Author: empty none
Link: https://juejin.cn/post/6945753017878577165
Logback is an old logging framework in JAVA. It has been iterating for more than ten years since its first version in 2006. However, the latest stable version of logback is still in 2017 and has not been updated for several years; The last stable version of logback's brother slf4j is also 2017, which means it's a little cool.
Moreover, the asynchronous performance of logback is really stretched, the function is simple, and the configuration is cumbersome. It is far less than the new generation logging framework of Apache - Log4j2
At present, Log4j2 is the king, and other log frameworks are not rivals
Log4j2 introduction
Apache Log4j 2 is an upgraded version of Log4j(1), which is better than its ancestor log4j 1 X has been greatly improved compared with logback. In addition to the adjustment of internal design, there are major upgrades in the following points:
- Simpler configuration
- More powerful parameter formatting
- The most exaggerated asynchronous performance
Log4j 2 is divided into two modules: API (log4j API) and Implementation (log4j core). API and slf4j are one type, belonging to log abstraction / facade, while the implementation part is the core of log4j 2.
- org.apache.logging.log4j » log4j-api
- org.apache.logging.log4j » log4j-core
Best performance
Strongest asynchronous performance
This feature is the strongest part of log4j2. Log4j2 in the current logging framework in JAVA, the performance of asynchronous logging is the highest, not one.
Let's take a look at the comparison results of several log frameworks (log4j2 official test results):
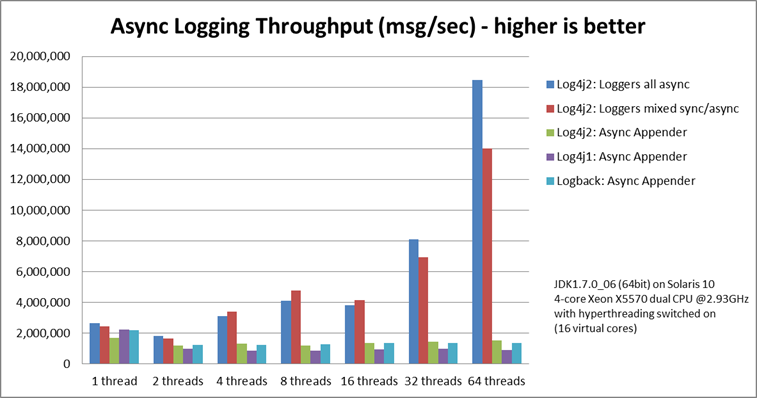 From figure
From figure
It can be seen from the above that the performance of log4j2 under asynchronous (fully asynchronous and non mixed mode) is far better than that of log4j1 and logback, which is almost a sling. The greater the pressure, the greater the gap in throughput.
Under the 64 thread test, the throughput of log4j2 reached 180w+/s, while that of logback/log4j1 was less than 20w, a difference of nearly ten times
Zero GC (garbage free)
Since version 2.6 (2016), log4j2 has been running in zero GC mode by default. What is zero GC? No GC due to log4j2.
All Message objects, string arrays and byte arrays in log4j 2 are reused without repeated creation, which greatly reduces the creation of useless objects, so as to achieve "zero GC".
Support for higher performance I/O writes
log4j also provides a MemoryMappedFile appender. The I/O part is implemented by MemoryMappedFile, which can get very high I/O performance.
However, before using MemoryMappedFile appender, make sure you know enough about MemoryMappedFile, otherwise don't use it easily.
More powerful parameter formatting
Compared with slf4j, API module provides richer parameter formatting functions.
Format parameters using {} placeholders
In slf4j, we can use {} to realize the function of "format" (the parameter will directly replace the placeholder with toString), as follows:
logger.debug("Logging in user {} with birthday {}", user.getName(), user.getBirthdayCalendar());Use string Format parameters in the form of format
Log4j 2 supports not only the parameter placeholder of {}, but also string Format:
public static Logger logger = LogManager.getFormatterLogger("Foo");
logger.debug("Logging in user %s with birthday %s", user.getName(), user.getBirthdayCalendar());
logger.debug("Logging in user %1$s with birthday %2$tm %2$te,%2$tY", user.getName(), user.getBirthdayCalendar());
logger.debug("Integer.MAX_VALUE = %,d", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
logger.debug("Long.MAX_VALUE = %,d", Long.MAX_VALUE);Note if you want to use string In the form of format, you need to use logmanager Getformatterlogger instead of logmanager getLogger
Use logger Printf format parameters
There is also a printf method in the Logger interface of log4j2, which does not need to create logmanager Getformatterlogger, you can use string Format form
logger.printf(Level.INFO, "Logging in user %1$s with birthday %2$tm %2$te,%2$tY", user.getName(), user.getBirthdayCalendar());
logger.debug("Opening connection to {}...", someDataSource);lazy logging
Although this function is small, it is very practical.
In some business processes, in order to keep the root or trace the problem, it is necessary to print the input parameters completely. Generally, the input parameters are serialized with JSON/XML and printed at the debug level:
logger.debug("Incoming message:{}",JSON.toJSONString(policyDTO));If problems need to be traced, the log level of the system will be adjusted to debug/trace so that it can be printed. But there is a problem here. Although debug will not output content at the info level, JSON The serialized code tojsonstring() will be executed, which will seriously affect the execution efficiency under the normal process.
The expected result is that no serialization is performed at the info level. Here, you can judge whether the debug level under the current configuration can be output through isdebugnenable:
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Incoming message:{}",JSON.toJSONString(policyDTO));
}Although this can avoid unnecessary serialization, it is still a little uncomfortable to write this everywhere. One line becomes three lines.
The logger object of log4j2 provides a series of lambda support. Through these interfaces, you can achieve "lazy" logging:
void debug(String message, Supplier<?>... paramSuppliers);
void info(String message, Supplier<?>... paramSuppliers);
void trace(String message, Supplier<?>... paramSuppliers);
void error(String message, Supplier<?>... paramSuppliers);
//It is equivalent to the following: judge first and then print
logger.debug("Incoming message:{}",() -> JSON.toJSONString(policyDTO));
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Incoming message:{}",JSON.toJSONString(policyDTO));
}This form of Supplier + Lambda is equivalent to judging isdebugnenable first and then printing. Three lines of code become one line. Well, it smells good.
Simpler configuration
Log4j 2 supports XML/JSON/YML/Properties configuration files at the same time, but the most popular way is XML, which is the most intuitive.
Let's take a look at the configuration files of logback and log4j2. Under the configuration of the same function:
logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<appender name = "File" class= "ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>logs/app.log</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>logs/archives/app-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log.gz</fileNamePattern>
<!--More than in one day size Separate them-->
<maxFileSize>1 GB</maxFileSize>
</rollingPolicy>
</appender>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="File"/>
</root>
</configuration>log4j2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude"
status="warn" name="XInclude">
<Appenders>
<RollingFile name="File" fileName="logs/app.log" filePattern="logs/archives/app-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%i.log.gz">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %5p [%t] %-40.40c{1.} : %m%n"/>
<Policies>
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy />
<!--More than in one day size Separate them-->
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="1 GB"/>
</Policies>
</RollingFile>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Root level="INFO">
<AppenderRef ref="File"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>In log4j 2, the configuration of Appender is more concise in syntax from the form of using Appender to implement name tag signature:
<RollingFile name="File"> <!-- Equivalent to logback Medium --> <appender name = "File" class= "ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
Adapt to other log abstractions / facade
log4j2 is divided into two parts: API and implementation, so it may also need to be adapted to other logging frameworks. Please refer to my other article for detailed logging framework adaptation scheme.
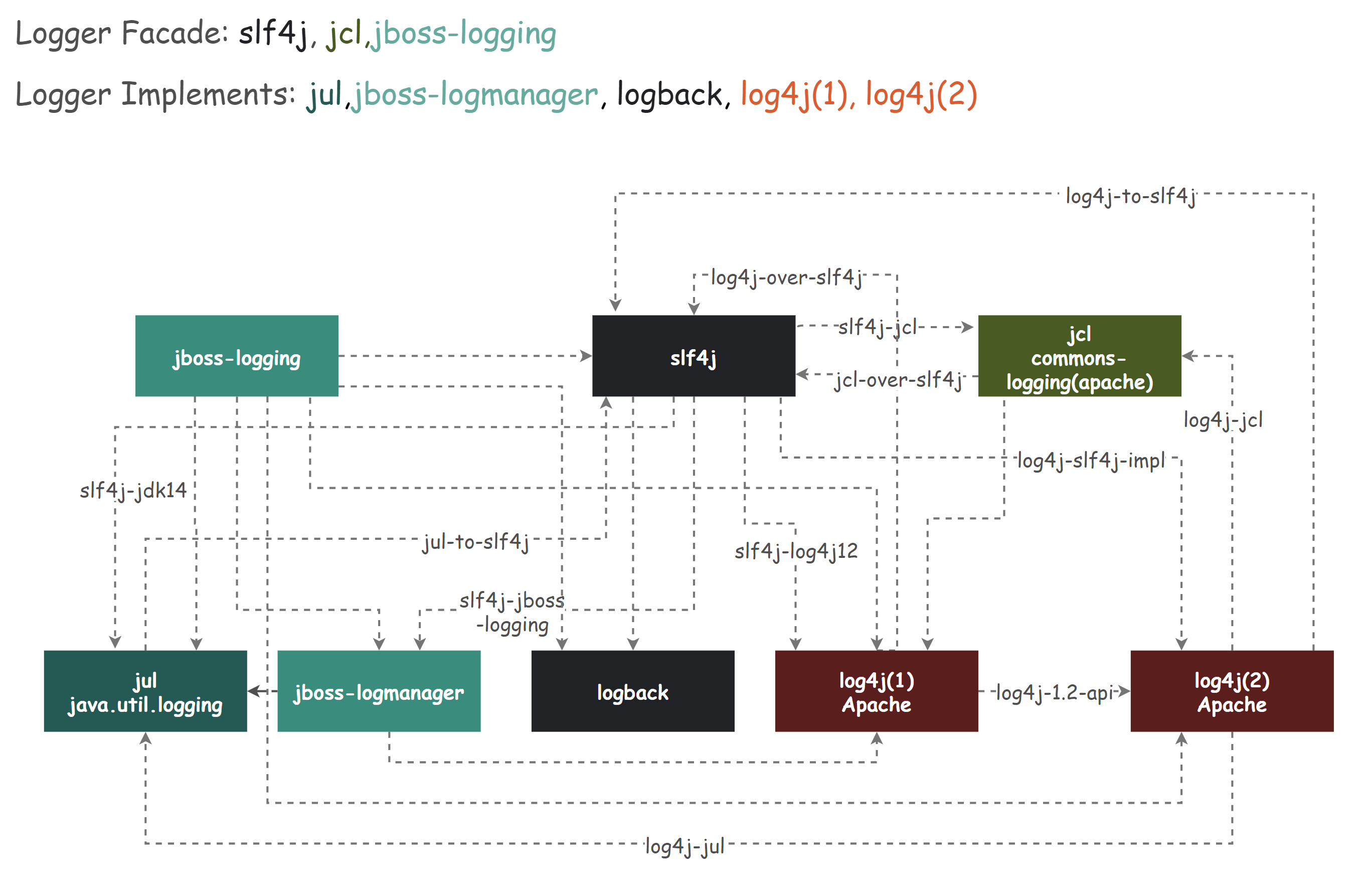
Other features
- Asynchronous queues use high-performance queues - * LMAX Disruptor*
- There are abundant Appenders, supported by JMS/JPA/KAFKA/Http/MONGODB/CouchDB/Socket/Script and other Appenders
- Support custom log level
- ......
Basic Usage
Finally, I have introduced the power of Log4j2. Now let's introduce the basic use of Log4j2.
maven dependency referencing log4j2
Log4j API already has dependencies in log4j core. You can directly rely on the core
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.14.1</version>
</dependency>Note that when referring to log4j2, you need to pay attention to whether there are multiple sets of log frameworks coexisting / conflicting in the project and whether they need to be adapted. For details, please refer to the above to adapt to other log abstractions / facade
Configuration file example
The first is the configuration file. The default configuration file path is: classpath: log4j2 xml (xml is recommended)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude"
status="warn" name="XInclude">
<Properties>
<Property name="PATTERN" value="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %5p [%t] %-40.40c{1.} : %m%n"/>
</Properties>
<Appenders>
<!-- Output to console, only used in local development environment -->
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<PatternLayout pattern="${PATTERN}"/>
</Console>
<!--Output to log file, scroll and split log file, and package automatically gz-->
<RollingFile name="File" fileName="logs/app.log" filePattern="logs/archives/app-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%i.log.gz">
<PatternLayout pattern="${PATTERN}"/>
<Policies>
<!--One file per day by default-->
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy />
<!--More than in one day size Separate them-->
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="1 GB"/>
</Policies>
</RollingFile>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<!-- Add your customizations logger,It is generally used to distinguish the logs of package names. Different package names have different levels/appender -->
<!-- additivity It means that after calling the current appender,Continue calling parent logger appender,default true-->
<Logger name="your logger/package name" level="debug" additivity="false"/>
<!--default Root Logger level-->
<Root level="INFO">
<!--It is necessary to distinguish the environment (cooperation) maven profile (something like that)-->
<!-- Development environment usage Console Appender,Production environment usage File Appender -->
<AppenderRef ref="Console"/>
<AppenderRef ref="File"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>XML configuration file syntax
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>;
<Configuration>
<Properties>
<Property name="name1">value</property>
<Property name="name2" value="value2"/>
</Properties>
<filter ... />
<Appenders>
<appender ... >
<filter ... />
</appender>
...
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Logger name="name1">
<filter ... />
</Logger>
...
<Root level="level">
<AppenderRef ref="name"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>Create Logger
Use the api of log4j2 directly:
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager; import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger; Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(Log4j2Test.class); logger.error(...); logger.warn(...); logger.info(...); logger.debug(...); logger.trace(...);
If it is used in conjunction with slf4j, it is also possible. Just make the adaptation in advance according to the above, and then use the api of slf4j. However, if it is a new system, it is recommended to go directly to the api of log4j2 to enjoy all the functions of log4j2. When using APIs such as slf4j, the above-mentioned functions such as parameter formatting cannot be used.
Fully asynchronous configuration (important!!)
It is recommended to configure log4j2 all async and add a system variable configuration in your startup script:
-Dlog4j2.contextSelector=org.apache.logging.log4j.core.async.AsyncLoggerContextSelector
summary
Log4j2 now has the strongest performance and function, and is continuously updated and maintained.
What are you waiting for? It's time to replace your logback/log4j1!
Recent hot article recommendations:
1.600 + Java interview questions and answers (2021 latest edition)
2.Finally got the IntelliJ IDEA activation code through the open source project. It's really fragrant!
3.Ali Mock tools are officially open source and kill all Mock tools on the market!
4.Spring Cloud 2020.0.0 is officially released, a new and subversive version!
5.Java development manual (Songshan version) is the latest release. Download it quickly!
Feel good, don't forget to like + forward!