Foreword
Share a case of using some crawler technology to simply crawl articles from media web pages on demand and save them to the local designated folder for reference only. In the learning process, do not visit the website frequently and cause web page paralysis. Do what you can!!!
Simple use of beautiful soup: https://inganxu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/122783587
Crawling demand
Crawl address: Construction Archives - construction industry whole industry chain content co construction platform
Technologies involved in crawling: Requests (access), beautiful soup, Re (parsing), Panda (save)
Climbing purpose: only used to practice and consolidate reptile technology
Climb target:
- Save the title of the article in excel and the title of the article in excel as the location of the first page
- Save the text of each article to the document in the specified location and name it with the article title
- Save the picture of each article to the folder in the specified location, and name it with the article title + picture serial number
Crawling idea
Initiate a homepage request to obtain the response content
Analyze the homepage data and obtain the title, author, release time and article link information of the article
Summarize the home page information of the website and save it in excel
Initiate an article web page request to obtain the response content
Analyze the web page data of the article and obtain the text, picture and link information of the article
Save the content of the article to the specified document
Initiate a picture web page request to obtain the response content
Save pictures to the specified folder
Code explanation
The following explains the implementation method and precautions of each step in the order of crawler ideas
Step 1: import related libraries
import requests # It is used to initiate a web page request and return the response content import pandas as pd # Generate two-dimensional data and save it to excel import os # file save import time # Slow down the reptile import re # Extract and parse content from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # Parse data for response content
Install without related libraries
Press win + r to call up the CMD window and enter the following code
pip install Missing library name
Step 2: set anti reptile measures
"""
Record crawler time
Set basic information for accessing web pages
"""
start_time = time.time()
start_url = "https://www.jzda001.com"
header = {'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/96.0.4664.45 Safari/537.36'}
hearder: header. Copy the header of the browser by yourself. If you can't find it, you can copy it directly
Step 3: visit the home page and parse the response content
response = requests.get(url=start_url, headers=header) # Initiate request
html = response.text # Extract response content
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # Parse response content
content = soup.find_all('div', attrs={'class': 'content-left'})[0] # Filter and extract crawler only content
# Use the list to load crawler information
item = {}
href_list = []
title_list = []
author_list = []
releasetime_list = []
# Get article links
for href in content.find_all('a', href=re.compile('^/index/index/details')):
if href['href'] not in href_list:
href_list.append(href['href'])
# Get article title
for title in content.find_all('p', class_=re.compile('(twoline|sub oneline|oneline)'))[:-1]:
title_list.append(title.text)
# Get article author and release time
for author_time in content.find_all('p', attrs={'class': 'name'}):
if len(author_list) < 20:
author = re.findall(r'(?<=\s)\D+(?=\s\.)', author_time.text)[0]
author_list.append(author.replace(' ', ''))
if len(releasetime_list) < 20:
time = re.findall(r'\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}\s\d{1,2}:\d{1,2}:\d{1,2}', author_time.text)
releasetime_list.append(time[0])During the parsing process, it is found that there is unnecessary information at the head or tail of the obtained content, so the list slicing method is used to eliminate the elements
Step 4: data cleaning
# Main page data cleaning
author_clear = []
for i in author_list:
if i != '.':
author_clear.append(i.replace('\n', '').replace(' ', ''))
author_list = author_clear
time_clear = []
for j in releasetime_list:
time_clear.append(j.replace('\n', '').replace(' ', '').replace(':', ''))
releasetime_list = time_clear
title_clear = []
for n in title_list:
title_clear.append(
n.replace(': ', ' ').replace('!', ' ').replace('|', ' ').replace('/', ' ').replace(' ', ' '))
title_list = title_clearViewing the web page structure, you can see that there are some system sensitive characters in the title, author and publishing time (affecting the subsequent inability to create folders)
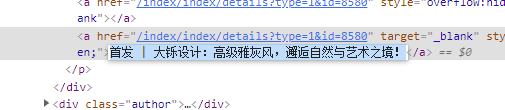
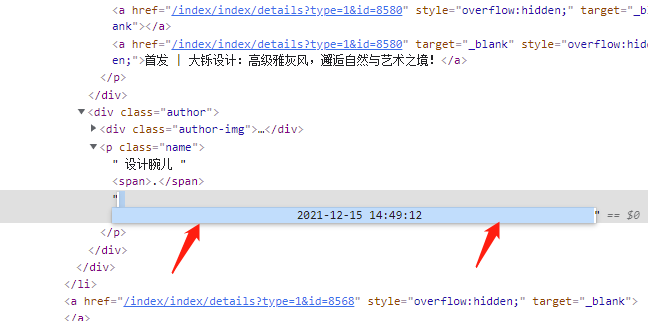
Therefore, the parsed data can only be used after data cleaning
Step 5: visit the article link and parse and extract the response content
By comparing the @ href attribute link of the web page structure with the real link of the article, it can be seen that the parsed url needs to be spliced into the home page of the web address
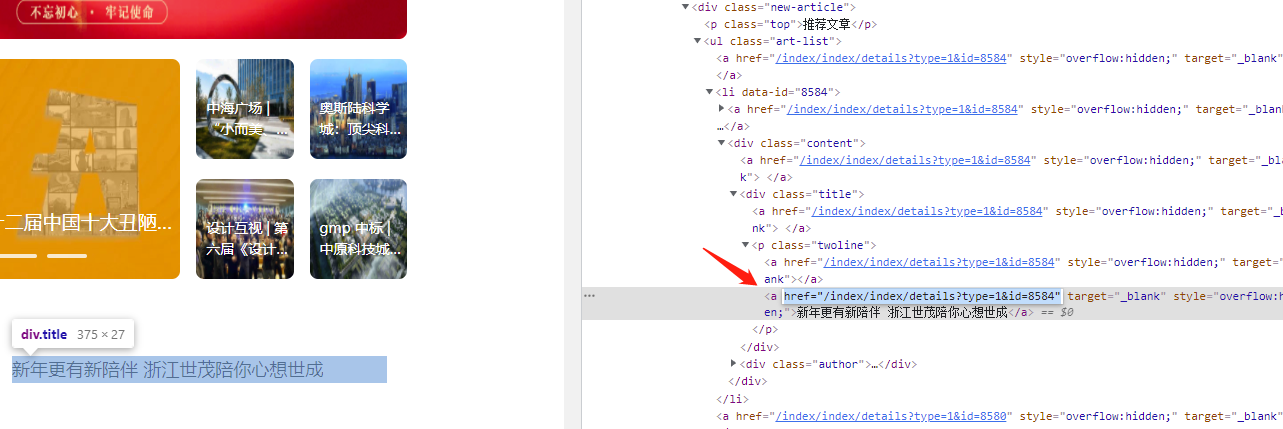
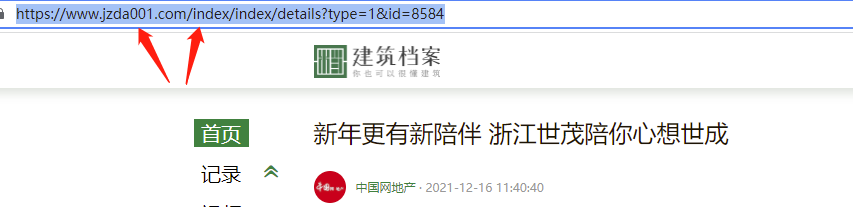
# Access the article and save the text information and pictures to the specified folder
for nums in range(20):
text_list = []
img_url_list = []
article_url = start_url + href_list[nums]
response_url = requests.get(article_url, headers=header, timeout=1)
html_text = response_url.text
soup_article = BeautifulSoup(html_text, 'lxml')
# Get sub page text (use find_all method)
content_article = soup_article.find_all('div', attrs={'class': 'content'})[-1]
text = ''
for i in content_article:
text = text + i.text
text_list.append(text)
# Get the picture link of the sub page (using the select method)
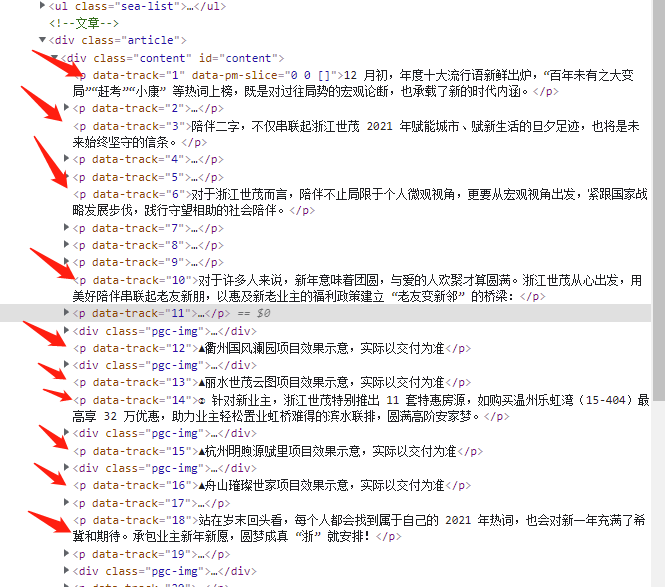
soup_article_url = content_article.select('.pgc-img > img')
for url in soup_article_url:
img_url_list.append(url['src'])Splicing text content is because the obtained text information is separated paragraph by paragraph and needs to be spliced together, which is the complete text information of the article
Step 6: create multi tier folders
New multi tier folder
file_name = "Building archives crawler folder" # Folder name
path = r'd:/' + file_name
url_path_file = path + '/' + title_list[nums] + '/' # Splice folder address
if not os.path.exists(url_path_file):
os.makedirs(url_path_file)Because the created folder is: ". / crawler folder name / article title name /", you need to use OS Make dirs to create multi tier folders
Note that the file name ends with "/"
Step 7: save sub page pictures
When the folder is set up, start accessing the image links of each article and save them
# Save sub page picture
for index, img_url in enumerate(img_url_list):
img_rep = requests.get(img_url, headers=header, timeout=5) # Set timeout
index += 1 # Display quantity + 1 for each picture saved
img_name = title_list[nums] + ' picture' + '{}'.format(index) # Picture name
img_path = url_path_file + img_name + '.png' # Picture address
with open(img_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(img_rep.content) # Write in binary
f.close()
Step 8: save sub page text
You can save the text first and then the picture. You need to pay attention to the writing methods of the two
# Save page text
txt_name = str(title_list[nums] + ' ' + author_list[nums] + ' ' + releasetime_list[nums]) # Text name
txt_path = url_path_file + '/' + txt_name + '.txt' # Text address
with open(txt_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(str(text_list[0]))
f.close()Step 9: summary of article information
Save all article titles, authors, publishing time and article links on the front page of the website to an excel folder
# Main page information saving
data = pd.DataFrame({'title': title_list,
'author': author_list,
'time': releasetime_list,
'url': href_list})
data.to_excel('{}./data.xls'.format(path), index=False)Complete code (Process Oriented Version)
# !/usr/bin/python3.9
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @author:inganxu
# CSDN:inganxu.blog.csdn.net
# @Date: February 3, 2022
import requests # It is used to initiate a web page request and return the response content
import pandas as pd # Generate two-dimensional data and save it to excel
import os # file save
import time # Slow down the reptile
import re # Extract and parse content
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # Parse data for response content
start_time = time.time()
start_url = "https://www.jzda001.com"
header = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/96.0.4664.45 Safari/537.36'}
response = requests.get(url=start_url, headers=header) # Initiate request
html = response.text # Extract response content
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') # Parse response content
content = soup.find_all('div', attrs={'class': 'content-left'})[0] # Filter and extract crawler only content
# Use the list to load crawler information
item = {}
href_list = []
title_list = []
author_list = []
releasetime_list = []
# Get article links
for href in content.find_all('a', href=re.compile('^/index/index/details')):
if href['href'] not in href_list:
href_list.append(href['href'])
# Get article title
for title in content.find_all('p', class_=re.compile('(twoline|sub oneline|oneline)'))[:-1]:
title_list.append(title.text)
# Get article author and release time
for author_time in content.find_all('p', attrs={'class': 'name'}):
if len(author_list) < 20:
author = re.findall(r'(?<=\s)\D+(?=\s\.)', author_time.text)[0]
author_list.append(author.replace(' ', ''))
if len(releasetime_list) < 20:
time = re.findall(r'\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}\s\d{1,2}:\d{1,2}:\d{1,2}', author_time.text)
releasetime_list.append(time[0])
# Main page data cleaning
author_clear = []
for i in author_list:
if i != '.':
author_clear.append(i.replace('\n', '').replace(' ', ''))
author_list = author_clear
time_clear = []
for j in releasetime_list:
time_clear.append(j.replace('\n', '').replace(' ', '').replace(':', ''))
releasetime_list = time_clear
title_clear = []
for n in title_list:
title_clear.append(
n.replace(': ', ' ').replace('!', ' ').replace('|', ' ').replace('/', ' ').replace(' ', ' '))
title_list = title_clear
# Access the article and save the text information and pictures to the specified folder
for nums in range(20):
text_list = []
img_url_list = []
article_url = start_url + href_list[nums]
response_url = requests.get(article_url, headers=header, timeout=1)
html_text = response_url.text
soup_article = BeautifulSoup(html_text, 'lxml')
print("Climbing to the third{}Pages!!!".format(nums + 1))
# Get sub page text (use find_all method)
content_article = soup_article.find_all('div', attrs={'class': 'content'})[-1]
text = ''
for i in content_article:
text = text + i.text
text_list.append(text)
# Get the picture link of the sub page (using the select method)
soup_article_url = content_article.select('.pgc-img > img')
for url in soup_article_url:
img_url_list.append(url['src'])
# New multi tier folder
file_name = "Building archives crawler folder" # Folder name
path = r'd:/' + file_name
url_path_file = path + '/' + title_list[nums] + '/' # Splice folder address
if not os.path.exists(url_path_file):
os.makedirs(url_path_file)
# Save sub page picture
for index, img_url in enumerate(img_url_list):
img_rep = requests.get(img_url, headers=header, timeout=5) # Set timeout
index += 1 # Display quantity + 1 for each picture saved
img_name = title_list[nums] + ' picture' + '{}'.format(index) # Picture name
img_path = url_path_file + img_name + '.png' # Picture address
with open(img_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(img_rep.content) # Write in binary
f.close()
print('The first{}Pictures saved successfully at:'.format(index), img_path)
# Save page text
txt_name = str(title_list[nums] + ' ' + author_list[nums] + ' ' + releasetime_list[nums]) # Text name
txt_path = url_path_file + '/' + txt_name + '.txt' # Text address
with open(txt_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(str(text_list[0]))
f.close()
print("The text of this page was saved successfully,The text address is:", txt_path)
print("Crawl succeeded!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!")
print('\n')
# Main page information saving
data = pd.DataFrame({'title': title_list,
'author': author_list,
'time': releasetime_list,
'url': href_list})
data.to_excel('{}./data.xls'.format(path), index=False)
print('Saved successfully,excel File address:', '{}/data.xls'.format(path))
print('Crawling completed!!!!')
end_time = time.time()
print('Time for climbing:', end_time - start_time)
epilogue
Later, we will expand anti creep measures (ip pool, header pool, response access) and data processing (data analysis, data visualization) for this case