Implementation of stack and queue related algorithms
In the process of learning data structure and algorithm, in order to better understand the implementation of the algorithm, this paper implements the algorithms of stack and queue in the course. This article only provides algorithm code reference. For detailed explanation of relevant algorithms, please refer to the video course of Mr. Wang Zhuo of Qingdao University: Data and structure of Qingdao University (Wang Zhuo)
Implementation of stack
Define identifier
#include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Function result status code #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define INFEASIBLE -1 #define OVERFLOW -2 #define MAXSIZE 100 //Status is the type of function and its value is the result status code of the function typedef int Status; typedef int SElemType; // Define data element types
Chain implementation of stack
Define chain stack data structure
// Define chain stack data structure
typedef struct StackNode {
SElemType data; // Data domain
struct StackNode* next; // Pointer field
}StackNode,*LinkStack;
Initialize chain stack
// Initialization of chain stack
void InitStack(LinkStack& S) {
S = NULL;
}
Judge whether the chain stack is empty
// Judge whether the chain stack is empty
Status StackEmpty(LinkStack S) {
if (S == NULL)return TRUE;
else return FALSE;
}
Push
// Input of chain stack
Status Push(LinkStack& S, SElemType e) {
LinkStack p = new StackNode; // Generate new node p
p->data = e; // Set the new node data field to e
p->next = S; // Insert the new node into the top of the stack
S = p; // Modify stack top pointer
return OK;
}
Out of stack
// Out of chain stack
Status Pop(LinkStack& S, SElemType& e) {
if (S == NULL)return ERROR;
e = S->data;
LinkStack p = S;
S = S->next;
delete p;
return OK;
}
Access stack top element
// Get stack top element
int GetTop(LinkStack S, SElemType &e) {
if (S != NULL) {
e = S->data;
return OK;
}
else {
e = -2;
return OVERFLOW;
}
}
Test code and output results
Test code:
The input data field is [0, + ∞]. If the input data is - 1, the stack out operation will be executed.
int main()
{
SElemType data;
LinkStack S;
SElemType head_data;
int code;
InitStack(S);
for (int i = 0; i <= MAXSIZE; i++) {
cout << "Merge input data elements into stack:";
cin >> data;
if (data == -1) { // Enter - 1 to perform the queue out operation
Pop(S, head_data);
cout << "Add stack top element:" << head_data << " Out of stack" << endl;
} // if
else {
cout << data << " Push " << endl;
Push(S, data);
} // else
code = GetTop(S, head_data);
cout << "At this time, the top element of the stack is:" << head_data << endl;
if (StackEmpty(S) == TRUE) {
cout << "All data has been out of the stack" << endl;
break;
} // if
} // for
system("pause");
return 0;
}
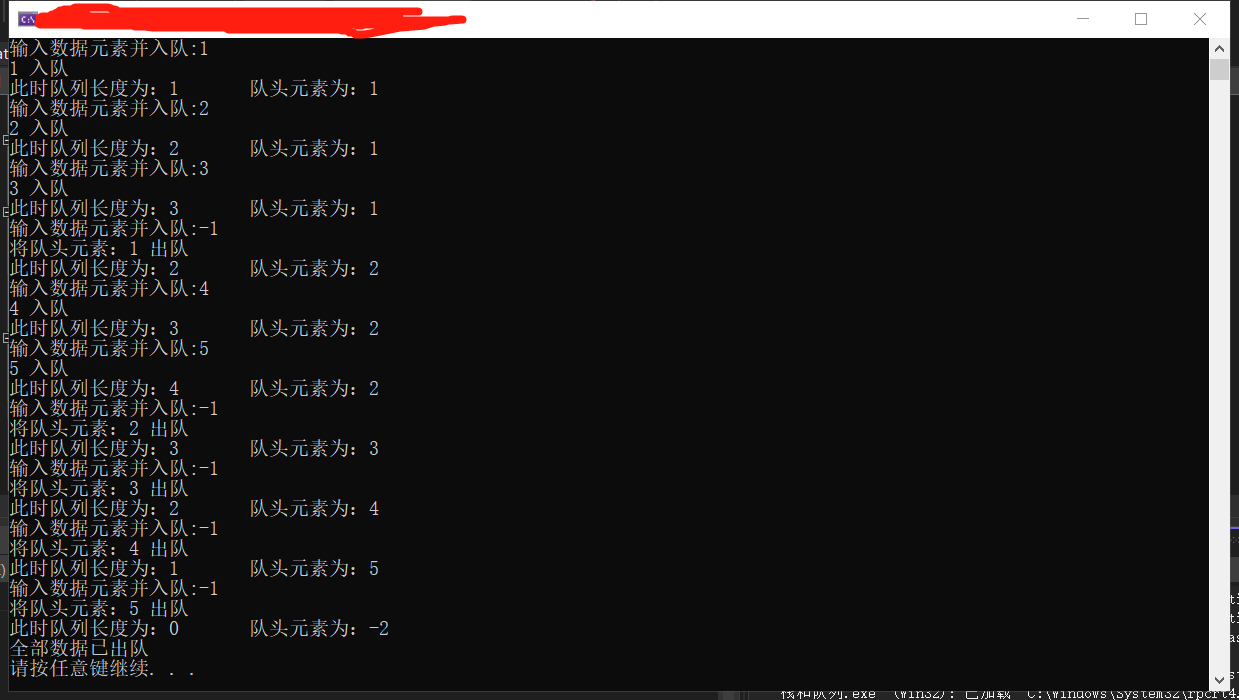
Output result:
Sequential implementation of stack
Define sequential stack data structure
typedef struct {
SElemType *base; // Stack bottom pointer
SElemType *top; // Stack top pointer
int stacksize; // Maximum available capacity of stack
}SqStack;
Initialization sequence stack
// Initialization stack
Status InitStack(SqStack& S) { // Construct an empty stack
S.base = new SElemType[MAXSIZE]; //or
if (!S.base)exit(OVERFLOW); // Storage allocation failed
S.top = S.base; // Stack top pointer equals stack bottom pointer
S.stacksize = MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
Destroy sequence stack
// Destroy stack
Status DestroyStack(SqStack& S) {
if (S.base) {
delete S.base;
S.stacksize = 0;
S.base = S.top = NULL;
}
return OK;
}
Empty sequence stack
// Empty stack
Status ClearStack(SqStack S) {
if (S.base)S.top = S.base;
return OK;
}
Judge whether the sequence stack is empty
// Judge whether it is an empty stack
Status StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
// If the stack is empty, return true; Otherwise, false is returned
if (S.top == S.base)return TRUE;
else return FALSE;
}
Find the length of sequential stack
// Find the length of the stack
int StackLength(SqStack S) {
return S.top - S.base;
}
Push
// Stack operation
// Judge whether the stack is full. If it is full, an error (overflow) will be reported
// Push element e into the top of the stack
// Stack top pointer plus 1
Status Push(SqStack& S, SElemType e) {
if (S.top - S.base == S.stacksize)return ERROR; // Stack full
*S.top++ = e;
return OK;
}
Out of stack
// Stack out operation
// Judge whether the stack is empty. If it is empty, there will be an error (underflow)
// Get stack top element e
// Stack top pointer minus one
Status Pop(SqStack& S, SElemType& e) {
if (S.top == S.base)return ERROR;
e = *--S.top;
return OK;
}
Access order stack top element
// Get stack top element
int GetTop(SqStack S, SElemType& e) {
if (S.top == S.base) {
e = -2;
return OVERFLOW;
}
else {
e = *--S.top;
return OK;
}
}
Test code and output results
Test code:
The input data field is [0, + ∞]. If the input data is - 1, the stack out operation will be executed.
int main()
{
SElemType data;
SqStack S;
SElemType head_data;
int code;
InitStack(S);
for (int i = 0; i <= MAXSIZE; i++) {
cout << "Merge input data elements into stack:";
cin >> data;
if (data == -1) { // Enter - 1 to perform the stack out operation
Pop(S, head_data);
cout << "Add stack top element:" << head_data << " Out of stack" << endl;
} // if
else {
cout << data << " Push " << endl;
Push(S, data);
} // else
code = GetTop(S, head_data);
int Slen = StackLength(S);
cout << "At this time, the stack length is:" << Slen << "\t Stack top elements are:" << head_data << endl;
if (StackEmpty(S) == TRUE) {
cout << "All data has been out of the stack" << endl;
break;
} // if
} // for
system("pause");
return 0;
}
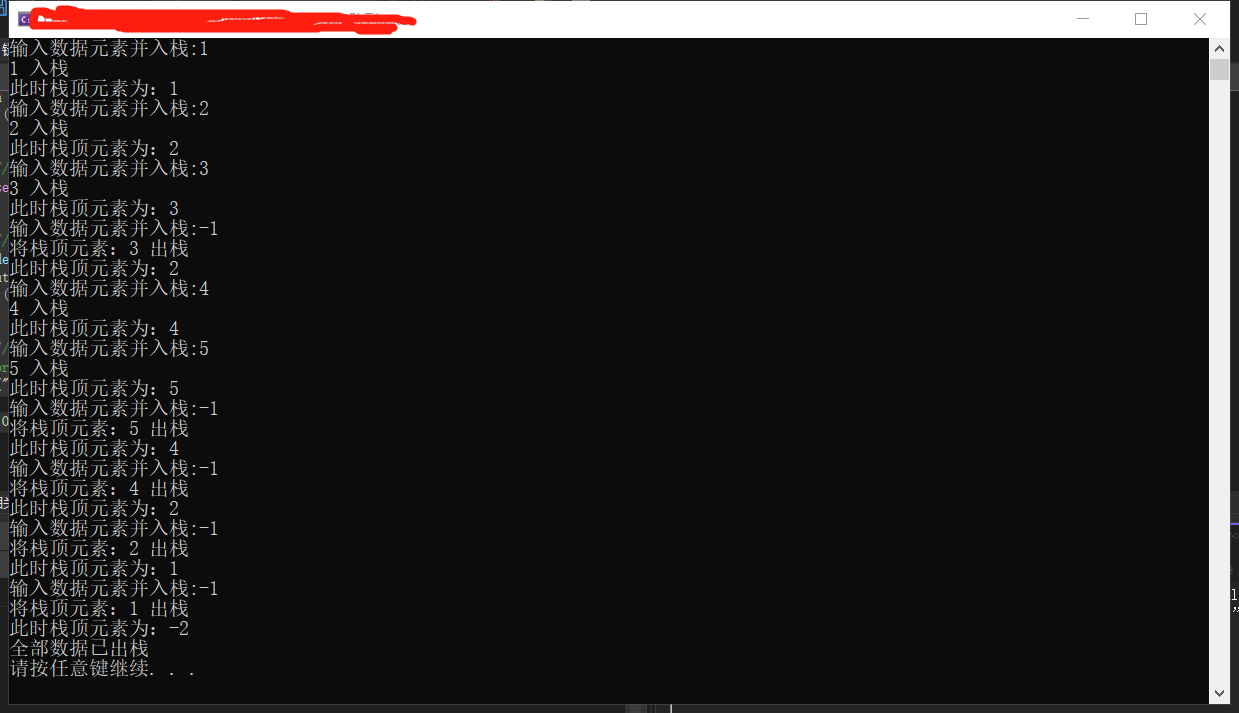
Output result:
Implementation of queue
Define identifier
#include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Function result status code #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define INFEASIBLE -1 #define OVERFLOW -2 #define MAXSIZE 100 #define MAXQSIZE 100 / / maximum queue length //Status is the type of function and its value is the result status code of the function typedef int Status; typedef int QElemType; // Define data element types
Chain implementation of queue
Define chained queue data structure
Define data node structure
typedef struct Qnode {
QElemType data; // Data domain
struct Qnode* next; // Pointer field
}Qnode,*QuenePtr;
Defines the head and tail pointer of a chained queue
typedef struct {
QuenePtr front; // Queue head pointer
QuenePtr rear; // Tail pointer
}LinkQueue;
Initialize chained queue
// Queue initialization
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue& Q) {
Q.front = Q.rear = new Qnode;
if (!Q.front)exit(OVERFLOW);
Q.front->next =NULL;
return OK;
}
Destroy chain queue
// Queue destruction
Status DestroyQueue(LinkQueue& Q) {
while (Q.front) {
QuenePtr p = Q.front->next;
delete Q.front;
Q.front = p;
}
return OK;
}
Join the team
// Queue up
Status EnQueue(LinkQueue& Q, QElemType e) {
QuenePtr p = new Qnode;
if (!p)exit(OVERFLOW);
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
Q.rear->next = p;
Q.rear = p;
return OK;
}
Out of the team
// Queue out
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue& Q, QElemType& e) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear)return ERROR;
QuenePtr p = Q.front->next;
e = p->data;
Q.front->next = p->next;
if (Q.rear == p)Q.rear = Q.front;
delete p;
return OK;
}
Access queue header element
// Queue header element
Status GetHead(LinkQueue Q,QElemType &e) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return OVERFLOW;
}// if
else {
e = Q.front->next->data;
return OK;
}
}
Test code and output structure
Test code:
The input data field is [0, + ∞]. If the input data is - 1, the stack out operation will be executed.
int main()
{
QElemType data;
LinkQueue Q;
QElemType head_data;
int code;
InitQueue(Q);
for (int i = 0; i <= MAXQSIZE; i++) {
cout << "Enter data elements and join the team:";
cin >> data;
if (data == -1) { // Enter - 1 to perform the queue out operation
DeQueue(Q, head_data);
cout << "Add team leader element:" << head_data << " Out of the team" << endl;
} // if
else {
cout << data << " Join the team" << endl;
EnQueue(Q, data);
} // else
code = GetHead(Q, head_data);
cout <<"\t The team head elements are:" << head_data << endl;
if (code == -2) {
cout << "All data out of the queue,Perform the destroy queue operation" << endl;
DestroyQueue(Q);
cout << "Queue destroyed" << endl;
break;
} // if
} // for
system("pause");
return 0;
} // main
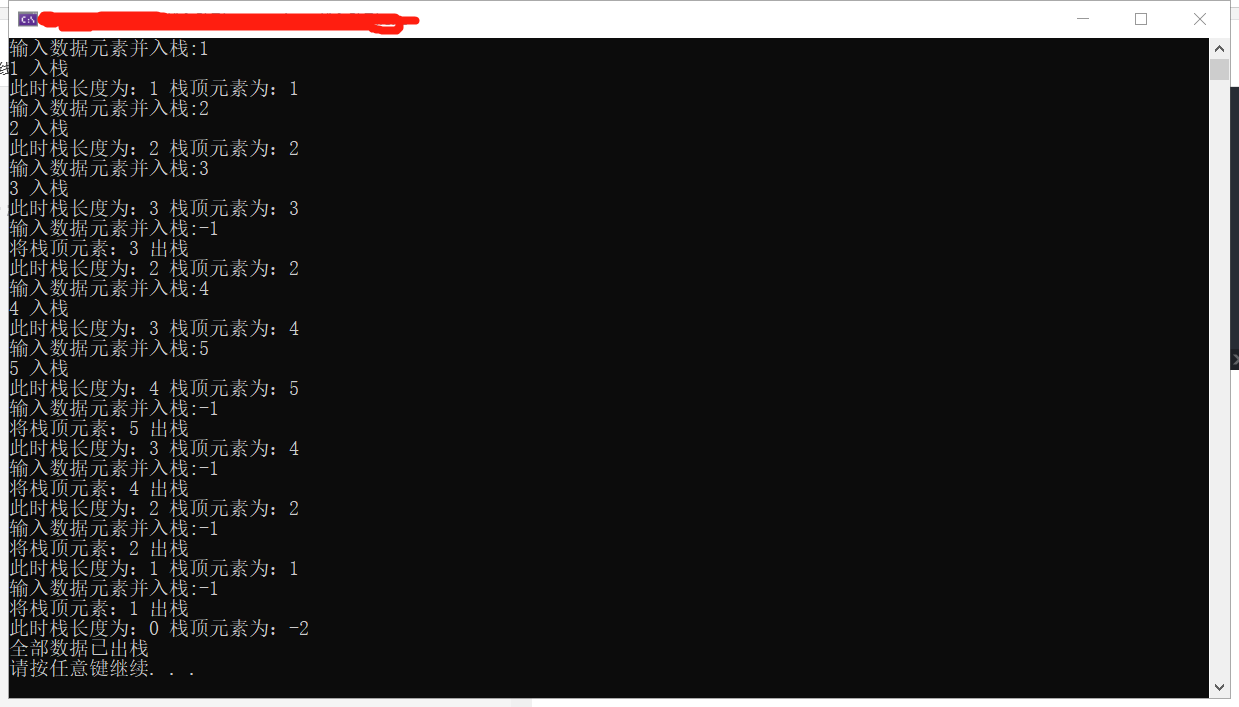
Output result:
Sequential implementation of queue
Define sequential queue data structure (circular queue)
// Define sequential queue data structure
typedef struct {
QElemType* base; //Initialize dynamic allocation of sequential space
int front; // Head pointer
int rear; // Tail pointer
}SqQueue;
Initialize sequential queue
// Queue initialization
Status InitQueue(SqQueue& Q) {
Q.base = new QElemType[MAXQSIZE]; // Allocate array space
if (!Q.base)exit(OVERFLOW); // memory allocation failed
Q.front = Q.rear = 0; // The head pointer and tail pointer are set to 0 and the queue is empty
return OK;
}
Get sequence queue length
// Find the length of the queue
int QueueLength(SqQueue Q) {
return ((Q.rear - Q.front + MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE);
}
Queue up (circular queue)
// Queue up of circular queue
Status EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, QElemType e) {
if ((Q.rear + 1) % MAXQSIZE == Q.front)return ERROR; // Team full
Q.base[Q.rear] = e; // New elements added to the tail of the team
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MAXQSIZE; // Tail pointer + 1
return OK;
}
Out of line (circular queue)
// Out of queue of circular queue
Status DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, QElemType& e) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear)return ERROR; // Team air
e = Q.base[Q.front]; // Save queue header element
Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MAXQSIZE; // Team leader pointer + 1
return OK;
}
Access queue header element
// Take the team head element
Status GetHead(SqQueue Q) {
if (Q.front != Q.rear) {
return Q.base[Q.front]; // Return queue header element
}
else {
return OVERFLOW; // Return error code
}
}
Test code and output structure
Test code:
The input data field is [0, + ∞]. If the input data is - 1, the stack out operation will be executed.
int main()
{
QElemType data;
SqQueue Q;
QElemType head_data;
InitQueue(Q);
for (int i = 0; i <= MAXQSIZE; i++) {
cout << "Enter data elements and join the team:";
cin >> data;
if (data == -1) { // Enter - 1 to perform the queue out operation
DeQueue(Q, head_data);
cout << "Add team leader element:" << head_data << " Out of the team" << endl;
} // if
else {
cout << data << " Join the team" << endl;
EnQueue(Q, data);
} // else
int Qlen = QueueLength(Q);
head_data = GetHead(Q);
cout << "At this time, the queue length is:" << Qlen << "\t The team head elements are:" << head_data << endl;
if (QueueLength(Q) == 0) {
cout << "All data are out of the queue" << endl;
break;
} // if
} // for
system("pause");
return 0;
} // main
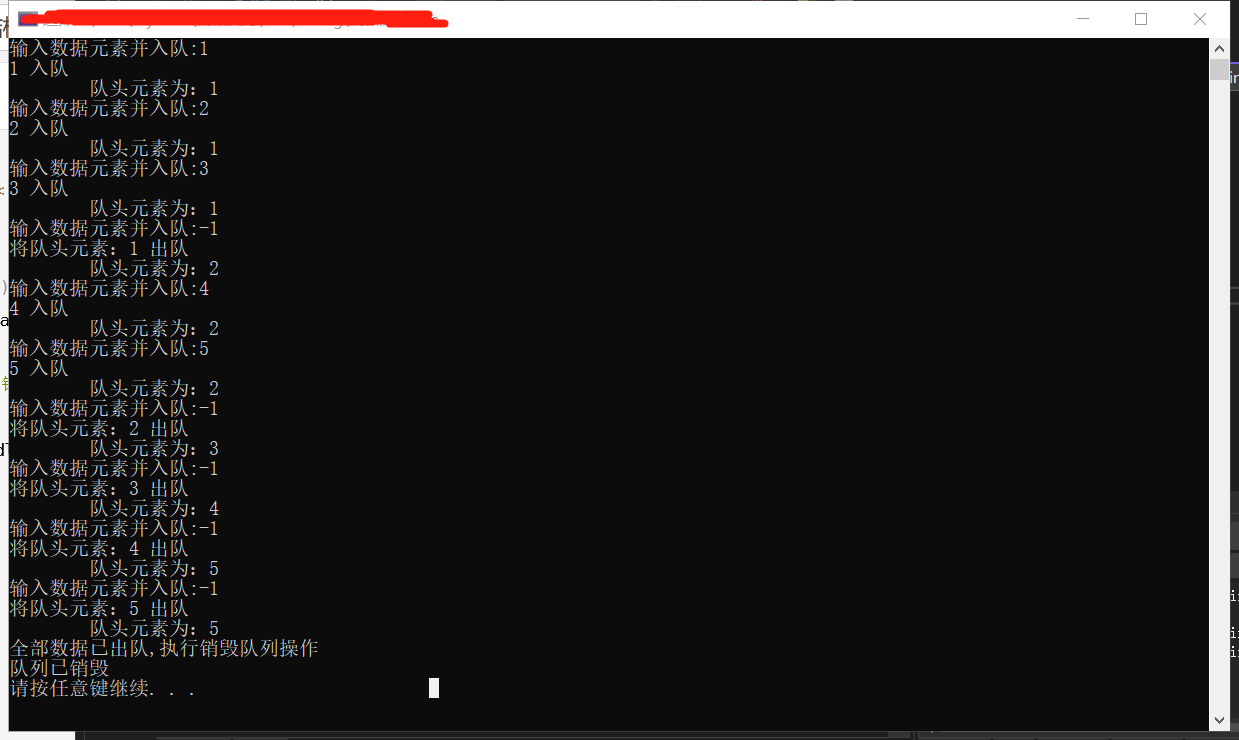
Output result: