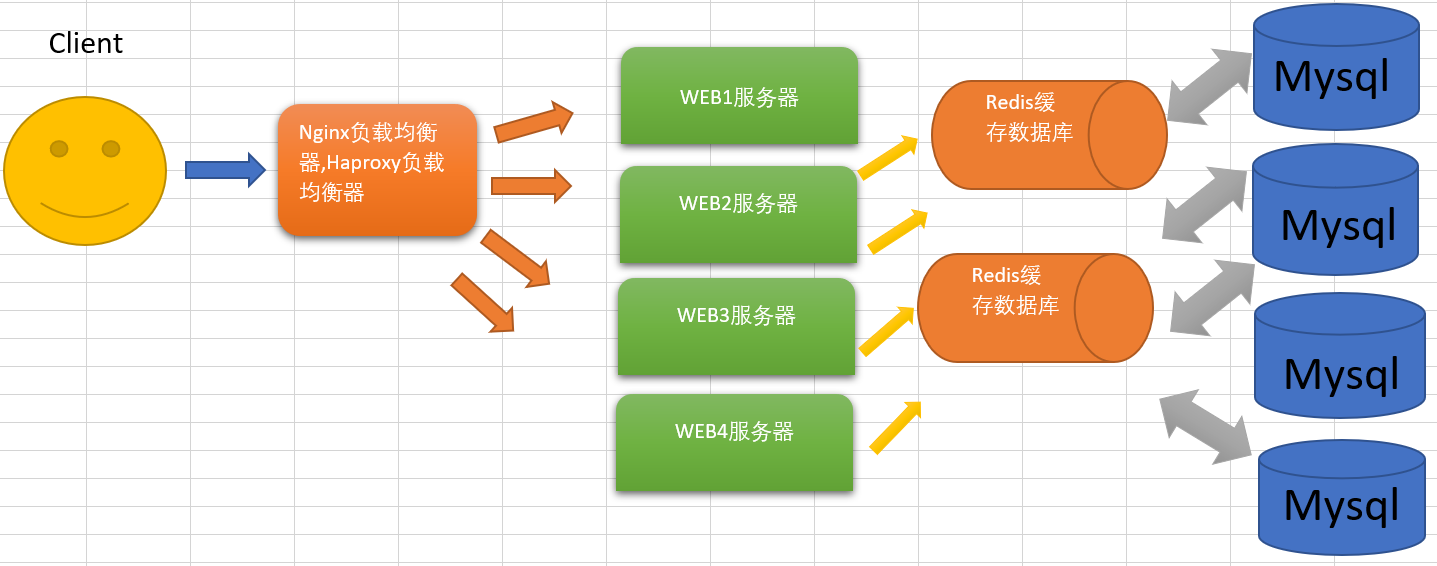
Architecture diagram
Install Redis service
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-2.8.6.tar.gz tar -xvf redis-2.8.6.tar.gz cd redis-2.8.6 make mkdir /usr/local/redis/etc cp redis.conf /usr/local/redis/etc/
ps: make error
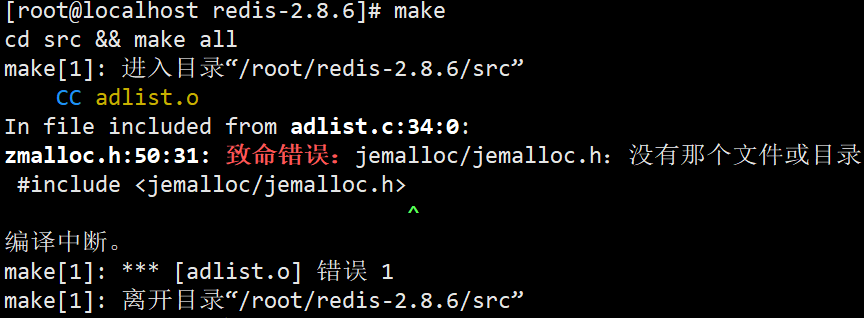
resolvent:
Execute the command make MALLOC=libc
Modify the profile to start the service
vim /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.conf daemonize yes # Running as a daemon does not occupy the shell exchange interface # Start redis /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server /usr/local/redis/etc/redis-server # Turn off redis pkill -9 redis-server or killall redis-server
Common Redis commands
5 big data types
- string
- hash
- list
- set
- zset
string is the simplest type
A key corresponds to a value, and the string type is binary safe. redis's string can contain any data
hash is a mapping table of field and value of string type
Its addition and deletion operations are 0 (1) average; Hash is especially suitable for storing objects. Compared with storing each field of an object as a single string type, storing an object in hash type will occupy less memory and can access the whole object more conveniently.
List is a linked list structure. Its main functions are push, pop, obtaining all values in a range, etc
In operation, key is understood as the name of the linked list. Redis's list type is actually a two-way linked list in which each child element is of string type. We can add or delete elements from the head or tail of the linked list through push and pop operations.
Set is a set. It is an unordered set of string type.
Set is realized through hash table, including set, intersection and difference sets. Through these operations, we can realize the friend recommendation and blog tag functions in social networking sites. Duplicate values are not allowed in the collection.
zset is an upgraded version of set. It adds an order attribute on the basis of set. This attribute can be specified when adding and modifying elements. After each assignment, zset will automatically adjust the order according to the new value.
It can be understood as a mysql table with two columns, one for value and the other for order. In operation, key is understood as the name of zset.
Key values String operation
ln -s /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli /usr/local/bin/redis-cli redis-cli # -h IP: connect to the specified redis server # -p 6379: specify the port of the redis server # -A password: log in with a password # -n database number: specifies which database to connect to # --raw: redis supports storing Chinese 127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 v1 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "v1" 127.0.0.1:6379> exists k1 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> type k1 string 127.0.0.1:6379> dbsize (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> del k1 (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 (nil) 127.0.0.1:6379>
Command for value operation
- exists(key): confirm whether a key exists
- del(key): deletes a key
- type(key): the type of return value
- keyrename(oldname, newname): renames the key
- dbsize: returns the number of key s in the current database
- expire: set the active time of a key (s)
- ttl: get the activity time of a key
- flushdb: deletes all key s in the currently selected database
- Flush all: delete all key s in all databases
Hash type operation
127.0.0.1:6379> hmset zhangsan name zhangsan age 18 sex man OK 127.0.0.1:6379> hmset lisi name lisi age 25 sex man OK 127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall zhangsan 1) "name" 2) "zhangsan" 3) "age" 4) "18" 5) "sex" 6) "man" 127.0.0.1:6379> hgetall lisi 1) "name" 2) "lisi" 3) "age" 4) "25" 5) "sex" 6) "man"

list operation
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush zhangsan zhangsan (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> rpush zhangsan 18 (integer) 2 127.0.0.1:6379> rpush zhangsan sex (integer) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> lrange zhangsan 0 -1 1) "zhangsan" 2) "18" 3) "sex" 127.0.0.1:6379>

set data type
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd mset 1 2 3 4 5 6 (integer) 6 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers mset 1) "1" 2) "2" 3) "3" 4) "4" 5) "5" 6) "6" 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd mset1 zhangsan lisi wangwu (integer) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> smembers mset1 1) "wangwu" 2) "zhangsan" 3) "lisi"
Modify redis password
vim /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.conf requirepass 123456 redis-cli -a 123456
Redis semi persistent RDB
vim /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.server save 900 1 save 300 10 save 60 10000 # Modify the key once in 900 seconds # Modify 10 key s in 300 seconds # Modify 10000 key s in 60 seconds
When the default match is added and takes effect, a file named dump. Will be generated in the / usr/local/redis directory RDB file
Modify the configuration line dbfilename dump RDB can modify the default file name
Redis fully persistent AOF
vim /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.server appendonly yes appendfilename appendonly.aof auto - aof - rewrite- percentage 100 auto - aof - rewrite- min- size 64MB appendfsync always # appendfsync everysec # appendfsync no
appendonly yes: enable AOF persistence.
appendfilename appendonly.aof: AOF persistent save file name.
Auto AOF rewrite percentage 100: when the AOF file size exceeds the percentage of the AOF file size at the time of the last rewrite, it will be rewritten again. If it has not been rewritten before, it will be based on the AOF file size at startup.
Auto AOF rewrite min size 64MB: the minimum AOF file size allowed to be rewritten configures the mechanism that requires the system to refresh the hard disk cache after writing the AOF file.
Appendsync always: synchronization is performed every time a write is performed, which is the safest and slowest.
Redis master-slave copy read-write separation
- The master server Maset does not need to be configured
- Configure from server
vim /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.server slaveof 192.168.126.135 6379 # Start service # Or execute the command in redis slaveof 192.168.126.135 6379
- Persistence: persistence is the simplest high availability method (sometimes it is not even classified as a high availability method). Its main function is data backup, that is, data is stored on the hard disk to ensure that data will not be lost due to process exit.
- Replication: replication is the basis of highly available Redis. Sentinels and clusters achieve high availability on the basis of replication. Replication mainly realizes multi machine backup of data, load balancing for read operation and simple fault recovery. Defect: failure recovery cannot be automated; The write operation cannot be load balanced; The storage capacity is limited by a single machine.
- Sentry: on the basis of replication, sentry realizes automatic fault recovery. Defect: write operation cannot be load balanced; The storage capacity is limited by a single machine.
- Cluster: through cluster, Redis solves the problem that the write operation cannot be load balanced and the storage capacity is limited by a single machine, and realizes a relatively perfect high availability scheme.