26.
Title:
Sword finger Offer 26 Substructure of tree https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-de-zi-jie-gou-lcof/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-de-zi-jie-gou-lcof/
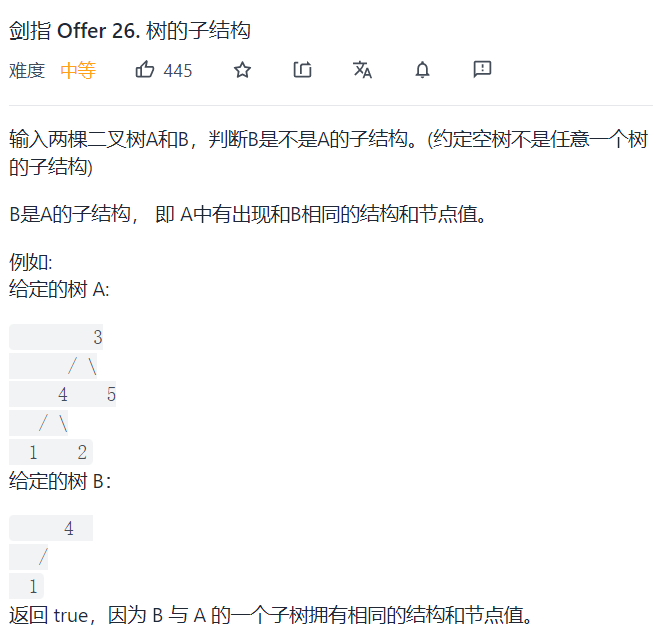
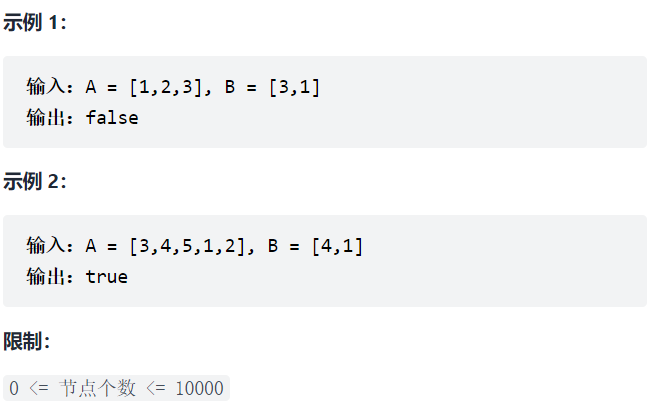
Idea: first, find the root node of B in A. if it is found, compare AB from now on. Otherwise, return false
Note that when B==null, it is not a substructure of any tree and can be judged first
Two recursions are involved:
Recursion - findBsRoot
- Function function? Find the root node of B in A
Input: TreeNode A, TreeNode B
Return value: None - Termination condition of recursion?
A = = null (found A) or flag = = true (found) - The relationship between recursion of this layer and the next layer
If the second node A =. Val = B is found, then judge whether the second node A =. Val = B is included
Otherwise, recursively traverse the left child of A / the right child of A and B to find B in A
Recursive binary compare
- Function function? Judge whether B is the substructure of A
Input: TreeNode A, TreeNode B
Return value: If yes, return true; otherwise, return false - Termination condition of recursion?
B==null indicates that B traverses first, that is, A contains B
A==null indicates that a traverses first, that is, a does not contain B - The relationship between recursion of this layer and the next layer
This layer needs to determine whether A.val==B.val is set up and then call the right child of A.B's left child /A.B.
Note: the return value of each layer should be the same as the operation and operation of the previous layer, that is, it is the substructure only when it is all the same
code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean flag=false;
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
//Note that when B==null, it is not a substructure of any tree and can be judged first
if(B==null) return false;
findBsRoot(A,B);
return flag;
}
//Find the root node of B in A
void findBsRoot(TreeNode A, TreeNode B){
//When flag is true, it indicates that the substructure has been found and the traversal ends
if(A==null||flag)
return;
if(A.val==B.val)
//Find the root node, continue to compare the child nodes, and judge whether B is the substructure of A
flag=compare(A,B);
findBsRoot(A.left,B);
findBsRoot(A.right,B);
}
//Check if B is a substructure of A
boolean compare(TreeNode A, TreeNode B){
//Judge whether B is empty first
if(B==null)
return true;
//Then judge whether A is empty
if(A==null)
return false;
//Check whether A.val is equal to B.val, and recursively check the left and right subtrees of A and B
return A.val==B.val && compare(A.left,B.left) && compare(A.right,B.right);
}
}
result:
27.
Title:


Idea: just exchange the left and right nodes of all nodes in turn
recursion
- Function function? Swap all the left and right children of the root node
Input: TreeNode root
Return value: None - Termination condition of recursion?
Root = = null (after traversing root) - The relationship between recursion of this layer and the next layer
Preorder traversal
Exchange the left and right children of this node, and then recursively traverse its left and right children
code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
//Code 1:
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
//First, judge whether there is a root node, and the subsequent steps can be omitted
recursion(root);
return root;
}
void recursion(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
TreeNode tmp=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=tmp;
recursion(root.left);
recursion(root.right);
}
}Refer to others and find that nodes can be returned directly in recursion
code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
//Code 2:
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode leftRoot = mirrorTree(root.right);
TreeNode rightRoot = mirrorTree(root.left);
root.left = leftRoot;
root.right = rightRoot;
return root;
}
}result:
28.
Title:

Idea:
Recursive binary compare
- Function function? Judge whether the two incoming trees L.R are mirrored
Input: TreeNode L, TreeNode R
Return value: If yes, return true; otherwise, return false - Termination condition of recursion?
L==null and R==null - > all look the same in the end - > Image
L==null.R!=null or l= null. R = = null - > description left and right are different - > non mirror
L.val!=R.val - The relationship between recursion of this layer and the next layer
After judging the nodes of this layer, you need to judge whether the left child of L tree is the same as the right child of R tree
Note: an empty tree must be a mirror image. You can judge it first
code:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? true : recur(root.left, root.right);
}
boolean recur(TreeNode L, TreeNode R) {
if(L == null && R == null)
return true;
if(L == null || R == null || L.val != R.val)
return false;
return recur(L.left, R.right) && recur(L.right, R.left);
}
}result:
