introduce
Protagonist of this issue: ShardingCore A high-performance, lightweight solution for reading and writing separation of tables and databases under ef core, with zero dependency, zero learning cost and zero business code intrusion
The only fully automatic sub table and multi field sub table framework under dotnet has high performance, zero dependency, zero learning cost, zero business code intrusion, and supports read-write separation, dynamic sub table and sub library. The same route can be completely customized. Through this framework, you can not only learn a lot of ideas and skills of segmentation, but also learn the wonderful use of Expression
Project address
- github address https://github.com/xuejmnet/sharding-core
- gitee address https://gitee.com/dotnetchina/sharding-core
background
When using ShardingCore, a small partner asked me if I could use ShardingCore's sub database function to realize multi tenancy. My answer is yes, but I need to write routing for sub database objects, which is equivalent to that my project needs to realize multi tenancy, and all tables need to implement sub databases, This will be impractical in practical application, so although the sub database can be used for multi tenancy, generally no one will really operate like this, so there is no way to use a reasonable multi tenancy outdoor plus sub database in ShardingCore. To solve this problem, ShardingCore is in the new version X.4 x. Implemented in X +
function
ShardingCorex. What functions are implemented in version 4. X.x +
- Multiple configurations are supported. You can configure separate tables, databases, read and write links for each tenant or this configuration
- Multi database configuration supports multiple configurations. Each configuration can have its own database to separate reading and writing of tables and databases
- Dynamic multi configuration, which supports dynamic addition of multi configuration (dynamic deletion of multi configuration is not supported at present, and it will be supported later if necessary)
scene
Suppose we have such a multi tenant system. After we create an account, the system will assign us a separate database and corresponding table information, and then users can use the tenant configuration information for operation and processing
First, we create an AspNetCore project

It's only used here webapi for Net6
Add dependency
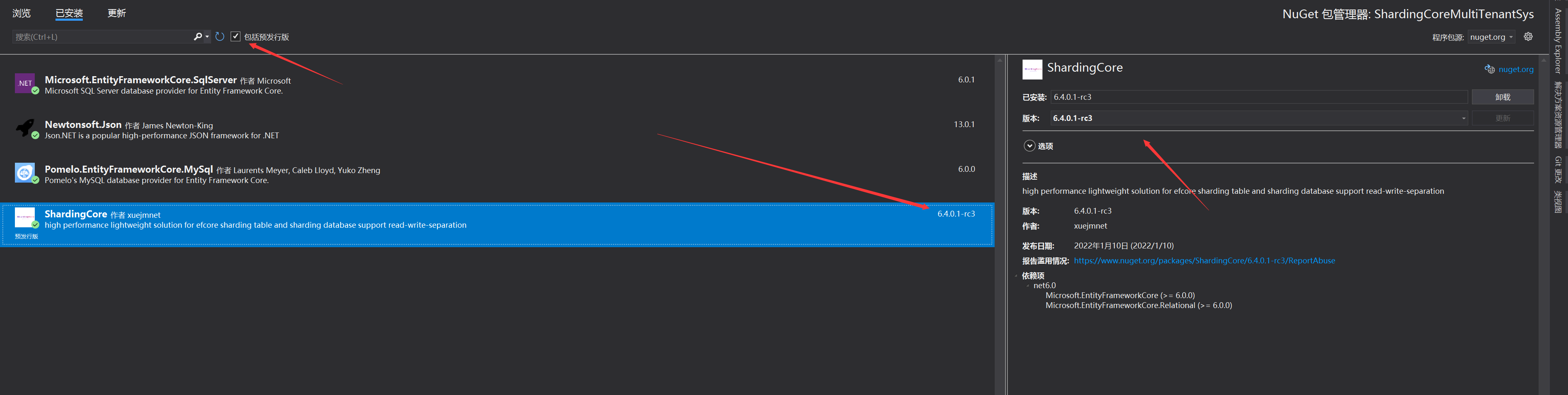
Here we have added three packages, ShardingCore and Microsoft EntityFrameworkCore. SqlServer,Pomelo. EntityFrameworkCore. In MySql, ShardingCore uses the preview version. If it is not checked, it will not be displayed. Why do we need to add two additional database drivers? The reason is that we need to implement different database configurations under different tenants. For example, the agreement signed between tenant A and US states that the system uses open source database, Or if you want to use the Linux platform, you can configure MySql or PgSql for tenant A. tenant B is a senior soft powder. If you need to use MSSQL, you can configure MSSQL for it In general, we may not have multiple databases, but in order to take into account special circumstances, we also support this situation.
Public user storage
First of all, there is no database when I haven't created a tenant, so my data will not exist under the current tenant naturally. Here we use to store it in other databases. Suppose we use a public database as the user system
Create user system
Create the mapping relationship between system users and system users in the database
public class SysUser
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public DateTime CreationTime { get; set; }
public bool IsDeleted { get; set; }
}
public class SysUserMap:IEntityTypeConfiguration<SysUser>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<SysUser> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(o => o.Id);
builder.Property(o => o.Id).IsRequired().IsUnicode(false).HasMaxLength(50);
builder.Property(o => o.Name).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(50);
builder.Property(o => o.Password).IsRequired().IsUnicode(false).HasMaxLength(50);
builder.HasQueryFilter(o => o.IsDeleted == false);
builder.ToTable(nameof(SysUser));
}
}Create the configuration information table of this database to facilitate reconstruction after later startup
public class SysUserTenantConfig
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string UserId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
///Add Json package for ShardingCore configuration
/// </summary>
public string ConfigJson { get; set; }
public DateTime CreationTime { get; set; }
public bool IsDeleted { get; set; }
}
public class SysUserTenantConfigMap:IEntityTypeConfiguration<SysUserTenantConfig>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<SysUserTenantConfig> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(o => o.Id);
builder.Property(o => o.Id).IsRequired().IsUnicode(false).HasMaxLength(50);
builder.Property(o => o.UserId).IsRequired().IsUnicode(false).HasMaxLength(50);
builder.Property(o => o.ConfigJson).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(2000);
builder.HasQueryFilter(o => o.IsDeleted == false);
builder.ToTable(nameof(SysUserTenantConfig));
}
}Create corresponding system user storage DbContext
public class IdentityDbContext:DbContext
{
public IdentityDbContext(DbContextOptions<IdentityDbContext> options):base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.ApplyConfiguration(new SysUserMap());
modelBuilder.ApplyConfiguration(new SysUserTenantConfigMap());
}
}Create a tenant's DbContext
public class TenantDbContext:AbstractShardingDbContext,IShardingTableDbContext
{
public TenantDbContext(DbContextOptions<TenantDbContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
public IRouteTail RouteTail { get; set; }
}At present, we first define the internal tenant code to be written later
Create dynamic tenant parameters
Dynamic tenant fragment configuration information only needs to implement the ivirtualdatasourceconfigurationparams < tshardingdbcontext > interface in ShardingCore, but this interface has many parameters to fill in, so the framework here has an abstract class abstractvirtualdatasourceconfigurationparams < tshardingdbcontext > for the default parameters of this interface. Here, we configure the configuration parameters by creating a new json configuration object
public class ShardingTenantOptions
{
public string ConfigId { get; set;}
public int Priority { get; set;}
public string DefaultDataSourceName { get; set;}
public string DefaultConnectionString { get; set;}
public DbTypeEnum DbType { get; set; }
}The current database is configured in the parameter. This is relatively simple. We will temporarily use the single table sub database mode to realize it. At present, we will not demonstrate each tenant sub database for the time being. Then write the configuration support of SqlServer and MySql
public class SqlShardingConfiguration : AbstractVirtualDataSourceConfigurationParams<TenantDbContext>
{
private static readonly ILoggerFactory efLogger = LoggerFactory.Create(builder =>
{
builder.AddFilter((category, level) => category == DbLoggerCategory.Database.Command.Name && level == LogLevel.Information).AddConsole();
});
public override string ConfigId { get; }
public override int Priority { get; }
public override string DefaultDataSourceName { get; }
public override string DefaultConnectionString { get; }
public override ITableEnsureManager TableEnsureManager { get; }
private readonly DbTypeEnum _dbType;
public SqlShardingConfiguration(ShardingTenantOptions options)
{
ConfigId = options.ConfigId;
Priority = options.Priority;
DefaultDataSourceName = options.DefaultDataSourceName;
DefaultConnectionString = options.DefaultConnectionString;
_dbType = options.DbType;
//Used to quickly determine whether there are tables in the database
if (_dbType == DbTypeEnum.MSSQL)
{
TableEnsureManager = new SqlServerTableEnsureManager<TenantDbContext>();
}
else if (_dbType == DbTypeEnum.MYSQL)
{
TableEnsureManager = new MySqlTableEnsureManager<TenantDbContext>();
}
else
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
public override DbContextOptionsBuilder UseDbContextOptionsBuilder(string connectionString,
DbContextOptionsBuilder dbContextOptionsBuilder)
{
switch (_dbType)
{
case DbTypeEnum.MSSQL:
{
dbContextOptionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(connectionString).UseLoggerFactory(efLogger);
}
break;
case DbTypeEnum.MYSQL:
{
dbContextOptionsBuilder.UseMySql(connectionString, new MySqlServerVersion(new Version())).UseLoggerFactory(efLogger);
}
break;
default: throw new NotImplementedException();
}
return dbContextOptionsBuilder;
}
public override DbContextOptionsBuilder UseDbContextOptionsBuilder(DbConnection dbConnection,
DbContextOptionsBuilder dbContextOptionsBuilder)
{
switch (_dbType)
{
case DbTypeEnum.MSSQL:
{
dbContextOptionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(dbConnection).UseLoggerFactory(efLogger);
}
break;
case DbTypeEnum.MYSQL:
{
dbContextOptionsBuilder.UseMySql(dbConnection, new MySqlServerVersion(new Version())).UseLoggerFactory(efLogger);
}
break;
default: throw new NotImplementedException();
}
return dbContextOptionsBuilder;
}
}Write user registration interface
[Route("api/[controller]/[action]")]
[ApiController]
[AllowAnonymous]
public class PassportController:ControllerBase
{
private readonly IdentityDbContext _identityDbContext;
public PassportController(IdentityDbContext identityDbContext)
{
_identityDbContext = identityDbContext;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Register(RegisterRequest request)
{
if (await _identityDbContext.Set<SysUser>().AnyAsync(o => o.Name == request.Name))
return BadRequest("user not exists");
var sysUser = new SysUser()
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n"),
Name = request.Name,
Password = request.Password,
CreationTime=DateTime.Now
};
var shardingTenantOptions = new ShardingTenantOptions()
{
ConfigId = sysUser.Id,
Priority = new Random().Next(1,10),
DbType = request.DbType,
DefaultDataSourceName = "ds0",
DefaultConnectionString = GetDefaultString(request.DbType,sysUser.Id)
};
var sysUserTenantConfig = new SysUserTenantConfig()
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n"),
UserId = sysUser.Id,
CreationTime = DateTime.Now,
ConfigJson = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(shardingTenantOptions)
};
await _identityDbContext.AddAsync(sysUser);
await _identityDbContext.AddAsync(sysUserTenantConfig);
await _identityDbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
//Configuration generation is performed after registration
DynamicShardingHelper.DynamicAppendVirtualDataSourceConfig(new SqlShardingConfiguration(shardingTenantOptions));
return Ok();
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Login(LoginRequest request)
{
var sysUser = await _identityDbContext.Set<SysUser>().FirstOrDefaultAsync(o=>o.Name==request.Name&&o.Password==request.Password);
if (sysUser == null)
return BadRequest("name or password error");
//The secret key is the header. The Hmacsha256 algorithm is used here. A 256 bit key is required
var securityKey = new SigningCredentials(new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("123123!@#!@#123123")), SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
//Many default parameter names are predefined in Claim and JwtRegisteredClaimNames. You can also define your own key name like the following Guid
//ClaimTypes also predefines many types, such as role, email and name. Role is used to grant permissions. Different roles can access different interfaces
//Equivalent to payload
var claims = new Claim[] {
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Iss,"https://localhost:5000"),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Aud,"api"),
new Claim("id",Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n")),
new Claim("uid",sysUser.Id),
};
SecurityToken securityToken = new JwtSecurityToken(
signingCredentials: securityKey,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddHours(2),//Expiration time
claims: claims
);
var token = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(securityToken);
return Ok(token);
}
private string GetDefaultString(DbTypeEnum dbType, string userId)
{
switch (dbType)
{
case DbTypeEnum.MSSQL: return $"Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=DB{userId};Integrated Security=True;";
case DbTypeEnum.MYSQL: return $"server=127.0.0.1;port=3306;database=DB{userId};userid=root;password=L6yBtV6qNENrwBy7;";
default: throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
public class RegisterRequest
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public DbTypeEnum DbType { get; set; }
}
public class LoginRequest
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
}For a brief explanation, we use the user id as the tenant id and the tenant id as the database configuration to support the multi configuration mode. So far, our user system has been completed. Is it very simple? Just a few pieces of code. After the user registers, the corresponding database and corresponding table will be created. If you are divided into tables, the corresponding database table and other information will be automatically created.
Tenant system
In the tenant system, we will make a simple demonstration of the order, using the order id to take the module, and taking the module to take 5 to perform the table splitting operation
Order information of new tenant system
public class Order
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public DateTime CreationTime { get; set; }
public bool IsDeleted { get; set; }
}
public class OrderMap:IEntityTypeConfiguration<Order>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Order> builder)
{
builder.HasKey(o => o.Id);
builder.Property(o => o.Id).IsRequired().IsUnicode(false).HasMaxLength(50);
builder.Property(o => o.Name).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(100);
builder.HasQueryFilter(o => o.IsDeleted == false);
builder.ToTable(nameof(Order));
}
}New order routing
public class OrderVirtualTableRoute:AbstractSimpleShardingModKeyStringVirtualTableRoute<Order>
{
public OrderVirtualTableRoute() : base(2, 5)
{
}
public override void Configure(EntityMetadataTableBuilder<Order> builder)
{
builder.ShardingProperty(o => o.Id);
}
}Simple string modulo
Add tenant Middleware
Add tenant middleware. If multiple configurations are used in the system, you must specify which configuration the dbcontext created this time uses
public class TenantSelectMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly IVirtualDataSourceManager<TenantDbContext> _virtualDataSourceManager;
public TenantSelectMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IVirtualDataSourceManager<TenantDbContext> virtualDataSourceManager)
{
_next = next;
_virtualDataSourceManager = virtualDataSourceManager;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
if (context.Request.Path.ToString().StartsWith("/api/tenant", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
if (!context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
await _next(context);
return;
}
var tenantId = context.User.Claims.FirstOrDefault((o) => o.Type == "uid")?.Value;
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(tenantId))
{
await DoUnAuthorized(context, "not found tenant id");
return;
}
using (_virtualDataSourceManager.CreateScope(tenantId))
{
await _next(context);
}
}
else
{
await _next(context);
}
}
private async Task DoUnAuthorized(HttpContext context, string msg)
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 403;
await context.Response.WriteAsync(msg);
}
}The middleware intercepts all requests under the / api/tenant path and adds corresponding tenant information for these requests
Configure tenant extension initialization data
public static class TenantExtension
{
public static void InitTenant(this IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var scope = serviceProvider.CreateScope())
{
var identityDbContext = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IdentityDbContext>();
identityDbContext.Database.EnsureCreated();
var sysUserTenantConfigs = identityDbContext.Set<SysUserTenantConfig>().ToList();
if (sysUserTenantConfigs.Any())
{
foreach (var sysUserTenantConfig in sysUserTenantConfigs)
{
var shardingTenantOptions = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<ShardingTenantOptions>(sysUserTenantConfig.ConfigJson);
DynamicShardingHelper.DynamicAppendVirtualDataSourceConfig(
new SqlShardingConfiguration(shardingTenantOptions));
}
}
}
}
}Here, because we initialize the tenant information instead of hard coding, we need to add the tenant information dynamically at startup
Configure multi tenancy
Start configuration Startup
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddAuthentication();
#region user system configuration
builder.Services.AddDbContext<IdentityDbContext>(o =>
o.UseSqlServer("Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=IdDb;Integrated Security=True;"));
//Generate key
var keyByteArray = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("123123!@#!@#123123");
var signingKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(keyByteArray);
//Authentication parameters
builder.Services.AddAuthentication("Bearer")
.AddJwtBearer(o =>
{
o.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
IssuerSigningKey = signingKey,
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidIssuer = "https://localhost:5000",
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidAudience = "api",
ValidateLifetime = true,
ClockSkew = TimeSpan.Zero,
RequireExpirationTime = true,
};
});
#endregion
#Configuring ShardingCore for region
builder.Services.AddShardingDbContext<TenantDbContext>()
.AddEntityConfig(op =>
{
op.CreateShardingTableOnStart = true;
op.EnsureCreatedWithOutShardingTable = true;
op.AddShardingTableRoute<OrderVirtualTableRoute>();
})
.AddConfig(op =>
{
//One is configured by default
op.ConfigId = $"test_{Guid.NewGuid():n}";
op.Priority = 99999;
op.AddDefaultDataSource("ds0", "Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=TestTenantDb;Integrated Security=True;");
op.UseShardingQuery((conStr, b) =>
{
b.UseSqlServer(conStr);
});
op.UseShardingTransaction((conn, b) =>
{
b.UseSqlServer(conn);
});
}).EnsureMultiConfig(ShardingConfigurationStrategyEnum.ThrowIfNull);
#endregion
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
app.Services.GetRequiredService<IShardingBootstrapper>().Start();
//Initialize startup configuration tenant information
app.Services.InitTenant();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseAuthorization();
//Enable tenant selection middleware after authentication
app.UseMiddleware<TenantSelectMiddleware>();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();Write tenant actions
[Route("api/tenant/[controller]/[action]")]
[ApiController]
[Authorize(AuthenticationSchemes = "Bearer")]
public class TenantController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly TenantDbContext _tenantDbContext;
public TenantController(TenantDbContext tenantDbContext)
{
_tenantDbContext = tenantDbContext;
}
public async Task<IActionResult> AddOrder()
{
var order = new Order()
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n"),
CreationTime = DateTime.Now,
Name = new Random().Next(1,100)+"_name"
};
await _tenantDbContext.AddAsync(order);
await _tenantDbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(order.Id);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> UpdateOrder([FromQuery]string id)
{
var order =await _tenantDbContext.Set<Order>().FirstOrDefaultAsync(o=>o.Id==id);
if (order == null) return BadRequest();
order.Name = new Random().Next(1, 100) + "_name";
await _tenantDbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(order.Id);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> GetOrders()
{
var orders =await _tenantDbContext.Set<Order>().ToListAsync();
return Ok(orders);
}
}Start project
After we have basically configured what we need, we can start the project directly

Here, we registered a TenantA user through the interface and chose to use MSSQL. This achievement helped us automatically generate the corresponding database table structure Next, we register another TenantB user and select MySql

Through the screenshot, we can see that ShardingCore has also created the corresponding database and table information for us
Login tenant
First, let's log in
TenantA user token
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2xvY2FsaG9zdDo1MDAwIiwiYXVkIjoiYXBpIiwiaWQiOiJkNGMwZjZiNzI5MzE0M2VlYWM0Yjg3NzUwYzE4MWUzOSIsInVpZCI6ImMxMWRkZjFmNTY0MjQwZjc5YTQzNTEzZGMwNmVjZGMxIiwiZXhwIjoxNjQxODI4ODQ0fQ.zJefwnmcIEZm-kizlN7DhwTRgGxiCg52Esa8QmHiEKY
TenantB user token
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2xvY2FsaG9zdDo1MDAwIiwiYXVkIjoiYXBpIiwiaWQiOiIwNzY4NzUwMmVjYzY0NTMyOGFkNTcwZDRkYjMwNDI3MSIsInVpZCI6ImVkODg4YTc3MzAwYTQ4NjZhYmUyNWY2MTE1NmEwZTQzIiwiZXhwIjoxNjQxODI4ODgxfQ.cL0d010jdXLXNGT8M0wsRMqn3VeIxFnV0keM0H3SPzo
Next, we will cross process the two tenants respectively
AddOrder
Tenant A inserts an order. Order Id: aef6905f512a4f72baac5f149ef32d21
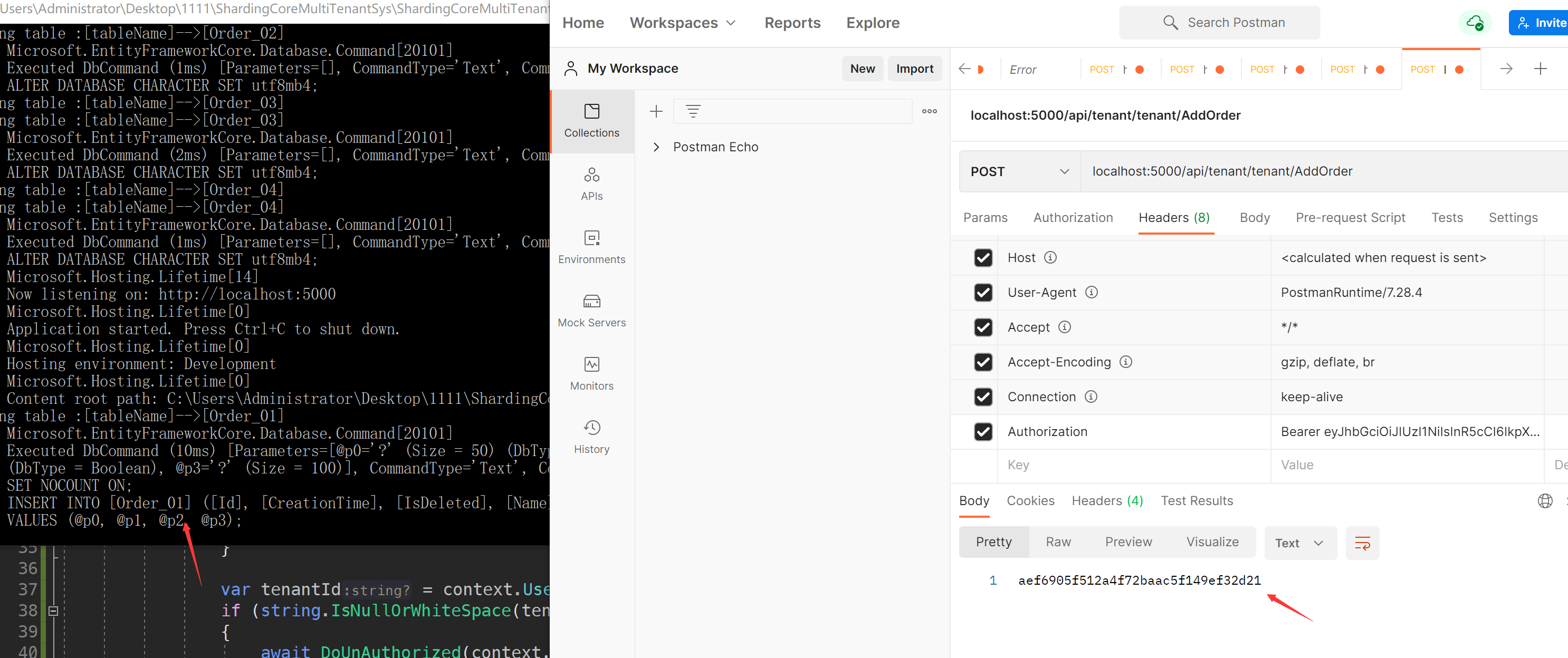
TenantB user also inserts an order. Order ID: 450f5dd0e82442eca33dfcf3d57fa3
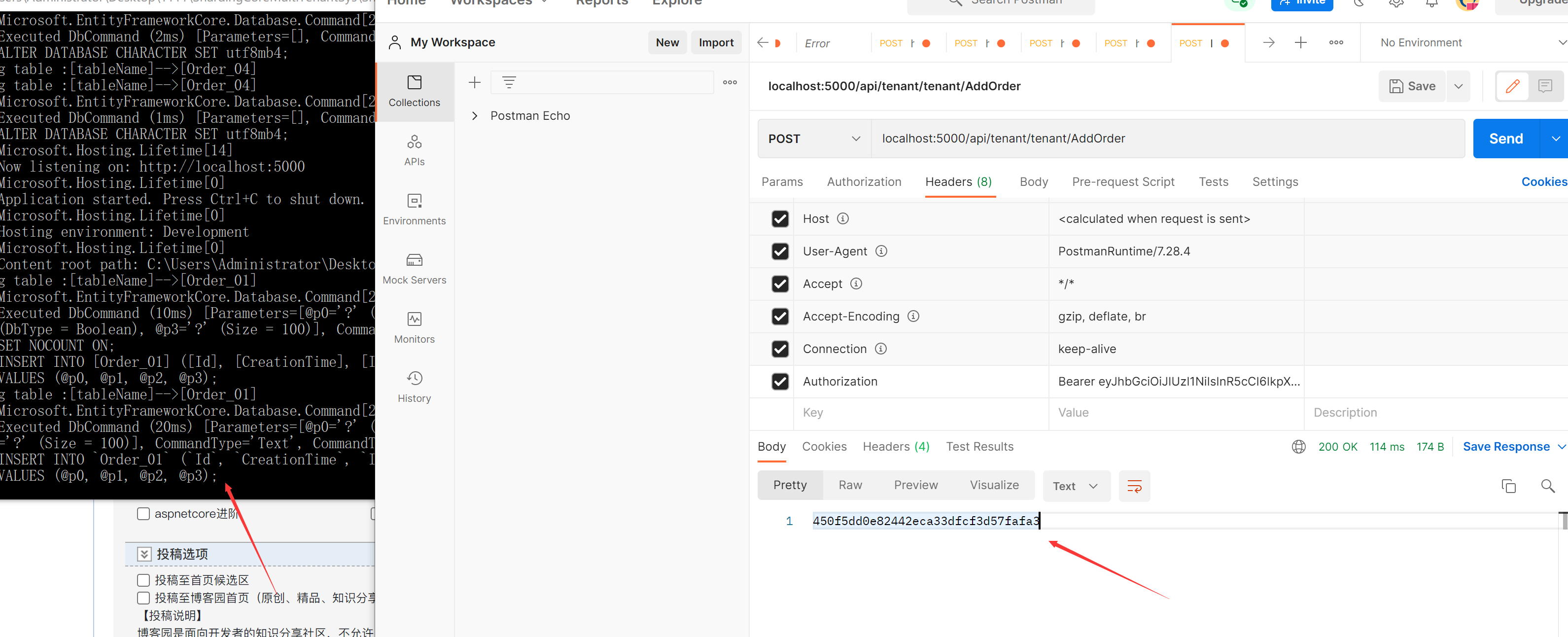
Two user processing
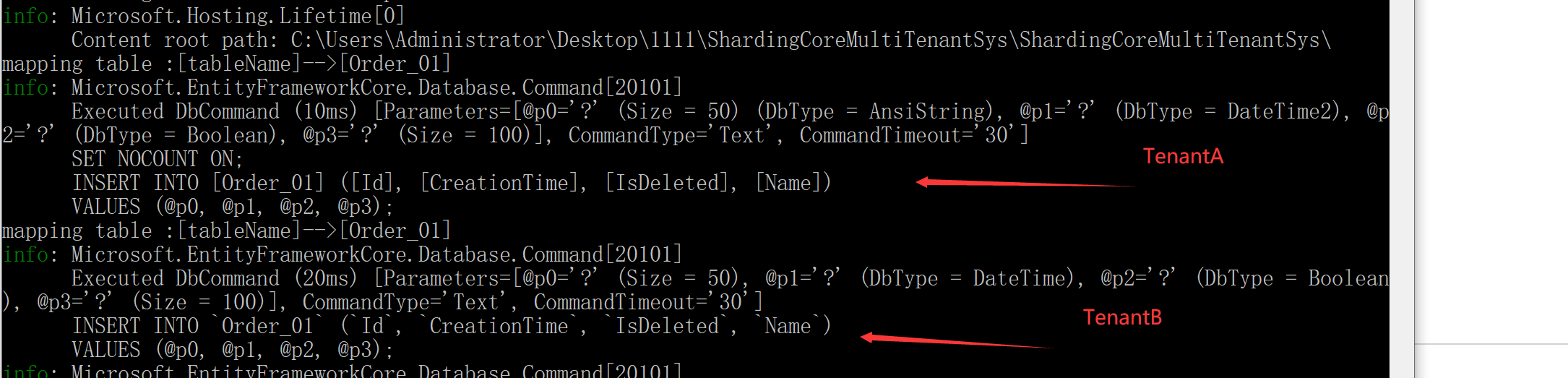
Through log printing, we can clearly feel that the two are different databases
UpdateOrder
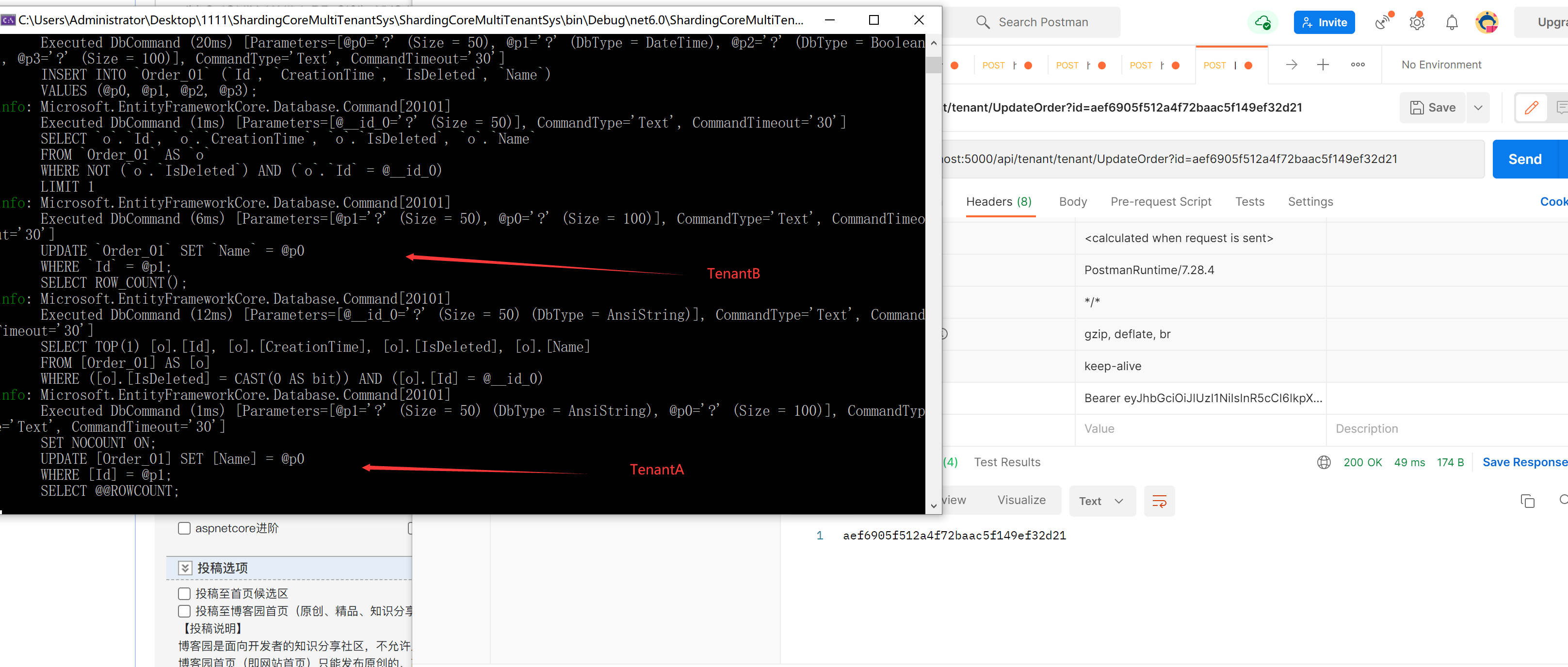
GetOrders

summary
Through the demonstration of the above functions, I believe that many small partners should already know their specific operation process. By configuring multiple tenant information and realizing multi configuration and dynamic configuration on ShardingCore, we can ensure that the read-write separation of tables and databases in multi tenant mode can still be used and has good universality. If you need to develop a large program, the leader is the database and table. In the past, you probably spent a lot of energy on dealing with fragmentation, and whether the final project can be completed and used is still a huge problem, but now it is different. After all, ShardingCore did not have a very easy-to-use fragmentation component in the past Net and has perfect orm as support. Basically, there is no framework to say that multi tenant mode can choose a database. Previously, you can only choose one database for all multi tenants in the market. At present Net is open source. I believe there will be better and better component frameworks. After all, such a good language with rich ecology will be all The gospel of Neter.