Don't stay in pursuit of the wind and the moon. The spring mountain is at the end of Pingwu.
1, Web page analysis
Open URL Comparison verification platform
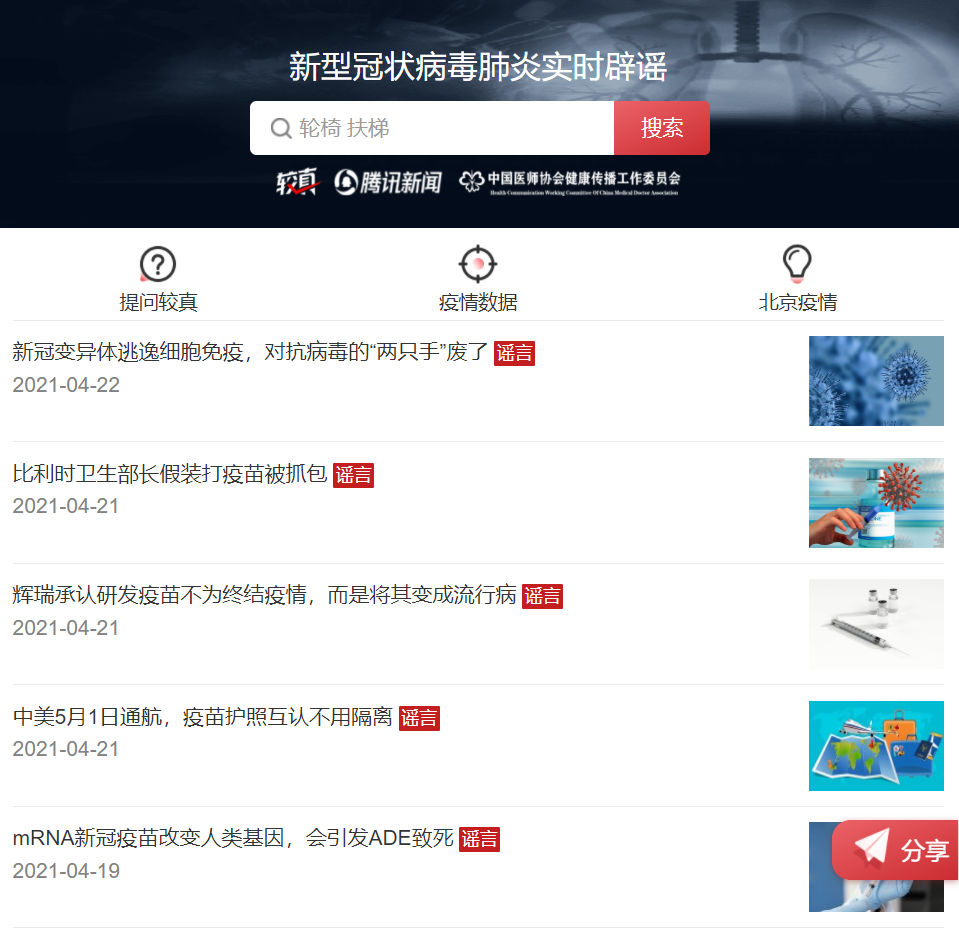
Open the developer mode and refresh the web page. When you look down, you notice a request for refresh URL
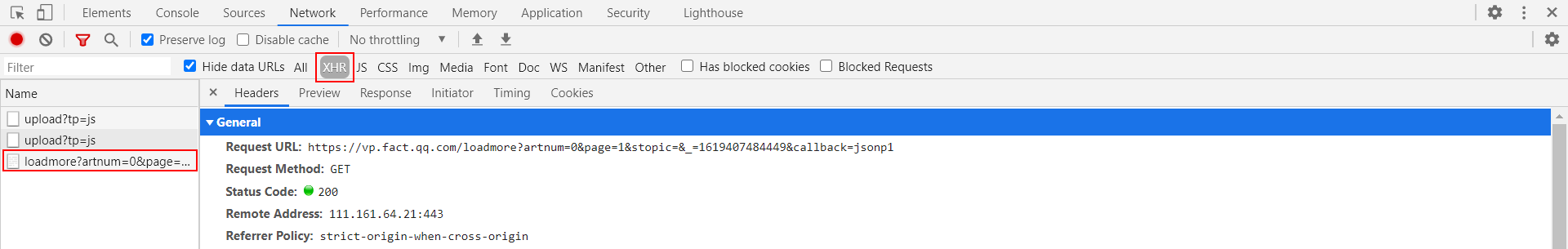
The requested data is
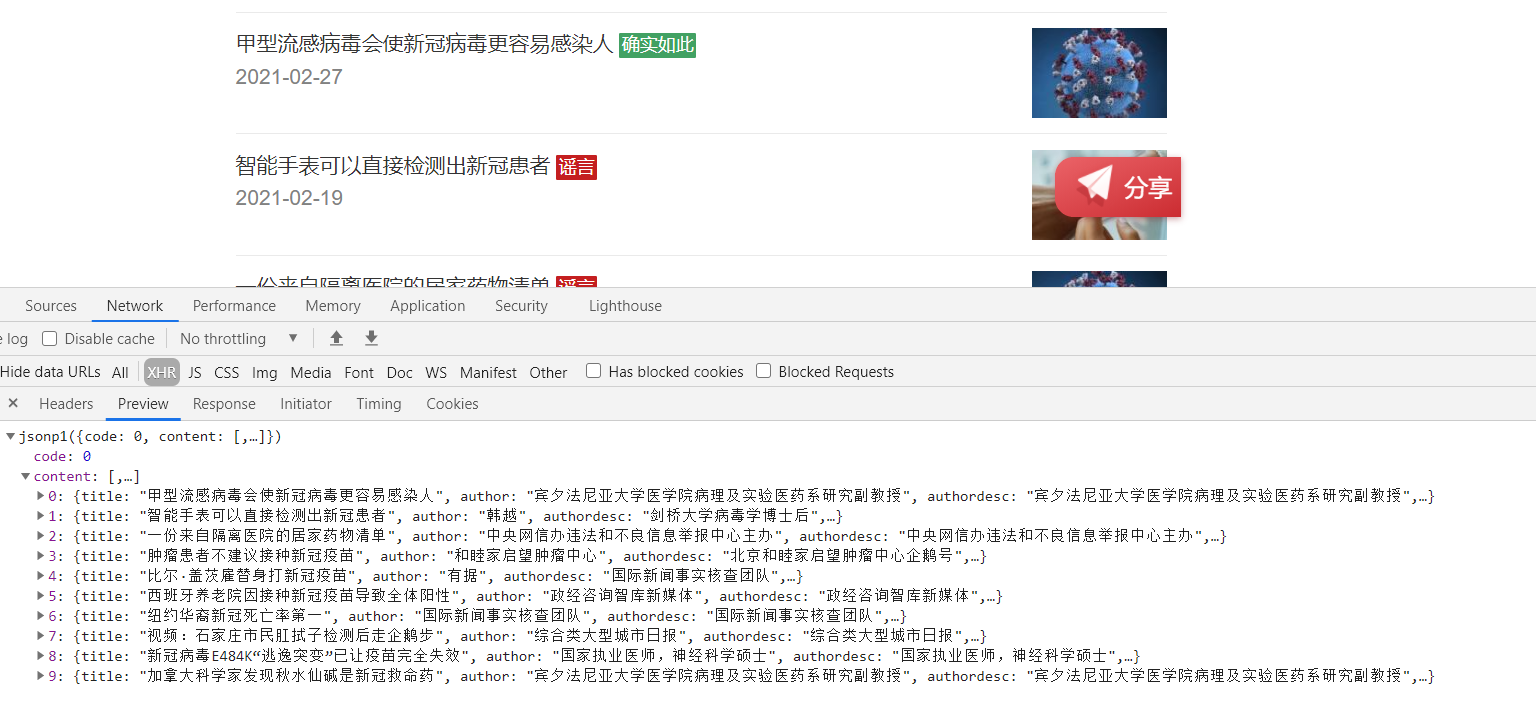
It just corresponds to the content in the web page.
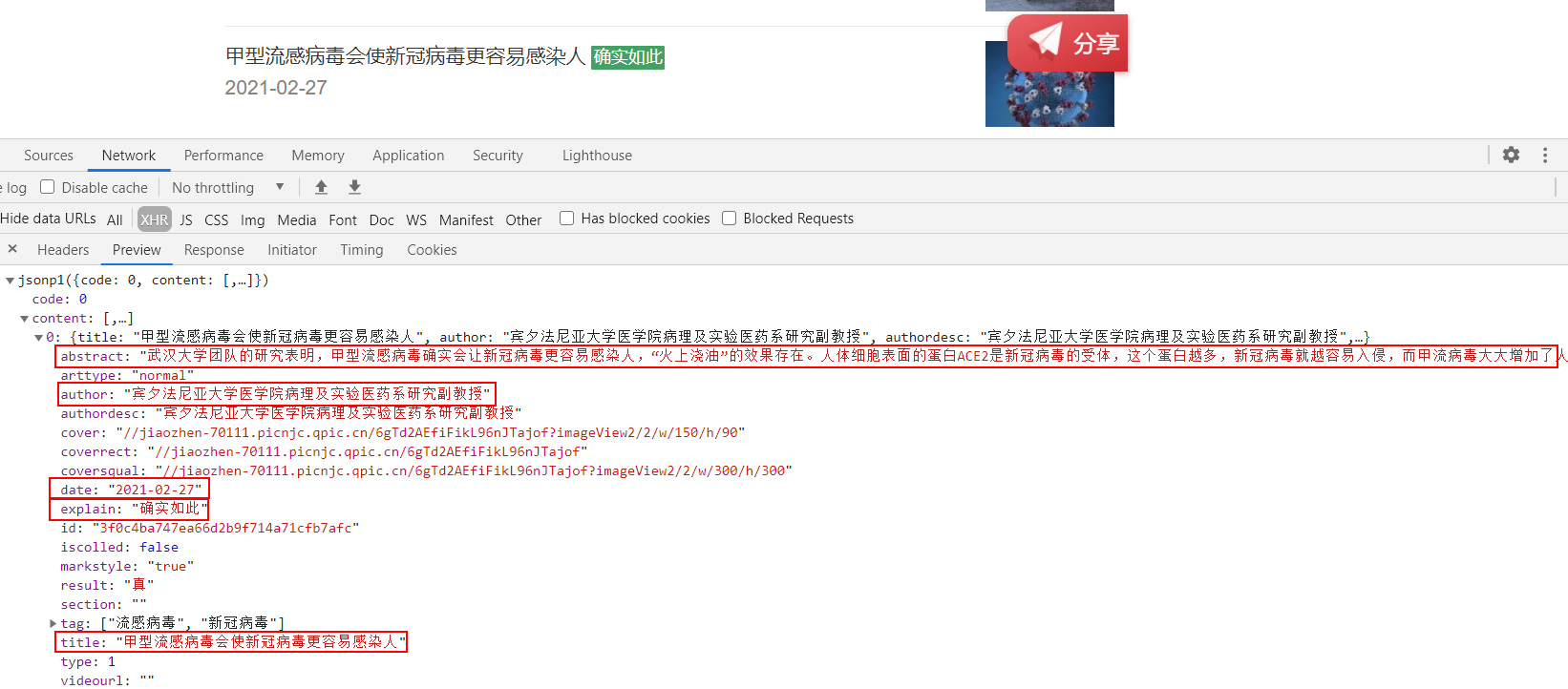
It also includes the title, the authenticity of the speech, the time, the key points of verification and the verifier.
2, Interface analysis
url analysis
https://vp.fact.qq.com/loadmore?artnum=0&page=1&stopic=&_=1619407484449&callback=jsonp1
We can easily find that page=1 indicates the number of pages. We can verify that when page=0, we actually return the data of the first page.
stopic=&_= 1619407484449. When you see the following 13 digits, the first response is a timestamp, and it is also a millisecond timestamp. That's the fact.

Return analysis data
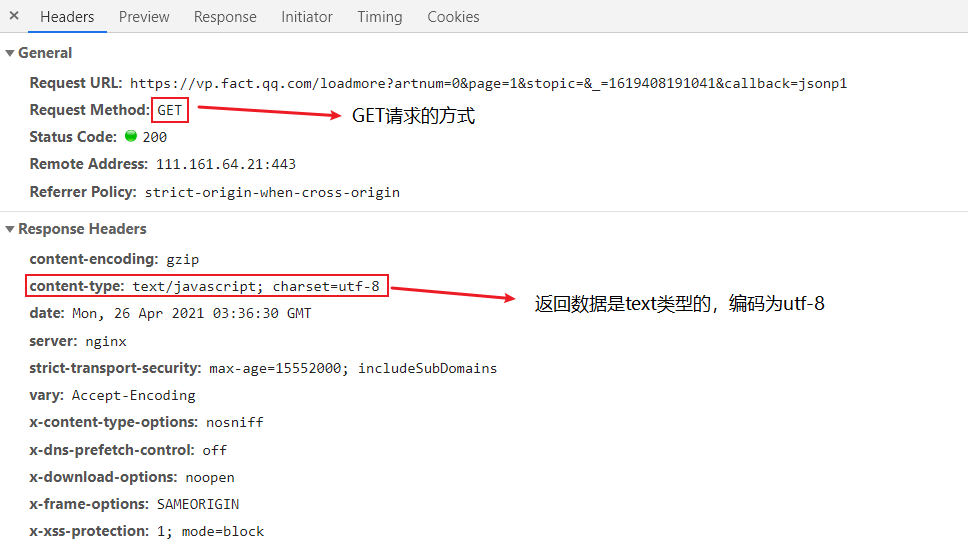
Although the displayed return data type is text, the browsing format always feels like JSON format

It is found that the returned data is in the format of json_data (jsonp1), so we just need to remove jsonp1() and extract the content in the middle to format it into JSON data
3, Write code
Knowing the url rules and the format of the returned data, our task now is to construct the url and then request the data
We can set two variables, page and timestamp, to represent the number of pages and timestamp
The page change is very simple. Just use the for loop to cycle directly
for page in range(0, 100):
timestamp is generated with the help of time library
timestamp = int(time.time()*1000)
Now construct the url:
url = "https://vp.fact.qq.com/loadmore?artnum=0&page={}&stopic=&_={}&callback=jsonp1".format(page, timestamp)
Next, generate the url of the first 100 pages:
for page in range(0, 100):
timestamp = int(time.time()*1000)
url = "https://vp.fact.qq.com/loadmore?artnum=0&page={}&stopic=&_={}&callback=jsonp1".format(page, timestamp)
For each url, we need to use the get method in the requests library to request data:
So for convenience, we write the code of requesting the web page as the function get_html(url), the passed in parameter is url, and the returned content is the requested content.
def get_html(url):
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.82 Safari/537.36"
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding
time.sleep(3) # Add 3s delay to prevent reverse climbing
return response.text
Now we use requests Get () only passes in two parameters, URL and headers. In fact, there are more parameters. Please Baidu yourself.
This website only needs these two parameters.
The purpose of passing in headers is to simulate browser access and prevent it from being crawled back.
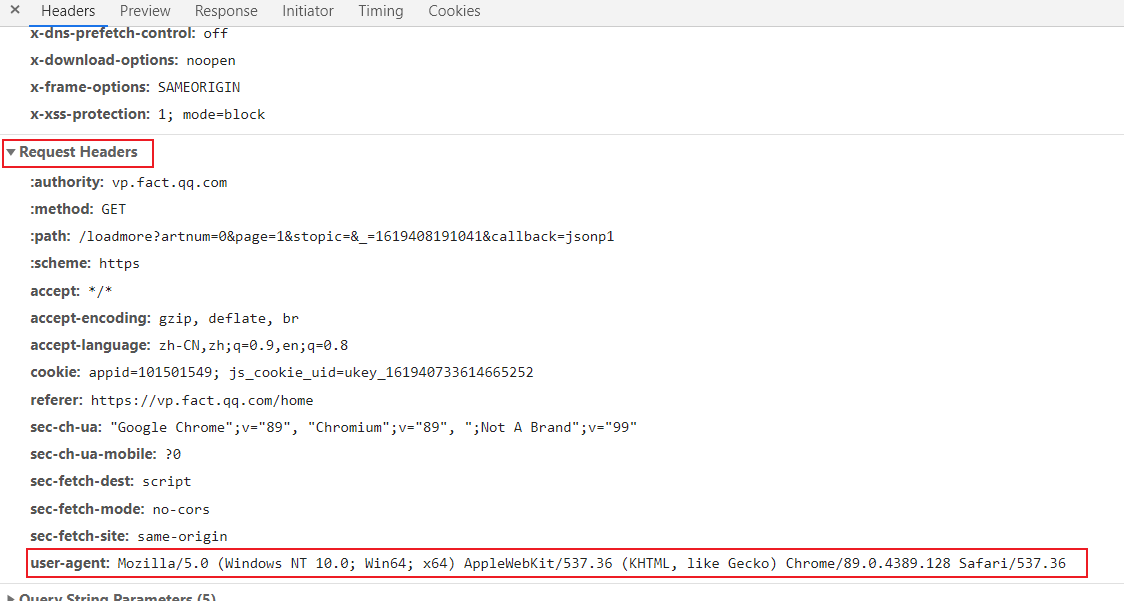
You can find the relevant information of headers here. Now we only need the user agent.
As mentioned above, the returned data is actually in pseudo json format. We can turn it into json format data after processing
for page in range(0, 100):
timestamp = int(time.time()*1000)
url = "https://vp.fact.qq.com/loadmore?artnum=0&page={}&stopic=&_={}&callback=jsonp1".format(page, timestamp)
html = get_html(url) # At this time, the data stored in html is in pseudo json format
html = html[7:-1] # Use string extraction to extract the content of json format in the middle
We use the json library to format the data to make it more convenient for us to extract later
response = json.loads(html)
At this point, the data processing part is completed, and the next step is data extraction.
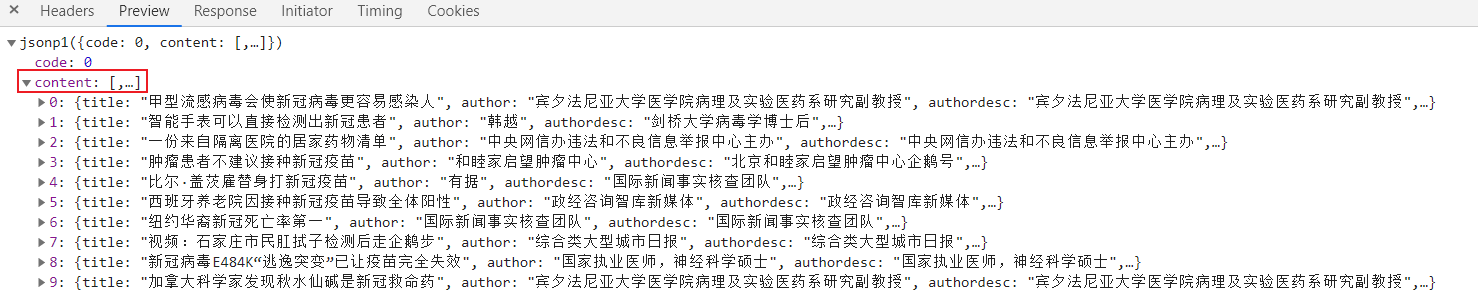
We found that the data is under the content tag, so we use
response = response['content']
To extract the data in the list. At this time, the response is a list type of data
Then let's traverse the list, extract the required data and coexist in a dictionary
for i in response:
data = {}
data['explain'] = i['explain']
data['title'] = i['title']
data['date'] = i['date']
data['result'] = i['result']
data['author'] = i['author']
data['abstract'] = i['abstract']
Then the next step is to save. I also wrote a function save_data(data) is data of dictionary type
def save_data(data):
title = ["title", "date", "explain", "result", "author", "abstract"]
with open("Epidemic rumor data.csv", "a", encoding="utf-8", newline="")as fi:
fi = csv.writer(fi) # Import csv Library
fi.writerow([data[i] for i in title]) # write file
Extract the data and call the save function OK.
for i in response:
data = {}
data['explain'] = i['explain']
data['title'] = i['title']
data['date'] = i['date']
data['result'] = i['result']
data['author'] = i['author']
data['abstract'] = i['abstract']
save_data(data)
Complete code
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @time: 2021/4/26 11:05
# @Author: pioneer
# @Environment: Python 3.7
import json
import requests
import csv
import time
def get_html(url):
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.82 Safari/537.36"
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = response.apparent_encoding # Automatically identify and set codes
time.sleep(3) # Add 3s delay to prevent reverse climbing
return response.text
def save_data(data):
title = ["title", "date", "explain", "result", "author", "abstract"]
with open("Epidemic rumor data.csv", "a", encoding="utf-8", newline="")as fi:
fi = csv.writer(fi) # Import csv Library
fi.writerow([data[i] for i in title]) # write file
def get_data():
for page in range(0, 100):
timestamp = int(time.time()*1000)
url = "https://vp.fact.qq.com/loadmore?artnum=0&page={}&stopic=&_={}&callback=jsonp1".format(page, timestamp)
html = get_html(url) # At this time, the data stored in html is in pseudo json format
html = html[7:-1] # Use string extraction to extract the content of json format in the middle
response = json.loads(html)
response = response['content'] # Extract data list
for i in response:
data = {}
data['explain'] = i['explain']
data['title'] = i['title']
data['date'] = i['date']
data['result'] = i['result']
data['author'] = i['author']
data['abstract'] = i['abstract']
save_data(data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_data()
Screenshot of some data obtained

Welcome to triple CLICK!
Which website crawler do you want to see? Welcome to leave a message. Maybe what you want to analyze next time is what you want to see!