Must do problem sorting
- At 21:40 on April 11, 2021, I was very skeptical about life after the exam. I originally wanted to rely on professional courses to score points. I also expected that there would be a large number of applicants for specialized courses this year. In addition, the reform of professional courses should be simpler, but I didn't expect that there was no need to think about the simple topic. The foundation of the exam was the foundation of the exam. I felt that there was no hope to rely on professional courses to score points, However, I'd better send out the data I typed by myself. I sorted out the test questions specially inserted in this exam over the years. I thought I could get five questions, but I didn't get one. I didn't even get a ranking. It may increase the difficulty next year. If necessary, I can collect it
- I also made a super detailed political thinking map. I will upload the test questions over the years and my own notes to CSDN. If there is no member, I can send a private message to QQ email to me. My email will be a favor, but don't forget to support it for three consecutive times
Connect two strings
-
char* Strcat(char* str1, const char* str2) { int n = strlen(str1); int i = 0; while (str1++[i + n] = str2++[i]); return str1; } char* Strcat(char* str1,char* str2) { char * p1= str1,*p2 = str2; int len1 = 0,len2 = 0; if(str1==NULL){ return str2; } if(str2 ==NULL){ return str1; } while (*p1++!='\0') { len1++; } while (*p2++!='\0') { len2++; } char * str3 = malloc(sizeof(char)*(len1+len2)); int i=0; for (p1 = str1;*p1!='\0';p1++) { *(str3+i) = *p1; i++; } for (p2 = str2;*p2!='\0';p2++) { *(str3+i) = *p2; i++; } *(str3+i) ='\0'; return str3; }
prime number
/***********Judge whether it is a prime number************/
int prime(int n)
{
int i;
for(i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++)//This involves the prime judgment using the root sign
{
if(n%i==0)
{
return 0;//Return 0 if it is not a prime
}
}
return 1;//Is a prime number and returns 1
}
void print(int n)
{
int i;
for(i=2;i<=n/2;i++)
{
if(prime(i)&&prime(n-i))//Judge whether the two numbers split are also prime numbers
{
printf("%d=%d+%d\n",n,i,n-i);
}
}
}
Narcissistic number
-
void daffodilNum(){ int x,y,z; for (int i = 100;i<1000;i++) { x = i/100; y = i/10%10; z = i%10; if(i == x*x*x + y*y*y + z*z*z){ printf("%4d",i); } } }
All sort
choice
-
#define swap(A,B) int temp=A;A =B;B=temp; void selectSort1(int array[],int length){ for (int i=0;i<length;i++) { int min =i; for (int j = i;j<length;j++) { if(array[min]>array[j]){ min = j; } } swap(array[min], array[i]); } }
insert
-
void InsertSort2(int array[],int length){ int j ; for (int i = 1;i<length;i++) { int k = array[i]; for (j = i;j>0 && k<array[j-1] ;j--) { array [j] = array[j-1]; } array [j] = k; } }
Bubbling
-
void bubbleSort(int array[],int length){ for (int i=1;i<length;i++) { for (int j=i;j>0;j--) { if(array[j]<array[j-1]){ swap(array[j], array[j-1]); } } } }
shell
-
void shellSort(int array[],int lenght){ for (int shell = lenght/2;shell>0;shell/=2) { for (int i = shell;i<lenght;i++) { if (array[i-shell]>array[i]) { swap(array[i-shell],array[i]); } } } }
Merge
-
void mergeab(int array[],int left,int right){ int i = left; int mid = (left+right)/2; int j = mid +1; int k=left; while ((i<=mid)&&(j<=right)) { if(array[i]<array[j]){ b[k++] = array[i++]; }else { b[k++] = array[j++]; } } if(i>mid){ for (i=j;i<=right;i++) { b[k++] = array[i]; } //Section j not completed }else { for (;i<=mid;i++) { b[k++] = array[i]; } // Section i not completed } } void copy(int a[],int b[],int left,int right){ for (int i =left;i<=right;i++) { a [i] = b[i]; } } void mergeSort(int array[],int left,int right){ int m = (left +right)/2; if(right<= left){ return; } mergeSort(array,left,m); mergeSort(array,m+1,right); mergeab(array, left, right); copy(array,b,left,right); }
fast
-
//partition int partition(int array[],int left,int rigth){ int i=left ,j = rigth+1; int standarn = array[left]; while (1) { while (standarn>array[++i]) { if(i==rigth){ break; } } while (standarn<array[--j]) { } if(i>=j){ break; } swap(array[i], array[j]); } swap(array[j], array[left]); return j; } int randomi (int minIndex,int maxIndex){ return minIndex+(maxIndex-minIndex)*(1.0*rand()/RAND_MAX); } int randomPartition(int array[],int minIndex,int maxIndex){ int i = randomi(minIndex,maxIndex); swap(array[i], array[i]); return partition(array, minIndex, maxIndex); } //quicksort void quickSort(int array[],int minIndex,int maxIndex){ if(minIndex>maxIndex)return; int standarn = randomPartition(array, minIndex, maxIndex); quickSort(array, minIndex, standarn-1); quickSort(array, standarn+1, maxIndex); }
base
-
#define radix 10 void RadixSort(int array[],int length){ int pow=1,max =-1; int * temp_array=(int *) malloc(sizeof(int )*length); for (int i=0;i<length;i++) { if(max< array[i]){ max= array[i]; } } while (max/pow) { int count[radix]={0}; for (int i=0;i<length;i++) { ++count [array[i]/pow%radix]; } for (int i=1;i<radix;i++) { count[i] += count[i-1]; } for (int i=length-1;i>=0;i--) { temp_array[--count[array[i]/pow%radix]] = array[i]; } for (int i=0;i<length;i++) { array [i]= temp_array[i]; } pow *=radix; } free(temp_array); }
Number reverse order
-
void intarrayReverse(int array[],int length){ for (int i=0;i<length/2;i++) { int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[length-1-i]; array[length-1-i] = temp; } } //Negative number reverse int reverse(int n){ int sign=1,m; if(n<0){ sign =-1; } n = (n>=0?n:-n); m=n%10; while (n>=10) { n = n/10; m = m*10+n%10; } return sign*m; }
Binary tree left and right children exchange
-
void TreeReverse(Tree * p){ Tree * temp; if(p){ temp = p->left; p->left = p->rigth; p ->rigth = temp; TreeReverse(p->left); TreeReverse(p->rigth); } }
The binary tree finds the sibling node of x
-
Tree * findNode(Tree * p ,int x){ Tree *temp = p; if(p){ if(p->left!=NULL || p->rigth!=NULL){ if(p->left->x == x){ if(p->rigth){ p = p->rigth; printf("\n find succee %d",p->x); return p; } } if(p->rigth->x == x){ if(p->left){ p = p->left; printf("\n find succee %d",p->x); return p; } } } temp = findNode(p->left,x); if(temp){ return temp; } temp = findNode(p->rigth,x); return temp; }else { return NULL; } }
Binary tree recursive search
-
Tree * finderNode(Tree * p,int data){ Tree * temp = p; if(p){ if(p->x ==data){ return p; } temp = finderNode(p->left,data); if(temp){ return temp; } temp = finderNode(p ->rigth,data); return temp; }else { return NULL; } }
Binary search tree lookup
-
Tree * findSearch(Tree* p ,int data){ while (p) { if(p->x >data){ p = p->left; }else if(p -> x <data){ p= p->rigth; }else { break ; } } return p; }
Algorithm for inserting an element at the end of a linked list
Binary search tree insertion node
-
void binaryTreeInsertNode(Tree * head,int data){ Tree * node = newNode(data); Tree * p =head; Tree * partent =p; while (p) { partent = p; if(p->x < data){ p = p->rigth; }else if(p->x >data){ p = p->left; }else { return; //The same element node cannot be inserted } } if(head == NULL){ //Empty tree partent = node; }else { if(partent->x < data){ partent->rigth = node; }else { partent->left = node; } } }
Binary tree to find the maximum
-
int TreeMaxNode(Tree * p ,int data){ int max =data; if(p){ if(max<p->x){ max = p->x; } max = TreeMaxNode(p->left,max); max = TreeMaxNode(p->rigth,max); return max; }else { return max; } }
Binary search
-
int binarySearch(int array[],int left ,int right,int data){ int i = left; int j = right; while (i <= j) { int mid = (i + j)/2; if(data == array[mid])return mid; else { if(data <array[mid]) { j =mid-1; }else { i = mid+1; } } } return -1; }
Reverse order of linked list
-
Link* linkReverse(Link * L){ Link * left = NULL ,*mid = L->next ,*right = NULL; while (right) { right = mid->next; mid ->next = left ; left = mid; mid = right; } right = newNode(0); right ->next =mid; return right; } //Reverse order of nodes with header Link ListReverse(List & L){ link last = 0 ,cur= L->first , next; while (cur) { next = cur ->next ; cur ->next = last; last = cur; cur = next; } L->first = last; } //Linked list of nodes without header in the book
Merging two ordered single linked lists
- If you are too lazy to write, judge the blank, determine the L3 point header, and p1&&p2 cycle judgment to connect to L3
- Process the remaining elements, disconnect L1L2 and return L3
Two decreasing ordered linked lists are merged into an increasing ordered list, lc points to
- You can sort two decreasing ordered tables incrementally and then merge them
- Or merge two decreasing ordered tables into one ordered table, and then reverse the decreasing ordered table directly
Yanghui triangle
-
#include "stdio.h" #include "string.h" #include "math.h" #include "stdlib.h" #define N 10 int main(){ int i,j; int s[N][N]={0};//Initialization must be done well // Initialization, first column, diagonal for (i=0;i<N;i++){ s[i][0]=1; s[i][i]=1; } // Middle content, starting from s[1][0], the value is 2, s[i][j]=s[i-1][j-1]+s[i-1][j]; for (i=2;i<N;i++) { for (j=1;j<=i-1;j++) { s[i][j]=s[i-1][j]+s[i-1][j-1]; } } // Output for J = 0; J < I triangle output for(i=0;i<N;i++){ for (j=0;j<=i;j++){ printf("%5d",s[i][j]); } putchar(10); } } 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 5 10 10 5 1 1 6 15 20 15 6 1 1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1 1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1 1 9 36 84 126 126 84 36 9 1
Fibonacci
-
//Recursion int fibonacci(int n){ if(n<=1)return 1; return fibonacci(n-1)+factorial(n-2); } //dynamic programming //Save the solution of the calculated subproblem to avoid repeated calculation int Fibonacci(int n){ int *f =(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(n+1)); f[0]=f[1]=1; for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) { f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2]; } free(f); return f[n]; } //dynamic programming //Only two positions are used, which is very exquisite. When the number is singular, it is stored in 1 bit, and when the number is even, it is stored in 0 bit. Repeat the superposition, and finally stop all the superposition in the singular int fibonacci2(int n){ int f[2] ; f[0]=f[1]=1; while (--n) { f[n&1]=f[0]+f[1]; } return f[1]; }
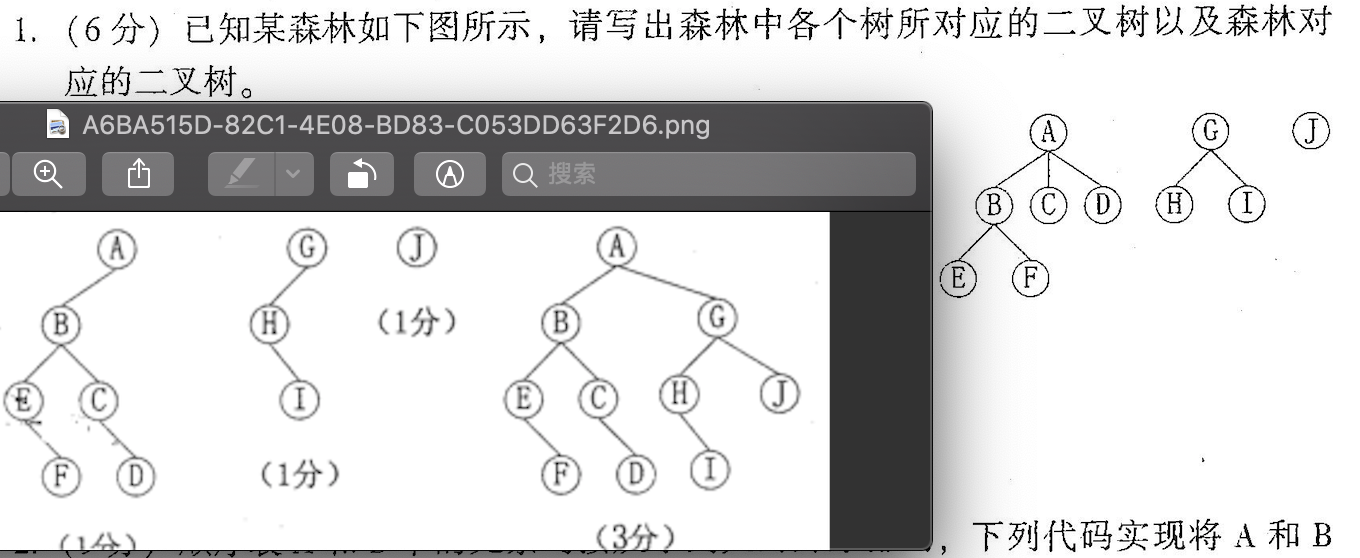
##Forest to binary tree