BFS template
void BFS(int s){
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
Take out the team head element front;
Access team leader element front;
Take the first element out of the team;
take front All nodes that have not been queued in the next layer of nodes are queued, and the queued nodes are set
}
}DFS template
recursion
priority_ cmp function template for queue:
struct fruit{
string name;
int price;
}
struct cmp{
bool operator () (fruit f1,fruit f2){
return f1.price > f2.price;
}
}
int main(){
priority_queue<fruit,vector<fruit>,cmp> q;
return 0;
}Template for reconstructing binary tree by combining middle sequence sequence with pre sequence sequence, post sequence and sequence sequence:
//Remember the create function template. No matter who the middle order cooperates with, the template is as follows
//postL is the left endpoint of the post sequence
//postR is the right endpoint of the post sequence
//inL is the left endpoint of the middle order sequence
//inR is the right endpoint of the middle order sequence
//postOrder is a post order sequence
//inOrder is a middle order sequence
node* create(int postL,int postR,int inL,int inR){
if(postL>postR){
return NULL;
}
int in = postOrder[postR];
node* root = new node;
root->data = in;
int k;
for(k=inL;k<=inR;k++){
if(inOrder[k]==in){
break;
}
}
int numLeft = k-inL;//This step must have
root->lChild = create(postL,postL+numLeft-1,inL,inL+numLeft-1);
root->rChild = create(postL+numLeft,postR-1,inL+numLeft+1,inR);
return root;
}And search the set to find the template of the root node:
//Recursive writing
int findFather(int n){
if(n==father[n]){
return n;
}
else{
//Parentheses and brackets should be separated
return findFather(father[n]);
}
}Query the template of consolidation set:
void unionS(int a,int b){
int fA = findFather(a);
int fB = findFather(b);
if(fA != fB){
father[fA] = fB;
}
return;
}Dijestra algorithm + adding point weight + finding the number of shortest paths:
void Dij()
{
//The following three lines are initialization work:
//The distance from the starting point to the starting point is 0;
//There is 1 shortest path from the starting point to the starting point;
//Cumulative maximum resources available from starting point to starting point = resources owned by the starting point itself
d[now] = 0;
shortestNum[now] =1;
maxRescue[now] = cityRescue[now];
//Where i is not used in the whole for loop, i is only used for counting
for(int i=0; i<cityNum; i++)
{
int u = -1;
int minLen = inf;
//Find the point with the shortest distance from the current starting point
for(int j=0; j<cityNum; j++)
{
if(!vis[j] && d[j]<minLen)
{
u = j;
minLen = d[j];
}
}
if(u==-1)
{
return;
}
//It means that u has been visited
vis[u] = true;
int len = save[u].size();
//Update via u
for(int j=0; j<len; j++)
{
int number = save[u][j].num;
int roadLen = save[u][j].road;
//First, make sure that the node has not been accessed
if(!vis[number])
{
if(d[number]> d[u]+roadLen)
{
d[number] = d[u]+roadLen;
shortestNum[number] = shortestNum[u];
//If the shortest path changes, the cumulative maximum resources will change unconditionally
maxRescue[number] = maxRescue[u]+cityRescue[number];
}
else if(d[number]==d[u]+roadLen)
{
shortestNum[number] += shortestNum[u];
//If the shortest path does not change, the accumulated maximum resources must be conditionally changed
if(maxRescue[u]+cityRescue[number]>maxRescue[number]){
maxRescue[number] = maxRescue[u]+cityRescue[number];
}
}
}
}
}
}Freud algorithm template
void Floyed()
{
for(int k=0; k<n; k++)
{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
if(dis[i][k]!=INF && dis[k][j]!=INF && dis[i][k]+dis[k][j]<dis[i][j])
{
dis[i][j] = dis[i][k]+dis[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}Prim algorithm template
//G is the graph, which is generally set as a global variable; Array d is the shortest distance between vertices and set S
Prime(G,d[]){
initialization;
for(loop n second){
u = send d[u]The label of the smallest vertex that has not been accessed;
remember u Accessed;
for(from u All the vertices that can be reached by departure v){
if(v Not accessed && with u For the mediation point v And set S Shortest distance d[v]Better){
take G[u][v]Assign to v And set S Shortest distance d[v];
}
}
}
}Prime template
//Given a number, judge whether it is a prime number
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
//Core code
bool isPrime(int n){
if(n<=1){
return false;
}
int a = (int)sqrt(1.0*n);//Round down
for(int i=2; i<=a; i++){
if(n%i==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
bool is = isPrime(n);
if(is){
printf("Yes");
}
else{
printf("No");
}
return 0;
}
Template of prime table (Elsevier sieve method)
//Find all primes between 1 and n,
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
bool is[maxn] = {false};
int prime[maxn];
int p=0;
int n;
//Core code
void findPrime(){
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(!is[i]){
prime[p] = i;
p++;
for(int j=i+i;j<=n;j = j+i){
is[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
findPrime();
for(int i=0; i<p;i++){
printf("%d\n",prime[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Template for solving the maximum common divisor
//Given two numbers n and m, find the maximum common divisor a of n and m
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
//Core code; Don't worry about the size of a and B. the default is a > B. even if a < B, it will become a > b after a round of iteration
int gcd(int a,int b){
if(b==0){
return a;
}
else{
return gcd(b,a%b);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
int m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int a = gcd(n,m);
printf("%d",a);
return 0;
}
Template for solving least common multiple
//Given two numbers n and m, find the least common multiple b of n and m
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
//Core code
int gcd(int a,int b){
if(b==0){
return a;
}
else{
return gcd(b,a%b);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
int m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int a = gcd(n,m);
int b = (n/a)*m;//First find the greatest common divisor, and then find the least common multiple
printf("%d",b);
return 0;
}
Finding fiboracci sequence template (dynamic programming method)
A problem can be solved by dynamic programming method, which needs to meet the following two conditions:
- There are overlapping subproblems.
- There is an optimal substructure (the optimal solution of the global problem can be composed of the optimal solution of the local problem)
//When n is 45, F(n) already has 10 digits. When it exceeds 45, it exceeds the limit of int, and int is a signed number, and the sign bit has changed
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
int dp[maxn];
//Core code
int F(int n){
if(n==0 || n==1){
return 1;
}
//This step reduces the computational complexity a lot
else if(dp[n]!=-1){
return dp[n];
}
else{
dp[n] = F(n-1)+F(n-2);
return dp[n];
}
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<maxn; i++){
dp[i] = -1;
}
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int a = F(n);
printf("%d",a);
return 0;
}
sort function
Before using the sort function, make the following Declaration:
#include <algorithm> using namespace std;
Sort (first element address (required), next address of last element address (required), comparison function (not required))
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const double pi = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
#define EQU(a,b) (fabs((a)-(b))<eps)
#define GREATER(a,b) (((a)-(b))>eps)
#define LESS(a,b) (((a)-(b))<(-eps))
#define GREATER_EQU(a,b) (((a)-(b))>(-eps))
#define LESS_EQU(a,b) (((a)-(b))<(eps))
struct node{
int id;
string name;
double grade;
}tmp[3];
bool cmp2(node a,node b){
if(EQU(a.grade,b.grade)){
//If the scores are the same, they are arranged in dictionary order
return a.name >b.name;
}
else{
//The high achievers are ahead
return GREATER(a.grade,b.grade);
}
}
bool cmp(double a,double b){
return a>b;
}
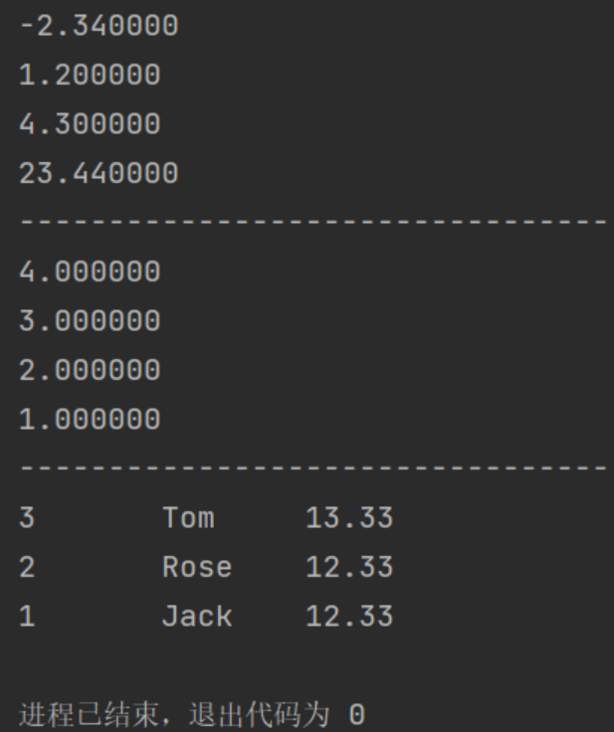
int main() {
double a[] = {1.2,4.3,-2.34,23.44};
sort(a,a+3);
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
printf("%lf\n",a[i]);
}
printf("---------------------------------\n");
double b[] = {1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0};
sort(b,b+4,cmp);
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
printf("%lf\n",b[i]);
}
printf("---------------------------------\n");
tmp[0].grade=12.33;
tmp[0].id=1;
tmp[0].name="Jack";
tmp[1].grade=12.33;
tmp[1].id=2;
tmp[1].name="Rose";
tmp[2].grade=13.33;
tmp[2].id=3;
tmp[2].name="Tom";
sort(tmp,tmp+3,cmp2);
for(int i=0; i<3; i++){
printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\n",tmp[i].id,tmp[i].name.c_str(),tmp[i].grade);
}
return 0;
}
priority_ Custom priority in queue
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct fruit{
string name;
int price;
friend bool operator < (fruit f1,fruit f2){
return f1.price>f2.price;
}
}f1,f2,f3;
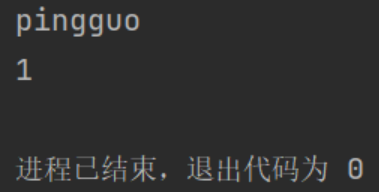
int main() {
priority_queue<fruit> q;
f1.name = "taozi";
f1.price = 3;
f2.name = "lizi";
f2.price = 4;
f3.name = "pingguo";
f3.price = 1;
q.push(f1);
q.push(f2);
q.push(f3);
cout<<q.top().name<<endl<<q.top().price<<endl;
return 0;
}
Convert string type variables to int, long, float and double type variables
C language conversion form:
std::string str; int i = atoi(str.c_str());
C + + conversion form (C++11):
std::string str; int i = std::stoi(str);
Similarly, you can use stol(long), stof(float), stod(double), etc
Convert int, long, float and double variables to string variables
to_ The string() function method is a new function added in C++11 to convert numbers to string objects. The main function interfaces are as follows:
std::to_string C++ Strings library std::basic_string Defined in header <string> std::string to_string( int value ); std::string to_string( long value ); std::string to_string( long long value ); std::string to_string( unsigned value ); std::string to_string( unsigned long value ); std::string to_string( unsigned long long value ); std::string to_string( float value ); std::string to_string( double value ); std::string to_string( long double value );
The function is really powerful and convenient. Use the following:
#include<sstream> #include<string> using namespace std; string str = to_String(123405);
Convert single character char to string
Using push_back()
char c = 'a'; string s1; s1.push_back(c);
More methods:
const char c = 'a'; //1. Use string constructor string s(1,c); //2. Push char after declaring string_ back string s1; s1.push_back(c); //3. Use stringstream stringstream ss; ss << c; string str2 = ss.str(); //Pay attention to the use of to_ The string method will be converted to the ascii code corresponding to char. The reason is to_string does not accept the function prototype of char type parameters, //There is a function prototype whose parameter type is int, so when you pass in char characters, you actually convert char into int ascii code first, and then into //string, the following output is 97 cout << to_string(c) << endl;
Converts a single character string to char
Use c_str() converts a string into a char array. In fact, this array has only one element, which is the char element we want
string f = "m";
const char *g1 = f.c_str();
printf("%s\n",g1);Conversion of numeric characters and numbers
//For a 1-bit number, there is a '0' difference between the integer form and the character form
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Character to number
char a='3';
int b = a-'0';
int c = b+2;
printf("%d\n",c);
//Numeric variable character
int d = 6;
char e = d+'0';
printf("%c\n",e);
return 0;
}
Conversion of lowercase and uppercase letters
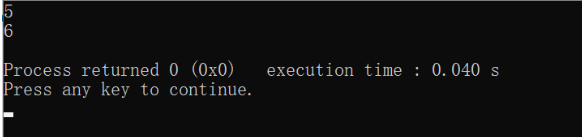
//Lowercase letters are 32 times larger than uppercase letters
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a = 'A';
printf("%c\n",a+32);
char b = 'g';
printf("%c\n",b-32);
return 0;
}
Converts an array of type int to an integer of type int
//The user specifies to input a digits, and then input a digits to form an int type array, and then convert the int type array into an int type integer
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
int num[maxn];
int a;
int toInt(){
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<a; i++){
sum = sum*10 + num[i];
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&a);
for(int i=0; i<a; i++){
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
}
int result = toInt();
printf("%d",result);
return 0;
}
Converts an integer of type int to an array of type int
There is a lesson to be learned when writing this Code:
Global variables and local variables cannot have the same name, otherwise an undetectable error will occur
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
int n;
int num[maxn];
int k=0;
//Core code
void toArray(){
for(int i=0; i<k; i++){
num[i] = n%10;
n /=10;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n>=pow(10,k)){
k++;
}
toArray();
for(int i=0; i<k; i++){
printf("%d\n",num[i]);
}
return 0;
}
sscanf and sprintf templates
The function is to realize the conversion of string and number.
sscanf and sprintf are in the stdio.h header file.
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("%d",n);It can be written as follows. Screen represents the screen:
scanf(screen,"%d",&n);//Write the string entered by the user on the screen to n (from left to right) printf(screen,"%d",n);//Displays the contents of n as a string on the screen (from right to left)
Replace screen with character array str, which is the usage of sscanf and sprintf:
sscanf(str,"%d",&n);//Write the contents of str to n (from left to right) sprintf(str,"%d",n);//Write the contents of n to str as a string (from right to left)
Typical applications are as follows:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
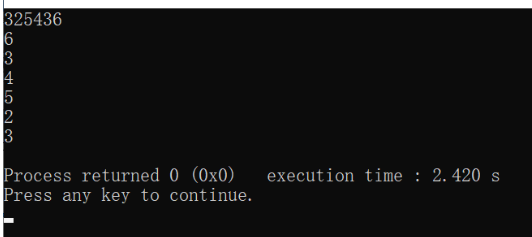
char str[10] = "123";
int a;
sscanf(str,"%d",&a);//Convert string to number
printf("%d\n",a);
int b = 124332;
char stt[20];
sprintf(stt,"%d",b);//Convert numbers to strings
printf("%s\n",stt);
return 0;
}
Advanced applications are as follows:
Prerequisite knowledge 1:
Syntax for reading in double variables:
double a;
scanf("%lf",&a);Syntax of output double variable:
printf("%f",a);perhaps
printf("%.2f",a);Prerequisite knowledge 2:
To initialize a character array:
char str[100]= "123a"; //Incorrect writing in comments //char str[100]; //str= "123a"; //Incorrect writing in comments //char str[100]; //str[100]= "123a";
Formal application 1:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
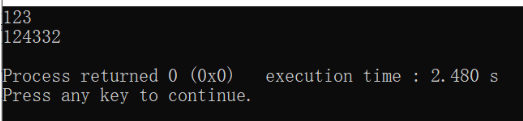
int n;
double db;
char str[100] = "2048:3.14,hello";//Method of initializing character array
char str2[100];
sscanf(str,"%d:%lf,%s",&n,&db,str2);//Syntax for reading in double variables:
printf("%d\n",n);
printf("%.2f\n",db);
printf("%s\n",str2);
return 0;
}
Formal application 2:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
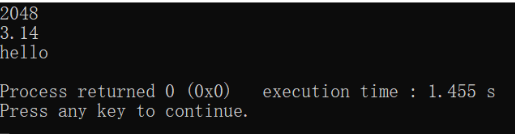
int n=12;
double db = 3.1415;
char str[100];
char str2[100] = "good";
sprintf(str,"%d:%.2f,%s",n,db,str2);
printf("%s",str);
return 0;
}
Comparison between PI and floating point number
The storage of floating-point numbers in the computer is not always accurate. It is necessary to introduce a decimal eps to correct this error. eps is generally 1e-8
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-8;
const double Pi = acos(-1.0);
//Note that Equ should be followed by parentheses
#define Equ(a,b) ((fabs((a)-(b)))<(eps))
#define More(a,b) (((a)-(b))>(eps))
#define Less(a,b) (((a)-(b))<(eps))
#define MoreEqu(a,b) (((a)-(b))>(-eps))
#define LessEqu(a,b) (((a)-(b))<(eps))
int main()
{
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
return 0;
}

Read an unknown number of string type strings
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
vector<string> now;
//getline(cin,str)!=NULL and getline (CIN, STR)=- 1 is all wrong
while(getline(cin,str)){
now.push_back(str);
}
int len = now.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
cout<<now[i]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Obtain the k-th position of the single linked list from the back to the front
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
int now[5002];
int i=0;
while(head->next != NULL){
now[i] = head->val;
i++;
head = head->next;
}
i = i-2;
ListNode* tmp;
tmp = head;
while(i>=0){
ListNode* a = new ListNode(now[i]);
tmp->next = a;
tmp = a;
i--;
}
return head;
}
};Bibliography: algorithm notes