Chatter
Recently, I saw the sand dune by Weishen. I think it's really beautiful. The soundtrack is wonderful, the composition is beautiful, and the scene is magnificent, but it's not suitable for everyone; Today, when all kinds of cheap popcorn films are full of mainstream commercial films, it's lucky to see such a masterpiece with such a classical narrative and representing the highest production level in Hollywood!
##Series articles
Analysis of Qualcomm msm-V4L2-Camera driver 1- first knowledge
Qualcomm msm-V4L2-Camera driver analysis 2-framework details
Analysis of Qualcomm msm-V4L2-Camera driver 3-session
Analysis of Qualcomm msm-V4L2-Camera driver 4-stream
Analysis of Qualcomm msm-V4L2-Camera driver 5-buffer
1, Design idea of session
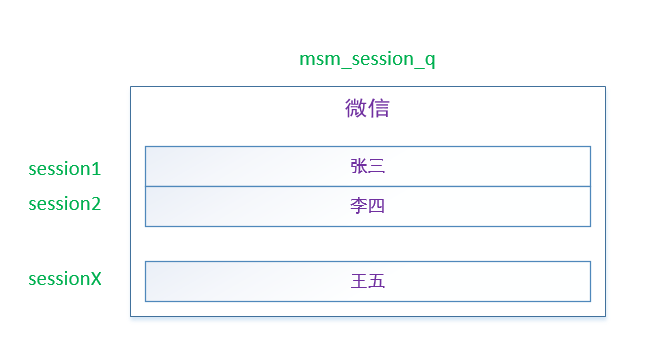
When chatting on wechat, if we want to communicate with people, we will create a session. If multiple people chat alone, there will be multiple sessions;
Each session is responsible for managing all resources, such as expression packs, pictures, chat records, etc.
Qualcomm's thinking is the same:
- Divide all functions of camera into different modules, and let the module decide its own affairs (high cohesion and low coupling). The module needs a unified interface and format.
- There is a port in the module, which connects the module through the port and hangs the module on the bus.
- The connection of each port is a stream. These streams are managed by pipeline.
- Each time a camera is started, a session is created to manage everything in the camera.
- For each session, the module is shared. It can be the hardware resources of camera or other resources (such as some software algorithms).
2, How is a session created
2.1. Data structure of session
msm_session
struct msm_session {
struct list_head list;
/* session index */
unsigned int session_id;
/* event queue sent by imaging server */
struct msm_event event_q;
/* ACK by imaging server. Object type of
* struct msm_command_ack per open,
* assumption is application can send
* command on every opened video node
*/
struct msm_queue_head command_ack_q;
/* real streams(either data or metadate) owned by one
* session struct msm_stream
*/
struct msm_queue_head stream_q;
struct mutex lock;
struct mutex lock_q;
struct mutex close_lock;
rwlock_t stream_rwlock;
struct kgsl_pwr_limit *sysfs_pwr_limit;
}
msm_event
/** msm_event:
*
* event sent by imaging server
**/
struct msm_event {
struct video_device *vdev;
atomic_t on_heap;
};
- struct list_head list: a linked list used to manage all sessions
- unsigned int session_id: session id
- msm_event event_q: video_device instance
- struct msm_queue_head command_ack_q: cmd queue
- struct msm_queue_head stream_q: Stream queue
The most important thing here is msm_event event_q. It's essentially a video_device instance.
In addition, cmd queue and stream queue are more important.
2.2 session and video_device relationship
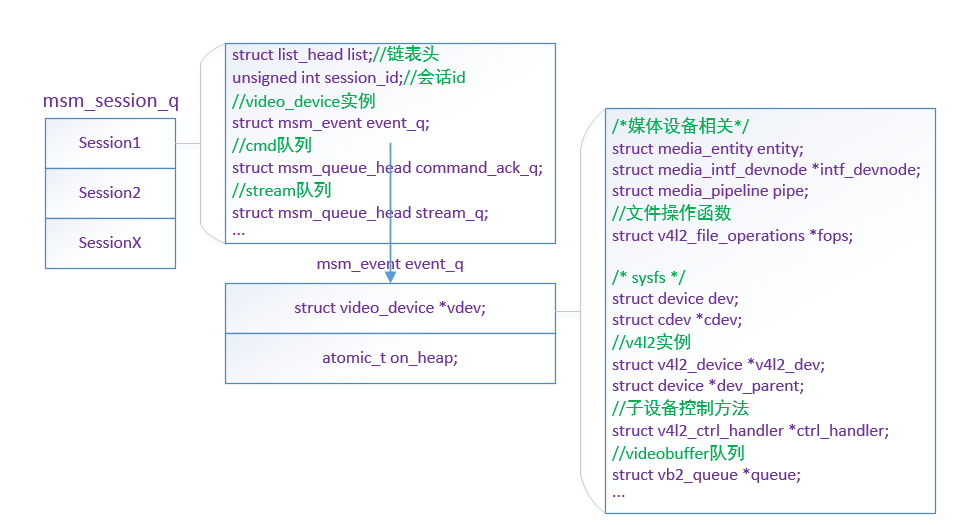
png)
2.3 video_device,v4l2_device and v4l2_subdev relationship
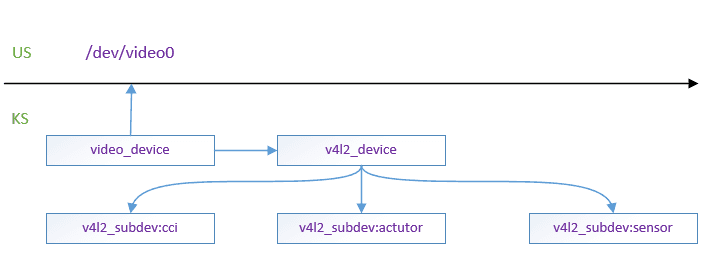
2.4 creation of session
- 1. Initialization of global session queue
struct msm_queue_head {
struct list_head list;
spinlock_t lock;
int len;
int max;
};
static struct msm_queue_head *msm_session_q;
static int msm_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
···
//Request memory
msm_session_q = kzalloc(sizeof(*msm_session_q), GFP_KERNEL);
//initialization
msm_init_queue(msm_session_q);
···
}
In msm_probe, MSM_ session_ The Q queue will request memory and then initialize.
- 2. Creation of session
int msm_create_session(unsigned int session_id, struct video_device *vdev)
{
struct msm_session *session = NULL;
//Judge msm_session_q is the queue empty
if (!msm_session_q) {
pr_err("%s : session queue not available Line %d\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -ENODEV;
}
//According to session_id to find whether the current session is in the global session queue
session = msm_queue_find(msm_session_q, struct msm_session,
list, __msm_queue_find_session, &session_id);
//If the session already exists, return directly
if (session) {
pr_err("%s: Session exist session_id=%d\n",
__func__, session_id);
return -EINVAL;
}
//Request memory space
session = kzalloc(sizeof(*session), GFP_KERNEL);
//Assignment session_id
session->session_id = session_id;
//Assign video_device device
session->event_q.vdev = vdev;
//Initialize cmd queue
msm_init_queue(&session->command_ack_q);
//Initial stream queue
msm_init_queue(&session->stream_q);
//Queue: add the new session to the global queue msm_session_q
msm_enqueue(msm_session_q, &session->list);
mutex_init(&session->lock);
mutex_init(&session->lock_q);
mutex_init(&session->close_lock);
rwlock_init(&session->stream_rwlock);
return 0;
}
- Video is maintained in a session_ Device, create cmd queue and stream queue at the same time, and finally add the session to the global queue msm_session_q for management, as shown in the figure below:
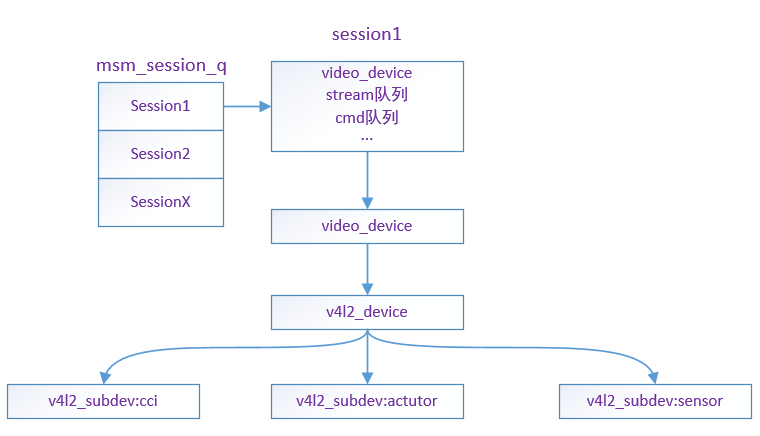
The session creation process was described in the previous article:
rc = msm_create_session(pvdev->vdev->num, pvdev->vdev);
The first parameter here is session_ id = pvdev->vdev->num;
That is, it corresponds to 1 and 2 in our video1/video2;
session_id = 1 or 2
Stay Hungry,Stay Foolish!