Why learn to parse Json files?
Work needs!
Recently, in the work project, there is a need to parse Json string, but I only use QT to parse Json, and the supervisor stipulates that C/C + + language should be used to parse. It is said that it is to facilitate transplantation to other projects for use
There's no way but to bite the bullet and find out if there's any analysis on the Internet. Jason's open source library can be used in C/C + +.
I found a lot and provided a lot on the Internet. Finally, I chose cJOSN. Why not? It's because it's small and exquisite and pure C!
Spent a week or two to study and record some commonly used JSON string parsing!
Finally, let's briefly introduce what json is:
json is a lightweight data storage and exchange language, which is stored in the form of key value pairs, for example: {"key": "value"}
Note: the key needs to be enclosed in double quotation marks. If the value is a string, it also needs to be enclosed in double quotation marks. It is not required for other types.
json is mainly used for network data transmission!
1, Prepare cJSON open source library
cjosn library download website: https://sourceforge.net/projects/cjson/
After downloading, you will get a compressed package. Unzip it and enter it to copy cjson C and cjson H file into your own project.
Finally, add these two files to your project!
You can use both Linux and Window!
2, Introduction to cJSON
-
First, let's introduce json data:

The json data in the figure above is what this blog will operate on. It will be created, parsed, modified and deleted.
This includes encapsulation and parsing commonly used in projects. -
cJSON mainly stores data through the structure cJSON:
typedef struct cJSON { struct cJSON *next,*prev; /* next Is to get the next element data, prev is to get the previous element data */ struct cJSON *child; /* Get the first element data. When you need to get the next one, you have to use next */ int type; /* The current json type object, array, string, number, null, true, false, etc */ char *valuestring; /* String value, if type==cJSON_String */ int valueint; /* Integer type value, if type==cJSON_Number */ double valuedouble; /* Floating point type value, if type==cJSON_Number */ char *string; /* This is the key */ } cJSON; -
type, which is judged with the following macro
/* cJSON Types: */ #define cJSON_False 0 // true #define cJSON_True 1 // false #define cJSON_NULL 2 // NULL #define cJSON_Number 3 // number #define cJSON_String 4 // character string #define cJSON_Array 5 // array #define cJSON_Object 6 // object
-
A function that generates a cjson pointer from a string. After use, you need to call cJSON_Delete to release
extern cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value); // Release cjson_ Pointer returned by parse extern void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c);
-
cjson pointer function to generate string
// The format of the generated string has to be adjusted extern char *cJSON_Print(cJSON *item); // There is no format adjustment, but a line of string display extern char *cJSON_PrintUnformatted(cJSON *item);
When using these two functions, you must release the pointer memory returned by them, otherwise it will cause memory leakage.
...
I can't use any of the others below!
3, Package Jason
-
{ }
"interest": { "basketball": "Basketball", "badminton": "badminton" }The code achieves the above effect:
// Define object {} cJSON *interest = cJSON_CreateObject(); // Insert element, corresponding to key value pair cJSON_AddItemToObject(interest, "basketball", cJSON_CreateString("Basketball")); // When the value is a string, you need to use the function cJSON_CreateString() create cJSON_AddItemToObject(interest, "badminton", cJSON_CreateString("badminton")); // Or use macros to add //cJSON_ Addstringtoobject (interest, "badmenton", "badminton"); // Or write it like this -
[ ]
"color": [ "black", "white"]
The code achieves the above effect:
// Define [] array cJSON *color = cJSON_CreateArray(); // Adding elements to an array cJSON_AddItemToArray(color, cJSON_CreateString("black")); cJSON_AddItemToArray(color, cJSON_CreateString("white")); -
[ { }, { } ]
"like": [ { "game": "Mario", "price": 66.6 }, { "game": "Contra", "price": 77.7 } ]The code achieves the above effect:
// Define {} object cJSON *likeObject1 = cJSON_CreateObject(); cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject1, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Mario")); cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject1, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(66.6)); // When the value is a number, you need to use the function cJSON_CreateNumber() create //cJSON_AddNumberToObject(likeObject1, "price", 66.6); // Or write it like this cJSON *likeObject2 = cJSON_CreateObject(); cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject2, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Contra")); cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject2, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(77.7)); // Define [] array cJSON *like = cJSON_CreateArray(); // Adding elements to an array cJSON_AddItemToArray(like, likeObject1); cJSON_AddItemToArray(like, likeObject2); -
[ [ ], [ ] ]
"education": [ [ "primary school", "junior high school" ], [ "high school", "university" ] ]The code achieves the above effect:
// Define [] array cJSON *education1 = cJSON_CreateArray(); cJSON_AddItemToArray(education1, cJSON_CreateString("primary school")); cJSON_AddItemToArray(education1, cJSON_CreateString("junior high school")); cJSON *education2 = cJSON_CreateArray(); cJSON_AddItemToArray(education2, cJSON_CreateString("high school")); cJSON_AddItemToArray(education2, cJSON_CreateString("university")); // Define [] array cJSON *education = cJSON_CreateArray(); cJSON_AddItemToArray(education, education1); cJSON_AddItemToArray(education, education2); -
{ { }, { } }
"languages": { "serialOne": { "language": "chinese", "grade": 10 }, "serialTwo": { "language": "English", "grade": 6} }The code achieves the above effect:
// Define object {} cJSON *serialOne = cJSON_CreateObject(); cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialOne, "language", cJSON_CreateString("chinese")); cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialOne, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(10)); cJSON *serialTwo = cJSON_CreateObject(); cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialTwo, "language", cJSON_CreateString("English")); cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialTwo, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(6)); // Define object {} cJSON *languages = cJSON_CreateObject(); cJSON_AddItemToObject(languages, "serialOne", serialOne); cJSON_AddItemToObject(languages, "serialTwo", serialTwo); -
Define the root node, which is the outermost layer {}
// Create the following object cJSON *root = cJSON_CreateObject();
-
Insert both {} and [] defined above into the following node {}
// Insert child into root cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString("Xiao Ming")); // "name": "Xiao Ming" cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "age", cJSON_CreateNumber(23)); // "age": 23 cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "interest", interest); cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "color", color); cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "like", like); cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "education", education); cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "languages", languages); cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "vip", cJSON_CreateTrue()); // "vip": true Cjson is required to insert Boolean data_ Createbool function cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "address", cJSON_CreateNull()); // "address": null Inserting null values requires cJSON_CreateNull function //cJSON_AddTrueToObject(root, "vip"); //cJSON_AddNullToObject(root, "address"); // Or it can be written like this -
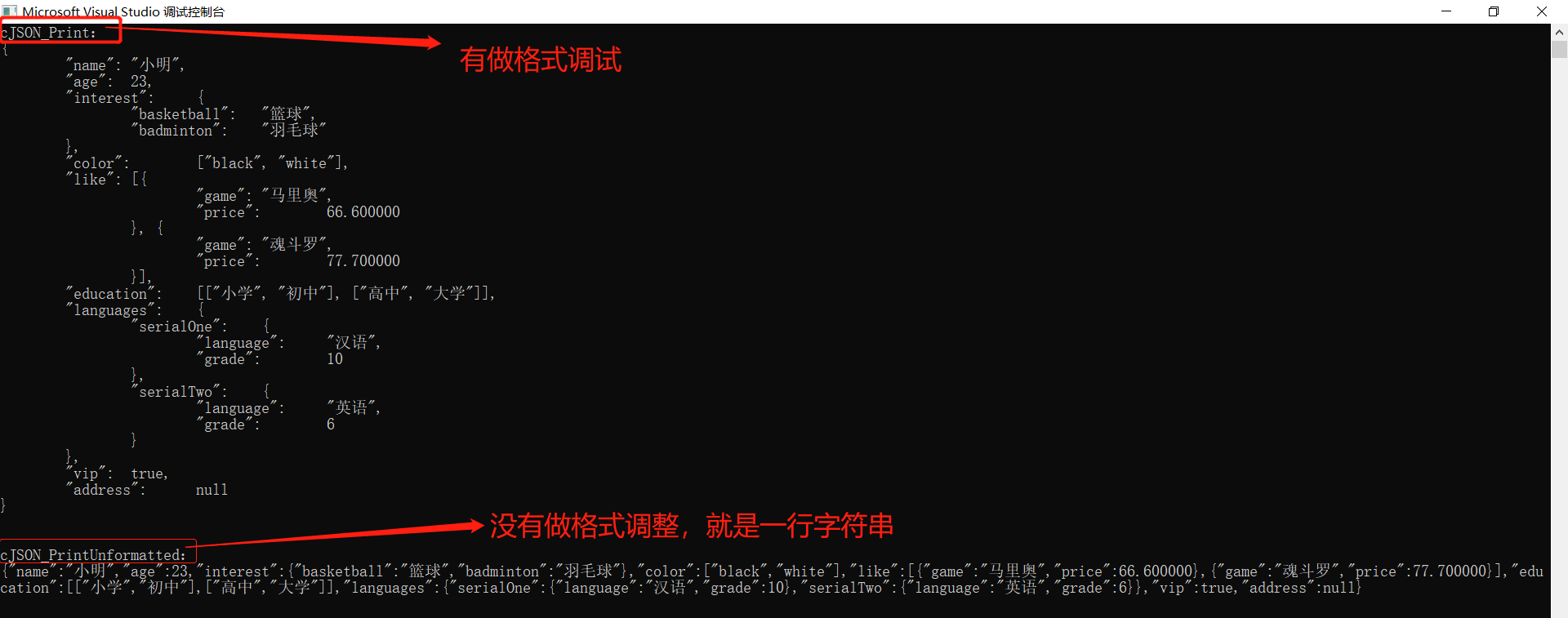
Print console view
// Print console view char *cPrint = cJSON_Print(root); char *cPrintUnformatted = cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root); printf("cJSON_Print: %s ", cPrint); // cJSON_Print: format adjustment printf("cJSON_PrintUnformatted: %s ", cPrintUnformatted); // cJSON_PrintUnformatted: no format adjustment is made // The returned string pointer needs to be released by itself free(cPrint); free(cPrintUnformatted);Remember to use cJSON_Print and cjson_ The character pointer returned by printunformatted needs free memory!
-
Write to file
// Open file FILE *file = NULL; file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w"); // FILE_NAME ==> "jss.json" if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file fail! "); // Freeing pointer memory cJSON_Delete(root); return; } char *cjValue = cJSON_Print(root); // write file //int ret = fwrite(cjValue, sizeof(char), strlen(cjValue), file); int ret = fputs(cjValue, file); if (ret == EOF) { printf("Failed to write file! "); } fclose(file); free(cjValue); -
Release the cJSON pointer
//Freeing pointer memory
cJSON_Delete(root); -
After the code is written, it will be compiled and run. A JSON file will be created in its own project path and the contents will be written. The contents of the file are as follows:
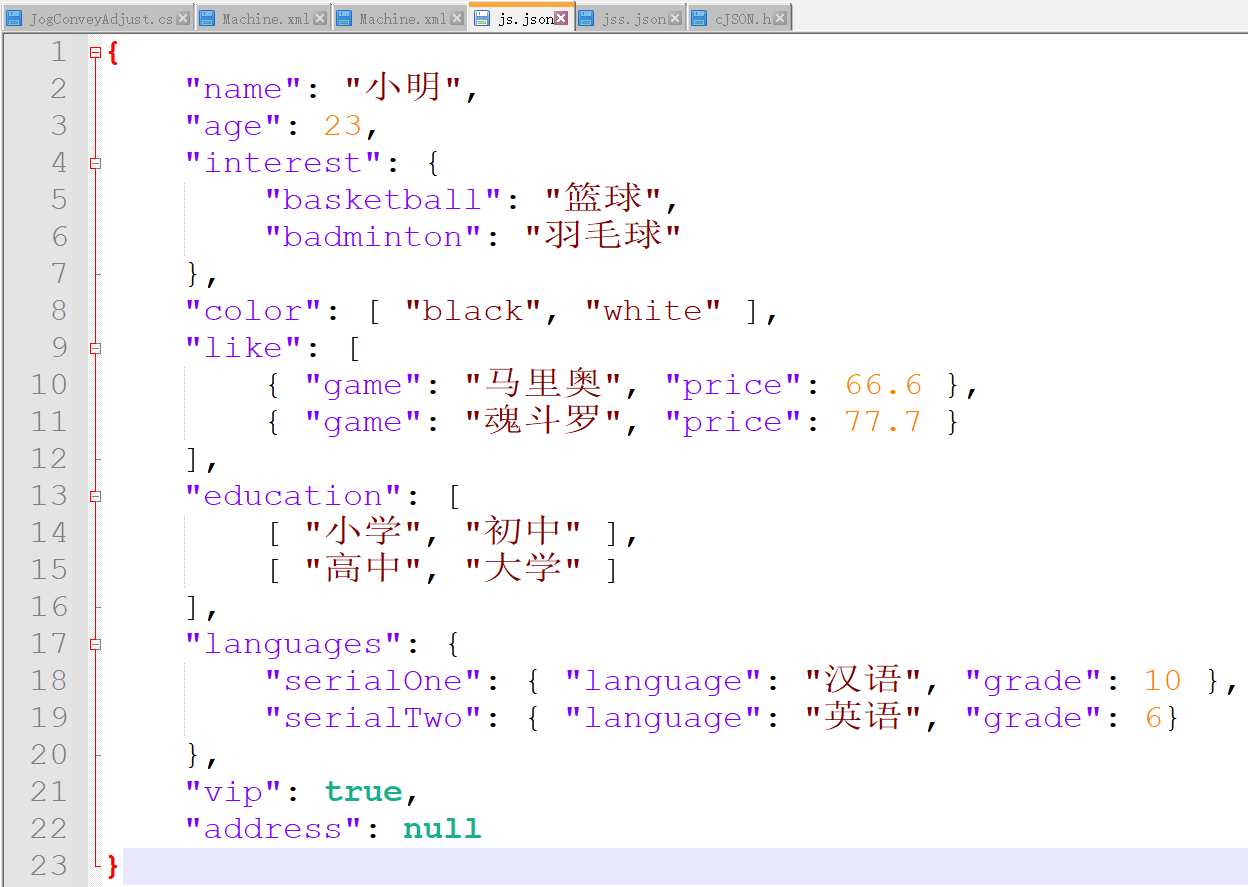
4, Parse Jason
When parsing, you need to use the type type in the structure to judge. This is for security reasons!
You can also use cjson when parsing_ Print function to get the string or use valuestring in the structure to get it, but note that cjson is used_ The print function needs to free the obtained pointer to get the string, otherwise it will cause memory leakage!
The following two methods are provided for parsing. The first is fixed and write dead; The second is a flexible way to analyze!
-
Open file to read josn data
// Open file FILE *file = NULL; file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r"); if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file fail! "); return; } // Get file size struct stat statbuf; stat(FILE_NAME, &statbuf); int fileSize = statbuf.st_size; printf("File size:%d ", fileSize); // Allocate memory that matches the file size char *jsonStr = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * fileSize + 1); memset(jsonStr, 0, fileSize + 1); // Read json string in file int size = fread(jsonStr, sizeof(char), fileSize, file); if (size == 0) { printf("Failed to read file! "); return; } printf("%s ", jsonStr); fclose(file); -
Initialize the cJSON pointer with the read json data
// Convert the read json string into a json variable pointer cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(jsonStr); if (!root) { const char *err = cJSON_GetErrorPtr(); printf("Error before: [%s] ", err); free((void *)err); free(jsonStr); return; } free(jsonStr); -
Define some variables that need to be used below
cJSON *item = NULL; char *v_str = NULL; double v_double = 0.0; int v_int = 0; bool v_bool = false;
-
Parsed directly by key
// Resolution: "name": "Xiao Ming", item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "name"); if (item != NULL) { /* Writing method 1:*/ // Determine whether it is a string type //if (item->type == cJSON_String) { // v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Get value through function // printf("name = %s ", v_str); // free(v_str); // The pointer returned through the function needs to be free by itself, otherwise it will lead to memory leakage // v_str = NULL; //} /* Method 2: */ // Determine whether it is a string type if (item->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = item->valuestring; // This assignment is a shallow copy and does not need to free memory now printf("name = %s ", v_str); } } // Resolution: "age": "23", item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "age"); if (item != NULL) { // Legitimacy check if (item->type == cJSON_Number) { // Judge whether it is a number v_int = item->valueint; // Get value printf("age = %d ", v_int); } } // Parsing: "vip": true, item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "vip"); if (item != NULL) { if (item->type == cJSON_True || item->type == cJSON_False) { v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Since bool type structure is not given, string is used instead printf("vip = %s ", v_str); free(v_str); v_str = NULL; } } // Resolution: "address": null item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "address"); if (item != NULL && item->type == cJSON_NULL) { v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Since the NULL type structure is not given, a string is used instead printf("address = %s ", v_str); free(v_str); v_str = NULL; } -
Resolve object {}
That is to say, analyze the following figure:
Resolution code:
{ /*************** Mode 1***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest"); // Get object object name if (item != NULL) { cJSON *val = NULL; val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "basketball"); // Get the basketball data inside according to the object object name if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = val->valuestring; printf("basketball = %s ", v_str); } val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "badminton"); // Get the badmenton data inside according to the object object name if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = val->valuestring; printf("badminton = %s ", v_str); } } /*************** Mode 2***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *obj = item->child; // Get "basketball": "basketball" while (obj) { if (obj->type == cJSON_String) { char *v_str = obj->valuestring; printf("%s = %s ", obj->string, v_str); // You can get the key through string } // Get next element obj = obj->next; } } } -
Parse array []
That is to say, analyze the following figure: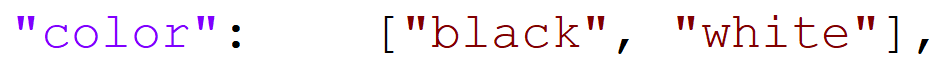
Resolution code:{ /*************** Mode 1***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color"); if (item != NULL) { int size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item); // Get the number of arrays for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { cJSON *arr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i); // Gets the value in the array based on the index if (arr != NULL && arr->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = arr->valuestring; printf("color = %s ", v_str); } } } /*************** Mode 2***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *arr = item->child; // Get "black" while (arr) { if (arr->type == cJSON_String) { char *v_str = arr->valuestring; printf("color = %s ", v_str); } // Get next element arr = arr->next; } } } -
Parse object in array [{}]
That is to say, analyze the following figure:

Resolution code:{ /*************** Mode 1***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like"); if (item != NULL) { int size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item); // Gets the size of the array for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { cJSON *obj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i); // obj in the obtained array cJSON *val = NULL; if (obj != NULL && obj->type == cJSON_Object) { // Judge whether the element in the number is of obj type val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj, "game"); // Get the value in obj if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = val->valuestring; printf("game = %s ", v_str); } val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj, "price"); if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_Number) { v_double = val->valuedouble; printf("price = %.2f ", v_double); } } } } /*************** Mode 2***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *obj = item->child; // Get {game ":" Mario "," price": 66.6} while (obj) { if (obj->type == cJSON_Object) { cJSON *objValue = obj->child; // Get "game": "Mario" while (objValue) { // Then distinguish by type if (objValue->type == cJSON_String) { char *v_str = objValue->valuestring; printf("%s = %s ", objValue->string, v_str); } else if (objValue->type == cJSON_Number) { double v_double = objValue->valuedouble; printf("%s = %.2f ", objValue->string, v_double); } // Get next element objValue = objValue->next; } } // Get the next set of elements obj = obj->next; } } } -
Parse array []]
That is to say, analyze the following figure:

Resolution code:{ /*************** Mode 1***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education"); if (item != NULL) { int size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item); // Gets the size of the array for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { cJSON *arr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i); // Analytical acquisition ["primary school", "junior high school"] if (arr != NULL && arr->type == cJSON_Array) { int arrSize = cJSON_GetArraySize(arr); for (int j = 0; j < arrSize; j++) { cJSON *arr2 = cJSON_GetArrayItem(arr, j); // Further analysis can get the elements in the array if (arr2 != NULL && arr2->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = arr2->valuestring; printf("education = %s ", v_str); } } } } } /*************** Mode 2***************/ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *arr = item->child; // Obtain ["primary school", "junior high school"] while (arr) { if (arr->type == cJSON_Array) { cJSON *arrValue = arr->child; // Get "primary school" while (arrValue) { if (arrValue->type == cJSON_String) { char *v_str = arrValue->valuestring; printf("education = %s ", v_str); } arrValue = arrValue->next; // Get next element } } // Get next group arr = arr->next; } } } -
Resolve object {{}} in object
That is to say, analyze the following figure:

Resolution code:{ /*************** Mode 1***************/ char *arrStr[] = { "serialOne", "serialTwo" }; // You can define the object key to be parsed in advance, so you can use the for loop to parse item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *val = NULL; int size = sizeof(arrStr) / sizeof(char *); // By traversing the pointer array, the key of each object is obtained, and the parsing operation is carried out (if the for loop is not used for parsing, write the code honestly and complete the parsing of all the numbers) for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { cJSON *obj1 = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, arrStr[i]); if (obj1 != NULL && obj1->type == cJSON_Object) { val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj1, "language"); if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) { v_str = val->valuestring; printf("education = %s ", v_str); } val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj1, "grade"); if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_Number) { v_int = val->valueint; printf("grade = %d ", v_int); } } } } /*************** Mode 2***************/ // Available without knowing what the key is and without knowing how many elements there are item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages"); if (item != NULL) { // Get the first child element in languages cJSON *obj = item->child; // That is: "serialone": {"language": "Chinese", "grade": 10} while (obj) { if (obj->type == cJSON_Object) { // Gets the child element of the child element cJSON *value = obj->child; // That is: {language ":" Chinese "," grade": 10} while (value) { if (value->type == cJSON_String) { printf("%s = %s ", value->string, value->valuestring); } else if (value->type == cJSON_Number) { printf("%s = %d ", value->string, value->valueint); } // You can freely obtain the elements inside through next value = value->next; } } // Get the next set of child elements obj = obj->next; } } } -
The analytical results are as follows:
Because there are two parsing methods, they both print twice!
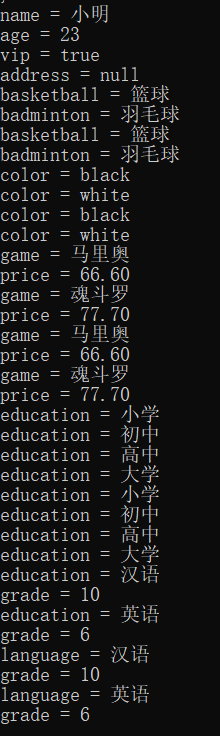
5, Modified by Jason
Only two functions can be used for modification:
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem); extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem);
Just locate the corresponding cJSON pointer first!
-
Open the file, read the json data, and initialize cJSON, which are the same as above
// Convert the read json string into a json variable pointer cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(jsonStr);
-
Define the variables needed below
// This variable is used to receive the located cJSON cJSON *item = NULL;
-
Direct modification
/* "name": "Xiao Ming“ ====> "name": "Little red" */ // Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString("Xiao Hong")); /* "age": 23 ====> "age": 20 */ cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(root, "age", cJSON_CreateNumber(20)); /* "vip": true ====> "vip": false */ // Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(root, "vip", cJSON_CreateBool(false));Before modification:

After modification:
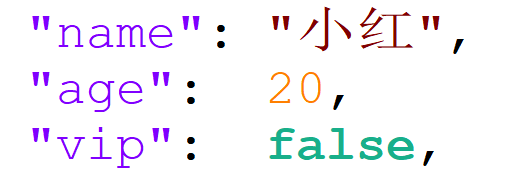
-
Modify the value in {}
/* "interest": { After modification: "interest": { "basketball": "Basketball ", ====> "basketball": "Yao Ming", "badminton": "Badminton“ "badminton": "Lindane" } } */ // First, get the pointer that needs to be modified item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest"); if (item != NULL) { // Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(item, "basketball", cJSON_CreateString("Yao Ming")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(item, "badminton", cJSON_CreateString("lindane")); }Before modification:

After modification:

-
Modify elements in array []
/* "color": ["black", "white"] ====> "color":["red", "blue"] */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color"); if (item != NULL) { // You still have to use the index to locate the specific value that needs to be modified cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(item, 0, cJSON_CreateString("red")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(item, 1, cJSON_CreateString("blue")); }Before modification:
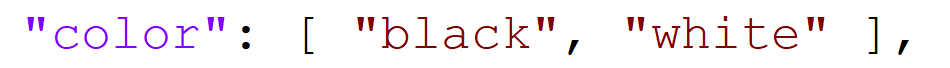
After modification:

-
Modify the value in [{}]
/* "like": [ After modification: "like":[ { "game": "Mario "," price": 66.6}, ====> {"game": "bomber", "price": 88.8}, { "game": "Soul duel "," price": 77.7} {"game": "Chinese chess", "price": 99.9} ], ], */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *arrObj = NULL; arrObj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Bomberman")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(88.8)); arrObj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 1); // Gets the value in the array based on the index cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Chinese chess")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(99.9)); }Before modification:

After modification:

-
Modify the value in []
/* "education": [ After modification: "education": [ [ "Primary school "," junior middle school "], ====> ["grade 6 of primary school", "grade 3 of junior middle school"], [ "High school "," University "] ["senior high school junior", "senior college"] ], ], */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *arrArr = NULL; arrArr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 0, cJSON_CreateString("Grade 6 of primary school")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 1, cJSON_CreateString("Junior high school junior high school")); arrArr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 1); // Gets the value in the array based on the index cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 0, cJSON_CreateString("Senior high school senior three")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 1, cJSON_CreateString("University Senior")); }Before modification:

After modification:

-
Modify the value in {{}}
/* "languages": { After modification: "languages": { "serialOne": { "language": "Chinese "," grade": 10}, ====> "Serialone": {"language": "Cantonese", "grade": 9}, "serialTwo": { "language": "English "," grade": 6} "Serialtwo": {"language": "vernacular", "grade": 8} }, }, */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON *obj = NULL; obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "serialOne"); // Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "language", cJSON_CreateString("Cantonese")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(9)); obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "serialTwo"); // Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "language", cJSON_CreateString("vernacular")); cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(8)); }Before modification:

After modification:

-
write file
// Open file file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w"); if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file fail! "); // Freeing pointer memory cJSON_Delete(root); return; } char *cjValue = cJSON_Print(root); // write file int ret = fwrite(cjValue, sizeof(char), strlen(cjValue), file); if (ret == 0) { printf("Failed to write file! "); } fclose(file); free(cjValue); -
Release the root pointer
//Cjson is used_ After parse, remember to call cJSON_Delete function release
cJSON_Delete(root);
6, Delete Jason
Only two functions can be used to delete:
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which); extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string);
After finding the corresponding cJOSN pointer, delete the specified index of the array and the specified key of the object!
-
Open the file, read the json data, and initialize cJSON, which are the same as above
// Convert the read json string into a json variable pointer cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(jsonStr);
-
Define the variables needed below
// This variable is used to receive the located cJSON cJSON *item = NULL;
-
Delete directly
/* Delete: "name": "Little red" */ // Use this function to delete directly cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(root, "name"); // Delete with key
-
Delete value in {}
/* Delete: "interest": { "badminton": "Lin Dan“ } */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest"); // After obtaining the corresponding node object, you can delete it directly if (item != NULL) { cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(item, "badminton"); }Before deletion:

After deletion:

-
Delete elements in array []
/* Delete: "color": ["blue"] */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color"); // Get the corresponding node array and you can delete it directly if (item != NULL) { cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(item, 1); // Delete by index }Before deletion:

After deletion:

-
Delete {} in []
/* Delete: "like": [ { "game": "Bomber "," price ": 88.800000 }, ] */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(item, 0); You can also continue to delete further //cJSON *arrObj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index //if (arrObj != NULL) { // cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(arrObj, "price"); //} }Before deletion:

After deletion:

-
Delete [] from []
/* Delete: "education": [["senior three", "senior four"]] */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(item, 1); You can also continue to delete further //cJSON *arrArr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index //if (arrArr != NULL) { // cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(arrArr, 1); //} }Before deletion:

After deletion:

-
Delete {} from {}
/* delete "languages": { "serialTwo": { "language":"Vernacular "," grade":8} } */ item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages"); if (item != NULL) { cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(item, "serialTwo"); You can also continue to delete further //cJSON *obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "serialOne"); //if (obj != NULL) { // cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(obj, "grade"); //} }Before deletion:

After deletion:

-
write file
// Open file file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w"); if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file fail! "); // Freeing pointer memory cJSON_Delete(root); return; } char *cjValue = cJSON_Print(root); // write file int ret = fwrite(cjValue, sizeof(char), strlen(cjValue), file); if (ret == 0) { printf("Failed to write file! "); } fclose(file); free(cjValue); -
Free cJSON pointer memory
//Cjson is used_ After parse, remember to call cJSON_Delete function release
cJSON_Delete(root);
7, All codes
In VS2017 and above, create an empty project, copy the code, and then import it into cjson H and cjson C file can be run!
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h> // Get file size
#include "cJSON.h"
#define FILE_NAME "jss.json"
// Package Jason
void createJson ();
// Parse Jason
void parseJson();
// Modify Jason
void alterJson();
// Delete Jason
void delJson();
int main (void) {
createJson();
parseJson();
alterJson();
delJson();
return 0;
}
void createJson () {
/*
"interest": {
"basketball": "Basketball ",
"badminton": "Badminton“
},
*/
// Define object {}
cJSON *interest = cJSON_CreateObject();
// Insert element, corresponding to key value pair
cJSON_AddItemToObject(interest, "basketball", cJSON_CreateString("Basketball")); // When the value is a string, you need to use the function cJSON_CreateString() create
cJSON_AddItemToObject(interest, "badminton", cJSON_CreateString("badminton"));
//cJSON_ Addstringtoobject (interest, "badmenton", "badminton"); // Or write it like this
/*
"color": [ "black", "white" ],
*/
// Define [] array
cJSON *color = cJSON_CreateArray();
// Adding elements to an array
cJSON_AddItemToArray(color, cJSON_CreateString("black"));
cJSON_AddItemToArray(color, cJSON_CreateString("white"));
/*
"like": [
{ "game": "Mario "," price": 66.6},
{ "game": "Soul duel "," price": 77.7}
],
*/
// Define {} object
cJSON *likeObject1 = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject1, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Mario"));
cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject1, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(66.6)); // When the value is a number, you need to use the function cJSON_CreateNumber() create
//cJSON_AddNumberToObject(likeObject1, "price", 66.6); // Or write it like this
cJSON *likeObject2 = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject2, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Contra"));
cJSON_AddItemToObject(likeObject2, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(77.7));
// Define [] array
cJSON *like = cJSON_CreateArray();
// Adding elements to an array
cJSON_AddItemToArray(like, likeObject1);
cJSON_AddItemToArray(like, likeObject2);
/*
"education": [
[ "Primary school "," junior middle school "],
[ "High school "," University "]
],
*/
// Define [] array
cJSON *education1 = cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(education1, cJSON_CreateString("primary school"));
cJSON_AddItemToArray(education1, cJSON_CreateString("junior high school"));
cJSON *education2 = cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(education2, cJSON_CreateString("high school"));
cJSON_AddItemToArray(education2, cJSON_CreateString("university"));
// Define [] array
cJSON *education = cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(education, education1);
cJSON_AddItemToArray(education, education2);
/*
"languages": {
"serialOne": { "language": "Chinese "," grade": 10},
"serialTwo": { "language": "English "," grade": 6}
},
*/
// Define object {}
cJSON *serialOne = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialOne, "language", cJSON_CreateString("chinese"));
cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialOne, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(10));
cJSON *serialTwo = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialTwo, "language", cJSON_CreateString("English"));
cJSON_AddItemToObject(serialTwo, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(6));
// Define object {}
cJSON *languages = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(languages, "serialOne", serialOne);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(languages, "serialTwo", serialTwo);
// Create the following object
cJSON *root = cJSON_CreateObject();
// Insert child into root
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString("Xiao Ming")); // "name": "Xiao Ming"
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "age", cJSON_CreateNumber(23)); // "age": 23
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "interest", interest);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "color", color);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "like", like);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "education", education);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "languages", languages);
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "vip", cJSON_CreateTrue()); // "vip": true Cjson is required to insert Boolean data_ Createbool function
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "address", cJSON_CreateNull()); // "address": null Inserting null values requires cJSON_CreateNull function
//cJSON_AddTrueToObject(root, "vip");
//cJSON_AddNullToObject(root, "address"); // Or it can be written like this
// Print console view
char *cPrint = cJSON_Print(root);
char *cPrintUnformatted = cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root);
printf("cJSON_Print:
%s
", cPrint); // cJSON_Print: format adjustment
printf("cJSON_PrintUnformatted:
%s
", cPrintUnformatted); // cJSON_PrintUnformatted: no format adjustment is made
// The returned string pointer needs to be released by itself
free(cPrint);
free(cPrintUnformatted);
// Open file
FILE *file = NULL;
file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w"); // FILE_NAME ==> "jss.json"
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Open file fail!
");
// Freeing pointer memory
cJSON_Delete(root);
return;
}
char *cjValue = cJSON_Print(root);
// write file
//int ret = fwrite(cjValue, sizeof(char), strlen(cjValue), file);
int ret = fputs(cjValue, file);
if (ret == EOF) {
printf("Failed to write file!
");
}
fclose(file);
free(cjValue);
// Freeing pointer memory
cJSON_Delete(root);
}
void parseJson () {
// Open file
FILE *file = NULL;
file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Open file fail!
");
return;
}
// Get file size
struct stat statbuf;
stat(FILE_NAME, &statbuf);
int fileSize = statbuf.st_size;
printf("File size:%d
", fileSize);
// Allocate memory that matches the file size
char *jsonStr = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * fileSize + 1);
memset(jsonStr, 0, fileSize + 1);
// Read json string in file
int size = fread(jsonStr, sizeof(char), fileSize, file);
if (size == 0) {
printf("Failed to read file!
");
return;
}
printf("%s
", jsonStr);
fclose(file);
// Convert the read json string into a json variable pointer
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(jsonStr);
if (!root) {
const char *err = cJSON_GetErrorPtr();
printf("Error before: [%s]
", err);
free((void *)err);
free(jsonStr);
return;
}
free(jsonStr);
cJSON *item = NULL;
char *v_str = NULL;
double v_double = 0.0;
int v_int = 0;
bool v_bool = false;
// Resolution: "name": "Xiao Ming",
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "name");
if (item != NULL) {
/* Writing method 1:*/
// Determine whether it is a string type
//if (item->type == cJSON_String) {
// v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Get value through function
// printf("name = %s
", v_str);
// free(v_str); // The pointer returned through the function needs to be free by itself, otherwise it will lead to memory leakage
// v_str = NULL;
//}
/* Method 2: */
// Determine whether it is a string type
if (item->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = item->valuestring; // This assignment is a shallow copy and does not need to free memory now
printf("name = %s
", v_str);
}
}
// Resolution: "age": "23",
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "age");
if (item != NULL) { // Legitimacy check
if (item->type == cJSON_Number) { // Judge whether it is a number
v_int = item->valueint; // Get value
printf("age = %d
", v_int);
}
}
// Parsing: "vip": true,
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "vip");
if (item != NULL) {
if (item->type == cJSON_True || item->type == cJSON_False) {
v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Since bool type structure is not given, string is used instead
printf("vip = %s
", v_str);
free(v_str);
v_str = NULL;
}
}
// Resolution: "address": null
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "address");
if (item != NULL && item->type == cJSON_NULL) {
v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Since the NULL type structure is not given, a string is used instead
printf("address = %s
", v_str);
free(v_str);
v_str = NULL;
}
/* Resolution:
"interest": {
"basketball": "Basketball ",
"badminton": "Badminton“
},
*/
{
/*************** Mode 1***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest"); // Get object object name
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *val = NULL;
val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "basketball"); // Get the basketball data inside according to the object object name
if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = val->valuestring;
printf("basketball = %s
", v_str);
}
val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "badminton"); // Get the badmenton data inside according to the object object name
if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = val->valuestring;
printf("badminton = %s
", v_str);
}
}
/*************** Mode 2***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *obj = item->child; // Get "basketball": "basketball"
while (obj) {
if (obj->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = obj->valuestring;
printf("%s = %s
", obj->string, v_str); // You can get the key through string
}
// Get next element
obj = obj->next;
}
}
}
/* Resolution:
"color": ["black", "white"],
*/
{
/*************** Mode 1***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color");
if (item != NULL) {
int size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item); // Get the number of arrays
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cJSON *arr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
if (arr != NULL && arr->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = arr->valuestring;
printf("color = %s
", v_str);
}
}
}
/*************** Mode 2***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *arr = item->child; // Get "black"
while (arr) {
if (arr->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = arr->valuestring;
printf("color = %s
", v_str);
}
// Get next element
arr = arr->next;
}
}
}
/*
"like": [
{ "game": "Mario "," price": 66.6},
{ "game": "Soul duel "," price": 77.7}
],
*/
{
/*************** Mode 1***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like");
if (item != NULL) {
int size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item); // Gets the size of the array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cJSON *obj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i); // obj in the obtained array
cJSON *val = NULL;
if (obj != NULL && obj->type == cJSON_Object) { // Judge whether the element in the number is of obj type
val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj, "game"); // Get the value in obj
if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = val->valuestring;
printf("game = %s
", v_str);
}
val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj, "price");
if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_Number) {
v_double = val->valuedouble;
printf("price = %.2f
", v_double);
}
}
}
}
/*************** Mode 2***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *obj = item->child; // Get {game ":" Mario "," price": 66.6}
while (obj) {
if (obj->type == cJSON_Object) {
cJSON *objValue = obj->child; // Get "game": "Mario"
while (objValue) {
// Then distinguish by type
if (objValue->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = objValue->valuestring;
printf("%s = %s
", objValue->string, v_str);
} else if (objValue->type == cJSON_Number) {
double v_double = objValue->valuedouble;
printf("%s = %.2f
", objValue->string, v_double);
}
// Get next element
objValue = objValue->next;
}
}
// Get the next set of elements
obj = obj->next;
}
}
}
/*
"education": [
[ "Primary school "," junior middle school "],
[ "High school "," University "]
],
*/
{
/*************** Mode 1***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education");
if (item != NULL) {
int size = cJSON_GetArraySize(item); // Gets the size of the array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cJSON *arr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, i); // Analytical acquisition ["primary school", "junior high school"]
if (arr != NULL && arr->type == cJSON_Array) {
int arrSize = cJSON_GetArraySize(arr);
for (int j = 0; j < arrSize; j++) {
cJSON *arr2 = cJSON_GetArrayItem(arr, j); // Further analysis can get the elements in the array
if (arr2 != NULL && arr2->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = arr2->valuestring;
printf("education = %s
", v_str);
}
}
}
}
}
/*************** Mode 2***************/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *arr = item->child; // Obtain ["primary school", "junior high school"]
while (arr) {
if (arr->type == cJSON_Array) {
cJSON *arrValue = arr->child; // Get "primary school"
while (arrValue) {
if (arrValue->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = arrValue->valuestring;
printf("education = %s
", v_str);
}
arrValue = arrValue->next; // Get next element
}
}
// Get next group
arr = arr->next;
}
}
}
/*
"languages": {
"serialOne": { "language": "Chinese "," grade": 10},
"serialTwo": { "language": "English "," grade": 6}
},
*/
{
/*************** Mode 1***************/
char *arrStr[] = { "serialOne", "serialTwo" }; // You can define the object key to be parsed in advance, so you can use the for loop to parse
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *val = NULL;
int size = sizeof(arrStr) / sizeof(char *);
// By traversing the pointer array, the key of each object is obtained, and the parsing operation is carried out (if the for loop is not used for parsing, write the code honestly and complete the parsing of all the numbers)
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cJSON *obj1 = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, arrStr[i]);
if (obj1 != NULL && obj1->type == cJSON_Object) {
val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj1, "language");
if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_String) {
v_str = val->valuestring;
printf("education = %s
", v_str);
}
val = cJSON_GetObjectItem(obj1, "grade");
if (val != NULL && val->type == cJSON_Number) {
v_int = val->valueint;
printf("grade = %d
", v_int);
}
}
}
}
/*************** Mode 2***************/
// Available without knowing what the key is and without knowing how many elements there are
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages");
if (item != NULL) {
// Get the first child element in languages
cJSON *obj = item->child; // That is: "serialone": {"language": "Chinese", "grade": 10}
while (obj) {
if (obj->type == cJSON_Object) {
// Gets the child element of the child element
cJSON *value = obj->child; // That is: {language ":" Chinese "," grade": 10}
while (value) {
if (value->type == cJSON_String) {
printf("%s = %s
", value->string, value->valuestring);
} else if (value->type == cJSON_Number) {
printf("%s = %d
", value->string, value->valueint);
}
// You can freely obtain the elements inside through next
value = value->next;
}
}
// Get the next set of child elements
obj = obj->next;
}
}
}
// Cjson is used_ After parse, remember to call cJSON_Delete function release
cJSON_Delete(root);
}
void alterJson() {
// Open file
FILE *file = NULL;
file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Open file fail!
");
return;
}
// Get file size
struct stat statbuf;
stat(FILE_NAME, &statbuf);
int fileSize = statbuf.st_size;
printf("File size:%d
", fileSize);
// Allocate memory that matches the file size
char *jsonStr = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * fileSize + 1);
memset(jsonStr, 0, fileSize + 1);
// Read json string in file
int size = fread(jsonStr, sizeof(char), fileSize, file);
if (size == 0) {
printf("Failed to read file!
");
return;
}
printf("%s
", jsonStr);
fclose(file);
// Convert the read json string into a json variable pointer
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(jsonStr);
if (!root) {
const char *err = cJSON_GetErrorPtr();
printf("Error before: [%s]
", err);
free((void *)err);
free(jsonStr);
return;
}
free(jsonStr);
cJSON *item = NULL;
/* "name": "Xiao Ming“ ====> "name": "Little red" */
// Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString("Xiao Hong"));
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "name");
if (item != NULL) {
// Determine whether it is a string type
if (item->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = item->valuestring; // This assignment is a shallow copy and does not need to free memory now
printf("name = %s
", v_str);
}
}
/* "age": 23 ====> "age": 20 */
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(root, "age", cJSON_CreateNumber(20));
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "age");
if (item != NULL) {
// Determine whether it is a string type
if (item->type == cJSON_Number) {
int v_int = item->valueint;
printf("age = %d
", v_int);
}
}
/* "vip": true ====> "vip": false */
// Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(root, "vip", cJSON_CreateBool(false));
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "vip");
if (item != NULL) {
// Determine whether it is a string type
if (item->type == cJSON_False || item->type == cJSON_True) {
char *v_str = cJSON_Print(item); // Since bool type structure is not given, string is used instead
printf("vip = %s
", v_str);
free(v_str);
v_str = NULL;
}
}
/*
"interest": { After modification: "interest": {
"basketball": "Basketball ", ====> "basketball": "Yao Ming",
"badminton": "Badminton“ "badminton": "Lindane"
} }
*/
// First, get the pointer that needs to be modified
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest");
if (item != NULL) {
// Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(item, "basketball", cJSON_CreateString("Yao Ming"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(item, "badminton", cJSON_CreateString("lindane"));
}
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *obj = item->child; // Get "basketball": "basketball"
while (obj) {
if (obj->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = obj->valuestring;
printf("%s = %s
", obj->string, v_str); // You can get the key through string
}
// Get next element
obj = obj->next;
}
}
/* "color": ["black", "white"] ====> "color":["red", "blue"] */
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(item, 0, cJSON_CreateString("red"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(item, 1, cJSON_CreateString("blue"));
}
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *arr = item->child; // Get "black"
while (arr) {
if (arr->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = arr->valuestring;
printf("color = %s
", v_str);
}
// Get next element
arr = arr->next;
}
}
/*
"like": [ After modification: "like":[
{ "game": "Mario "," price": 66.6}, ====> {"game": "bomber", "price": 88.8},
{ "game": "Soul duel "," price": 77.7} {"game": "Chinese chess", "price": 99.9}
], ],
*/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *arrObj = NULL;
arrObj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Bomberman"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(88.8));
arrObj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 1); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "game", cJSON_CreateString("Chinese chess"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(arrObj, "price", cJSON_CreateNumber(99.9));
}
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *obj = item->child; // Get {game ":" Mario "," price": 66.6}
while (obj) {
if (obj->type == cJSON_Object) {
cJSON *objValue = obj->child; // Get "game": "Mario"
while (objValue) {
// Then distinguish by type
if (objValue->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = objValue->valuestring;
printf("%s = %s
", objValue->string, v_str);
} else if (objValue->type == cJSON_Number) {
double v_double = objValue->valuedouble;
printf("%s = %.2f
", objValue->string, v_double);
}
// Get next element
objValue = objValue->next;
}
}
// Get the next set of elements
obj = obj->next;
}
}
/*
"education": [ After modification: "education": [
[ "Primary school "," junior middle school "], ====> ["grade 6 of primary school", "grade 3 of junior middle school"],
[ "High school "," University "] ["senior high school junior", "senior college"]
], ],
*/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *arrArr = NULL;
arrArr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 0, cJSON_CreateString("Grade 6 of primary school"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 1, cJSON_CreateString("Junior high school junior high school"));
arrArr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 1); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 0, cJSON_CreateString("Senior high school senior three"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(arrArr, 1, cJSON_CreateString("University Senior"));
}
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *arr = item->child; // Obtain ["primary school", "junior high school"]
while (arr) {
if (arr->type == cJSON_Array) {
cJSON *arrValue = arr->child; // Get "primary school"
while (arrValue) {
if (arrValue->type == cJSON_String) {
char *v_str = arrValue->valuestring;
printf("education = %s
", v_str);
}
arrValue = arrValue->next; // Get next element
}
}
// Get next group
arr = arr->next;
}
}
/*
"languages": { After modification: "languages": {
"serialOne": { "language": "Chinese "," grade": 10}, ====> "Serialone": {"language": "Cantonese", "grade": 9},
"serialTwo": { "language": "English "," grade": 6} "Serialtwo": {"language": "vernacular", "grade": 8}
}, },
*/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON *obj = NULL;
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "serialOne");
// Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "language", cJSON_CreateString("Cantonese"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(9));
obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "serialTwo");
// Using cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject can be modified directly
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "language", cJSON_CreateString("vernacular"));
cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(obj, "grade", cJSON_CreateNumber(8));
}
// Analyze and print to see whether the modification is successful
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages");
if (item != NULL) {
// Get the first child element in languages
cJSON *obj = item->child; // That is: "serialone": {"language": "Chinese", "grade": 10}
while (obj) {
if (obj->type == cJSON_Object) {
// Gets the child element of the child element
cJSON *value = obj->child; // That is: {language ":" Chinese "," grade": 10}
while (value) {
if (value->type == cJSON_String) {
printf("%s = %s
", value->string, value->valuestring);
} else if (value->type == cJSON_Number) {
printf("%s = %d
", value->string, value->valueint);
}
// You can freely obtain the elements inside through next
value = value->next;
}
}
obj = obj->next;
}
}
// Open file
file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Open file fail!
");
// Freeing pointer memory
cJSON_Delete(root);
return;
}
char *cjValue = cJSON_Print(root);
// write file
int ret = fwrite(cjValue, sizeof(char), strlen(cjValue), file);
if (ret == 0) {
printf("Failed to write file!
");
}
fclose(file);
free(cjValue);
// Cjson is used_ After parse, remember to call cJSON_Delete function release
cJSON_Delete(root);
}
void delJson() {
// Open file
FILE *file = NULL;
file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Open file fail!
");
return;
}
// Get file size
struct stat statbuf;
stat(FILE_NAME, &statbuf);
int fileSize = statbuf.st_size;
printf("File size:%d
", fileSize);
// Allocate memory that matches the file size
char *jsonStr = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * fileSize + 1);
memset(jsonStr, 0, fileSize + 1);
// Read json string in file
int size = fread(jsonStr, sizeof(char), fileSize, file);
if (size == 0) {
printf("Failed to read file!
");
return;
}
printf("%s
", jsonStr);
fclose(file);
// Convert the read json string into a json variable pointer
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(jsonStr);
if (!root) {
const char *err = cJSON_GetErrorPtr();
printf("Error before: [%s]
", err);
free((void *)err);
free(jsonStr);
return;
}
free(jsonStr);
cJSON *item = NULL;
/* Delete: "name": "Little red" */
// Use this function to delete directly
cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(root, "name"); // Delete with key
/* Delete:
"interest": {
"badminton": "Lin Dan“
}
*/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "interest");
// After obtaining the corresponding node object, you can delete it directly
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(item, "badminton");
}
/* Delete: "color": ["blue"] */
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "color");
// Get the corresponding node array and you can delete it directly
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(item, 1); // Delete by index
}
/* Delete:
"like": [
{ "game": "Bomber "," price ": 88.800000 },
]
*/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "like");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(item, 0);
You can also continue to delete further
//cJSON *arrObj = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
//if (arrObj != NULL) {
// cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(arrObj, "price");
//}
}
/* Delete: "education": [["senior three", "senior four"]] */
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "education");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(item, 1);
You can also continue to delete further
//cJSON *arrArr = cJSON_GetArrayItem(item, 0); // Gets the value in the array based on the index
//if (arrArr != NULL) {
// cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(arrArr, 1);
//}
}
/* delete
"languages": {
"serialTwo": { "language":"Vernacular "," grade":8}
}
*/
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "languages");
if (item != NULL) {
cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(item, "serialTwo");
You can also continue to delete further
//cJSON *obj = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "serialOne");
//if (obj != NULL) {
// cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(obj, "grade");
//}
}
// Open file
file = fopen(FILE_NAME, "w");
if (file == NULL) {
printf("Open file fail!
");
// Freeing pointer memory
cJSON_Delete(root);
return;
}
char *cjValue = cJSON_Print(root);
// write file
int ret = fwrite(cjValue, sizeof(char), strlen(cjValue), file);
if (ret == 0) {
printf("Failed to write file!
");
}
fclose(file);
free(cjValue);
// Cjson is used_ After parse, remember to call cJSON_Delete function release
cJSON_Delete(root);
}
8, Summary
It took me a lot of time to write this blog, and I was really tired, but fortunately, I finally finished this blog according to my own wishes!
Among them, there are two parsing methods for parsing that module. It is recommended to use the second parsing method, which is more flexible. Even if several more nodes are added later, it can still be parsed without changing the code!
I personally feel that the operation of json in this blog should be very comprehensive, covering almost all the results. Now record it and share it with everyone who needs it!