Merge K sort lists
Title Description
Merge k sorted lists to return the merged sorted list. Example: Input: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] Output: 1 - > 1 - > 2 - > 3 - > 4 - > 4 - > 5 - > 6
Solving problems
The two links of the linked list are merged, and the last link list is the required result.
The consolidation method is: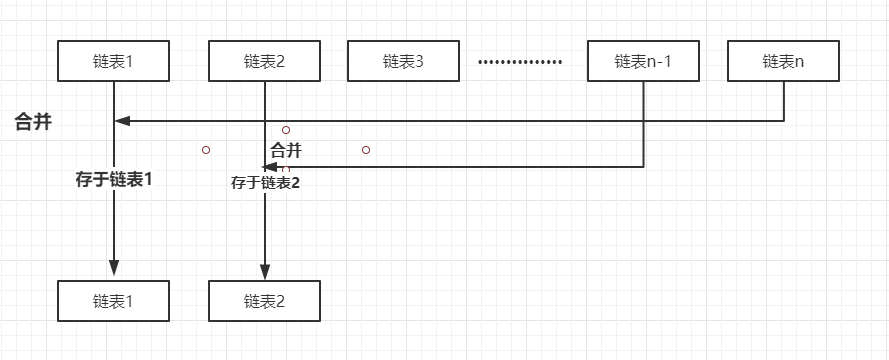
Code example
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Node> list = new ArrayList<>(); //Initialize node list initNodeLinked(list); //Output initialized list for (int i=0; i< list.size(); i++){ printValueList(list.get(i), i +""); } //merge Node nodeResult = mergeLinked(list); //Output initialized list printValueList(nodeResult, "[Final result]"); } private static Node mergeLinked(List<Node> list) { int size = list.size(); Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); while (size > 1){ for (int i = 0; i < size/2; i++){ //First and last linked list merging on the first end list.set(i, mergeTwoLinked(list.get(i), list.get(size - 1 - i))); } size = (size + 1)/2; } return list.get(0); } //Merge two linked lists private static Node mergeTwoLinked(Node node1, Node node2) { //The pointer start always points to the [first end] of the result set list Node start = new Node(-1); //Pointer p always points to the end of the result set list Node p = start; while (node1 != null && node2 != null){ if (node1.value > node2.value){ p.next = node2; node2 = node2.next; }else { p.next = node1; node1 = node1.next; } p = p.next; } if (node1 != null){ p.next = node1; } if (node2 != null){ p.next = node2; } return start.next; } private static void printValueList(Node node,String num) { ArrayList<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>(); while (node.next != null){ numList.add(node.value); node = node.next; } System.out.println("The first"+num+"Linked list value The collection is:"+numList); } private static void initNodeLinked(List<Node> list) { //1->2->3->4->5 Node node1 = new Node(10); for (int i=10; i>0; i--){ Node nodeTemp = new Node(i); nodeTemp.next = node1; node1 = nodeTemp; } //1->2->3->4->5 Node node2 = new Node(10); for (int i=10; i>0; i--,i--){ Node nodeTemp = new Node(i); nodeTemp.next = node2; node2 = nodeTemp; } //1->2->3->4->5 Node node3 = new Node(15); for (int i=15; i>0; i--,i--){ Node nodeTemp = new Node(i); nodeTemp.next = node3; node3 = nodeTemp; } //1->2->3->4->5 Node node4 = new Node(15); for (int i=15; i>0; i--,i--){ Node nodeTemp = new Node(i); nodeTemp.next = node4; node4 = nodeTemp; } //1->2->3->4->5 Node node5 = new Node(30); for (int i=30; i>0; i--,i--,i--,i--){ Node nodeTemp = new Node(i); nodeTemp.next = node5; node5 = nodeTemp; } list.add(node1); list.add(node2); list.add(node3); list.add(node4); list.add(node5); } } //Node node class Node{ public Integer value; public Node next; public Node(Integer value) { this.value = value; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "value=" + value + ", next=" + next + '}'; } }
Operation result

█▀█● colleagues, if my code is helpful to you, please give me a compliment. For the convenience of finding it next time, you can also pay attention to the collection
If you have any comments or suggestions, you can also discuss them in the message area

