1, Read write separation concept
Read write separation is to evenly distribute query requests to multiple data copies through master-slave configuration, so as to further improve the processing capacity of the system.
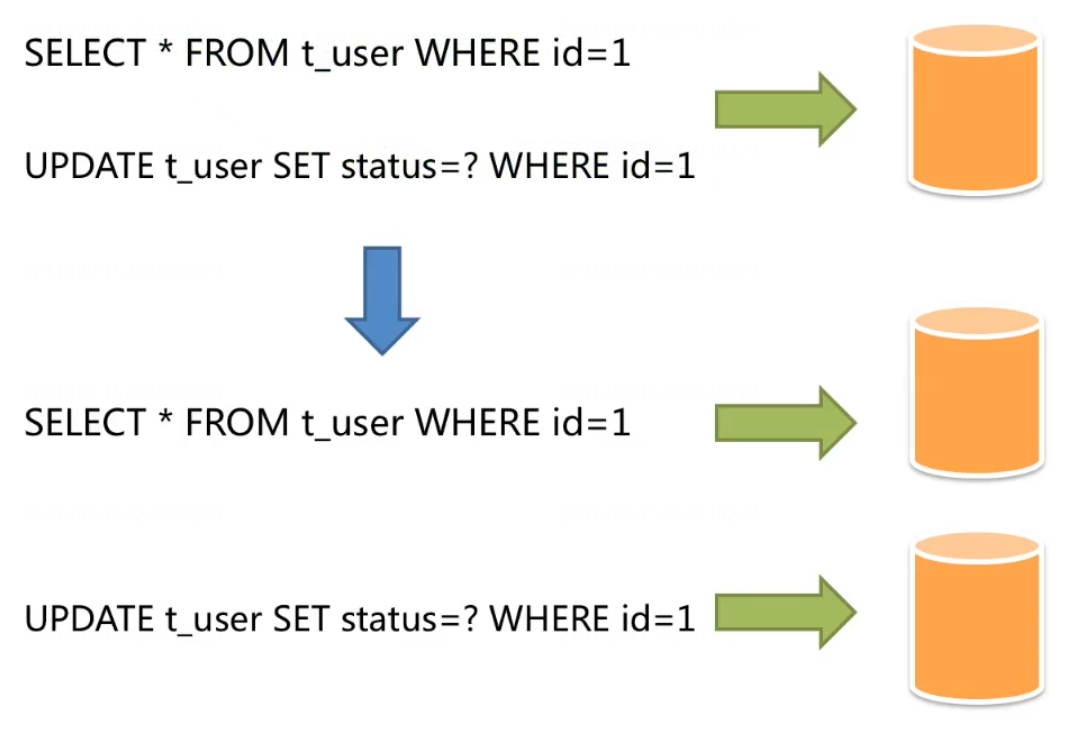
Master-slave architecture: read-write separation, which aims at high availability and read-write expansion. The contents of the master-slave database are the same, and the routing is carried out according to the SQL semantics.
Sub database and table architecture: data fragmentation for read-write expansion and storage expansion. The contents of the library and table are different, and the routing is carried out according to the fragment configuration.
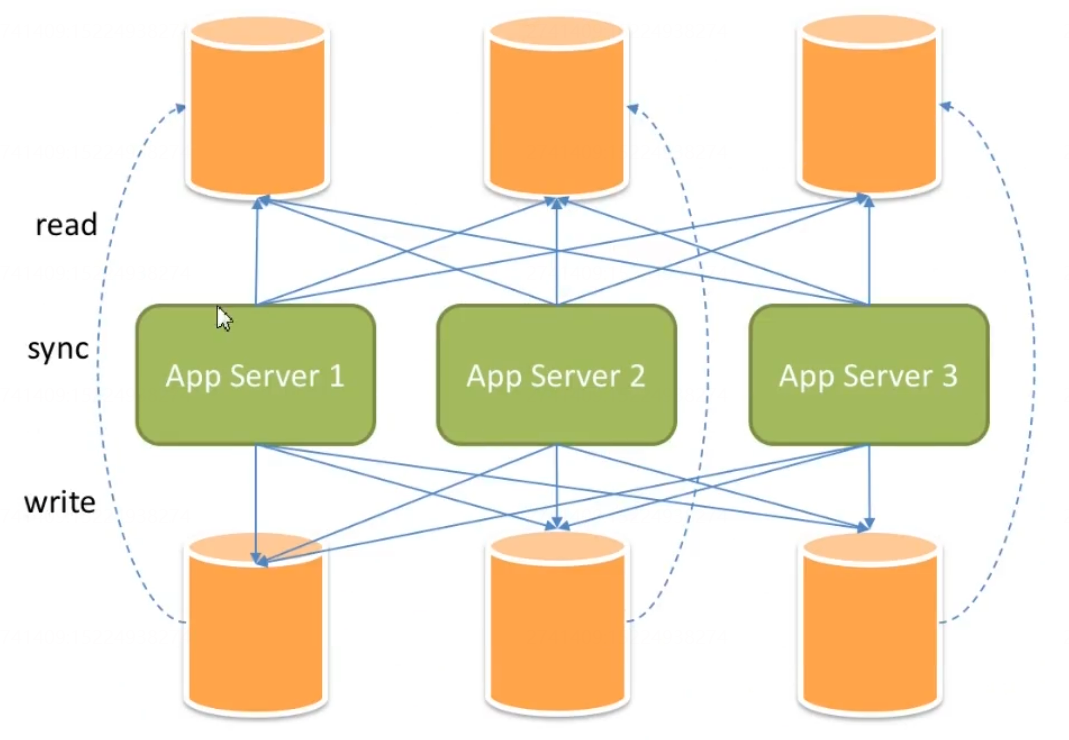
Although read-write separation can improve the throughput and availability of the system, it also brings problems of data inconsistency, including data consistency between multiple master databases and data consistency between master databases and slave databases. Moreover, read-write separation also brings the same problem as data fragmentation, which will also make the operation and maintenance of the database more complex for application developers and operation and maintenance personnel.
1, Read write separation application
- When the amount of data is not large, we can separate the reading and writing of the database to meet the needs of high concurrency, and alleviate the pressure of query by horizontally expanding the slave database. As follows:
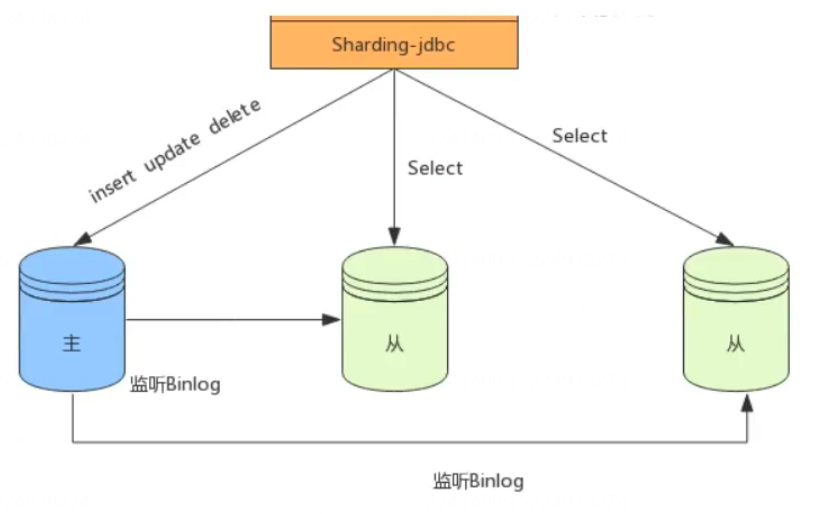
2. Separate tables + separate reading and writing
When the amount of data reaches 5 million, the amount of data is estimated to be 10 million. We can store the data in separate tables.

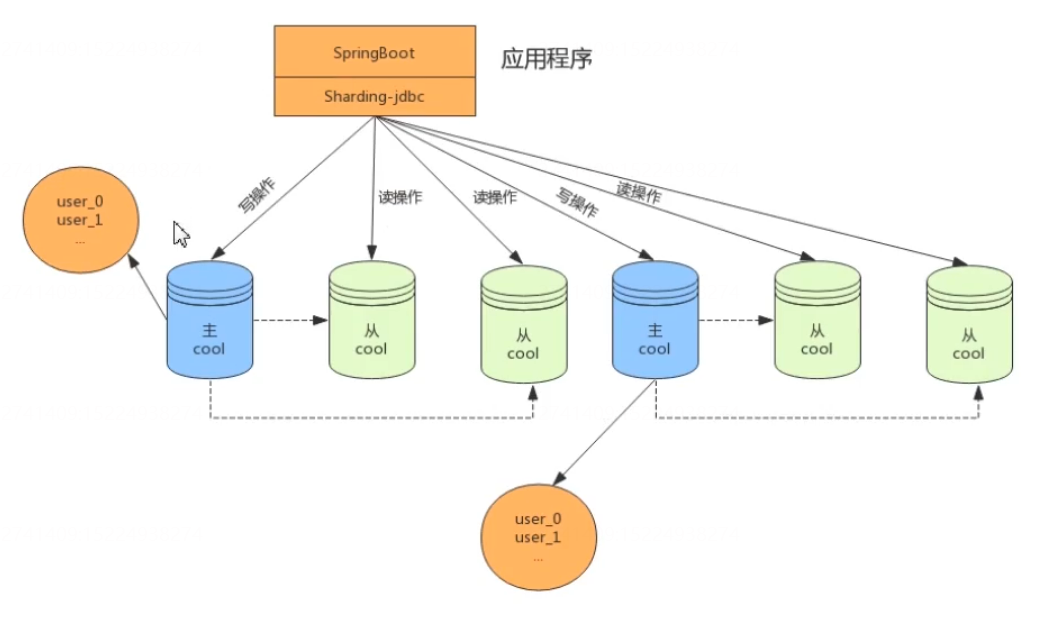
- Separate database and Table + separate reading and writing
When the data volume continues to expand, you can consider dividing the database into tables to store the data in different tables in different databases, as follows:
The main design goal of ShardingSphere's read-write separation module is to make the user use the master-slave database cluster as much as possible as using a database.
Master database, slave database, master-slave synchronization, load balancing
- Core functions
Provide a master-slave read-write separation configuration. Only single primary database is supported. It can be used independently or in combination with sub database and sub table
Use read-write separation independently and support SQL transparent transmission. SQL rewriting process is not required
Data consistency can be ensured in the same thread and in the same database connection. If there is a write operation, subsequent read operations are read from the main library.
Hint based forced master database routing. It can be forced to query real-time data in the master database to avoid the delay of master-slave synchronization data. - Item not supported
Data synchronization of master database and slave database
Data synchronization delay between master database and slave database
Main library double write or multi write
Inconsistent data across transactions between master and slave databases
3, Code demonstration (corresponding to entity class, table structure and data access interface)
1. Read write separation
Here, different libraries are used to represent the master-slave relationship
Mainly application Properties configuration is different
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=master,slave0 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master.password=000000 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.password=000000 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # master-slave spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.name=datasource spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.master-data-source-name=master spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.slave-data-source-names=slave0 spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.load-balance-algorithm-type=ROUND_ROBIN #id spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.city.key-generator.column=id spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.city.key-generator.type=CKWKEYID
Test:
- insert data
@Test
public void test4() {
for (int i = 1; i < 20; i++) {
CityEntity city = new CityEntity();
city.setName("Beijing" + i);
city.setProvince("Beijing" + i);
cityRepository.save(city);
}
}
It is obvious that the main library is inserted
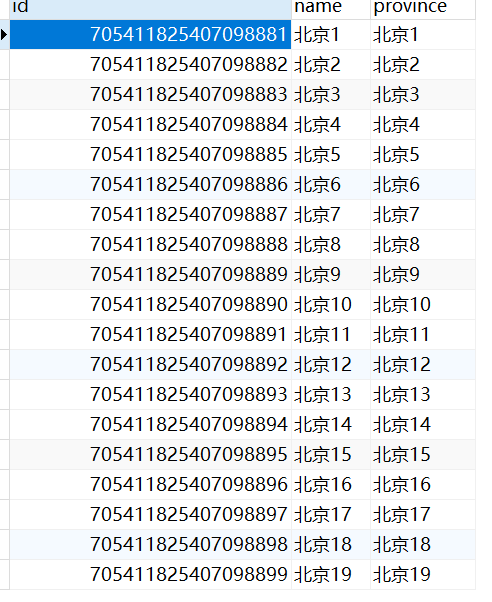
Query test:
@Test
public void test5() {
List<CityEntity> all = cityRepository.findAll();
all.forEach(System.out::println);
}
At this time, the data found is still empty, indicating the data queried from the database
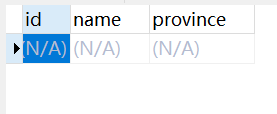
2. Separate database and Table + separate reading and writing
Here, the same node and different libraries are used to represent the master-slave relationship
Profile:
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=master0,slave0,slave1,master1,slave2,slave3
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master0.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master0.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master0.password=000000
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.password=000000
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave1.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave1.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere3?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave1.password=000000
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master1.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master1.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere4?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master1.password=000000
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.master1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave2.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave2.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere5?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave2.password=000000
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave3.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave3.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shardingsphere6?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave3.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave3.password=000000
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.slave3.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# master-slave
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.master0.master-data-source-name=master0
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.master0.slave-data-source-names=slave0,slave1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.master1.master-data-source-name=master1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.master1.slave-data-source-names=slave2,slave3
# The horizontal split sub library sub table is divided into two main libraries, master0 and master1. Each has two slave libraries to split the order table b_order0,b_order1
# Sub database strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=company_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=master${company_id % 2}
# Table splitting strategy
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=b_order${id % 2}
# Real database tables
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.actual-data-nodes=master${0..1}.b_order${0..1}
#id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.b_order.key-generator.type=CKWKEYID
Test insert data:
Test results:
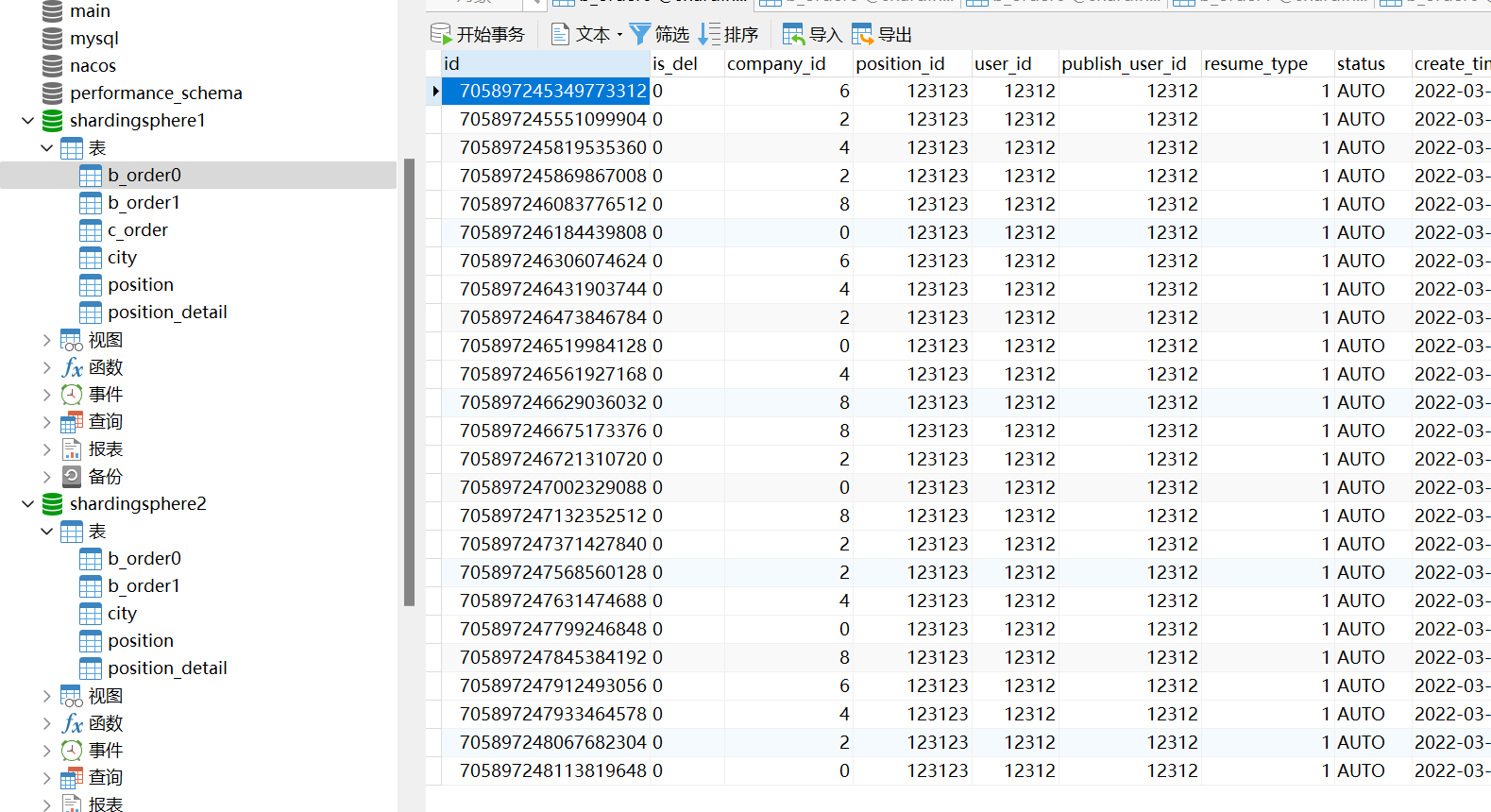
Both main libraries have data