Activiti Designer process designer
Installation of Activiti Designer
visit https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin Search for the actiBPM plug-in and download it (or search for the plug-in name and installation in the version conforming to the IDEA). The supported IDEA version is 2019.1.4, and the plug-in is not supported in higher versions.
Download address of other IDEA versions: https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/other.html
Use of Activiti Designer
New bpmnfile, command file name loan, and enter the process design page
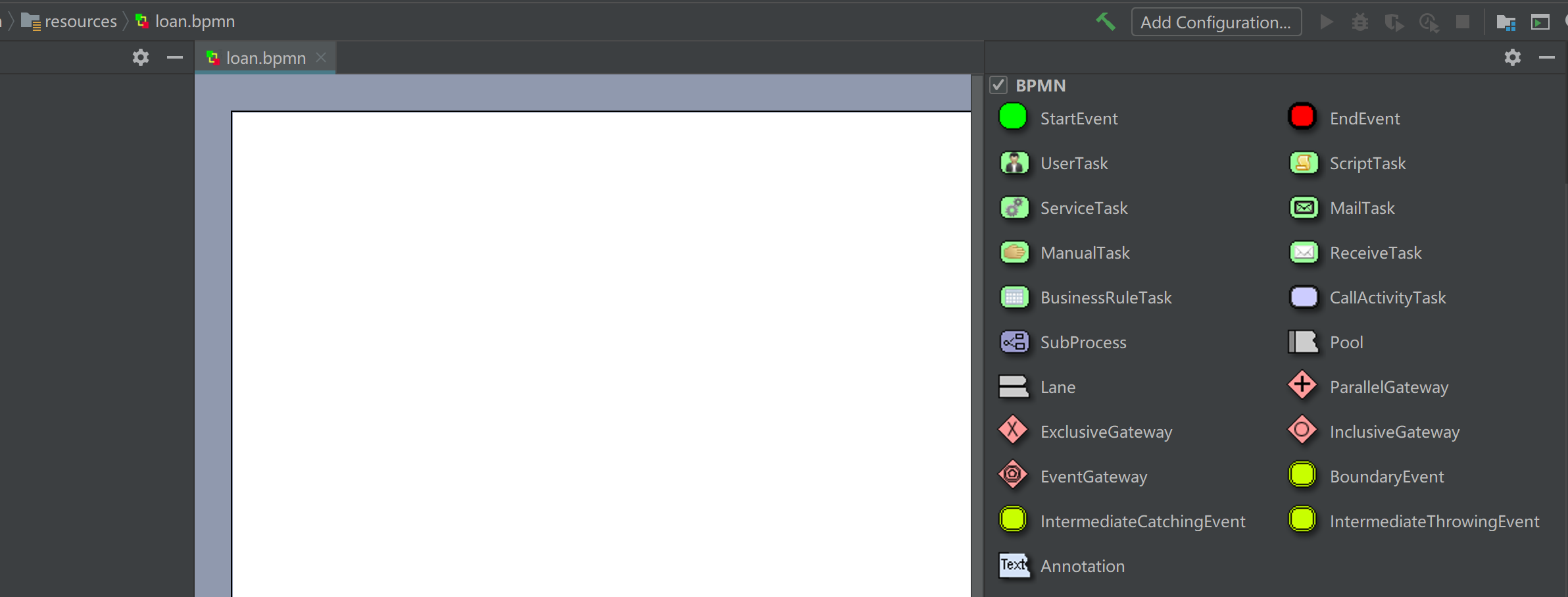
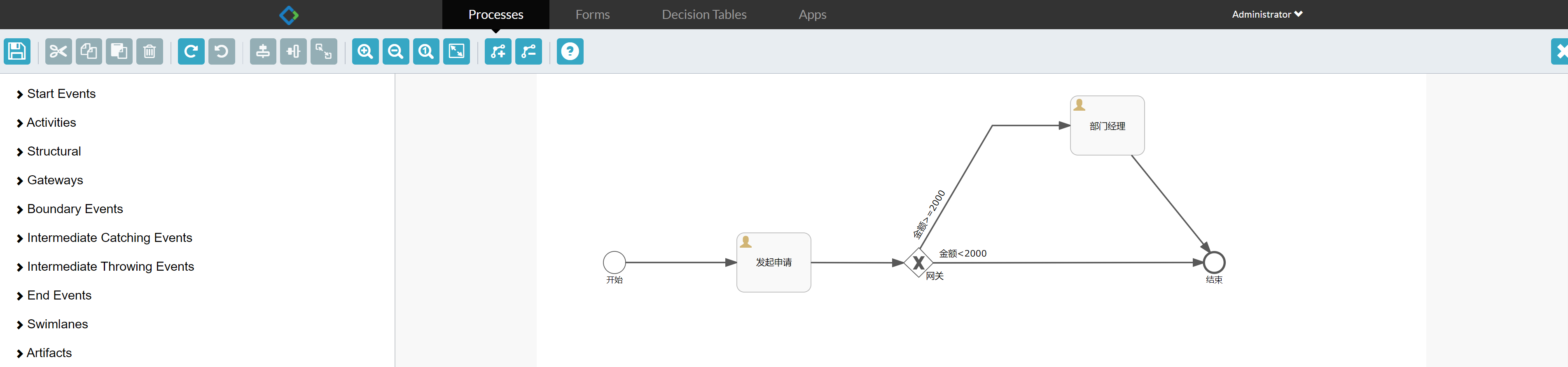
Draw a process, and specify the process definition key (identification of the process definition) and the process name.
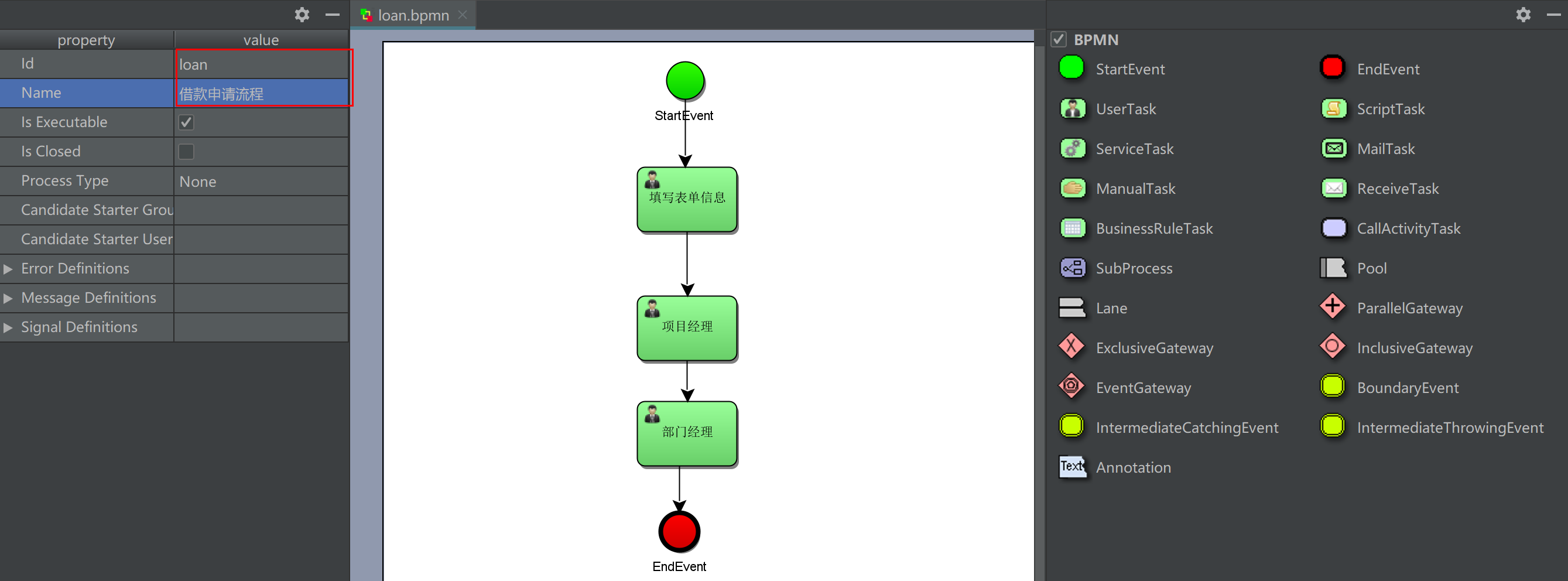
Select a task node and specify the person in charge of each task node in the left view
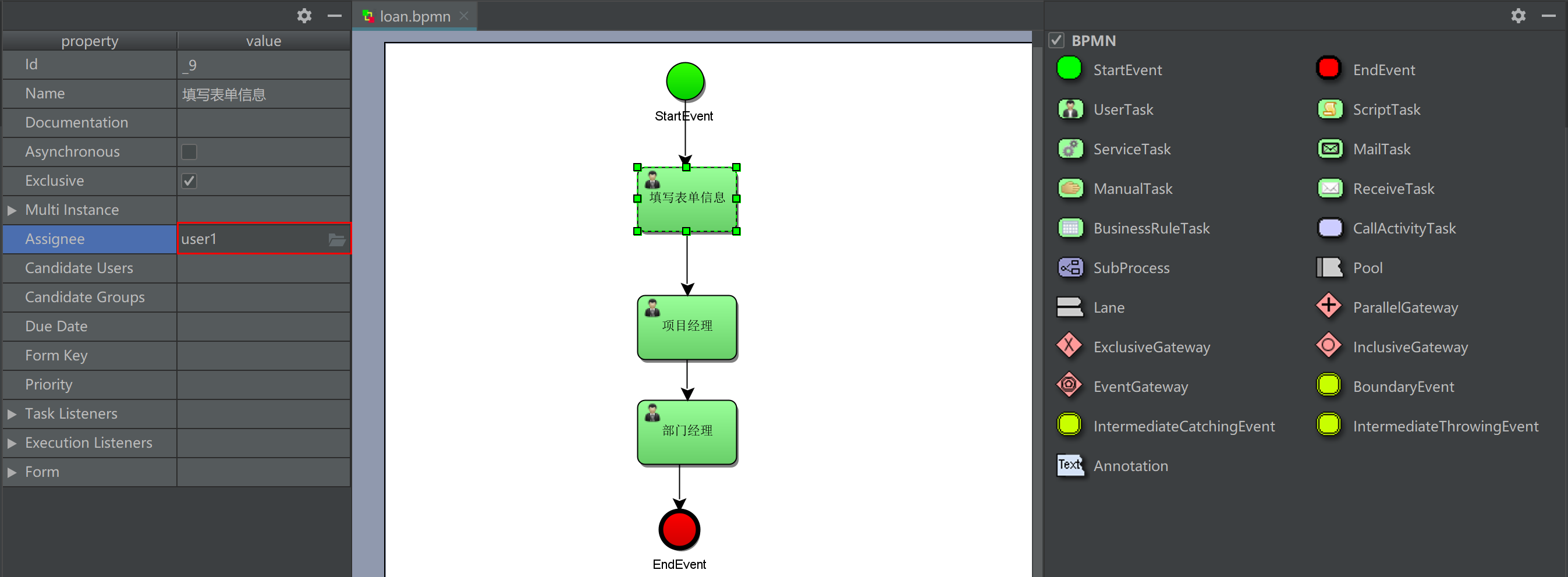
After the graphics are drawn, load Modify the BPM file to loan XML, select loan Right click the XML file diagrams - > show BPMN 2.0 designer to generate a preview and save it.
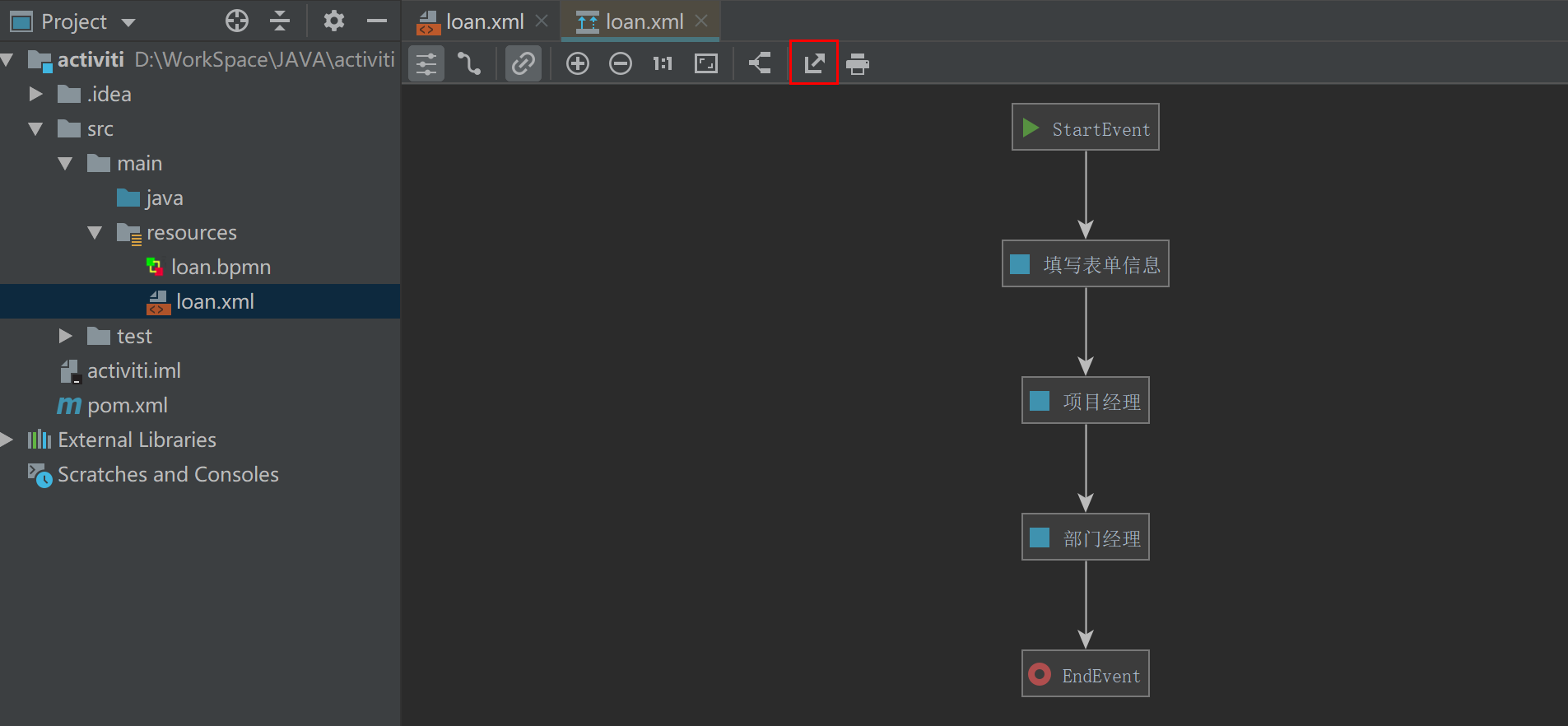
Use of activiti app
Download and deployment
Official website: https://www.activiti.org/get-started
Deployment: activiti app War is placed in webapps of tomcat. Start tomcat to run
visit: http://localhost:8080/activiti-app

Function overview
Enter the default user name / password to log in and create the process: admin/test
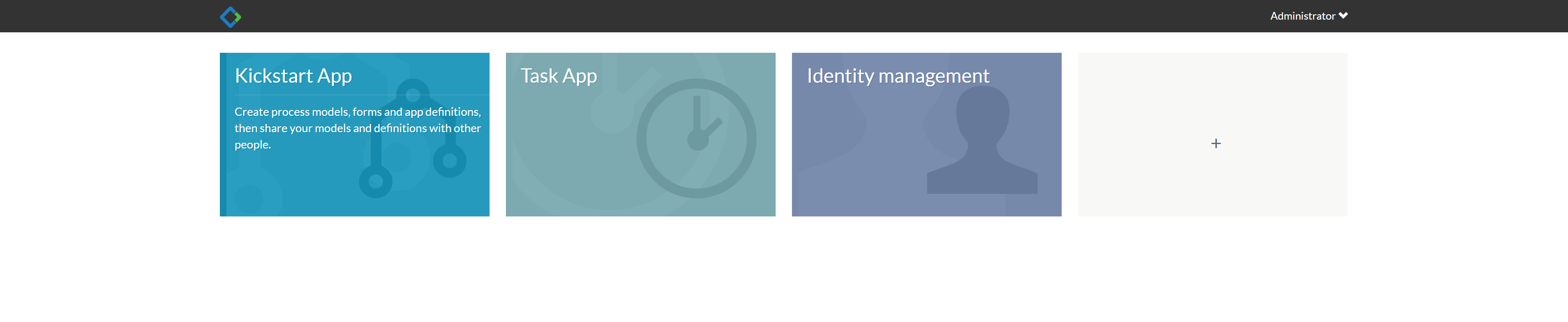
The three menus in the main interface mainly undertake the following functions:
Kickstart App
It is mainly used for process model management, form management and application( App)Management, an application can contain multiple process models, and the application can be published to other users.
Task App
Used to manage the entire activiti-app In this function, you can also start the process.
Idenity management
Identity information management can manage data such as users and user groups.
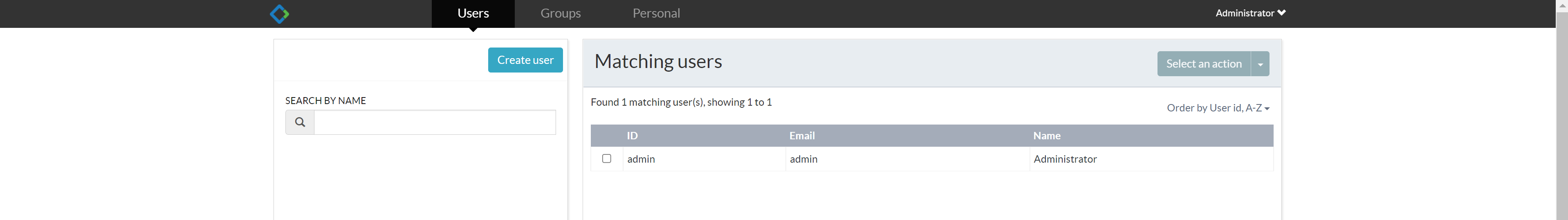
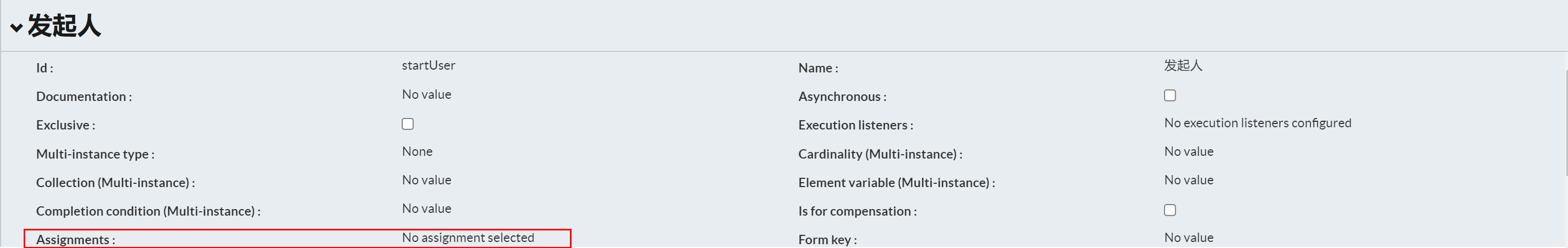
Create user
Click Identity management on the home page, and then select the Users tab to add some user data.
Create process definition
New process model
In the main interface, click Kickstart App to enter the main interface of process model management, and click "Create Process" to open the interface of creating a new process model
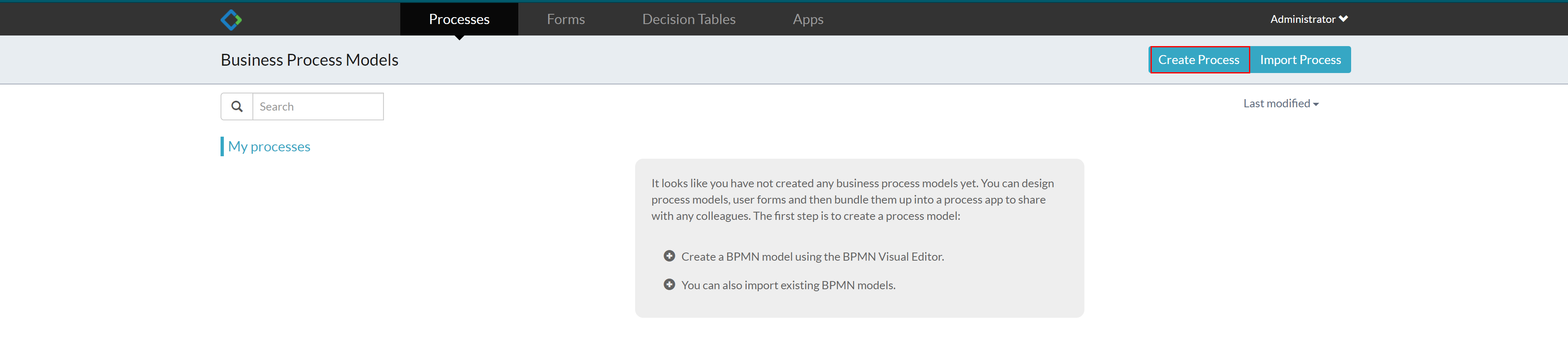
Fill in basic process information
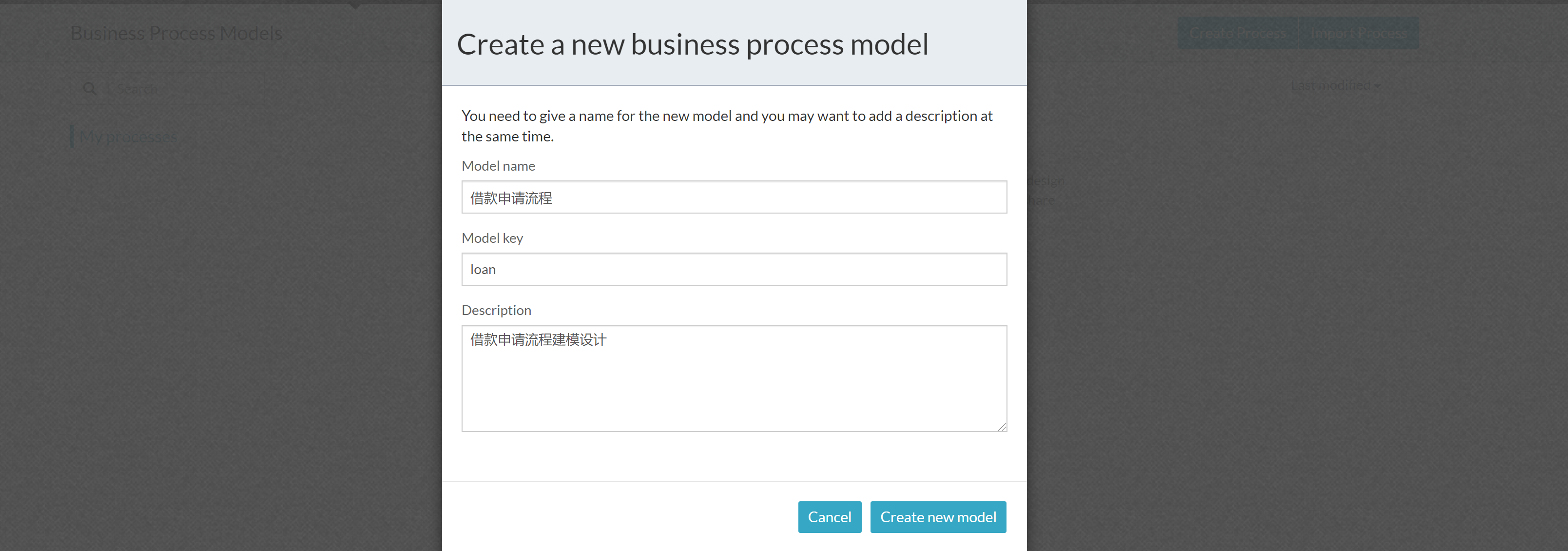
After entering the model information, you will enter the process model design interface
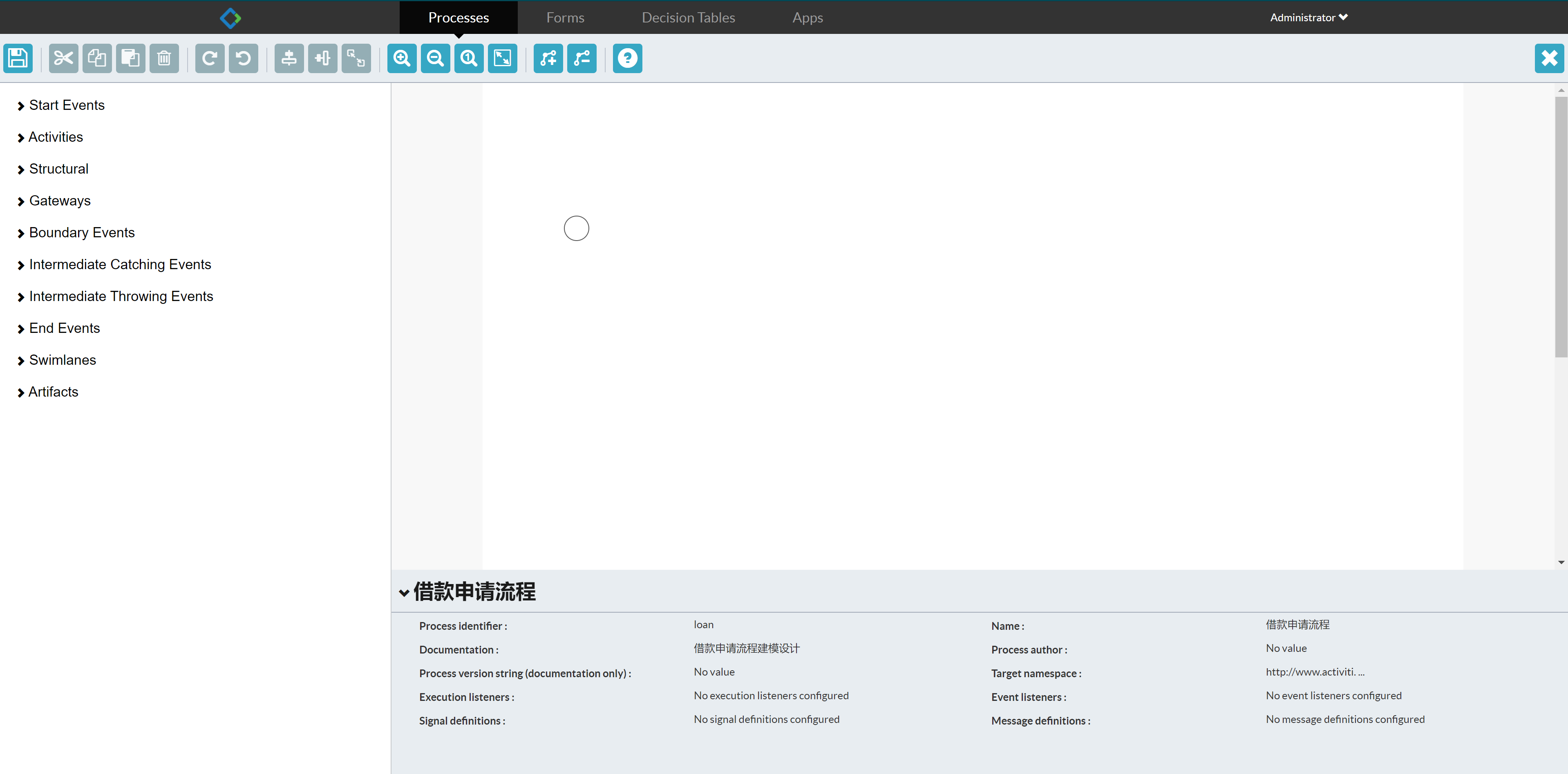
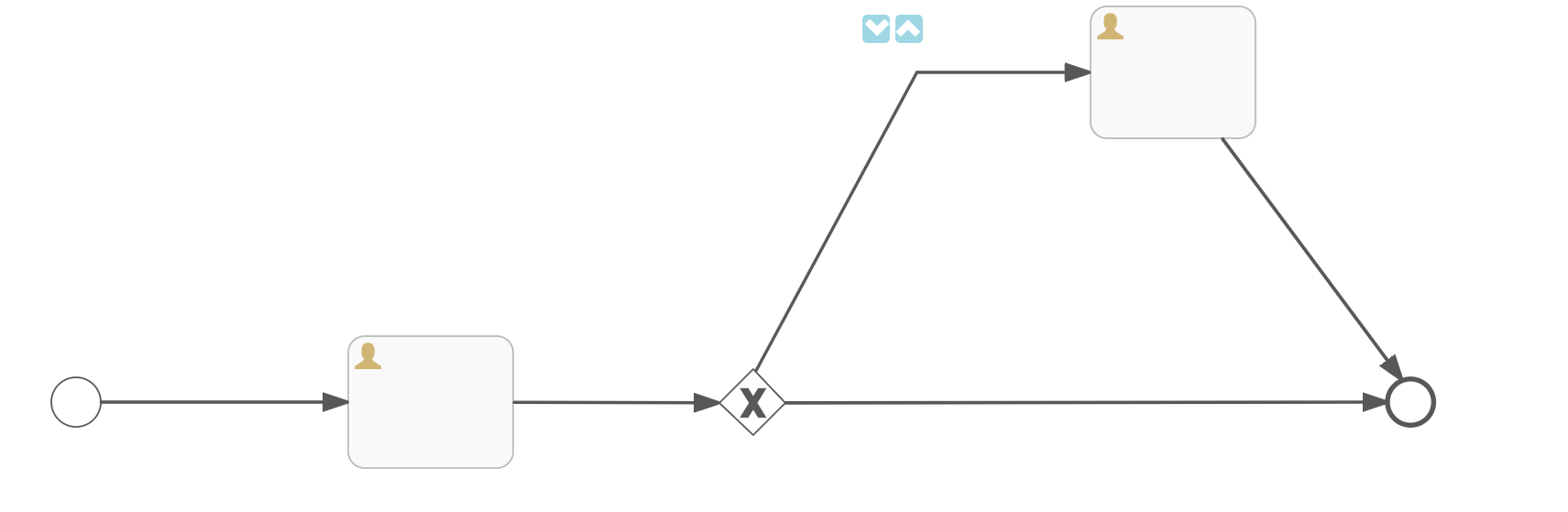
Node setting id and name
Set the id and name for each node

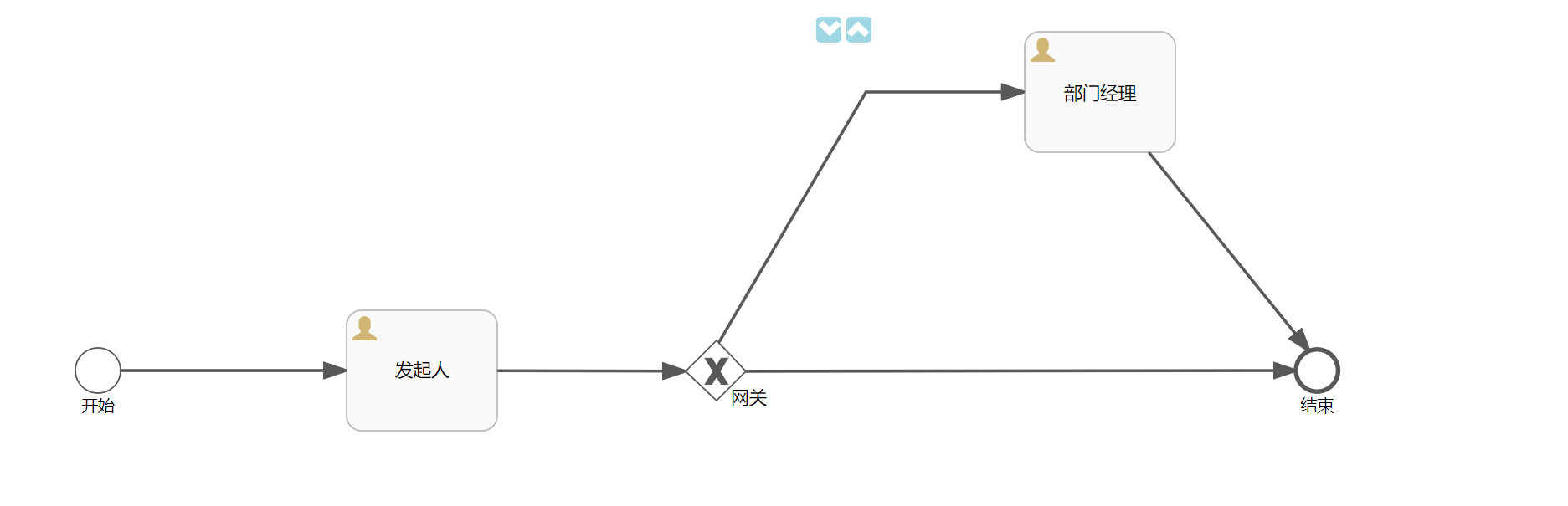
Person in charge of distribution
Set the person in charge for each task node
Select the created user
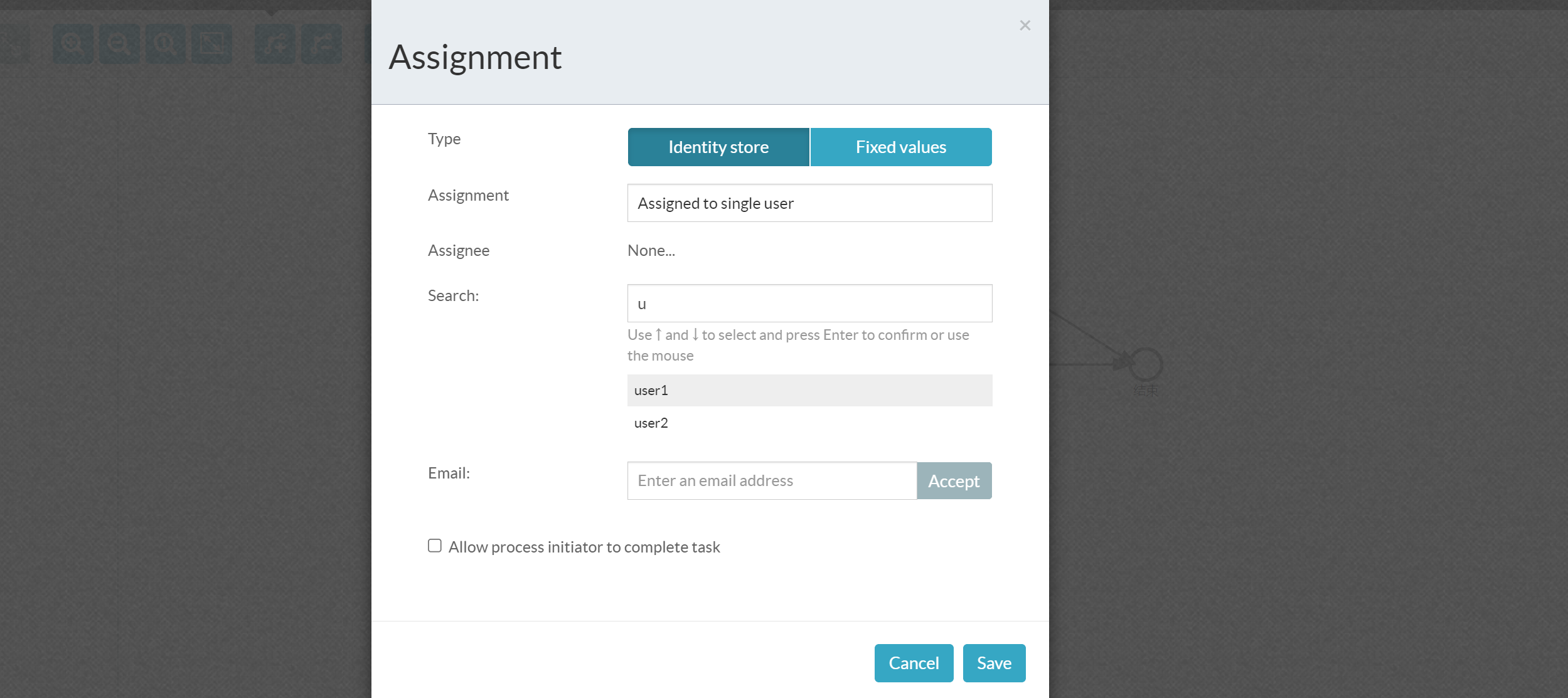
Task performers can be individual users, Candidate Users, and Candidate Groups
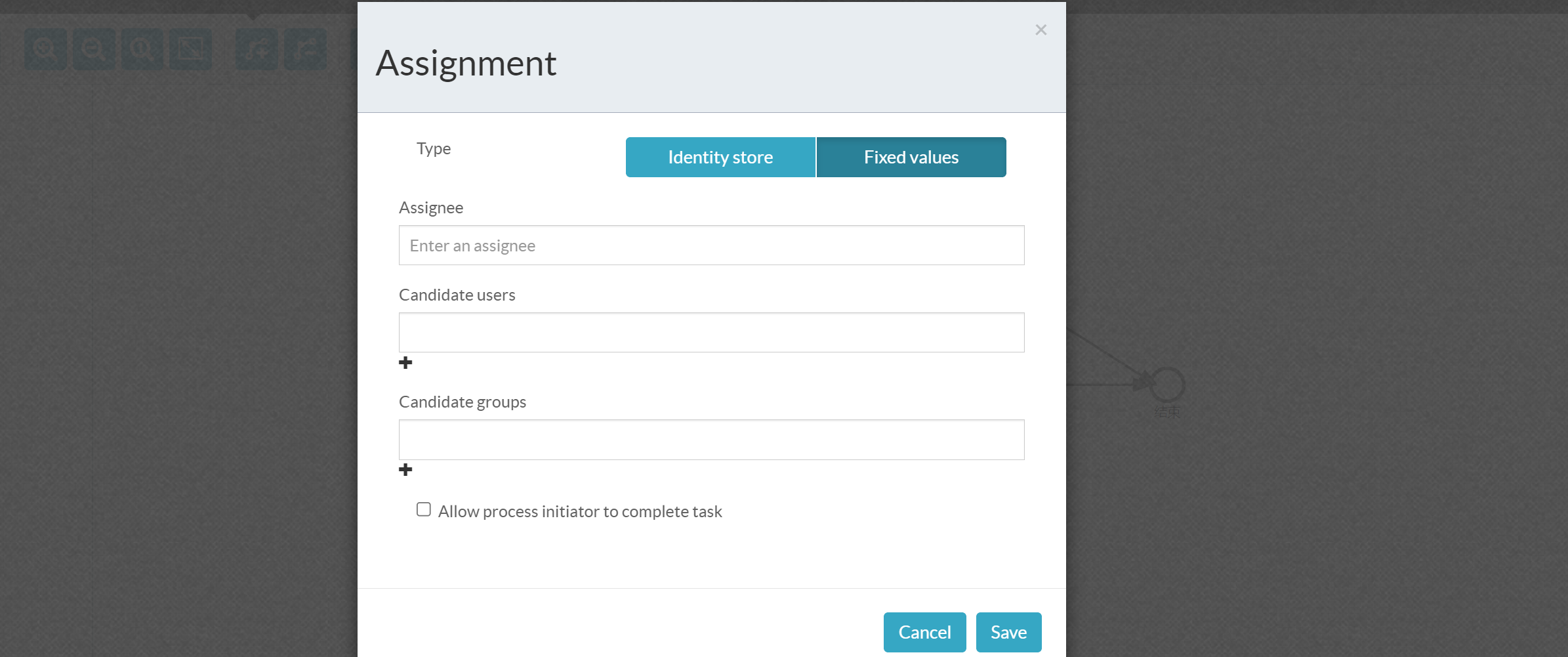
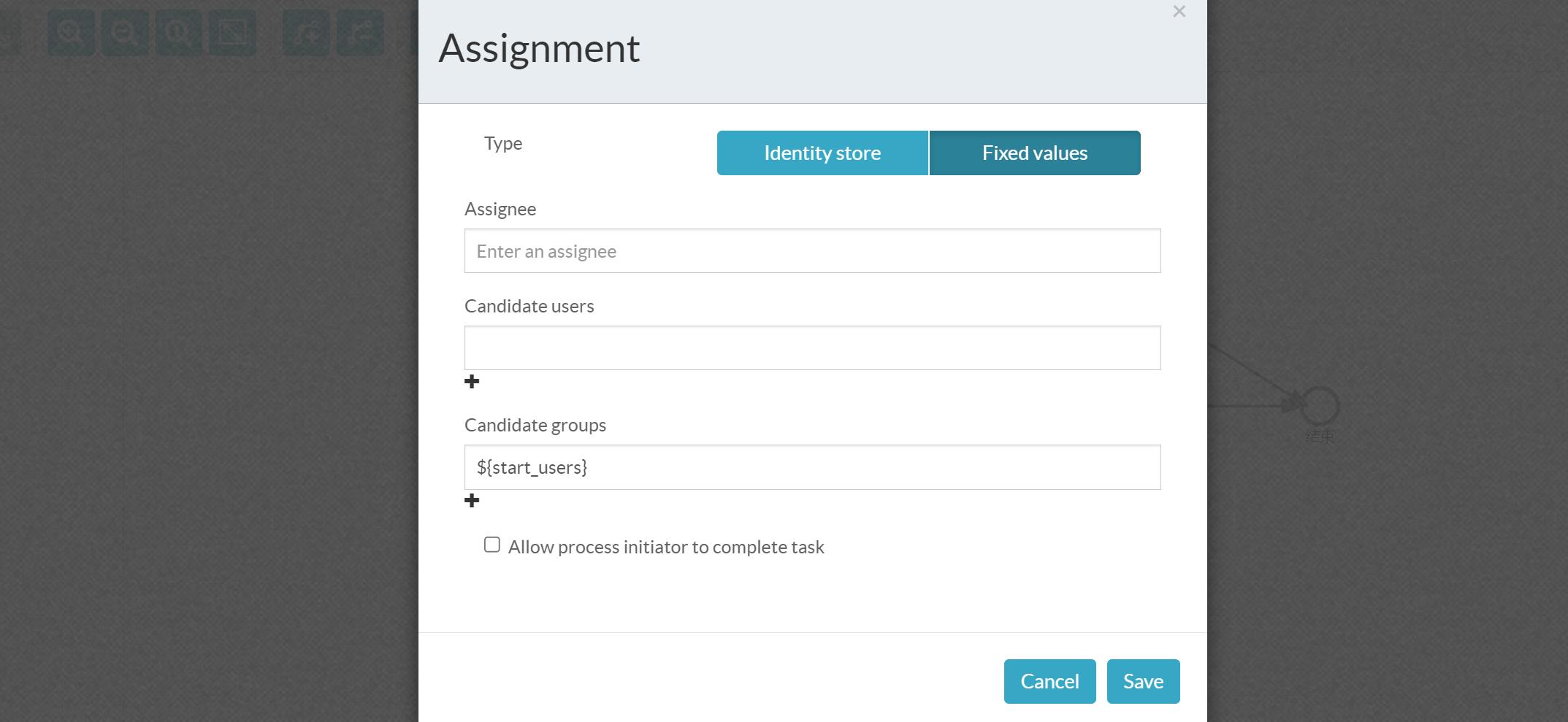
Set routing conditions

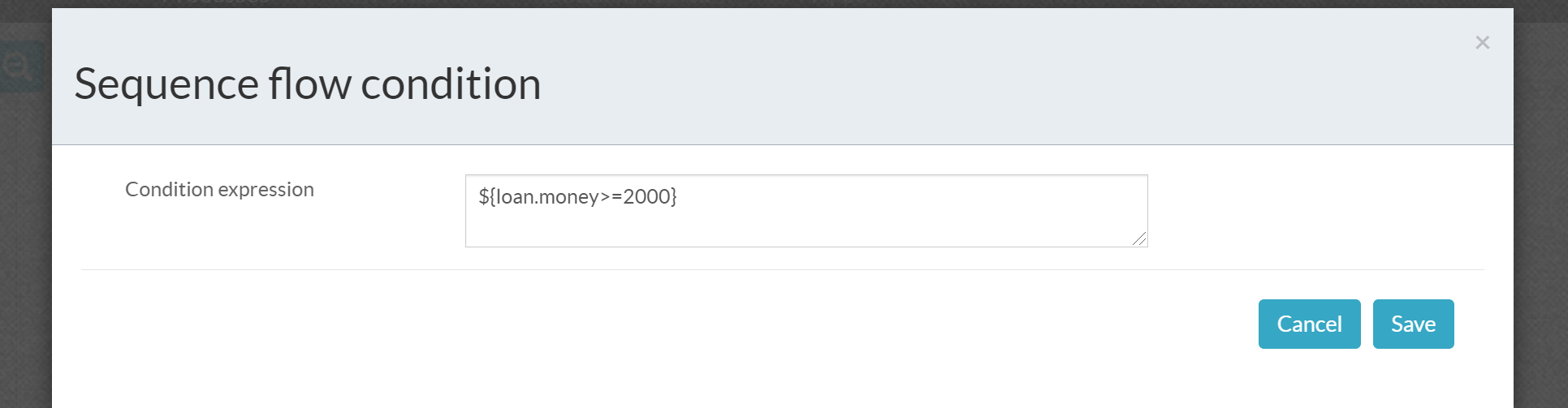
Export process design
Save after process design
Select a design item from the list of design process models
Download after entering
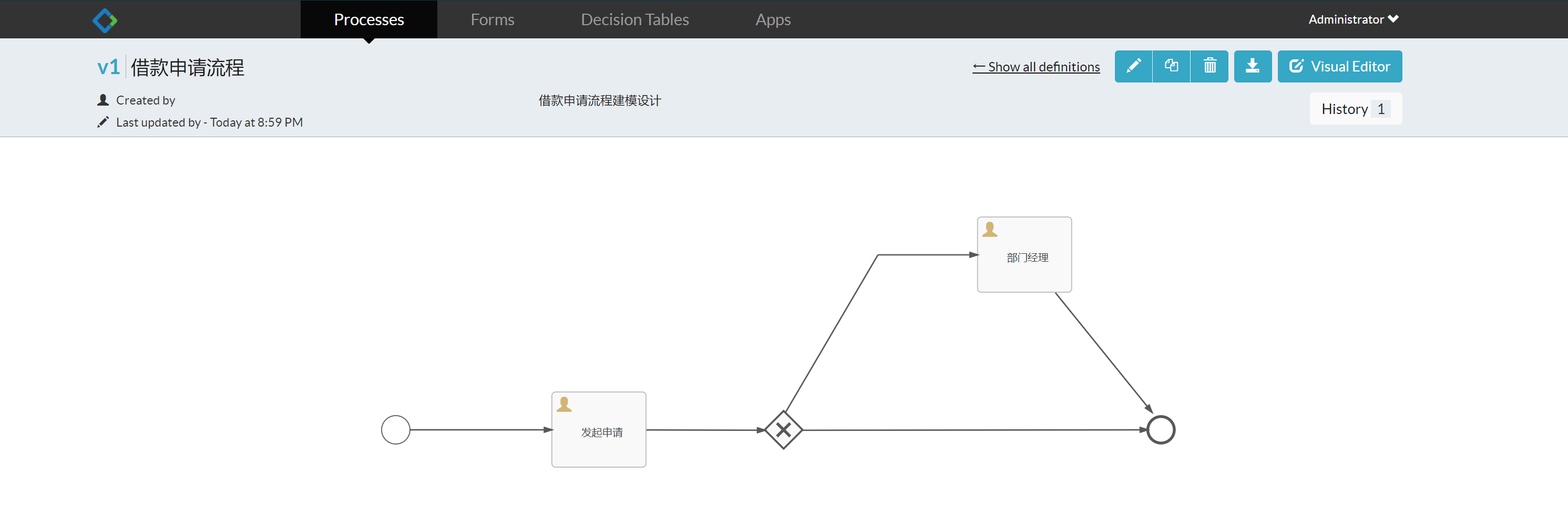
Basic use of process
Correlation dependency
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-engine</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-spring</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-bpmn-model</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-bpmn-converter</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-json-converter</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-bpmn-layout</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.activiti.cloud.rb</groupId>
<artifactId>activiti-cloud-services-api</artifactId>
<version>7.1.0.M6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Engine profile
Create activiti. XML under classpath cgf. XML file, activiti cfg. XML is the engine configuration file of activiti, including the definition of process engine configuration, data source definition, transaction manager, etc
The configuration class of the process engine. The workflow engine procecengine can be created through ProcessEngineConfiguration. There are two common methods
Using the StandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration class
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--Data source configuration dbcp-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activiti"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
<!--Configuration class of process engine, through ProcessEngineConfiguration Create workflow engine ProceccEngine
activiti Run alone ProcessEngine Configuration object,Activiti I'll handle my own affairs
Define a id by processEngineConfiguration of bean,Can use spring Build the engine with dependency injection
-->
<bean id="processEngineConfiguration" class="org.activiti.engine.impl.cfg.StandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration">
<!--data source-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!-- <property name="jdbcDriver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activiti" />
<property name="jdbcUsername" value="root" />
<property name="jdbcPassword" value="123456" />-->
<!--Processing strategy of data table-->
<property name="databaseSchemaUpdate" value="true"/>
</bean>
</beans>
atabaseSchemaUpdate parameter
false(Default): check the version of the database table and the version of the dependent library, and throw an exception if the version does not match true: When building the process engine, check and update if necessary. If the table does not exist, it is created create-drop: Create database tables when building the process engine, and delete these tables when closing the process engine drop-create: Delete the table before creating it create: Database tables are created when the process engine is built. These tables are not deleted when the process engine is closed
Integration with Spring using Spring process engine configuration
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.1.xsd">
<!-- Workflow engine configuration bean -->
<bean id="processEngineConfiguration" class="org.activiti.spring.SpringProcessEngineConfiguration">
<!-- data source -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!-- use spring Transaction manager -->
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
<!-- Database policy -->
<property name="databaseSchemaUpdate" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!-- Process engine -->
<bean id="processEngine" class="org.activiti.spring.ProcessEngineFactoryBean">
<property name="processEngineConfiguration" ref="processEngineConfiguration"/>
</bean>
<!-- Resource services service -->
<bean id="repositoryService" factory-bean="processEngine"
factory-method="getRepositoryService"/>
<!-- Process operation service -->
<bean id="runtimeService" factory-bean="processEngine"
factory-method="getRuntimeService"/>
<!-- task management service -->
<bean id="taskService" factory-bean="processEngine"
factory-method="getTaskService"/>
<!-- Historical management service -->
<bean id="historyService" factory-bean="processEngine"
factory-method="getHistoryService"/>
<!-- Engine management service -->
<bean id="managementService" factory-bean="processEngine"
factory-method="getManagementService"/>
<!-- data source -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activiti"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="3"/>
<property name="maxIdle" value="1"/>
</bean>
<!-- Transaction manager -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- notice -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- Communication behavior -->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- Slice, modify the tangent point configuration according to the specific project -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* cn.ybzy.demo.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
Generate database tables
Create ProcessEngineConfiguration, create ProcessEngine through ProcessEngineConfiguration, and create
Database tables are automatically created when ProcessEngine
General creation method
@Test
public void test() {
/**
* Create ProcessEngineConfiguration object
* First parameter: profile name
* The second parameter: the id of the bean of processEngineConfiguration
*/
ProcessEngineConfiguration configuration = ProcessEngineConfiguration.createProcessEngineConfigurationFromResource("activiti.cfg.xml");
// ProcessEngineConfiguration configuration = ProcessEngineConfiguration.createProcessEngineConfigurationFromResource("activiti.cfg.xml","processEngineConfiguration123");
//Create ProcesEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = configuration.buildProcessEngine();
// Get various services
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
}
Simple creation method
@Test
public void test() {
/**
* Two mandatory requirements shall be met:
* activiti Profile name: activiti cfg. xml
* bean id="processEngineConfiguration" of
*/
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
// Get various services
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
}
Automatically generate 25 tables
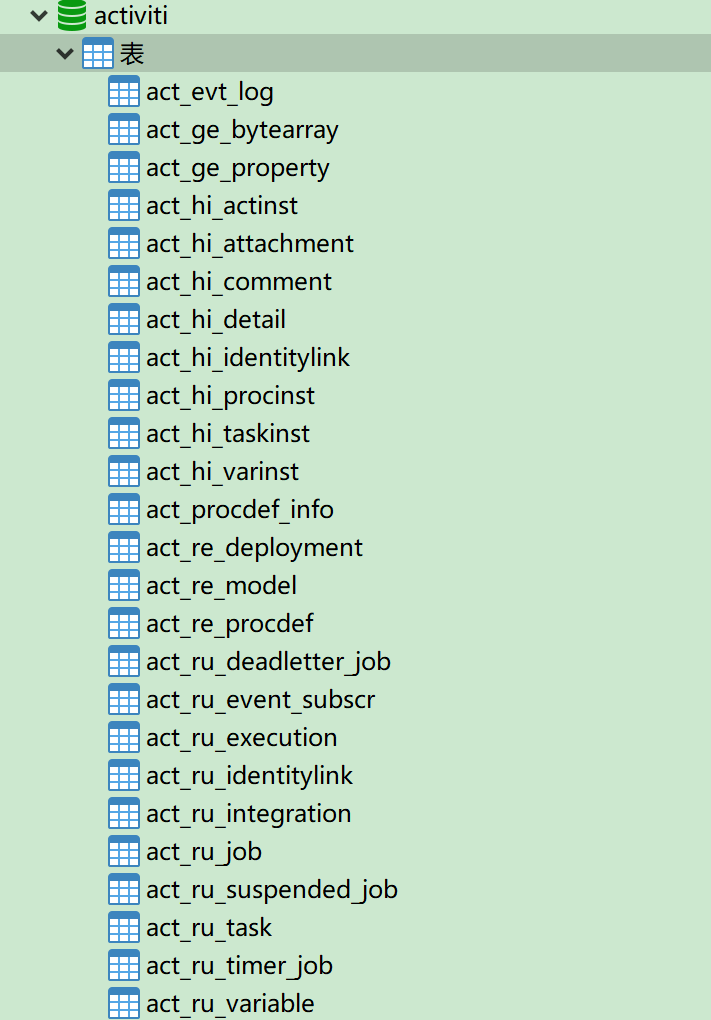
Table naming
All tables are in act_ At the beginning, the two letters in the second part indicate the purpose of the table, which also corresponds to the API of the service.
act_re_*: re express repository. The prefix table contains the process definition and process static resources (images, rules, etc.) act_ru_*: ru express runtime. These runtime tables contain running data such as process instances, tasks, variables, asynchronous tasks, etc. Activiti These data are saved only during the execution of the process instance, and these records will be deleted at the end of the process. In this way, the runtime table can always be small and fast act_hi_*: hi express history. These tables contain historical data, such as historical process instances, variables, tasks, and so on act_ge_*: ge express general. General data for different scenarios
Service
Create a Service through ProcessEngine, which is a Service provided by workflow engine for workflow deployment, execution and management
Service interface.
| service name | service description |
|---|---|
| RepositoryService | activiti's resource management class provides operations for managing and controlling process publishing packages and process definitions. |
| RuntimeService | activiti's process operation management class can get a lot of information about process execution from this service class |
| TaskService | activiti's task management class, from which you can obtain task information. |
| HistoryService | activiti's history management class can query historical information. When executing a process, the engine will save a lot of data. This service mainly obtains these data through the query function. |
| ManagerService | Activiti's engine management class provides the management and maintenance functions of activiti process engine. These functions are not used in workflow driven applications, but mainly used for daily maintenance of activiti system |
Deployment process definition
Add and deploy the bpmn and png files of the process definition to activiti by calling the api of activiti, or zip the two files for deployment.
Single file deployment mode
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create ProcessEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get the RepositoryService instance
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
// Save the specified bpm file and picture file in the activiti database
Deployment deployment = repositoryService.createDeployment()
.addClasspathResource("loan.bpmn")
.addClasspathResource("loan.png")
.name("Loan application process")
.deploy();
//Output deployment information
System.out.println(deployment.getName());
System.out.println(deployment.getId());
}
Compressed package deployment method
Add loan BPMN and loan Png compression is named loanbmn zip
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
//Convert ZipInputStream stream stream object
InputStream is = ActivitiDeployment.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("loanBPMN.zip");
//Convert inputstream stream to ZipInputStream stream stream
ZipInputStream zipInputStream = new ZipInputStream(is);
//deploy
Deployment deployment = repositoryService.createDeployment()
.addZipInputStream(zipInputStream)
.name("Loan application process")
.deploy();
//Output deployment information
System.out.println(deployment.getName()); // Loan application process
System.out.println(deployment.getId()); // 1
}
Tables involved
act_re_deployment The process definition deployment table records the process deployment information act_re_procdef The process definition table records the process definition information act_ge_bytearray Resource table, defined bpmn Documents and png file
act_re_deployment and act_re_procdef has a one to many relationship. One record is generated in the process deployment table at a time, but it is deployed at a time
Multiple process definitions can be deployed, and each process definition generates a record in the process definition table. Each process is defined in act_ge_bytearray will have two resource records, bpmn and png.
Suggestion: deploy one process at a time, so that the deployment table and process definition table have a one-to-one relationship, which is convenient to read process deployment and process definition
Semantic information.
Start process instance
After the process definition is deployed, the business process can be managed through the workflow, that is, the deployed loan application process can be used. Starting a process means initiating a new loan application process, which can be initiated multiple times.
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Get ProcessEngine object
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//Get RunService object
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//Create a process instance and start the process according to the process definition key
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("loan");
//Output information about the instance
System.out.println("Process deployment ID:" + processInstance.getDeploymentId()); // null
System.out.println("Process definition ID:" + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId()); // loan:1:4
System.out.println("Process instance ID:" + processInstance.getId()); // 2501
System.out.println("activity ID:" + processInstance.getActivityId()); // null
}
Reference table:
act_hi_actinst Completed activity information act_hi_identitylink Participant information act_hi_procinst Process instance act_hi_taskinst Task instance act_ru_execution Execution table act_ru_identitylink Participant information act_ru_task task
Task query - person in charge user1
After the process is started, the person in charge of each task can query the tasks they currently need to process, and the queried tasks are the user
To do tasks.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//According to the key defined in the process, the person in charge assigns to query the task list of the current user
List<Task> taskList = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey("loan")
.taskAssignee("user1")
.list();
//.singleResult();
//Display of task list
for (Task task : taskList) {
System.out.println("Process instance ID:" + task.getProcessInstanceId()); // 2501
System.out.println("task ID:" + task.getId()); // 2505
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee()); // user1
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName()); // Fill in form information
}
}
Task processing
The task leader queries the to-do task, selects the task for processing, and completes the task.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//Task id
String taskId = "2505";
//Processing tasks, combined with the query operation of the current user's task list
taskService.complete(taskId);
System.out.println("Complete the task id: " + taskId);
}
Reference table:
act_hi_actinst act_hi_identitylink act_hi_taskinst act_ru_identitylink act_ru_task
Task query - person in charge user2
After the person in charge user1 processes the task, query the task of person in charge user2
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//According to the key defined in the process, the person in charge assigns to query the task list of the current user
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey("loan")
.taskAssignee("user2")
.singleResult();
System.out.println("Process instance ID:" + task.getProcessInstanceId());
System.out.println("task ID:" + task.getId());
System.out.println("Task leader:" + task.getAssignee());
System.out.println("Task name:" + task.getName());
}
Process instance ID:2501 task ID:5002 Task leader:user2 Task name:project manager