Today, I recommend a small and lightweight crawler Library: mechanical soup
MechanicalSoup is also a reptile artifact! It is developed in pure Python. The bottom layer is based on Beautiful Soup and Requests to realize web page automation and data crawling
Project address:
https://github.com/MechanicalSoup/MechanicalSoup
2. Installation and common usage
Install dependent libraries first
#Install dependent Libraries pip3 install MechanicalSoup
Common operations are as follows:
2-1 # instantiate browser objects
You can instantiate a browser object by using the StatefulBrowser() method built into the mechanicalsoup
import mechanicalsoup #Instantiate browser objects browser = mechanicalsoup.StatefulBrowser(user_agent='MechanicalSoup')
PS: while instantiating, the parameters can execute User Agent and data parser. The default parser is lxml
2-2 # open website and return value
You can open a web page by using the open(url) of the browser instance object, and the return value type is requests models. Response
#Open a web site
result = browser.open("http://httpbin.org/")
print(result)
#Return value type: requests models. Response
print(type(result))
Through the return value, it can be found that opening a website with a browser object is equivalent to making a request for the website with the requests library
2-3 # web page element and current URL
Use the "URL" attribute of the browser object to obtain the URL address of the current page; The "page" attribute of the browser is used to obtain the contents of all web page elements of the page
Since the bottom layer of # mechanicalsup # is based on BS4, the syntax of BS4 # is applicable to # mechanicalsup
#Current web page URL address url = browser.url print(url) #View the contents of the web page page_content = browser.page print(page_content)
2-4 # form operation
Browser object built-in select_ The Form (selector) method is used to get the Form elements of the current page
If the current web page has only one Form, the parameter can be omitted
#Get a form element in the current web page
#Use action to filter
browser.select_form('form[action="/post"]')
#If the web page has only one Form, the parameters can be omitted
browser.select_form()
form.print_summary() is used to print out all the elements in the form
form = browser.select_form() #Print all elements inside the currently selected form form.print_summary()
As for the input general input box, radio box and check box in the form
#1. Common input box
#Set the value directly through the name attribute of input to simulate input
browser["norm_input"] = "Value of normal input box"
#2. Cell frame radio
#Select a value value through the name attribute value
# <input name="size" type="radio" value="small"/>
# <input name="size" type="radio" value="medium"/>
# <input name="size" type="radio" value="large"/>
browser["size"] = "medium"
#3. Check box
#Select some values through the name attribute value
# <input name="topping" type="checkbox" value="bacon"/>
# <input name="topping" type="checkbox" value="cheese"/>
# <input name="topping" type="checkbox" value="onion"/>
# <input name="topping" type="checkbox" value="mushroom"/>
browser["topping"] = ("bacon", "cheese")
Submit of browser object_ The selected (btnname) method is used to submit the form
It should be noted that the return value type after submitting the form is: requests models. Response
#Submit the form (simulate clicking the submit button)
response = browser.submit_selected()
print("The result is:",response.text)
#Result type: requests models. Response
print(type(response))
2-5 # debugging sharp tools
The browser object browser provides a method: launch_browser()
It is used to start a real Web browser and visually display the state of the current Web page. It is very intuitive and useful in the process of automatic operation
PS: instead of actually opening a web page, it creates a temporary page containing the content of the page and points the browser to the file
For more functions, please refer to:
https://mechanicalsoup.readthedocs.io/en/stable/tutorial.html
3. Practice
Let's take "wechat article search, crawling article title and link address" as an example
3-1 # open the target website and specify the random UA
Since many websites have anti crawled the User Agent, a UA is randomly generated and set in
PS: from the mechanical soup source code, you will find that UA is equivalent to setting it into the request header of Requests
import mechanicalsoup from faker import Factory home_url = 'https://weixin.sogou.com/' #Instantiate a browser object # user_agent: specify UA f = Factory.create() ua = f.user_agent() browser = mechanicalsoup.StatefulBrowser(user_agent=ua) #Open target site result = browser.open(home_url)
3-2 # submit the form and search once
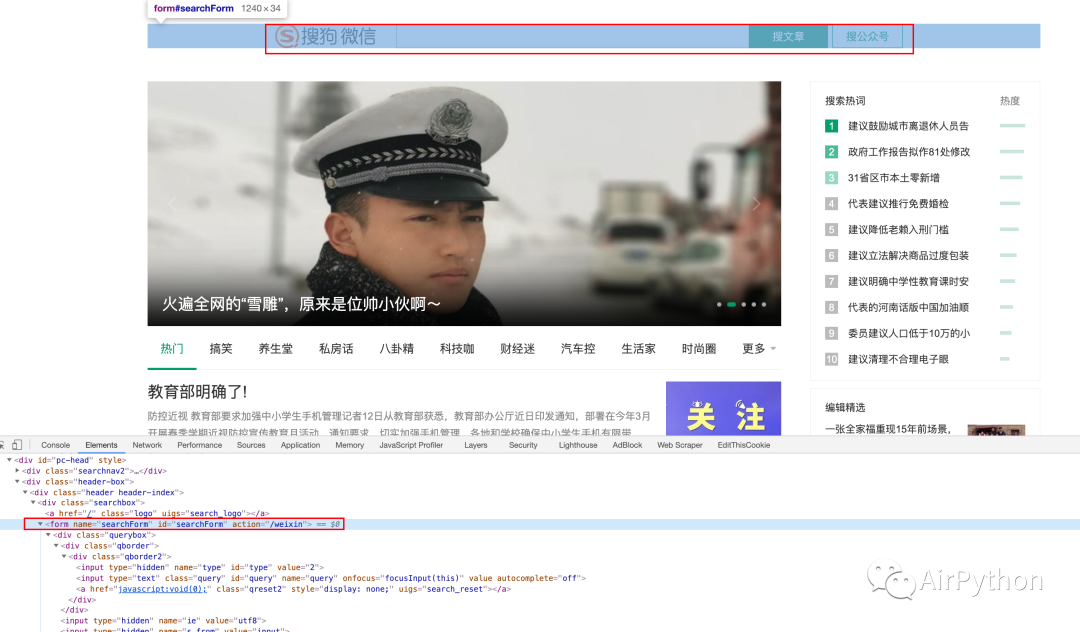
Use the browser object to obtain the form elements in the web page, then set the value to the input # input box in the form, and finally simulate the form submission
#Get form elements browser.select_form() #Print all element information in the form # browser.form.print_summary() #Fill in the content according to the name attribute browser["query"] = "Python" #Submit response = browser.submit_selected()
3-3 # data crawling
The data crawling part is very simple. The syntax is similar to BS4. I won't show it here
search_results = browser.get_current_page().select('.news-list li .txt-box')
print('Search results are:', len(search_results))
#Web data crawling
for result in search_results:
#a label
element_a = result.select('a')[0]
#Get href value
#Note: the address here is the real article address after being transferred
href = "https://mp.weixin.qq.com" + element_a.attrs['href']
text = element_a.text
print("title:", text)
print("address:", href)
#Close browser object
browser.close()
3-4 reverse climbing
MechanicalSoup , in addition to setting the , UA, you can also set the proxy IP through the "session.proxies" of the browser object
#Proxy ip
proxies = {
'https': 'https_ip',
'http': 'http_ip'
}
#Set proxy ip
browser.session.proxies = proxies4. Finally
Combined with the example of wechat article search, this paper completes an automation and crawler operation with "MechanicalSoup"
Compared with Selenium, the biggest difference is that Selenium can interact with JS; And mechanical soup can't
However, for some simple automation scenarios, MechanicalSoup # is a simple and lightweight solution