1. Cluster environment
The same is to install the Airflow cluster on Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS machine. This time, we will prepare three servers with the same configuration for testing, Previous article 🔗 [1] In, we have installed all components of airflow on Bigdata1 server. For those you haven't seen, you can click the link to see the previous article first. Now you only need to install worker components on the other two nodes.
Bigdata1(A) | Bigdata2(B) | Bigdata3(C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
Webserver | √ | ||
Scheduler | √ | ||
Worker | √ | √ | √ |
In the previous article, docker - compose There is no separation of deployment files and data directories in YML, which is not convenient for later management. Therefore, we can separate the database and data directories from the deployment files after the service is stopped
- Deployment file: docker compose yaml/. Env is stored in / apps/airflow directory
- MySQL and configuration files: put in / data/mysql
- Airflow data directory: placed in / data/airflow
In this way, it will facilitate the unified management in the later stage. 2. Deploy worker service
preparation in advance
mkdir /data/airflow/{dags,plugins} -pv
mkdir -pv /apps/airflow
mkdir -pv /logs/airflow
Deployment file of worker:
---
version: '3'
x-airflow-common:
&airflow-common
# In order to add custom dependencies or upgrade provider packages you can use your extended image.
# Comment the image line, place your Dockerfile in the directory where you placed the docker-compose.yaml
# and uncomment the "build" line below, Then run `docker-compose build` to build the images.
image: ${AIRFLOW_IMAGE_NAME:-apache/airflow:2.2.3}
# build: .
environment:
&airflow-common-env
AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR: CeleryExecutor
AIRFLOW__CORE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN: mysql+mysqldb://airflow:aaaa@$${MYSQL_HOST}:3306/airflow # modify the account and password corresponding to MySQL
AIRFLOW__CELERY__RESULT_BACKEND: db+mysql://airflow:aaaa@$${MYSQL_HOST}:3306/airflow # modify the account and password corresponding to MySQL
AIRFLOW__CELERY__BROKER_URL: redis://: xxxx@$${REDIS_HOST}:7480/0 # modify the password of Redis
AIRFLOW__CORE__FERNET_KEY: ''
AIRFLOW__CORE__DAGS_ARE_PAUSED_AT_CREATION: 'true'
AIRFLOW__CORE__LOAD_EXAMPLES: 'true'
AIRFLOW__API__AUTH_BACKEND: 'airflow.api.auth.backend.basic_auth'
_PIP_ADDITIONAL_REQUIREMENTS: ${_PIP_ADDITIONAL_REQUIREMENTS:-}
volumes:
- /data/airflow/dags:/opt/airflow/dags
- /logs/airflow:/opt/airflow/logs
- /data/airflow/plugins:/opt/airflow/plugins
- /data/airflow/airflow.cfg:/opt/airflow/airflow.cfg
user: "${AIRFLOW_UID:-50000}:0"
services:
airflow-worker:
<<: *airflow-common
command: celery worker
healthcheck:
test:
- "CMD-SHELL"
- 'celery --app airflow.executors.celery_executor.app inspect ping -d "celery@$${HOSTNAME}"'
interval: 10s
timeout: 10s
retries: 5
environment:
<<: *airflow-common-env
# Required to handle warm shutdown of the celery workers properly
# See https://airflow.apache.org/docs/docker-stack/entrypoint.html#signal-propagation
DUMB_INIT_SETSID: "0"
restart: always
hostname: bigdata-20-194 # Set the host name of the container here to check which worker it is in the flower
depends_on:
airflow-init:
condition: service_completed_successfully
airflow-init:
<<: *airflow-common
entrypoint: /bin/bash
# yamllint disable rule:line-length
command:
- -c
- |
function ver() {
printf "%04d%04d%04d%04d" $${1//./ }
}
airflow_version=$$(gosu airflow airflow version)
airflow_version_comparable=$$(ver $${airflow_version})
min_airflow_version=2.2.0
min_airflow_version_comparable=$$(ver $${min_airflow_version})
if (( airflow_version_comparable < min_airflow_version_comparable )); then
echo
echo -e "\033[1;31mERROR!!!: Too old Airflow version $${airflow_version}!\e[0m"
echo "The minimum Airflow version supported: $${min_airflow_version}. Only use this or higher!"
echo
exit 1
fi
if [[ -z "${AIRFLOW_UID}" ]]; then
echo
echo -e "\033[1;33mWARNING!!!: AIRFLOW_UID not set!\e[0m"
echo "If you are on Linux, you SHOULD follow the instructions below to set "
echo "AIRFLOW_UID environment variable, otherwise files will be owned by root."
echo "For other operating systems you can get rid of the warning with manually created .env file:"
echo " See: https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/start/docker.html#setting-the-right-airflow-user"
echo
fi
one_meg=1048576
mem_available=$$(($$(getconf _PHYS_PAGES) * $$(getconf PAGE_SIZE) / one_meg))
cpus_available=$$(grep -cE 'cpu[0-9]+' /proc/stat)
disk_available=$$(df / | tail -1 | awk '{print $$4}')
warning_resources="false"
if (( mem_available < 4000 )) ; then
echo
echo -e "\033[1;33mWARNING!!!: Not enough memory available for Docker.\e[0m"
echo "At least 4GB of memory required. You have $$(numfmt --to iec $$((mem_available * one_meg)))"
echo
warning_resources="true"
fi
if (( cpus_available < 2 )); then
echo
echo -e "\033[1;33mWARNING!!!: Not enough CPUS available for Docker.\e[0m"
echo "At least 2 CPUs recommended. You have $${cpus_available}"
echo
warning_resources="true"
fi
if (( disk_available < one_meg * 10 )); then
echo
echo -e "\033[1;33mWARNING!!!: Not enough Disk space available for Docker.\e[0m"
echo "At least 10 GBs recommended. You have $$(numfmt --to iec $$((disk_available * 1024 )))"
echo
warning_resources="true"
fi
if [[ $${warning_resources} == "true" ]]; then
echo
echo -e "\033[1;33mWARNING!!!: You have not enough resources to run Airflow (see above)!\e[0m"
echo "Please follow the instructions to increase amount of resources available:"
echo " https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/start/docker.html#before-you-begin"
echo
fi
mkdir -p /sources/logs /sources/dags /sources/plugins
chown -R "${AIRFLOW_UID}:0" /sources/{logs,dags,plugins}
exec /entrypoint airflow version
# yamllint enable rule:line-length
environment:
<<: *airflow-common-env
_AIRFLOW_DB_UPGRADE: 'true'
_AIRFLOW_WWW_USER_CREATE: 'true'
_AIRFLOW_WWW_USER_USERNAME: ${_AIRFLOW_WWW_USER_USERNAME:-airflow}
_AIRFLOW_WWW_USER_PASSWORD: ${_AIRFLOW_WWW_USER_PASSWORD:-airflow}
user: "0:0"
volumes:
- .:/sources
airflow-cli:
<<: *airflow-common
profiles:
- debug
environment:
<<: *airflow-common-env
CONNECTION_CHECK_MAX_COUNT: "0"
# Workaround for entrypoint issue. See: https://github.com/apache/airflow/issues/16252
command:
- bash
- -c
- airflow
Initialize detection and check whether the environment meets the following requirements:
cd /apps/ariflow/ echo -e "AIRFLOW_UID=$(id -u)" > .env # Note that airflow must be guaranteed here_ UID is the UID of an ordinary user, and it is guaranteed that this user has the permission to create these persistent directories docker-compose up airflow-init
If the database already exists, the initialization detection will not affect the existing database. Next, run the airflow worker service
docker-compose up -d

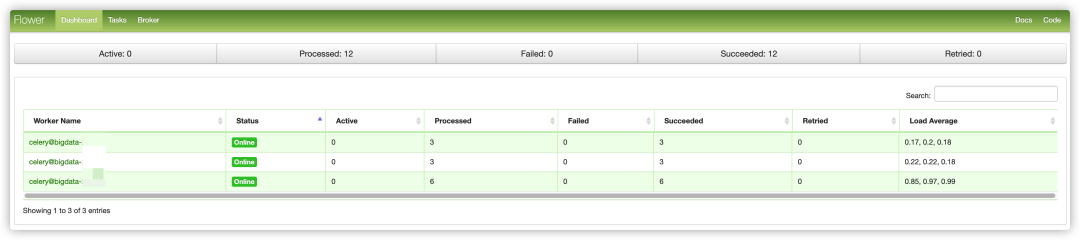
Next, install the airflow worker service on the bigdata3 node in the same way. After deployment, you can view the status of the broker through the flower:
3 persistent configuration file
In most cases, when using a cluster with multiple worker nodes, we need to persist the configuration file of airflow and synchronize airflow to all nodes. Therefore, we need to modify docker compose volumes of x-airflow-common in yaml CFG is attached to the container in the form of attachment volume. The configuration file can be copied in the container and then modified;
For early use, we need to write the values of some environment variables in the docker compose file to airflow Cfg file, such as the following information:
[core]
dags_folder = /opt/airflow/dags
hostname_callable = socket.getfqdn
default_timezone = Asia/Shanghai # Modify time zone
executor = CeleryExecutor
sql_alchemy_conn = mysql+mysqldb://airflow:aaaa@$${MYSQL_HOST}:3306/airflow
sql_engine_encoding = utf-8
sql_alchemy_pool_enabled = True
sql_alchemy_pool_size = 5
sql_alchemy_max_overflow = 10
sql_alchemy_pool_recycle = 1800
sql_alchemy_pool_pre_ping = True
sql_alchemy_schema =
parallelism = 32
max_active_tasks_per_dag = 16
dags_are_paused_at_creation = True
max_active_runs_per_dag = 16
load_examples = True
load_default_connections = True
plugins_folder = /opt/airflow/plugins
execute_tasks_new_python_interpreter = False
fernet_key =
donot_pickle = True
dagbag_import_timeout = 30.0
dagbag_import_error_tracebacks = True
dagbag_import_error_traceback_depth = 2
dag_file_processor_timeout = 50
task_runner = StandardTaskRunner
default_impersonation =
security =
unit_test_mode = False
enable_xcom_pickling = False
killed_task_cleanup_time = 60
dag_run_conf_overrides_params = True
dag_discovery_safe_mode = True
default_task_retries = 0
default_task_weight_rule = downstream
min_serialized_dag_update_interval = 30
min_serialized_dag_fetch_interval = 10
max_num_rendered_ti_fields_per_task = 30
check_slas = True
xcom_backend = airflow.models.xcom.BaseXCom
lazy_load_plugins = True
lazy_discover_providers = True
max_db_retries = 3
hide_sensitive_var_conn_fields = True
sensitive_var_conn_names =
default_pool_task_slot_count = 128
[logging]
base_log_folder = /opt/airflow/logs
remote_logging = False
remote_log_conn_id =
google_key_path =
remote_base_log_folder =
encrypt_s3_logs = False
logging_level = INFO
fab_logging_level = WARNING
logging_config_class =
colored_console_log = True
colored_log_format = [%%(blue)s%%(asctime)s%%(reset)s] {%%(blue)s%%(filename)s:%%(reset)s%%(lineno)d} %%(log_color)s%%(levelname)s%%(reset)s - %%(log_color)s%%(message)s%%(reset)s
colored_formatter_class = airflow.utils.log.colored_log.CustomTTYColoredFormatter
log_format = [%%(asctime)s] {%%(filename)s:%%(lineno)d} %%(levelname)s - %%(message)s
simple_log_format = %%(asctime)s %%(levelname)s - %%(message)s
task_log_prefix_template =
log_filename_template = {{ ti.dag_id }}/{{ ti.task_id }}/{{ ts }}/{{ try_number }}.log
log_processor_filename_template = {{ filename }}.log
dag_processor_manager_log_location = /opt/airflow/logs/dag_processor_manager/dag_processor_manager.log
task_log_reader = task
extra_logger_names =
worker_log_server_port = 8793
[metrics]
statsd_on = False
statsd_host = localhost
statsd_port = 8125
statsd_prefix = airflow
statsd_allow_list =
stat_name_handler =
statsd_datadog_enabled = False
statsd_datadog_tags =
[secrets]
backend =
backend_kwargs =
[cli]
api_client = airflow.api.client.local_client
endpoint_url = http://localhost:8080
[debug]
fail_fast = False
[api]
enable_experimental_api = False
auth_backend = airflow.api.auth.backend.deny_all
maximum_page_limit = 100
fallback_page_limit = 100
google_oauth2_audience =
google_key_path =
access_control_allow_headers =
access_control_allow_methods =
access_control_allow_origins =
[lineage]
backend =
[atlas]
sasl_enabled = False
host =
port = 21000
username =
password =
[operators]
default_owner = airflow
default_cpus = 1
default_ram = 512
default_disk = 512
default_gpus = 0
default_queue = default
allow_illegal_arguments = False
[hive]
default_hive_mapred_queue =
[webserver]
base_url = https://devopsman.cn/airflow # custom airflow domain name
default_ui_timezone = Asia/Shanghai # Set default time zone
web_server_host = 0.0.0.0
web_server_port = 8080
web_server_ssl_cert =
web_server_ssl_key =
web_server_master_timeout = 120
web_server_worker_timeout = 120
worker_refresh_batch_size = 1
worker_refresh_interval = 6000
reload_on_plugin_change = False
secret_key = emEfndkf3QWZ5zVLE1kVMg==
workers = 4
worker_class = sync
access_logfile = -
error_logfile = -
access_logformat =
expose_config = False
expose_hostname = True
expose_stacktrace = True
dag_default_view = tree
dag_orientation = LR
log_fetch_timeout_sec = 5
log_fetch_delay_sec = 2
log_auto_tailing_offset = 30
log_animation_speed = 1000
hide_paused_dags_by_default = False
page_size = 100
navbar_color = #fff
default_dag_run_display_number = 25
enable_proxy_fix = False
proxy_fix_x_for = 1
proxy_fix_x_proto = 1
proxy_fix_x_host = 1
proxy_fix_x_port = 1
proxy_fix_x_prefix = 1
cookie_secure = False
cookie_samesite = Lax
default_wrap = False
x_frame_enabled = True
show_recent_stats_for_completed_runs = True
update_fab_perms = True
session_lifetime_minutes = 43200
auto_refresh_interval = 3
[email]
email_backend = airflow.utils.email.send_email_smtp
email_conn_id = smtp_default
default_email_on_retry = True
default_email_on_failure = True
[smtp] # Mailbox configuration
smtp_host = localhost
smtp_starttls = True
smtp_ssl = False
smtp_port = 25
smtp_mail_from = airflow@example.com
smtp_timeout = 30
smtp_retry_limit = 5
[sentry]
sentry_on = false
sentry_dsn =
[celery_kubernetes_executor]
kubernetes_queue = kubernetes
[celery]
celery_app_name = airflow.executors.celery_executor
worker_concurrency = 16
worker_umask = 0o077
broker_url = redis://:xxxx@$${REDIS_HOST}:7480/0
result_backend = db+mysql://airflow:aaaa@$${MYSQL_HOST}:3306/airflow
flower_host = 0.0.0.0
flower_url_prefix =
flower_port = 5555
flower_basic_auth =
sync_parallelism = 0
celery_config_options = airflow.config_templates.default_celery.DEFAULT_CELERY_CONFIG
ssl_active = False
ssl_key =
ssl_cert =
ssl_cacert =
pool = prefork
operation_timeout = 1.0
task_track_started = True
task_adoption_timeout = 600
task_publish_max_retries = 3
worker_precheck = False
[celery_broker_transport_options]
[dask]
cluster_address = 127.0.0.1:8786
tls_ca =
tls_cert =
tls_key =
[scheduler]
job_heartbeat_sec = 5
scheduler_heartbeat_sec = 5
num_runs = -1
scheduler_idle_sleep_time = 1
min_file_process_interval = 30
dag_dir_list_interval = 300
print_stats_interval = 30
pool_metrics_interval = 5.0
scheduler_health_check_threshold = 30
orphaned_tasks_check_interval = 300.0
child_process_log_directory = /opt/airflow/logs/scheduler
scheduler_zombie_task_threshold = 300
catchup_by_default = True
max_tis_per_query = 512
use_row_level_locking = True
max_dagruns_to_create_per_loop = 10
max_dagruns_per_loop_to_schedule = 20
schedule_after_task_execution = True
parsing_processes = 2
file_parsing_sort_mode = modified_time
use_job_schedule = True
allow_trigger_in_future = False
dependency_detector = airflow.serialization.serialized_objects.DependencyDetector
trigger_timeout_check_interval = 15
[triggerer]
default_capacity = 1000
[kerberos]
ccache = /tmp/airflow_krb5_ccache
principal = airflow
reinit_frequency = 3600
kinit_path = kinit
keytab = airflow.keytab
forwardable = True
include_ip = True
[github_enterprise]
api_rev = v3
[elasticsearch]
host =
log_id_template = {dag_id}-{task_id}-{execution_date}-{try_number}
end_of_log_mark = end_of_log
frontend =
write_stdout = False
json_format = False
json_fields = asctime, filename, lineno, levelname, message
host_field = host
offset_field = offset
[elasticsearch_configs]
use_ssl = False
verify_certs = True
[kubernetes]
pod_template_file =
worker_container_repository =
worker_container_tag =
namespace = default
delete_worker_pods = True
delete_worker_pods_on_failure = False
worker_pods_creation_batch_size = 1
multi_namespace_mode = False
in_cluster = True
kube_client_request_args =
delete_option_kwargs =
enable_tcp_keepalive = True
tcp_keep_idle = 120
tcp_keep_intvl = 30
tcp_keep_cnt = 6
verify_ssl = True
worker_pods_pending_timeout = 300
worker_pods_pending_timeout_check_interval = 120
worker_pods_queued_check_interval = 60
worker_pods_pending_timeout_batch_size = 100
[smart_sensor]
use_smart_sensor = False
shard_code_upper_limit = 10000
shards = 5
sensors_enabled = NamedHivePartitionSensor
After the modification, restart the service.
docker-compose restart
4 data synchronization
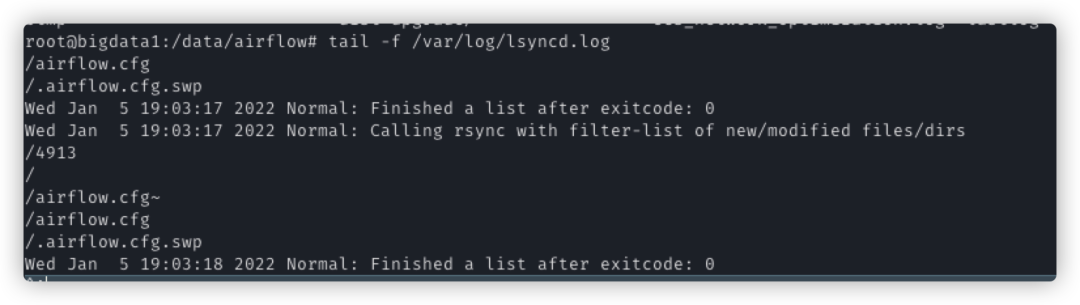
Because airflow uses three worker nodes, each node modifies the configuration, and other nodes need to be synchronized. At the same time, DAGS directory and plugins directory also need to be synchronized in real time. After the scheduler schedules the information to a node, if the corresponding DAGS file cannot be found, an error will be reported. Therefore, we use lsyncd for real-time data synchronization:
apt-get install lsyncd -y
Configure public key connection between nodes
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "airflow-sync" -b 4096 #Generate a pair of keys named airflow sync
for ip in 100 200;do ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/airflow-sync.pub ${USERNAME}@192.168.0.$ip -P12022;done
Then we can access other nodes through the private key.
Edit the synchronized configuration file and learn more parameters of lsyncd configuration. You can go directly to the official document [2]
settings {
logfile = "/var/log/lsyncd.log", # log file
statusFile = "/var/log/lsyncd.status", # Synchronization status information
pidfile = "/var/run/lsyncd.pid",
statusInterval = 1,
nodaemon = false, # Daemon
inotifyMode = "CloseWrite",
maxProcesses = 1,
maxDelays = 1,
}
sync {
default.rsync,
source = "/data/airflow",
target = "192.168.0.100:/data/airflow",
rsync = {
binary = "/usr/bin/rsync",
compress = false,
archive = true,
owner = true,
perms = true,
--delete = true,
whole_file = false,
rsh = "/usr/bin/ssh -p 12022 -l suoper -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i /home/username/.ssh/airflow-rsync"
},
}
sync {
default.rsync,
source = "/data/airflow",
target = "192.168.0.200:/data/airflow",
rsync = {
binary = "/usr/bin/rsync",
compress = false,
archive = true,
owner = true,
perms = true,
--delete = true,
whole_file = false,
rsh = "/usr/bin/ssh -p 12022 -l suoper -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -i /home/username/.ssh/airflow-rsync"
},
}
You can access the official website to see what the above parameters mean. Here is the ssh command defined by rsync's rsh, which can solve the scenarios where private keys, custom ports and other security measures are used. Of course, you can also configure non secret access and then use default rsync or default Rsyncsh, etc.
Configure service hosting for lsyncd
cat << EOF > /etc/systemd/system/lsyncd.service [Unit] Description=lsyncd ConditionFileIsExecutable=/usr/bin/lsyncd After=network-online.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] StartLimitBurst=10 ExecStart=/usr/bin/lsyncd /etc/lsyncd.conf Restart=on-failure RestartSec=120 EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/aliyun KillMode=process [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable --now lsyncd.service #Start the service and configure to enable self startup
In this way, the synchronization of data (dags,plugins,airflow.cfg) is completed. When using the CICD scene in the later stage, you can directly upload the dag file to the Bigdata1 node, and the other two nodes will be synchronized automatically. If there is a problem, you can debug by viewing the log
lsyncd -log all /etc/lsyncd.conf tail -f /var/log/lsyncd.log
5 reverse proxy [3]
If you need to put airflow after the reverse proxy, such as https://lab.mycompany.com/myorg/airflow/ You can complete the following configuration:
- At airflow Configuring base in CFG_ url
base_url = http://my_host/myorg/airflow enable_proxy_fix = True
- Configuration of nginx
server {
listen 80;
server_name lab.mycompany.com;
location /myorg/airflow/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}
Here, the installation of airflow distributed scheduling cluster is basically completed The specific effects are as follows.
See here that you are also using or interested in Airflow, and send you a learning Airflow material by the way;
https://livebook.manning.com/book/data-pipelines-with-apache-airflow/chapter-12/1
reference material
[1]Airflow 2.2.3 + MySQL8.0.27: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VncpyXcTtlvnDkFrsAZ5lQ
[2]lsyncd config file: https://lsyncd.github.io/lsyncd/manual/config/file/
[3]airflow-behind-proxy: https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/howto/run-behind-proxy.html