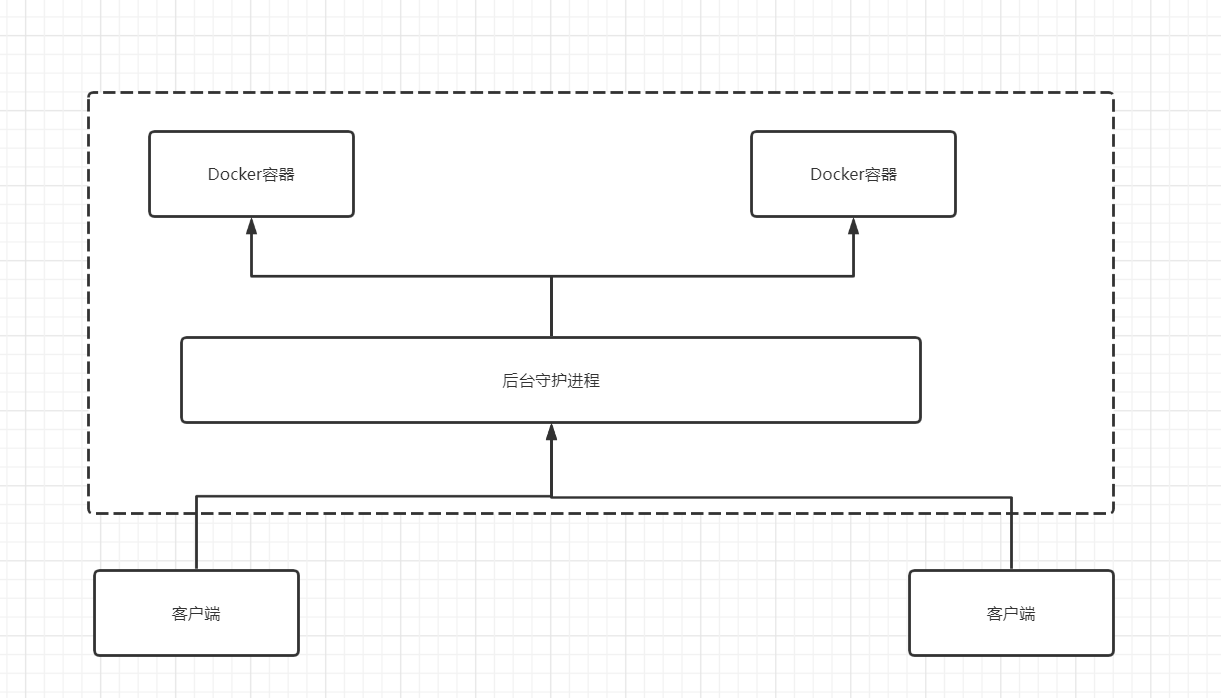
Each Docker container is like a small virtual machine, which is isolated from the host, and containers are isolated from each other. When Docker creates a new container, it does not need to reload an operating system kernel like a virtual machine, but directly use the operating system of the host, while the virtual machine needs to load the Guest OS.
Docker common commands
Contains basic commands, mirror commands, and container commands.
1 basic command
View some help of the command through the basic command
docker version #View the version information of docker docker info #View the system information of docker, including the number of images and containers docker command --help #Help command (optional parameters can be viewed) docker COMMAND --help
Help document address for the command: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/docker/
2 mirror command
View local images, search images, and download images from this site: https://hub.docker.com/search?q=mysql&type=image
1 docker images view all images of the local host
[root@192 ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest bf756fb1ae65 11 months ago 13.3kB #Explanation: 1.REPOSITORY Mirrored warehouse source 2.TAG Mirrored label 3.IMAGE ID mirrored id 4.CREATED Creation time of image 5.SIZE Mirror size # Optional parameters -a/--all List all mirrors -q/--quiet Show only mirrored id
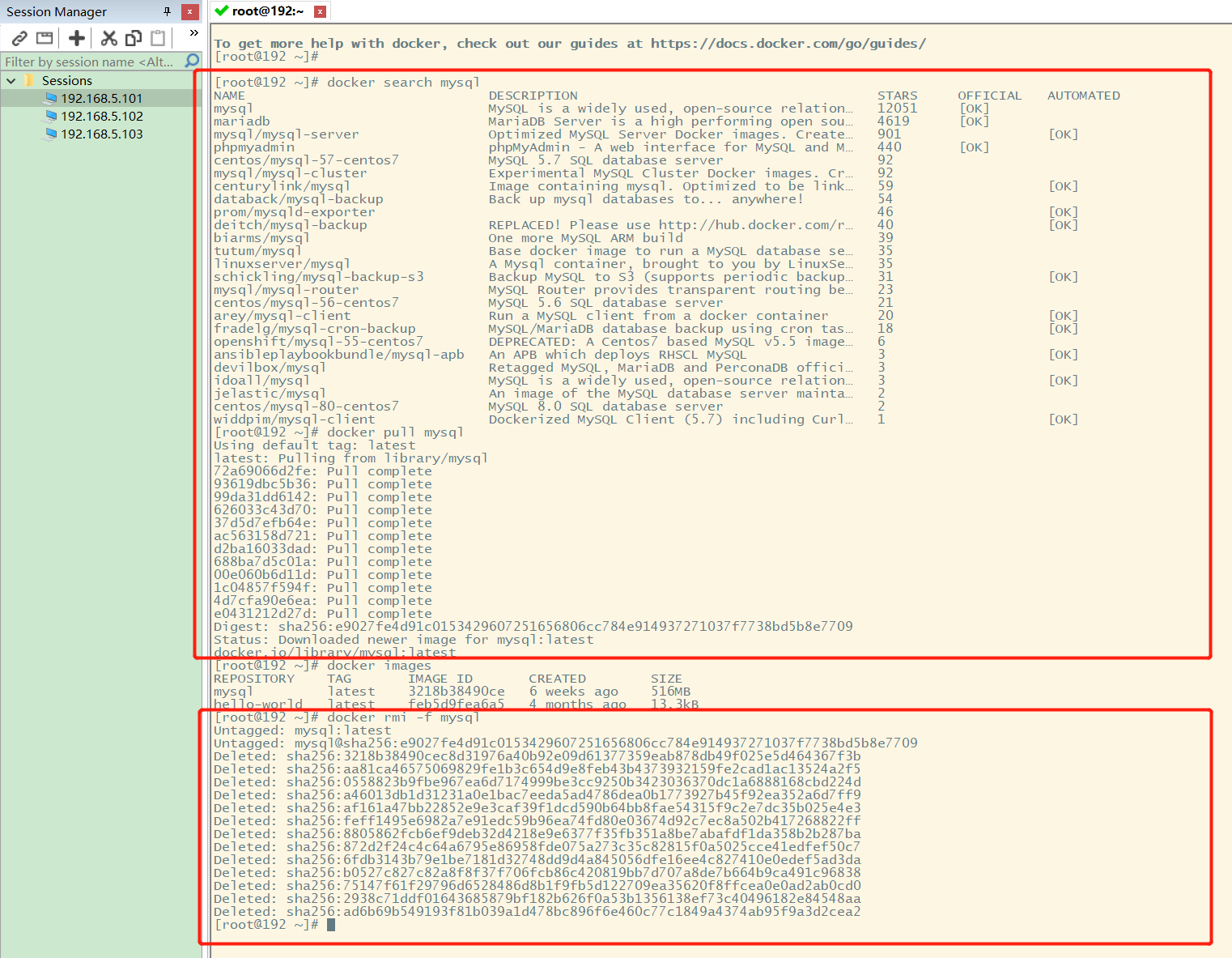
2 docker search search image
[root@192 ~]# docker search mysql
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 10308 [OK]
mariadb MariaDB is a community-developed fork of MyS... 3819 [OK]
mysql/mysql-server Optimized MySQL Server Docker images. Create... 754 [OK]
percona Percona Server is a fork of the MySQL relati... 517 [OK]
centos/mysql-57-centos7 MySQL 5.7 SQL database server 86
mysql/mysql-cluster Experimental MySQL Cluster Docker images. Cr... 79
centurylink/mysql Image containing mysql. Optimized to be link... 60 [OK]
#Optional parameters
Search the Docker Hub for images
Options:
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print search using a Go template
--limit int Max number of search results (default 25)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
#Search for images with more than 3000 collections
[root@192 ~]# docker search mysql --filter=STARS=3000
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 10308 [OK]
mariadb MariaDB is a community-developed fordockerk of MyS... 3819 [OK]
3 docker pull image name [: tag] Download Image
[root@192 ~]# docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest #If you do not write tag, the default is latest latest: Pulling from library/mysql 6ec7b7d162b2: Pull complete #Layered download, the core of docker image - federated file system fedd960d3481: Pull complete 7ab947313861: Pull complete 64f92f19e638: Pull complete 3e80b17bff96: Pull complete 014e976799f9: Pull complete 59ae84fee1b3: Pull complete ffe10de703ea: Pull complete 657af6d90c83: Pull complete 98bfb480322c: Pull complete 6aa3859c4789: Pull complete 1ed875d851ef: Pull complete Digest: sha256:78800e6d3f1b230e35275145e657b82c3fb02a27b2d8e76aac2f5e90c1c30873 #autograph Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest docker.io/library/mysql:latest #The real address of the download source #docker pull mysql is equivalent to docker pull docker io/library/mysql:latest
4 docker rmi delete image
#1. Delete the specified image id [root@192 ~]# docker rmi -f image id #2. Delete multiple image IDS [root@192 ~]# docker rmi -f image id image id image id #3. Delete all image IDS [root@192 ~]# docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq)
3 container command
Pull container, run container, enter container, exit container, list run containers, delete containers, start and stop containers
1. Pull the image
The premise of using the container is that the image exists, so first pull a centos container: docker pull centos
2 create, run and enter the container through image
docker run [Optional parameters] image #Parameter description --name="name" Specify container name -d Run in background mode -it Run interactively,Enter the container to view the contents -p Specify the port of the container ( -p ip:Host port:Container port configuration host ports are mapped to container ports -p Host port:Container port -p Container port ) -P Randomly assigned port(Capitalized P)
#Start and enter the container: [root@192 ~]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash [root@192 ~]# ls bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
If docker has no foreground application and does not provide services, it will stop automatically immediately. You can make the foreground script run by running it all the time:
#docker container runs in the background. There must be a foreground process, otherwise it will stop automatically #Write a shell script to execute circularly to keep the centos container running [root@192 ~]# docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo hi;sleep 5;done" c703b5b1911ff84d584390263a35707b6024816e1f46542b61918a6327a570dc [root@192 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c703b5b1911f centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 13 seconds ago Up 10 seconds pedantic_banach [root@192 ~]# docker logs -tf --tail 10 c703b5b1911f 2020-12-27T03:34:07.255599560Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:12.257641517Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:17.259706294Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:22.261693707Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:27.262609289Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:32.267862677Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:37.270382873Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:42.272414182Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:47.274823243Z hi 2020-12-27T03:34:52.277419274Z hi
3. Stop and exit the container
#Exit stop and exit the container (only exit if running in background mode) #Ctrl+P+Q do not stop container exit [root@192 ~]# exit exit [root@192 ~]#
4 start and stop the container
To start and stop the container, you can use the following commands, especially when running in the background.
container id #Start container docker restart container id #Restart container docker stop container id #Stop the currently running container docker kill container id #Force stop of current container
5 list containers
#docker ps [Optional] # Lists the currently running containers -a # List the operation records of all containers -n=? # Displays the n recently created containers -aq # Show all containers, only the container number [root@192 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@192 ~]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash [root@4a93ee953a85 /]# docker ps[root@192 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4a93ee953a85 centos "/bin/bash" About a minute ago Up About a minute nervous_kowalevski [root@192 ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES bca129320bb5 centos "/bin/bash" 4 minutes ago Exited (0) 3 minutes ago optimistic_shtern bd1b8900c547 centos "/bin/bash" 6 minutes ago Exited (0) 5 minutes ago cool_tesla cf6adbf1b506 bf756fb1ae65 "/hello" 5 hours ago Exited (0) 5 hours ago optimistic_darwin
6 delete container
docker rm container id #Delete the specified container. You cannot delete the running container. Force the deletion to use rm -f docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) #Force the deletion of all containers, including those in operation docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm #Delete all containers
4 other common commands
It includes viewing the running log, viewing the process information in the container, viewing the metadata of the container, and entering the currently running container
1 view the operation log
[root@192 ~]# docker logs --help
Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Fetch the logs of a container
Options:
--details Show extra details provided to logs
-f, --follow Follow log output
--since string Show logs since timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
-n, --tail string Number of lines to show from the end of the logs (default "all")
-t, --timestamps Show timestamps
--until string Show logs before a timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
Common commands are as follows:
docker logs -tf container id docker logs --tail number container id #num is the number of log entries to display
Try it out:
#docker container runs in the background. There must be a foreground process, otherwise it will stop automatically #Write a shell script to execute circularly to keep the centos container running [root@192 ~]# docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo tml;sleep 5;done" c2a9905be58b87056b97c1717f4bbd53ab8fdf9626b10243797ce2601e112eb2 [root@192 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c2a9905be58b centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 7 seconds ago Up 6 seconds zealous_shockley 1a89c6b0a6cf centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes wizardly_hofstadter 3b71711140a1 centos "/bin/bash" 18 minutes ago Up 17 minutes ecstatic_brattain [root@192 ~]# docker logs -tf --tail 10 c703b5b1911f c2a9905be58b "docker logs" requires exactly 1 argument. See 'docker logs --help'. Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER Fetch the logs of a container [root@192 ~]# docker logs -tf --tail 10 c2a9905be58b 2022-02-03T11:09:37.007194732Z tml 2022-02-03T11:09:42.010548527Z tml 2022-02-03T11:09:47.016344088Z tml 2022-02-03T11:09:52.019194397Z tml 2022-02-03T11:09:57.022509980Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:02.028690964Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:07.031701028Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:12.035592381Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:17.042442369Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:22.044663053Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:27.047141833Z tml 2022-02-03T11:10:32.051435050Z tml
2. View the process information in the container
Use the: docker top container ID command to kill the process
[root@192 ~]# docker top c2a9905be58b UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 10119 10099 0 19:09 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c while true;do echo tml;sleep 5;done root 10274 10119 0 19:12 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/coreutils --coreutils-prog-shebang=sleep /usr/bin/sleep 5 [root@192 ~]#
3. View metadata of container
Thoroughly understand the metadata in the container image: docker inspect container ID
4 enter the currently running container
Generally, our container runs in the background mode. Sometimes we need to enter the container to modify the configuration. At this time, there are two ways:
- After entering the container, open a new terminal, which can be operated inside
[root@192 ~]# docker exec -it c703b5b1911f /bin/bash [root@192 ~]# ls bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var [root@192 ~]# ps -ef UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1 0 0 03:31 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c while true;do echo hi;sleep 5;done root 279 0 0 03:54 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash root 315 1 0 03:56 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/coreutils --coreutils-prog-shebang=sleep /usr/bin/sleep 5 root 316 279 0 03:56 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -ef
- Entering the terminal where the container is executing will not start a new process
[root@192 ~]# docker attach c703b5b1911f
5 container host copy command
#Copy container files to host docker cp container id:In container path destination host path #Copy the files of the host to the container docker cp Destination host path container id:Path in container
Execute the following command to copy the container file to the host
[root@192 ~]# docker exec -it c2a9905be58b /bin/bash [root@192 ~]# cd home [root@192 ~]# ls #touch new file [root@192 ~]# touch test.java [root@192 ~]# ls test.java [root@192 ~]# exit exit [root@192 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c2a9905be58b centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 35 minutes ago Up 35 minutes pedantic_banach [root@192 ~]# docker cp c2a9905be58b:/home/test.java /home [root@192 ~]# ls /home test.java tml-1
To sum up
The concept of Docker warehouse is a bit like Maven [Jar package hosting warehouse] and GitHub [code hosting warehouse], which is a mirror hosting warehouse. This Blog introduces in detail how to download and install Docker and how to speed up the image, understands the basic operation process of Docker, and actually runs through the use process of Docker through common Docker commands such as basic commands, image commands, container commands and log commands. Next, we will further deepen our understanding of Docker through the study of principles!