1.String
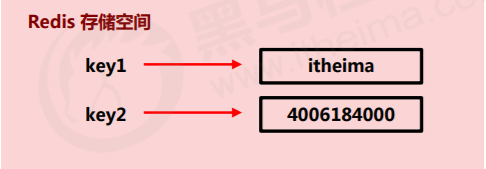
- Stored data: single data, the simplest data storage type and the most commonly used data storage type
- Format of stored data: one storage space holds one data
- Storage content: string is usually used. If the string is displayed in the form of integer, it can be used as digital operation
1.1 adding / modifying data
set key value
1.2 data acquisition
get key
1.3 deleting data
del key
1.4 adding / modifying multiple data
mset key1 value1 key2 value2 ...
1.5 obtaining multiple data
mget key1 key2 ...
1.6 get the number of data characters (string length)
strlen key
1.7 add information to the back of the original information (if the original information exists, add it, otherwise create a new one)
append key value
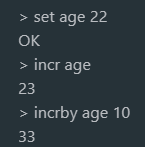
1.8 example 1

1.9 self increment (can be negative)
incr key //Self increase + 1 incrby key increment //Self increment + increment incrbyfloat key increment//Self increment + floating point number increment
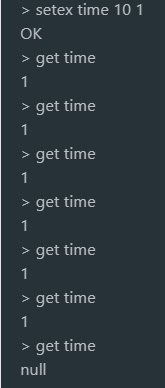
1.10 setting data has a specified life cycle (clearing data by time)
setex key seconds value psetex key milliseconds value
Set the value of time in 10s to 1. After 10s, there is no value in time
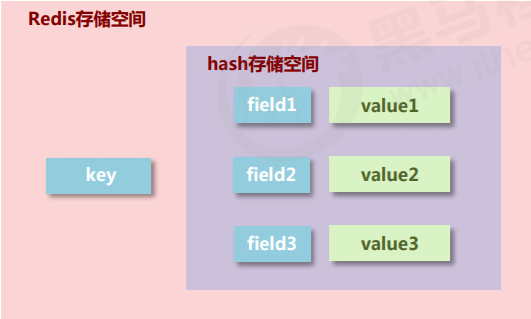
2.hash
- New storage requirements: organize a series of stored data to facilitate management, and store object information in typical applications
- Required storage structure: one storage space holds multiple key value pair data
2.1 adding / modifying data
hset key field value
2.2 data acquisition
hget key field hgetall key
2.3 deleting data
hdel key field1 [field2]
2.4 adding / modifying multiple data
hmset key field1 value1 field2 value2 ...
2.5 obtaining multiple data
hmget key field1 field2 ...
2.6 get the number of fields in the hash table
hlen key
2.7 get whether the specified field exists in the hash table
hexists key field
2.8 example 2
Zhang San's address is Shanghai and his telephone number is 110
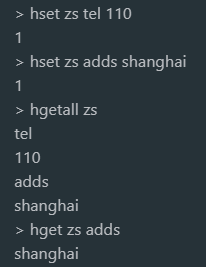
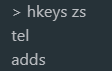
Gets the name of all fields in the hash table or 9.2
hkeys key hvals key
2.10 self increment
hincrby key field increment hincrbyfloat key field increment
3.list
- Data storage requirements: store multiple data and distinguish the order in which the data enters the storage space
- Required storage structure: one storage space holds multiple data, and the entry order can be reflected through the data
- List type: save multiple data, and the bottom layer is realized by using the storage structure of two-way linked list

3.1 adding / modifying data
lpush key value1 [value2] ......//Put data from the head of the team rpush key value1 [value2] ......//Release data from the tail of the team
3.2 obtaining data (subscript starts from 0)
lrange key start stop//Get stop from start lindex key index//Take the first data llen key
3.3 acquiring and removing data
lpop key rpop key
3.4 acquire and remove data within the specified time
blpop key1 [key2] timeout brpop key1 [key2] timeout brpoplpush source destination timeout
3.5 remove specified data
lrem key count value
3.6 example 3
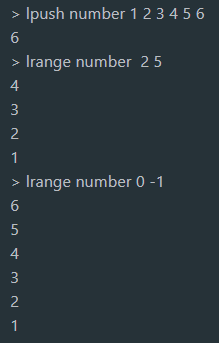
4.set
- New storage requirements: store a large amount of data and provide higher efficiency in query
- Required storage structure: it can save a large amount of data, and has an efficient internal storage mechanism to facilitate query
- set type: exactly the same as the hash storage structure. Only keys are stored, and values (nil) are not stored, and duplicate values are not allowed
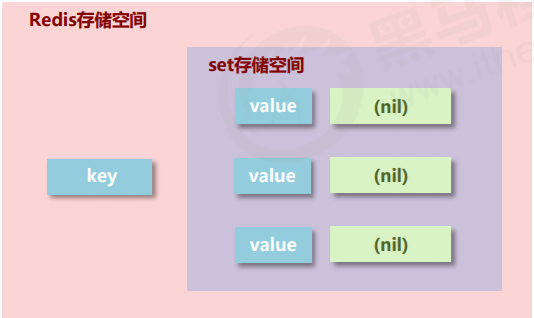
4.1 adding data
sadd key member1 [member2]
4.2 obtaining all data
smembers key
4.3 deleting data
srem key member1 [member2]
4.4 get total set data
scard key
4.5 judge whether the set contains specified data
sismember key member
4.6 randomly obtain the specified amount of data in the set
srandmember key [count]
4.7 randomly obtain a certain data in the set and move the data out of the set
spop key [count]
4.8 find the intersection, union and difference sets of two sets
sinter key1 [key2] sunion key1 [key2] sdiff key1 [key2]
4.9 find the intersection, union and difference sets of two sets and store them in the specified set
sinterstore destination key1 [key2] sunionstore destination key1 [key2] sdiffstore destination key1 [key2]
4.10 move the specified data from the original set to the target set
smove source destination member
5.sorted_set type
- New storage requirements: data sorting is conducive to the effective display of data. It needs to provide a way to sort according to its own characteristics
- Required storage structure: a new storage model can save sortable data
- sorted_set type: add sortable fields based on the storage structure of set
5.1 adding data
Here, the score is used as the ranking score
zadd key score1 member1 [score2 member2]
5.2 obtaining all data
zrange key start stop [WITHSCORES] zrevrange key start stop [WITHSCORES]
5.3 deleting data
zrem key member [member ...]
5.4 obtaining data according to conditions
zrangebyscore key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT] zrevrangebyscore key max min [WITHSCORES]
5.5 conditional deletion of data
zremrangebyrank key start stop zremrangebyscore key min max
5.6 get the total amount of set data
zcard key zcount key min max
5.7 get the index (ranking) corresponding to the data
zrank key member zrevrank key member
5.8score value acquisition and modification
zscore key member zincrby key increment member