Scrapy
scrapy framework, asynchronous crawler framework.
Synchronization and Asynchronization
Synchronization: The next method relies on the previous method. If the previous method is not finished, the next method will not be executed.
Asynchronous: The next method does not depend on the previous one. The previous one is not finished, and the next one will still be executed.
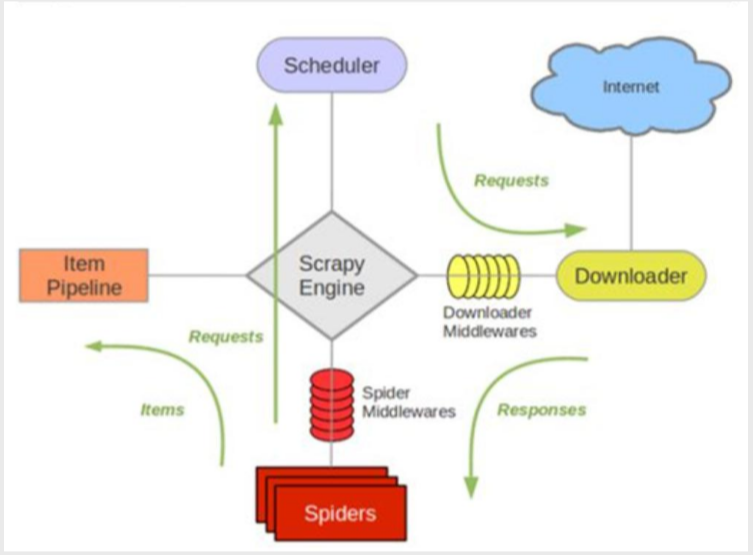
Composition: Pipeline, Scheduler, Downloader, Spiders.And the Scrapy Engine engine (queue)
Middleware: Spider Middlewares, Downloader Middlewares
Pipeline is mainly used to process IO storage and write to locally acquired Sydney
Scheduler Scheduler, sends all URLs to Downloader, and redoes the url to consolidate the queue
Downloader handles request requests and returns responses to Spiders
Spiders are our crawler files
The Scrapy Engine engine controls the entire operation
spider middlewares are generally not used, and crawlers process requests when they are handed over to a dispatcher.
Downloader Middlewares Join Request Header, Join Proxy ip
Use scrapy for the first time
Install scrapy
pip install scrapy
Create Project
#Create Project > scrapy start project project name > CD project name #Create a crawler file > scrapy genspider crawler name "host address" #Run the crawler file > scrapy crawl crawl name
Common Configurations
Settings Common configurations in: USER_AGENT = "" # User-Agent ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True|False # Compliance with Robot Protocol DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {} # Default Headers CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 16 # Maximum number of requests processed by Downloader DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3 # Download Delay SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES # Spider Middleware DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES # Downloader Middleware ITEM_PIPELINES # Pipeline File
create a file
>> scrapy genspider s1 "blog.csdn.net"
Created crawler file
import scrapy class S1Spider(scrapy.Spider): # Reptilian name name = 's1' # If the host of the url address does not belong to allowed_domains, the request is filtered out allowed_domains = ['blog.csdn.net'] # url address accessed at project startup start_urls = ['http://blog.csdn.net/'] # Access start_urls and get the method called after the response def parse(self, response): # reponse is the response object pass
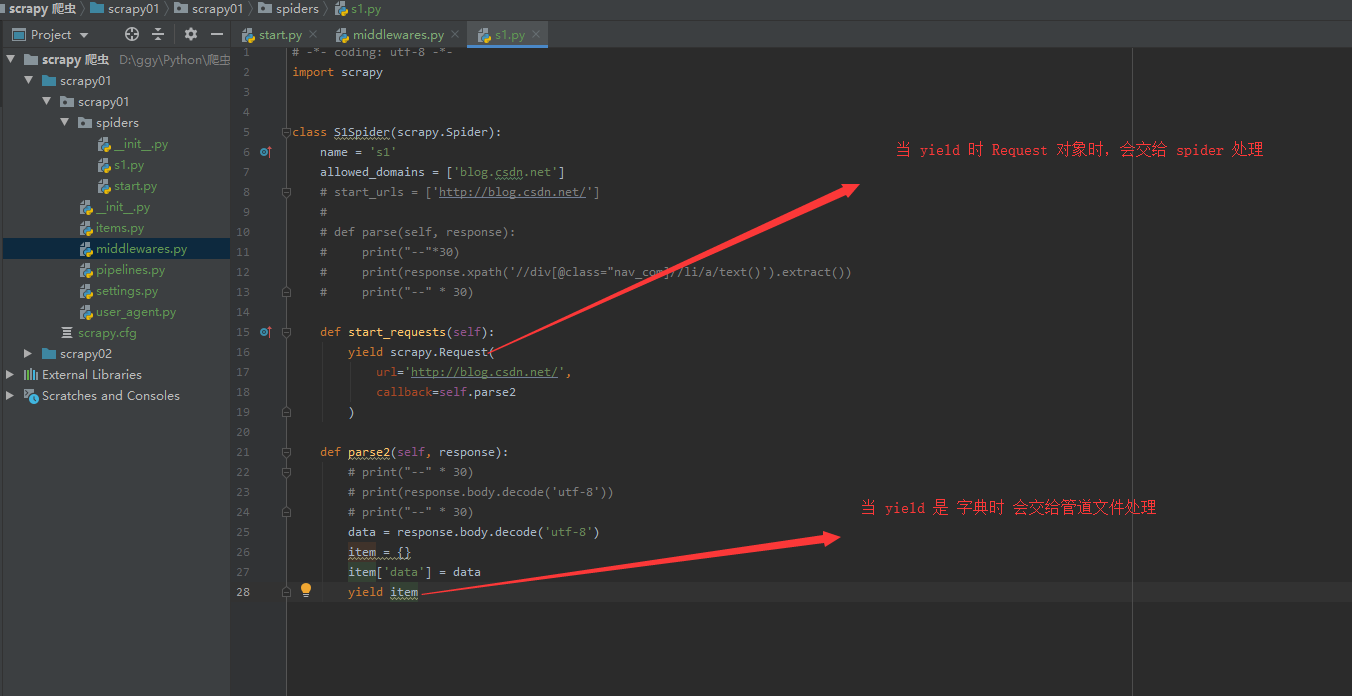
The following method executes equivalent to start_urls, but the qualified request header can be skipped
def start_requests(self): yield scrapy.Request( # Send a Request object to the dispatcher url = 'http://edu.csdn.net', # Request Address, Default GET Method callback = self.parse2 # Functions called when a response is received ) def parse2(self, respones): # Functions called when a response is received print(response.body) # Get data of byte type
When crawling web pages, the default robots are usually set to False
Join Request Header
# Add in this middleware class Scrapy01DownloaderMiddleware(object): # Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined, # scrapy acts as if the downloader middleware does not modify the # passed objects. def process_request(self, request, spider): request.headers = Headers( { 'User-Agent': user_agent.get_user_agent_pc() } ) # Called for each request that goes through the downloader # middleware. # Must either: # - return None: continue processing this request # - or return a Response object # - or return a Request object # - or raise IgnoreRequest: process_exception() methods of # installed downloader middleware will be called return None
Open this middleware
# settings.py uncomment this middleware DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { 'scrapy01.middlewares.Scrapy01DownloaderMiddleware': 543, # Numbers represent priority, the smaller the higher }
Join Agent Ip
def process_request(self, request, spider): request.headers = Headers( { 'User-Agent': user_agent.get_user_agent_pc() } ) request.meta['proxy'] = 'http://IP:PORT' + ur.urlopen("agent ip Interface").read().decode('utf-8').strip()
For our convenience, we can add a start.py
from scrapy import cmdline cmdline.execute('scrapy crawl s1'.split())
Save the file and modify it as follows
def parse2(self, response): # print("--" * 30) # print(response.body.decode('utf-8')) # print("--" * 30) data = response.body.decode('utf-8') item = {} item['data'] = data yield item
In setting s
# Open Pipeline File, in settings.py ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'scrapy01.pipelines.Scrapy01Pipeline': 300, # The smaller the number, the higher the priority, 'scrapy01.pipelines.Scrapy01Pipeline': 300, # If one more is added, the file is handed over to the next pipeline file for processing }
Log log
LOG_FILE = "Log file address" LOG_LEVEL = "log level" # Log level: CRITICAL Serious error (critical) ERROR General error(regular errors) WARNING Warning message(warning messages) INFO general information(informational messages) DEBUG Modal Information (debugging messages)
pymysql
import pymysql mysql_conn = pymysql.Connection( host='localhost', # Host Address port=3306, # Port number user='root', # log on user password="", # Logon Password database='Connection Database Name', charset='utf8', # utf-8 codes ) # Create Cursor Object cs = mysql_conn.cursor() # Define the SQL statement to execute cs.execute('SQL') mysql_conn.commit()
Redis's database structure
16 databases in Redis
Select [index] switch database
| type | Express |
|---|---|
| String (numbers are special strings) | String |
| Hash (Dictionary) | Hash |
| List (ordered, equivalent to list in python) | List |
| unordered set | Set |
| Ordered Set | Zset |
Key operations:
| operation | command |
|---|---|
| lookup | keys [ pattern ] |
| delete | del [ key ] |
| Check for existence | exists [ key ] |
| View Key Type | type [ key ] |
scrapy-redis principle
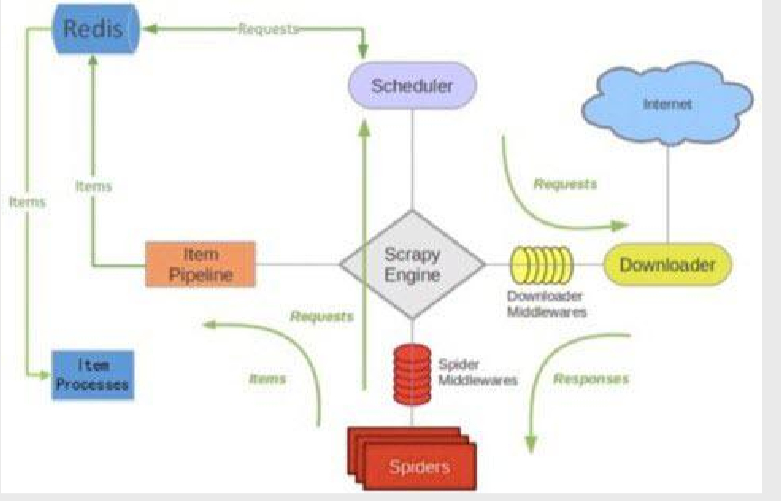
Will Scheduler and
# Start Scrapy-Redis Remove Filter to cancel Scrapy's Remove function DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter" # Enable Scheduler for Scrapy-Redis and Cancel Scheduler for Scrapy SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" # Scrapy-Redis Breakpoint Continuous Crawling SCHEDULER_PERSIST = True # Configure connections to Redis databases REDIS_URL = 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379'