summary
- Violent recursion is an attempt (local attempt)
- The problem is transformed into a sub problem of the same kind of problem with reduced scale
- Specify the condition for the end of recursion (base case)
- After getting the results of the subproblem, there is a decision-making process
- Do not record the solution of each sub problem, try the most important
Topic 1: Hanoi Tower problem

- Idea:
(1) Move layer 1 ~ n - 1 to the middle
(2) Move layer n to the far right
(3) Move layer 1 ~ n - 1 to the far right
public static void hanoi(int n){
if (n > 0){
move(n, "left", "mid", "right");
}
}
public static void move(int n, String from, String to, String temp){
//Moving from: the place of departure; to: destination; temp: auxiliary position
if (n == 1){
//Recursive end condition
System.out.println("Move 1 form " + from + " to " + to);
}
else {
//Reduction of the scale of the problem
//Move n - 1 from from to temp
move(n - 1, from, temp, to);
//Move n from to
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from " + from + " to " + to);
//Move n - 1 from temp to
move(n - 1, temp, to, from);
}
}
- Result demonstration:
When n = 3

Topic 2: all subsequences of strings

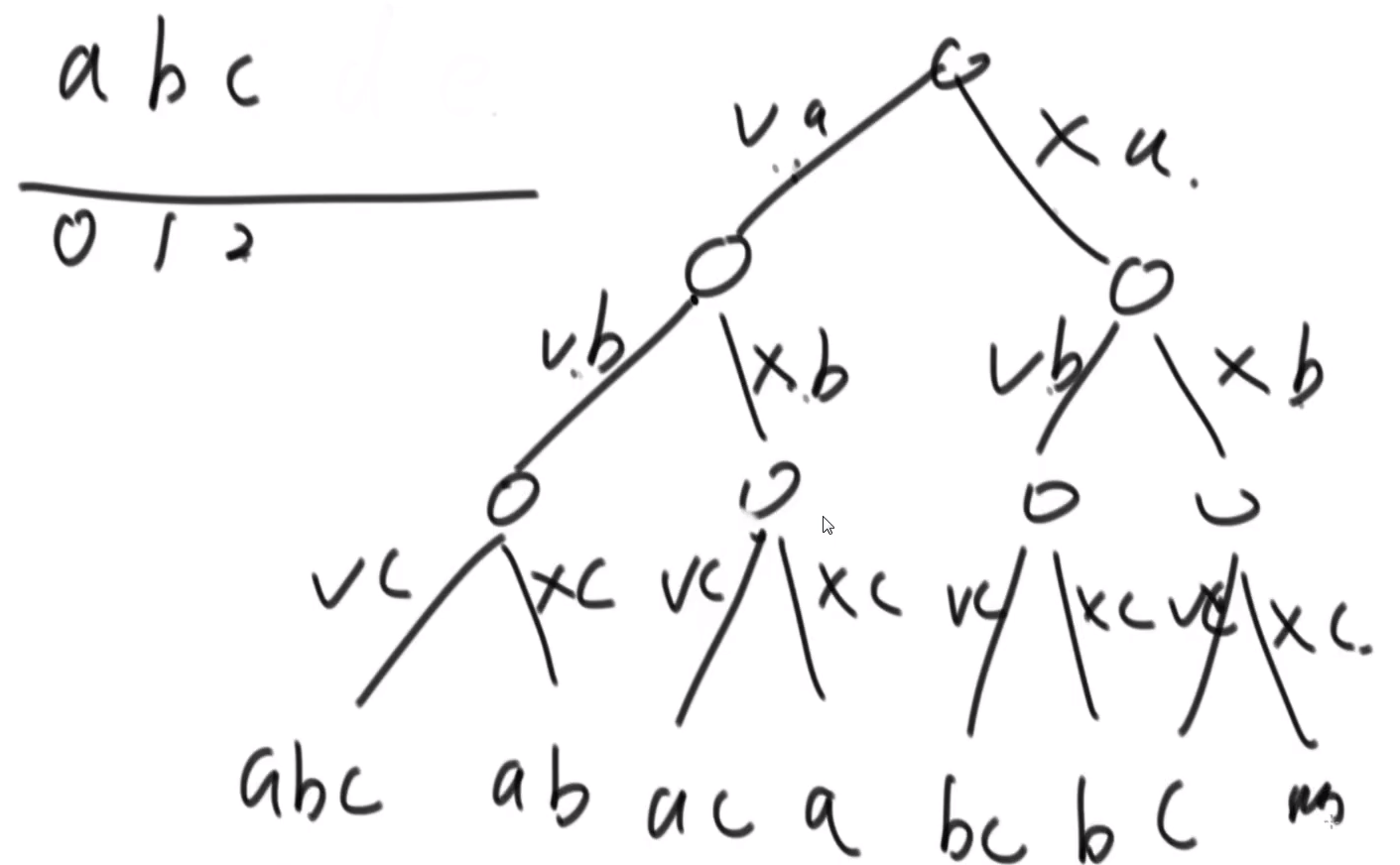
- Idea:
Try from 0 to n position
(1) Convert the string into a character array, and each character position is divided into yes and No
(2) The position of the problem from 0 to n is increased one position at a time
(3) End recursion when length equals n
Note: if the character array is changed after one recursion, the character array shall be restored before the next recursion
public static void printAllSubsquence(String str){
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
progress(chs, 0);
}
public static void progress(char[] chs, int index){
//index, the current position in the character array
if (index == chs.length){
//Complete character array
System.out.println(String.valueOf(chs));
return;
}
//Move back directly to reserve the index position and reduce the scale
progress(chs, index + 1);
char temp = chs[index];
//0 in ASCLL represents an empty character
chs[index] = 0;
//Replace the index with empty characters to reduce the scale
progress(chs, index + 1);
//Restore index location
chs[index] = temp;
}
- Result demonstration
str = "ljk"

Topic 3: full arrangement of strings (branch and bound)

- Idea:
If the length of the string is n
Try from 0 to n position
When repeated arrangement is not considered: use the method of exchange
(1) The first position can be exchanged with N positions
(2) The second position can have N - 1 positions to exchange with
......
(3) The N - 1 position has 2 positions that can be exchanged with it
(4) The nth position has only one position to exchange with (the condition for the end of recursion is to exchange to the nth position)
Note: if the character array is changed after one recursion, the character array should be restored before the next recursion
//Full arrangement
public static void permutation(String str){
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
progress(chs, 0);
}
public static void progress(char[] chs, int index){
//index, the current position in the character array
if (index == chs.length){
//Complete character array
System.out.println(String.valueOf(chs));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < chs.length; i++){
//The index position is swapped with the position behind it
swap(chs, index, i);
//Downsizing
progress(chs, index + 1);
//Recover the original character array at the end of one recursion
swap(chs, index, i);
}
}
public static void swap(char[] chs, int i, int j){
char temp = chs[i];
chs[i] = chs[j];
chs[j] = temp;
}
- Result demonstration
str = "abb"
- Idea:
If the length of the string is n, all characters are lowercase letters
When considering repeated arrangement: no position exchange occurs when the same letters appear
public static void permutation(String str){
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
progress(chs, 0);
}
public static void progress(char[] chs, int index){
//index, the current position in the character array
if (index == chs.length){
//Complete character array
System.out.println(String.valueOf(chs));
return;
}
//Record whether the 26 lowercase letters have the same
boolean[] visit = new boolean[26]; //The default is false
for (int i = index; i < chs.length; i++) {
if (!visit[chs[i] - 'a']) {
//The element at i position is not repeated and can be exchanged with index position
//The idea of branch and bound ends the impossible branch in advance
visit[chs[i] - 'a'] = true;
//The index position is swapped with the position behind it
swap(chs, index, i);
//Downsizing
progress(chs, index + 1);
//Recover the original character array at the end of one recursion
swap(chs, index, i);
}
}
}
public static void swap(char[] chs, int i, int j){
char temp = chs[i];
chs[i] = chs[j];
chs[j] = temp;
}
- Result demonstration:
str = "abb"
Topic 4: playing cards is the biggest problem

- Idea:
(1) There are two card holding methods, first hand and second hand. If the range is left ~ right
(2) The first hand is divided into left and right. If you take left, the value is the value of left position + the value of the second hand (left + 1 ~ right); If you take right, the value is the value of the right position + the value of the rear hand (left ~ right - 1 rear hand), and the larger of the two values is returned
(3) The backhand is divided into left or right. If the opponent takes left, the value is the value of the first hand (left + 1 ~ right first hand); If you take right, the value is the value of the first hand (left ~ right - 1 first hand), because the opponent must take the optimal solution, then the second hand must be the smaller of the two values
(4) If left == right, the first hand is the value of the left position, and the second hand is 0
public static int win(int[] arr){
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int valueA = first(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); //A's first hand
int valueB = second(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); //B's backhand
return Math.max(valueA, valueB);
}
public static int first(int[] arr, int left, int right){
//The best score obtained first
if (left == right){
//Recursive end condition
return arr[left];
}
int l = arr[left] + second(arr, left + 1, right); //Take the left
int r = arr[right] + second(arr, left, right - 1); //Take the right
return Math.max(l, r);
}
public static int second(int[] arr, int left, int right){
//The best score obtained first
if (left == right){
//Recursive end condition
return 0;
}
int l = first(arr, left + 1, right); //The opponent took the left
int r = first(arr, left, right - 1); //The opponent took the right
//Because the opponent will choose the best situation, leaving it to the backhand must be the worse choice of the two
return Math.min(l, r);
}
- Result demonstration:
arr = [1, 100, 2]
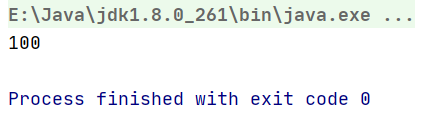
arr = [1, 2, 100, 4]
Topic 5: recursive reverse order stack

- Thinking:
(1) Using the performance of system stack to save data to solve the problem
(2) First of all, we need to implement the function to get the elements at the bottom of the stack. Using recursion to call this function all the time is to get the elements out of the stack. If the stack is empty, we will return the elements at the bottom of the stack, otherwise we will return the recursive temporary variables
(3) The implementation of the reverse order function. One reverse order is to get the elements at the bottom of the stack, call recursively until the stack is empty, and re press the saved data into the system stack
public static void reverse(Stack<Integer> stack){
//Reverse order stack
if (stack.isEmpty()){
//Stack empty return
return;
}
//Get the element at the bottom of the stack
int bottom = getBottom(stack);
//Recursive call
reverse(stack);
//When the stack is empty, press it in again, and use the data saved by the system stack
stack.push(bottom);
}
public static int getBottom(Stack<Integer> stack){
//Get the element at the bottom of the stack
int result = stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty()){
//Return at the bottom of the stack
return result;
}
//Recursive call
int temp = getBottom(stack);
//Push non stack bottom elements back into the stack
stack.push(result);
//temp saves recursive data in the system stack
return temp;
}
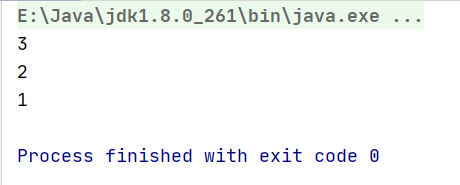
- Result demonstration:
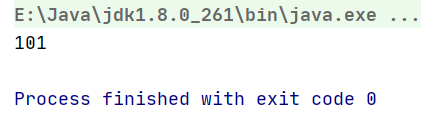
The elements in the stack are: 1, 2, 3
Topic 6: conversion of numbers and strings

- Idea:
An attempt from left to right
In the array, index is the current traversed position. After trying all possible conditions of the index position, index continues to move until the end of the array - Situation analysis:
(1) If 0 appears in the index position, it indicates an error in the previous conversion and returns 0
(2) If the index position is 1 or 2, it can be combined with the index + 1 position or transformed separately to produce two recursive methods: directly to the next position or skip the next position
(3) If the index position is 3 ~ 9, it will be directly converted separately, and there is no redundant situation. It will be directly recursive to the next position
(4) If the index is equal to the length of the array, the conversion ends and returns 1
public static int number(String str){
if (str == null || str.length() == 0){
return 0;
}
return process(str.toCharArray(), 0);
}
public static int process(char[] chs, int index){
//Traversal array
if (index == chs.length){
//index to the last note, this recursion has got a situation
return 1;
}
if (chs[index] == '0'){
//0 appears at the index position, indicating that there is an error in this recursion
return 0;
}
if (chs[index] == '1'){
//1 at index position
//Separate conversion index location
int result = process(chs, index + 1);
if (index + 1 < chs.length){
//Combined with index + 1 position conversion
result += process(chs, index + 2);
}
return result;
}
if (chs[index] == '2') {
//1 at index position
//Separate conversion index location
int result = process(chs, index + 1);
if (index + 1 < chs.length && (chs[index + 1] <= '6')){
//Combined position transformation
//In this conversion, the number is less than or equal to 26
result += process(chs, index + 2);
}
return result;
}
//The index position is 3 ~ 9
return process(chs, index + 1);
}
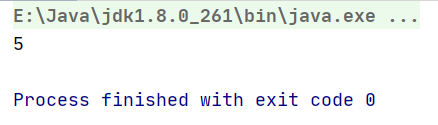
- Result demonstration:
str = "121451202"
Title 7: weight and value

- Idea:
Try positions 0 ~ i, divided into yes and No
(1) Record the current weight. If it exceeds bag, it cannot be obtained
(2) If you want to increase the current weight and value, traverse the next one; If you do not directly traverse to the next
(3) If all of them have been traversed, 0 will be returned
public static int maxValue(int[] weights, int[] values, int bag){
if (weights.length == 0){
return 0;
}
return process(weights, values, bag, 0, 0);
}
public static int process(int[] weights, int[] values, int bag, int index, int alreadyWeight){
//index: the current traversal position
//alreadyWeight: current weight
if (index == values.length){
//It has been completely traversed
return 0;
}
int getValue;
if (alreadyWeight + weights[index] <= bag){
//At present, you can still increase the weight of the index
//For the item in the index position, alreadyWeight increases and returns the increase of value
getValue = values[index] + process(weights, values, bag, index + 1, alreadyWeight + weights[index]);
}else {
//Cannot increase, same as noValue
getValue = process(weights, values, bag, index + 1, alreadyWeight);
}
//Do not use items in index position. Value and alreadyweight remain unchanged
int noValue = process(weights, values, bag, index + 1, alreadyWeight);
//Determine the larger value of both and return
return Math.max(getValue, noValue);
}
- Result demonstration:
weights = [10, 3, 7, 8, 9]
values = [4, 2, 3, 9, 5]
bag = 20
Title 8: Queen N problem

- Idea:
(1) Try placing a queen in a different column position in each row
(2) Requirements: the later ones cannot be placed in the same column or slash as the previous ones
public static int num(int n){
if (n < 0){
return 0;
}
//record[i] indicates the column in which the queen of row i - 1 is placed
int[] record = new int[n];
return process(0, record, n);
}
public static int process(int index, int[] record, int n){
//The row currently traversed by index
//n is the size of the chessboard
if (index == n){
//The traversal is completed normally, and the previous placement is correct
return 1;
}
int result = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < n; row++){
//Current index row, row column
if (isValid(record, index, row)){
//If location is valid
record[index] = row;
result += process(index + 1, record, n);
}
}
return result;
}
public static boolean isValid(int[] record, int index, int row){
//Judge whether the queen joined is legal
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++){
//Queen added before traversing
if (record[i] == row || Math.abs(record[i] - row) == Math.abs(i - index)){
//Judge whether it is in the same column or slash
//Judgment of the same column: whether the slope of two points is 1 (45 degrees), or - 1 (135 degrees)
//That is, whether the absolute value of row difference is the same as that of column difference
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
- Result demonstration:
n = 8