1, Role of regular expressions
What regular expressions do: 1) Check whether the string complies with the rules 2) Extract the content that conforms to the rules in the string.
2, Create regular expressions
+++ Create regular expressions
use RegExp Create regular expressions
var reg=new RegExp("regular expression ","Matching pattern");
Creating regular expressions using literals
var reg=/regular expression /Matching pattern
+++ Regular expression matching pattern
i ignore case
g Perform a global match (find all matches instead of stopping after the first match is found).
m Perform multiline matching
be careful:You can set multiple match patterns for an expression. The order doesn't matter.
var reg=/abc/ig
var reg=/abc/gi
2.1 creating regular expressions
1) Creating regular expressions using RegExp
//Create regular expressions
var reg=new RegExp("a");
console.log(reg.test("Hello! Small a")); //true
//Creates a regular expression with a matching pattern
var reg2=new RegExp("A","i");
console.log(reg2.test("Hello! Small a")); //true
2) Creating regular expressions using literals
//Create regular expressions
var reg=/a/;
console.log(reg.test("Hello! Small a")); //true
//Creates a regular expression with a matching pattern
var reg2=/A/i;
console.log(reg2.test("Hello! Small a")); //true
2.2 regular expression matching pattern
i ignore case
var reg=/reg/i;
var reg=new RegExp("a","i");
g Perform a global match (find all matches instead of stopping after the first match is found).
var reg=/reg/g;
var reg=new RegExp("a","g");
m Perform multiline matching (rarely used!!!)
be careful:You can set multiple match patterns for an expression. The order doesn't matter. var reg=/abc/ig var reg=/abc/gi
1) i ignore case
var str="eweAdfdfB 32323ewe wew ";
//Detects whether the string contains ad substrings
var reg=/ad/;
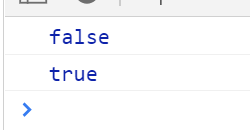
console.log(reg.test(str)) //false
//Detect whether the string contains ad substrings, ignoring case
var reg=/ad/i;
console.log(reg.test(str)) //true
2) g perform global matching
var str="eweadfdad 32323ewe wew ";
//Replace the ad substring in the string. Replace a stop
var reg=/ad/;
var newStr=str.replace(reg,'hlp');
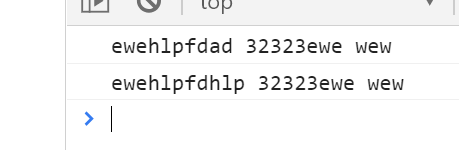
console.log(newStr)
//Replace the ad substring in the string. Global replace.
var reg=/ad/g;
var newStr=str.replace(reg,'hlp');
console.log(newStr)
3) Note: you can set multiple matching patterns for an expression. The order doesn't matter
var str="eweadfdaD 32323ewe wew ";
//Replace the ad substring in the string. Complete replacement. ignore case
var reg=/ad/ig;
var newStr=str.replace(reg,'hlp');
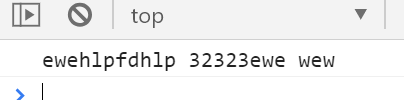
console.log(newStr)
3, Common methods of regular expressions
test() Check whether there is a rule in the string(Regular expression rules)Substring of. Compliance return true,otherwise false. exec() Gets that there are substrings in the string that conform to regular expression rules,Returns an array by default.
3.1 test() checks whether there are substrings in the string that meet the rules
>>>>>>Check whether the string has a substring
var s="a";
console.log(s.test(/a/)) //true
s="absdsdsd"
console.log(s.test(/a/)) //true
s="eweewewew"
console.log(s.test(/a/)) //false
>>>>>>Check whether the string has ab substring, ignoring case
var s="212aBwewewe";
//Detect whether there is ab substring in the string. false due to mismatch
console.log(s.test(/ab/)) //false
//Detect whether there is ab substring in the string. Ignore case, so true
console.log(s.test(/ab/i)) //true
3.2 exec() gets the substring that conforms to the rule in the string
>>>>>>Find matching strings in strings
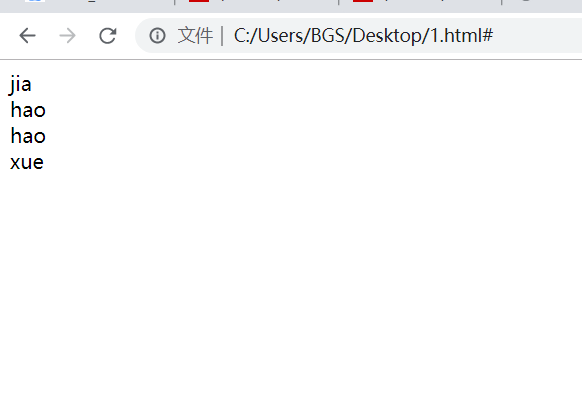
var str="da jia hao hao xue xi a";
var reg=/\b[A-Z]{3}\b/ig; //ignore case
var line=reg.exec(str)
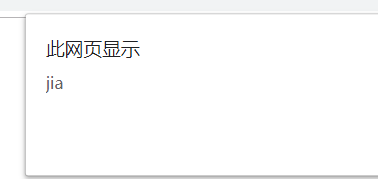
alert(line)// jia
>>>>>>Find all matching strings in a string
<body>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var str="da jia hao hao xue xi a";
var reg=/\b[A-Z]{3}\b/ig; //ignore case
var line="";
while((line=reg.exec(str))!=null){
document.write(line)
document.write("<br/>")
}
</script>
4, Regular expression syntax
4.1 or
| Meaning of or
>>>>>>Detects whether the string contains a or b substrings
var str="abcd";
//Detect whether the string contains a substring
var reg=/a/;
console.log(reg.test(str)); //true
//Detect whether the string contains a substring or b substring,
var reg=/a|b/;
console.log(reg.test(str)); //true
>>>>>>Detects whether the string contains ab or qww substrings
var str="ab212cd";
//Detect whether the string contains ab substring
var reg=/ab/;
console.log(reg.test(str)); //true
//Check whether the string contains ab substring or qww substring,
var reg=/ab|qww/;
console.log(reg.test(str)); //true
4.2 square brackets
[ ] Square brackets are used to query characters in a range The contents in square brackets also mean or. [^ ] Except for the characters in square brackets
[abc] express a,b,c Any character in. Equivalent to a|b|c [^abc] except a,b,c Any character in [a-z] Represents any lowercase letter [A-Z] Represents any capital letter [A-z] Represents any letter [0-9] Represents 0-9 Any number [4-9] Represents 4-9 Any number [0-9a-zA-Z] It can be any character in numbers or English letters (ab|bc|cd) express ab,bc,cd Any string in
>>>>>>Check whether a string contains a or b or c
//Create regular expressions
var reg=/a|b|c/;
console.log(reg.test("a21323")); //true
console.log(reg.test("21b323")); //true
console.log(reg.test("21c323")); //true
console.log(reg.test("2332323te")); //false
var reg='[abc]';
//Check whether the string contains a or b or c
console.log(reg.test("rewe")); //false
//Check whether the string contains a or b or c
console.log(reg.test("a434d"));//true
>>>>>>Check whether a string contains abc or adc or aec
var str="I am abc you aw";
var reg=/abc|adc|aec/;
console.log(reg.test(str))
var str="I am abc you aw";
var reg=/a[bcd]c/;
console.log(reg.test(str))
>>>>>> [ ]
Check whether the string contains numbers
//Check whether the string contains numbers
var reg=/[0-9]/
console.log(reg.test("dewwewe3")); //true
console.log(reg.test("dewwewe")); //false
Check whether the string contains 4-9 numbers
//Check whether the string contains 4-9 numbers
var reg=/[4-9]/
console.log(reg.test("dewwewe3")); //false
console.log(reg.test("dewwewe7")); //true
Check whether the string contains lowercase letters
//Check whether the string contains lowercase letters
var reg=/[a-z]/
console.log(reg.test("1213232323")); //false
console.log(reg.test("121212a")); //true
Check whether the string contains uppercase letters
//Check whether the string contains uppercase letters
var reg=/[A-Z]/
console.log(reg.test("1213232323")); //false
console.log(reg.test("121212a")); //false
console.log(reg.test("121212A")); //true
Check whether the string contains letters
//Check whether the string contains letters
var reg=/[A-z]/
console.log(reg.test("1213232323")); //false
console.log(reg.test("121212a")); //true
console.log(reg.test("121212A")); //true
>>>>>>[] mix
Detect whether there are numbers or uppercase letters in the string
//Detect whether there are numbers or uppercase letters in the string
var reg=/[0-9A-Z]/;
console.log(reg.test("ewe")) //false
console.log(reg.test("123232dwew")) //true
Detect whether there are numbers or English letters in the string
//Detect whether there are numbers or English letters in the string
var reg=/[0-9A-Za-z]/;
console.log(reg.test("ewe")) //true
console.log(reg.test("123232dwew")) //true
>>>>>>[^] except
[^] check whether the string contains characters other than those in brackets
var reg=/[^ab]/
console.log(reg.test("a")); //false
console.log(reg.test("b")); //false
console.log(reg.test("ab")); //false
console.log(reg.test("ab12")); //true
4.3 quantifiers
classifier: 1) You can set the number of occurrences of an element through quantifiers. 2) A quantifier only works on the content before it.
Quantifier grammar:
{m} appear m second
{m,n} appear m reach n second
{m,} appear m More than times
+ At least once, equivalent to{1,}
* 0 or more occurrences,amount to{0,}
? 0 or 1 occurrences. amount to{0,1}
example:
appear m second:
ab{3}c
(ab){3}c
appear m reach n second
ab{1,3}c
appear m More than times
ab{3,}
1) Key points of quantifier
>>>>>>>You can set the number of occurrences of an element through quantifiers
var reg=/aaa/
//Check whether the string contains a substring of aaa
console.log(reg.test("aabcccc"));//false
//Check whether the string contains a substring of aaa
console.log(reg.test("aaabcccc"));//true
//Equivalent to / aaa/
var reg=/a{3}/
//Check whether the string contains a substring of aaa
console.log(reg.test("aabcccc"));//false
//Check whether the string contains a substring of aaa
console.log(reg.test("aaabcccc"));//true
>>>>>>>The quantifier only works on the content before it
//amount to / abbb/
var reg=/ab{3}/
//amount to / ababab/
var reg2=/(ab){3}/
2) Quantifier grammar
>>>>>>{m} occurs m times
//Equivalent to / acbbb/
var reg=/acb{3}/
//Equivalent to / acbacbacb/
var reg=/(acb){3}/
>>>>>>{m,} occurs more than m times
//Equivalent to more than 3 occurrences of a
var reg=/a{3,}/
console.log(reg.test("abcaa")); //false
console.log(reg.test("abcaaa")); //true
>>>>>>{m, n} occurs m to N times
//It is equivalent to one to three occurrences of a
var reg=/a{1,3}/
console.log(reg.test("bcd")); //false
console.log(reg.test("abcd")); //true
console.log(reg.test("aaaabcd")); //true
>>>>>>+ at least 1 occurrence
//Equivalent to a appearing at least once
var reg=/a+/
console.log(reg.test("bcd")); //false
console.log(reg.test("abcd")); //true
console.log(reg.test("aaaaabcd")); //true
>>>>>>* 0 or more occurrences
//Equivalent to 0 or more occurrences of a
var reg=/a*/
console.log(reg.test("bcd")); //true
console.log(reg.test("abcd")); //true
console.log(reg.test("aaaaabcd")); //true
>>>>>> ? 0 or 1 occurrences
//Equivalent to 0 or 1 occurrence of a
var reg=/a?/
console.log(reg.test("bcd")); //true
console.log(reg.test("abcd")); //true
console.log(reg.test("aaaaabcd")); //true
^ Indicates the beginning /^abc/ Express with abc start & Indicates the end /abc$/ Express with abc ending /^a$/
4.4 metacharacters
Metacharacter: . Represents any character \w Any number, letter and underline. [0-9A-z_] \W Except for word characters. [^0-9A-z_] \d Any number. [0-9] \D Except numbers [^0-9] \s Space. \S Except for spaces. \b Word boundaries. \B Except word boundaries The so-called word boundary refers to the space before and after the word(Except at the beginning or end of the string) We can use spaces instead of word boundaries to find words, but not if the word is at the beginning or end. Word boundaries must be used at this time.
Regular expression escape: 1) [Use literal to create an escape in a regular expression Use in regular expressions\Represents a transfer character 2) [use RegExp Object to create escape in regular expression Use in constructors\\Represents a transfer character. Reason: when a regular object is created using a constructor, the parameter is a string. Because the escape character in the regular expression is \ , The escape character in the string is the same \ . And the escaped form of the string is a regular expression. In regular expressions, if you want to use\,Is required in the string\\To double escape. character string:\\. == > regular: \. character string:\\\\ == > regular: \\
1) Metacharacter points
>>>>>> . Represents any character
//Match any character
var reg=/./
console.log(reg.test("deggf")) //true
console.log(reg.test("#$%^%^%@#@"));//true
//Match
var reg=/\./
console.log(reg.test("#$%^%^%@#@"));//false
console.log(reg.test("#$%^%^%@#@."));//true
>>>>>>\ W and \ w (any number, letter and underscore) pi
Match any letters, numbers, underscores
//Match letters, numbers, underscores
var reg=/\w/
console.log(reg.test("deggf")) //true
console.log(reg.test("#$%^%^%@#@"));//false
//Match letters, numbers, underscores
var reg2=new RegExp("\\w");
console.log(reg2.test("deggf")) //true
console.log(reg2.test("#$%^%^%@#@"));//false
Match except letters, numbers, underscores
//Matches symbols other than letters, numbers, and underscores
var reg=/\W/
console.log(reg.test("deggf")) //false
console.log(reg.test("#$%^%^%@#@"));//true
>>>>>>\ D and \ D (any number)
Match any number
//Match any number
var reg=/\d/
console.log(reg.test("deggf")) //false
console.log(reg.test("4derer"));//true
Match except numbers
//Matches characters other than numbers
var reg=/\D/
console.log(reg.test("deggf")) //true
console.log(reg.test("232323"));//false
//Matches substrings where non characters appear three times
var reg=/\D{3}/
console.log(reg.test("deggf")) //true
console.log(reg.test("4de23er"));//false
>>>>>>\ S and \ S (spaces)
Match spaces
//Match spaces
var reg=/\s/
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //true
//Match two spaces
var reg=/\s{2}/
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //Only one space false
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //There are two spaces true
//Match three spaces
var reg=/\s{3}/
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //Only one space false
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //Only two spaces false
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //There are three spaces true
Match non spaces
//Matches 3 consecutive non whitespace characters
var reg=/\S{3}/
console.log(reg.test(" ")) //false
console.log(reg.test("32 323")) //true
>>>>>>\ B and \ B (word boundary)
Find words
var reg=/\bchild\b/
console.log(reg.test("hello child")) //true
console.log(reg.test("hello child Hello")) //true
console.log(reg.test("hello childc")) //false
We can use spaces instead of word boundaries to find words, but not if the word is at the beginning or end.
var reg=/\sworld\s/;
console.log(reg.test("wqqworld")) //false
console.log(reg.test("wqqworld ss")) //false
console.log(reg.test("wqq world")) //false
console.log(reg.test("wqq world wqq")) //true
2) Regular expression escape
>>>>>>Regular expressions use \ to escape special characters
Match characters
//Match any character
var reg=/./;
console.log(reg.test("232323")) ; //true
console.log(reg.test("2323.23")) ; //true
//Match characters
var reg=/\./;
console.log(reg.test("232323")) ; //false
console.log(reg.test("2323.23")) ; //true
Match character\
//Match character\
var reg=/\\/;
console.log(reg.test("23232\\3")) ; //true
console.log(reg.test("2323.23")) ; //false
>>>>>>Use RegExp to create regular expressions and escape\
The escaped form of a string is a regular expression.
If the regular expression itself has \, double escape is required in the string\
//Match characters
var reg=new RegExp("\\.")
console.log(reg) // ---->Equivalent to reg = \ \
//Match characters
var reg=new RegExp("\\\\")
console.log(reg) // ---->Equivalent to reg=\\

Create regular expressions using RegExp to match
//Match any character
var reg=new RegExp(".")
console.log(reg.test("232323")) ; //true
console.log(reg.test("2323.23")) ; //true
//Match characters
var reg=new RegExp("\\.")
console.log(reg) // ----> \\.\
console.log(reg.test("232323")) ; //false
console.log(reg.test("2323.23")) ; //true
//Match character\
var reg=new RegExp("\\\\")
console.log(reg) // ----> \\\\
console.log(reg.test("23232\\3")) ; //true
console.log(reg.test("2323.23")) ; //false
4.5 boundary matcher
^ Indicates the beginning $ Indicates the end /^str$/ The representation string must conform exactly to the regular expression
a) Match string starts with a
//Match string starts with a
var reg=/^a/
console.log(reg.test("abcd"));//true
console.log(reg.test("abc")); //true
console.log(reg.test("babdss"));//false
b) The matching string ends with a
//The matching string ends with a
var reg=/a$/
console.log(reg.test("abcd"));//false
console.log(reg.test("abc")); //false
console.log(reg.test("babdssa"));//true
console.log(reg.test("babda ssc"));//false
c) The matching string starts with a or ends with b
//The matching string starts with a or ends with b
var reg=/^a|b$/
console.log(reg.test("abcd"));//true
console.log(reg.test("abc")); //true
console.log(reg.test("babdssa"));//false
console.log(reg.test("babdssb"));//true
d) / ^ str $/, indicating that the string must match exactly
//Full string
var reg=/^ab$/
console.log(reg.test("ab")) ; //true
console.log(reg.test("ab ab")) ; //false
console.log(reg.test("a b")) ; //false
e) / ^ str $/, verify whether the string is a mobile phone number
//Verify whether it is a mobile phone number
//13852133975
// 11 is
// The first is 1
// The second digit is any number from 3 to 9
// The rest are any number from 0 to 9
var phoneReg=/^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$/
console.log(phoneReg.test("13654472825")) ; //true
console.log(phoneReg.test("136544728252323")) ; //false
4.6 regular details
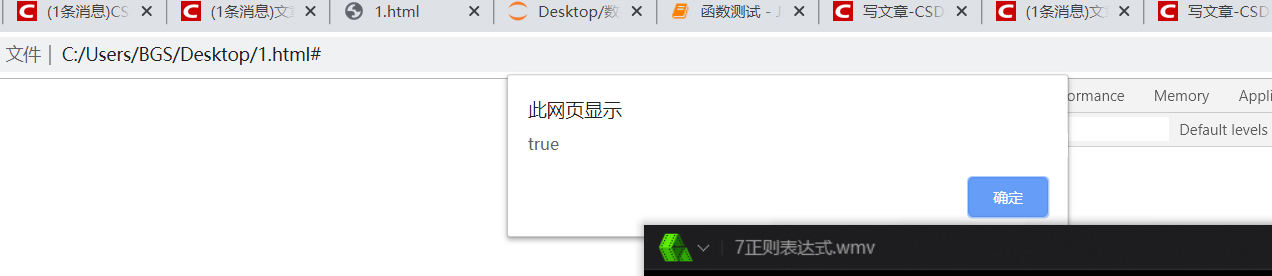
>>>>>>Regular returns true as long as it matches a part of the string, rather than matching the whole string.
var str="121212asd"; var reg=/[0-9]+/; var b=reg.test(str) alert(b)// true
>>>>>>If you want to match the entire string, you need to add a boundary matcher
^ Represents the beginning of a string $ Indicates the end of the string
var str="121212asd"; var reg=/^[0-9]+$/; var b=reg.test(str) alert(b)// false

Common regular
Verify mailbox:
var reg=/^[a-z0-9]\w+@[a-z0-9]+(\.[a-z0-9]+){1,2}$/ig
4, Regular expression application
4.1 removing spaces
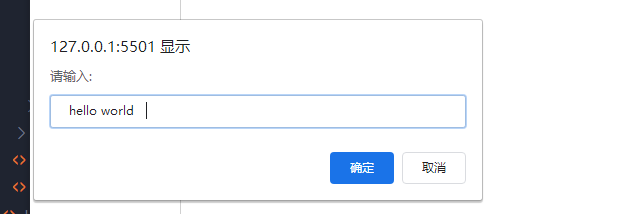
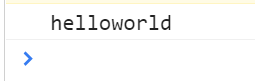
>>>>>>Remove all spaces from the string
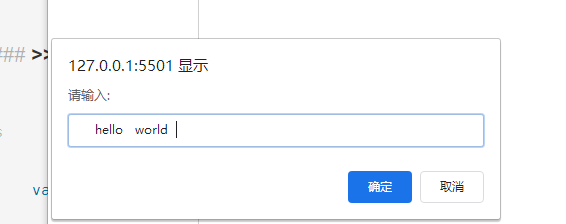
var str=prompt("Please enter:")
//Remove all spaces
var reg=/\s/g
str=str.replace(reg,"");
console.log(str)
>>>>>>Remove spaces at the beginning and end of the string
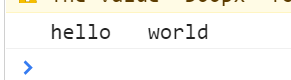
var str=prompt("Please enter:")
//Remove leading and trailing spaces
var reg=/^\s+|\s+$/g
str=str.replace(reg,"");
console.log(str)
4.2 regularity of mail

var reg=/^\w+(\.\w+)*@[0-9a-z]+\.[a-z]{2,5}(\.[a-z]{2,5})*$/
console.log(reg.test("554030346@qq.com"));
console.log(reg.test("554030346@qq.com.cn"));
console.log(reg.test("abc.1234@168.com.cn"));
4.3 application of regular expressions - form validation
>>>>>>Application of onsubmit event of form
Triggered when the form is submitted onsubmit Event, if onsubmit The method of the event returns true,
Then the form is submitted successfully, otherwise it fails.
onsubmit When binding functions, you must return This method
<form action="success.html" method="get" onsubmit="return test()">
The onsubmit bound method returns false. When you click the submit button, the submission fails.
<body>
<form action="success.html" method="get" onsubmit="return test()">
<input type="text" name="k"/>
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
return false;
}
</script>
The obsubmit bound method returns true. When you click the submit button, the submission fails.
<body>
<form action="success.html" method="get" onsubmit="return test()">
<input type="text" name="k"/>
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function test(){
return true;
}
</script>
>>>>>>Form validation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<style type="text/css">
.t{
text-align:center;
width:100px;
}
input{
margin-left:10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table width="500px" height="400px"style="margin:100px auto; table-layout:fixed; word-break:break-all;
" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<form action="success.html" method="get" onsubmit="return checkAll()">
<tr>
<td class="t">user name:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username" onblur="checkName()"/><span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">password:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="pwd" onblur="checkPwd()"/><span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">Confirm password:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="pwd" onblur="checkPwd2()"/><span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">mailbox:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="email" onblur="checkEmail()" /><span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">Gender:</td>
<td> <input type="radio" name="sex" value="man" />male <input type="radio" value="woman" name="sex" />female<span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">hobby:</td>
<td><input type="checkbox" name="like"/>Basketball <input type="checkbox" name="like"/>Football<span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">city:</td>
<td>
<select name="city">
<option value="nj">Nanjing</option>
<option value="bj">Beijing</option>
</select>
<span></span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="t">Self description:</td>
<td><input type="textarea" rows="4" cols="8" name="self"/><span></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" style="padding-left:400px"><input type="submit" /></td>
</tr>
</form>
</table>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
//Verify user name
function checkName(){
var obj=document.getElementsByName("username")[0];
var username=obj.value
var reg=/^[A-Z0-9]{6,9}$/ig
var flag=reg.test(username);
console.log(flag)
var p=obj.parentNode;
var s=p.childNodes[1]
if(flag){s.innerHTML="correct".fontcolor("green") ;return true}
s.innerHTML=" User name error".fontcolor("red")
}
//Verify password
function checkPwd(){
var obj=document.getElementsByName("pwd")[0];
var pwd=obj.value
var reg=/^[A-Z0-9]{6,9}$/ig
var flag=reg.test(pwd);
console.log(flag)
var p=obj.parentNode;
var s=p.childNodes[1]
if(flag){s.innerHTML="correct".fontcolor("green") ;return true}
s.innerHTML=" Password error".fontcolor("red")
}
function checkPwd2(){
var obj=document.getElementsByName("pwd")[0];
var obj1=document.getElementsByName("pwd")[1];
var pwd=obj.value
var pwd1=obj1.value
var p=obj1.parentNode;
var s=p.childNodes[1]
if(pwd==""||pwd!=pwd1){
s.innerHTML=" Inconsistent passwords".fontcolor("red")
}else{
s.innerHTML="correct".fontcolor("green");return true
}
}
//Check mailbox
function checkEmail(){
var obj=document.getElementsByName("email")[0];
var email=obj.value
//5454@qq.com 23323232@123.123.com.cn Regular matching mailbox
var reg=/^[a-z0-9]\w+@[a-z0-9]+(\.[a-z0-9]+){1,2}$/ig
var flag=reg.test(email);
console.log(flag)
var p=obj.parentNode;
var s=p.childNodes[1]
if(flag){s.innerHTML="correct".fontcolor("green") ;return true}
s.innerHTML=" Mailbox format error".fontcolor("red")
}
//When the form is submitted, recheck the form items
function checkAll(){
var f=checkName();
var f1=checkPwd();
var f2=checkPwd2();
var f3=checkEmail();
return f&&f1&&f2&&f3?true:false;
}
</script>
</html>
</script>
</html>
