2.1 what is thread communication and implementation steps
There are two models of inter thread communication: shared memory and message passing
In fact, thread communication is to realize the alternating work of threads and transmit information
Specific steps of communication between threads: (involving upper, middle and lower parts)
Create a resource class in which ship attributes and operation methods are displayed
Operation methods in resource class: judgment, operation and notification
Create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class
Prevent the problem of virtual wake-up (if interpretation, it will only be judged once)
2.2 synchronized cases
When operating a thread, the waiting thread uses wait()
Notify other thread operations with notify() and notifyAll()
Suppose there are two threads. In the process of execution, the thread judges the value (not the value to wait, let other threads grab), operates the value, and notifies the scheduling of another thread
Realize the operation of two threads on the value of num one thread plus 1 and one thread minus 1, and implement it alternately for many times
//The first step is to create a resource class and define properties and operation methods
class Share {
//Initial value
private int num = 0;
//+1 method
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//Step 2: judge the work notice
if(number != 0) { //Judge whether the number value is 0. If not, wait
this.wait(); //Wake up wherever you sleep
}
//If the number value is 0, the + 1 operation is performed
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+num);
//Notify other threads
this.notifyAll(); //Note that the notification here is random, that is, only all can be notified
}
//-1 method
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//judge
if(number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
//work
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" :: "+number);
//Notify other threads
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1 {
//The third step is to create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
//Create thread
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
try {
share.incr(); //+1
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
try {
share.decr(); //-1
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
}
}
You can see that at this time, the code is alternating, one + 1 and one thread - 1
But let's consider what happens if we add and subtract two threads at the same time?
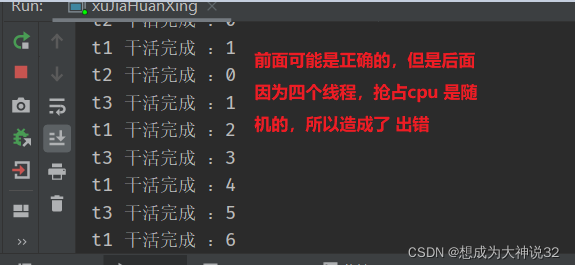
False wake-up: wait , is where to sleep and where to be awakened. It is judged only once , false wake-up is put in while , if judgment, it will be judged only once, so it is changed to while; Circular judgment will solve the false awakening; To solve this error
2.3 Lock case
The lock object to be created and the lock object to be used first
Place in resource class
private Lock lock= new ReentrantLock(); //Create a relocatable lock
private Condition condition= lock.newCondition();
//The object he can operateLock lock();
Unlock lock unlock();
The following are condition classes:
Wake up all waiting threads, signalall(), with the class name condition signalAll();
Wake up a waiting thread signal (), with the class name, condition signal();
This causes the current thread to be in a waiting state await() with the class name, condition. Before receiving the signal or being interrupted await();
The code of Lock implementation is basically the same. Note that locking and unlocking are manually done by yourself. finally, they should be unlocked
If it is not unlocked, the following threads will be affected
class LShare{
//This is a shared resource. Pay attention to the creation and use of locks. Others are basically the same as above
private int num=0;
private Lock lock= new ReentrantLock(); //Create a relocatable lock
private Condition condition= lock.newCondition();
//Method of creating operation
public void add (){
lock.lock(); //First, lock manually;
try { //Judge, work, inform
while (num!=0){
condition.await();
//It uses this object to call the method and wait
}
num++;
System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Work completion:"+num);
condition.signalAll(); //This notification method
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //Eventually, no matter what error occurs, it will be unlocked
}
}This realizes the communication between threads, that is, they can complete the alternating work according to the information
Here's how to customize communication? (alternate threads, but the work of each thread changes)