About NIOSOCKET
I won't introduce the underlying API of NIOSOCKET much here. Take the dry goods code directly
I mainly realize NIOSCOKET simulated chat communication here
I wrote an article about SOCKET and opened a new article about brother NIOSOCKET;
SOCKET server
niosocket service startup class is designed to establish a connection
Initiate tasks through thread pool processing
package niosocket.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class NioServerMain {
private static final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioServerMain nioServerMain = new NioServerMain();
nioServerMain.startSocket(7809);
}
public void startSocket(int port) {
try {
//Get a channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//Whether the configuration is blocked
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//Get socket
ServerSocket server = channel.socket();
//Binding services and ports
server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), port));
//Get selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//Register with selector to accept connections
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("Server socket Already started");
executorService.execute(new NioReadThread(selector));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Server processing business thread class
package niosocket.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class NioReadThread implements Runnable {
/**
* Message buffer
*/
private static ByteBuffer readBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
private Selector selector;
private int count = 0;
public NioReadThread(Selector selector) {
this.selector = selector;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
selector.select();
//Get the selection key instance of all received events
Set<SelectionKey> readKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = readKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//After processing, delete the key to prevent repeated processing
iterator.remove();
//Check whether the time is a new connection that is ready to be accepted
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
getConnect(key);
// key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE & SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
//Can I read data
if (key.isReadable()) {
getMessage(key);
}
//Check whether the socket is ready to write data
if (key.isWritable()) {
writeMessage(key);
// sendMessage(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Get connection
*
* @param key
* @throws Exception
*/
private void getConnect(SelectionKey key) {
try {
//message to operate on
ByteBuffer msg = ByteBuffer.wrap("connect success ".getBytes());
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//Receive a client connection
SocketChannel client = serverSocket.accept();
//Set non blocking
client.configureBlocking(false);
//Listen for read events
System.out.println("Read message thread socket" + client);
//Send connection to client successfully
client.write(msg);
//You must listen to the event written here. The client must establish a connection. No
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE|SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Read data
*
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getMessage(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
readBuf.clear();
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
try {
client.configureBlocking(false);
int count = client.read(readBuf);
if (count == -1) {
client.shutdownOutput();
client.shutdownInput();
client.close();
System.out.println("to break off scoket connect");
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
readBuf.flip();
readBuf.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, 0, count);
System.out.println("Client response:~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(message);
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
} catch (IOException e) {
key.cancel();
client.close();
System.out.println("Disconnect");
}
}
/**
* send data
*
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void sendMessage(SelectionKey key) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
try {
channel.configureBlocking(false);
String requestLine = "[Server] send message" + count;
//Write data
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(requestLine.getBytes()));
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
count++;
if (count > 10) {
channel.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Keyboard input analog chat send message
*
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void writeMessage(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//keyboard entry
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String message = scanner.nextLine();
if (message.equals("s")) {
break;
} else {
stringBuffer.append(message).append("\n");
}
}
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(stringBuffer.toString().getBytes()));
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
NIOSOCKET client
package niosocket.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class NioClientMain {
private static final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioClientMain nioClientMain = new NioClientMain();
nioClientMain.startClient(7809);
}
public void startClient(int port) {
try {
//Open socket channel
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
//Set non blocking
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//Connect to server - specify the host name and port
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), port));
//Open selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//socket actions registered to the server
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
executorService.execute(new ClientReadThread(selector));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Client processing business thread class
package niosocket.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class ClientReadThread implements Runnable {
/**
* Sign out of chat
*/
private static volatile boolean connected = true;
/**
* Message buffer
*/
private static ByteBuffer readBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
private int count = 0;
private Selector selector;
public ClientReadThread(Selector selector) {
this.selector = selector;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (connected) {
try {
//Get selector
selector.select();
//Gets the selected keyset of the selector
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
//The current key needs to be deleted after processing to prevent repeated processing
it.remove();
if (key.isConnectable()) {
System.out.println("The client [read / write thread] attempts to connect to the server.....");
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//Complete connection
// channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
channel.finishConnect();
//Listening to read event loop keysets will wait in the read thread next time
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("[[read / write thread] successfully connected");
}
//Is the data readable
if (key.isReadable()) {
getMessage(key);
}
//Check whether the socket is ready to write data
if (key.isWritable()) {
writeMessage(key);
// sendMessage(key);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* send data
*
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void sendMessage(SelectionKey key) {
//FIXME is a relatively common analog client and server-side long connection, sending messages, listening to write events and sending data
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
try {
channel.configureBlocking(false);
String requestLine = "[Client] send message" + count;
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(requestLine.getBytes()));
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
count++;
if (count > 10) {
channel.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* get data
*
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getMessage(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//Empty cache data
readBuf.clear();
//Read data
int count = channel.read(readBuf);
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
//Pop up data
readBuf.flip();
readBuf.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, 0, count);
System.out.println("Server response:~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println(message);
//When the monitoring event is a connect message, continue to listen for read events
// key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
if(!message.contains("connect")){
//FIXME if I listen to chat message events, I need to listen to my write message events and send back messages to the service
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}else{
//When I receive the connect content of the message sent by the server, I continue to listen to my read events, so that I can continue to receive the message sent by the client again
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
/**
* Keyboard input analog chat send message
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void writeMessage(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//keyboard entry
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuffer stringBuffer =new StringBuffer();
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String message = scanner.nextLine();
//FIXME here, I do an operation. If I continuously input multiple lines of information on the keyboard, only when one line only inputs s, launch the loop, send messages and listen for my message reading events
if(message.equals("s")){
break;
}else{
stringBuffer.append(message).append("\n");
}
}
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(stringBuffer.toString().getBytes()));
//Monitor read events
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
Test effect
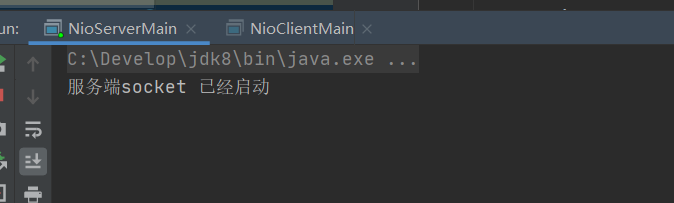
Server start
Only start the server
Client startup
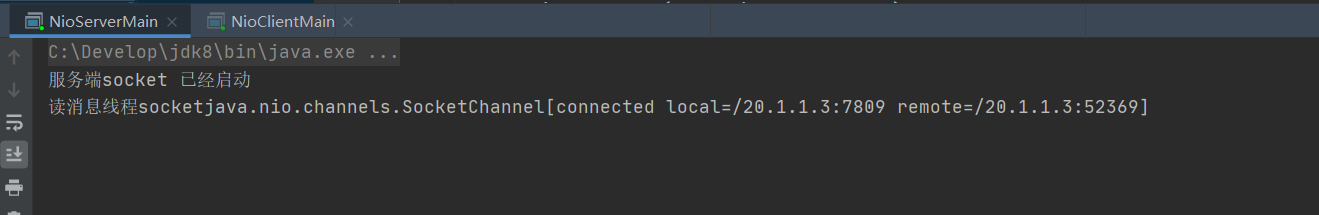
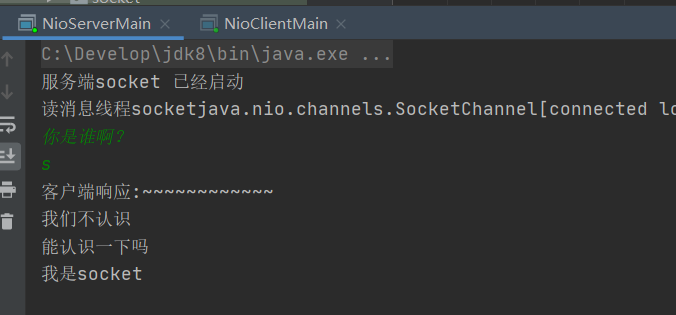
The server receives the client connection and outputs the information of the connected client
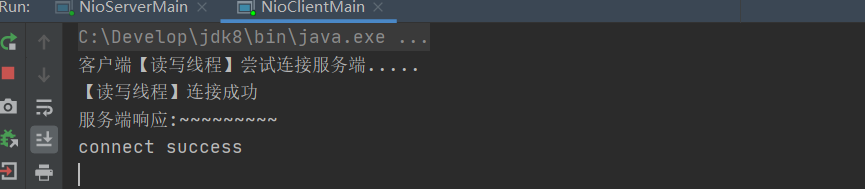
After the client successfully connects to the server, it will enter my link success and listen to the message sent by the client to tell me that the link is successful
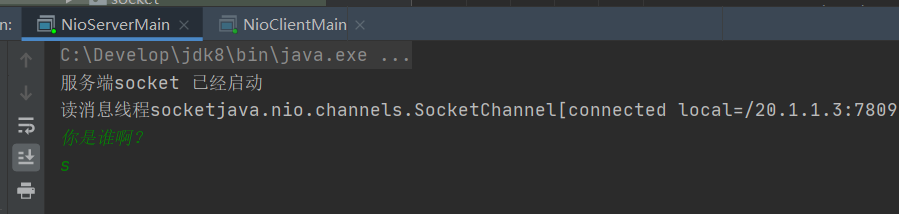
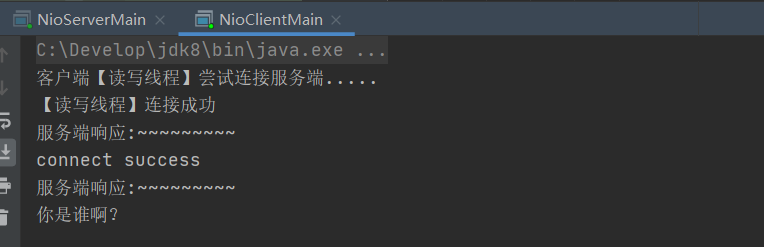
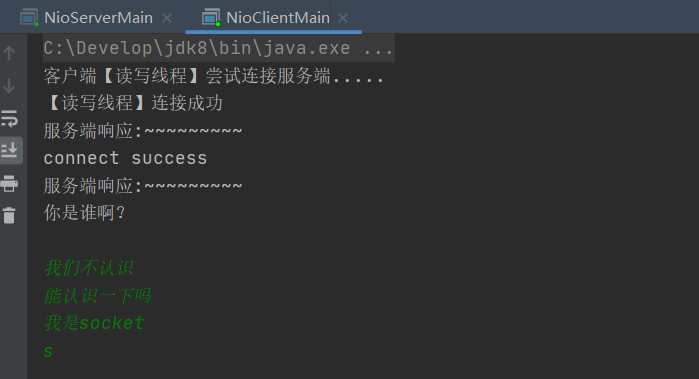
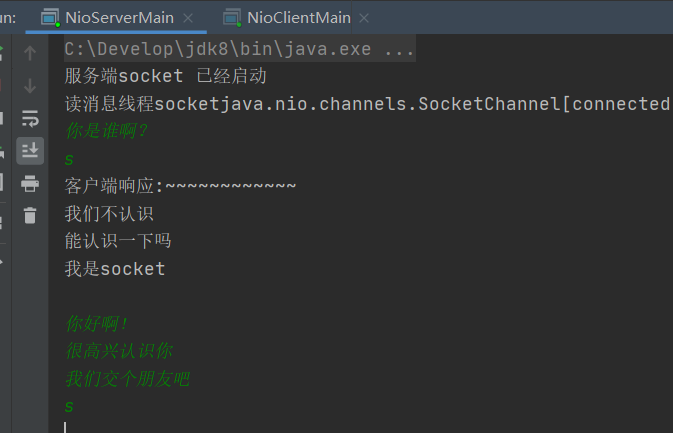
Simulation chat started
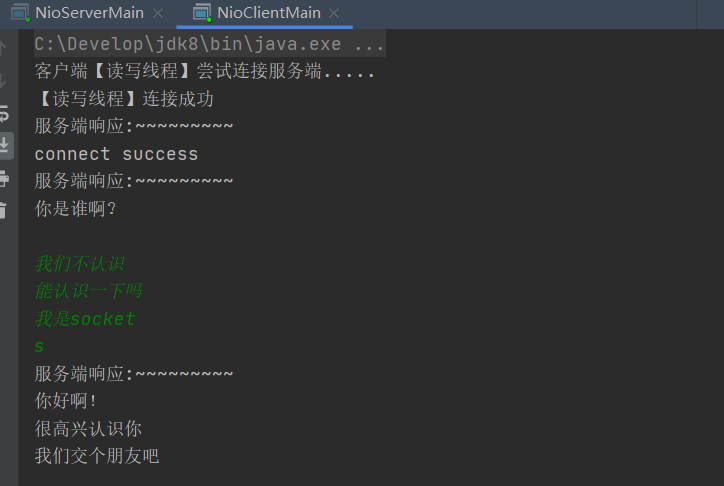
summary
be careful:
Because my test is to read the successful link message of the server on the client and continue to listen to the events read by the client,
So wait for the client to ask who you are for the first time,
Then the client can establish a more correct communication message.
The use of selectors. Here, the thread class directly handles the incoming use of selectors.
1. Many online read-write event monitoring cases are also used
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE|SelectionKey.OP_READ);
However, if it is not used properly, the communication of chat can not be realized.
2. Be sure to understand the purpose of this monitoring,
For example, I do many lines of keyboard input messages. When I use the last line s as the send message event, I exit the loop to listen for the read event.
Just like we used carriage return to send messages at the end of chatting about QQ, there is a trigger condition to terminate your current speech. Judge the following two event sets to be processed by the current thread class in the appropriate place
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
3. Many key processes have been written in the code. You can read the following carefully.