Android Advanced UI Components
1. Progress Bar ProgressBar
ProgressBar , a progress bar, which is divided into a long bar (to determine the time-consuming operation) and a circular bar (to determine the time-consuming operation). The default style is a circular progress bar.
Examples of use:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/indeterminateBar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
-
To use a bar progress bar:
-
Set the style property: style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
-
Set progress bar: android:progress="25"
A bar bar representing 25% of the current progress.
<ProgressBar android:id="@+id/determinateBar" style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:progress="25"/>By default, the progress bar has a maximum value of 100 and can be modified through the android:max property.
-
-
Basic use: Detect whether a time-consuming operation is completed in another thread, and update the progress bar when it is not completed; Hide the progress bar when finished.
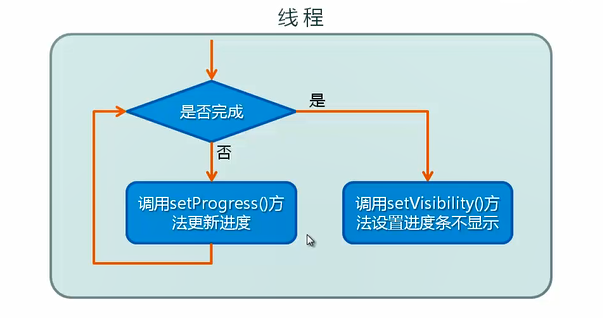
-
Since Android does not support updating UI components in the main thread, the update progress bar uses the Handle object provided by Android to send messages and update the UI
Give an example:
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.logging.LogRecord;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ProgressBar horizonP; //Horizontal progress bar
private int mProgressStatus = 0; //Progress towards completion
private Handler mHandler; //Declare an object of the Handler class used to process messages
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN); //Set Full Screen Display
horizonP = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progressBar1); //Get Horizontal Progress Bar
mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == 0x111) {
horizonP.setProgress(mProgressStatus); //Update Progress
} else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Time-consuming operation completed", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
horizonP.setVisibility(View.GONE); //Set the progress bar to not display and take up no space
}
}
};
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
mProgressStatus = doWork(); //Get the percentage of completed time-consuming operations
Message m = new Message();
if (mProgressStatus < 100) {
m.what = 0x111;
mHandler.sendMessage(m); //Send information
} else {
m.what = 0x110;
mHandler.sendMessage(m); //send message
break;
}
}
}
//Simulate a time-consuming operation
private int doWork() {
mProgressStatus += Math.random() * 10; //Change completion progress
try {
Thread.sleep(200); //Thread sleeps 200 milliseconds
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return mProgressStatus; //Return to new progress
}
}).start(); //Open a thread
}
}
2. Drag Bar SeekBar
SeekBar , the drag bar, is a subclass of ProgressBar.
In addition to inherited properties, there is a special property:
-
android:thumb
Set the style of the "small dot" on the drag bar.
Examples of use:
<SeekBar
android:id="@+id/seekbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="255"
android:progress="255"
/>
- You can set SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener To monitor progress bar changes.
Give an example:
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.SeekBar;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ImageView image; //Define Pictures
private SeekBar seekBar; //Define Drag Bar
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); //Get Pictures
seekBar = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekbar); //Get Drag Bar
//Set up listening events for drag bars
seekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(new SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener() {
// Trigger this method when the slider position of the drag bar changes
@Override
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar arg0, int progress,
boolean fromUser) {
// Change the transparency of the picture dynamically
image.setImageAlpha(progress);
}
@Override
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar bar) {
// Execute when starting touch
}
@Override
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar bar) {
// Execute when stopping touch
}
});
}
}
3. Star Rating Bar
RatingBar , Star Rating Bar, also a subclass of ProgressBar, requires component width to be set to wrap_content.
Main attributes:
| attribute | Explain |
|---|---|
| android:isIndicator | Is it non-interactive, value true or false |
| android:numStars | Number of stars |
| android:rating | Set ratings |
| android:stepSize | Rating step, default 0.5, so half a star can be selected |
Examples of use:
<!-- Star rating bar -->
<RatingBar
android:id="@+id/ratingBar1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:numStars="5"
android:rating="0"
android:layout_above="@+id/btn"
android:layout_marginBottom="60dp"/>
-
You can use <RatingBar> in Java. SetRatting (<int ratting>) or <RatingBar>. GetRatting (<int ratting>) to set or get the current rating.
-
Use <RatingBar>. SetOnRatingBarChangeListener () to set listening.
4. Display Image Component ImageView
ImageView To display the image.
Examples of use:
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/my_image"
android:contentDescription="@string/my_image_description"
/>
</LinearLayout>
Common properties:
| attribute | Explain |
|---|---|
| android:maxHeight | Maximum height |
| android:maxWidth | Maximum width |
| android:adjustViewBounds | Set to keep the aspect ratio of the picture and adjust the boundary of the View. For the maxHeight and maxWidth properties to take effect, they need to be set to true |
| android:scaleType | Controls how pictures fit into the size of ImageView |
| android:src | Set up picture resources |
| android:tint | Coloring the image |
5. Image Switch Display ImageSwitcher
ImageSwitcher To switch display pictures.
Examples of use:
<ImageSwitcher
android:id="@+id/imageswitcher"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
-
Set up Factory for ImageSwicher (used to make ImageView for ImageSwicher): <imageSwitcher>. SetFactory()
-
Set up a touch monitor for ImageSwicher: imageSwitcher.setOnTouchListener()
-
Set picture resources: <imageSwitcher>. SetImageRecource (<int RecourceID>)
Example: Implement an album (slide to switch pictures)
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.ImageSwitcher;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private int[] arrayPictures = new int[]{R.mipmap.img01, R.mipmap.img02, R.mipmap.img03,
R.mipmap.img04, R.mipmap.img05, R.mipmap.img06,
R.mipmap.img07, R.mipmap.img08, R.mipmap.img09,
};// Declare and initialize an array to hold the image ID to be displayed
private ImageSwitcher imageSwitcher; // Declare an image switcher object
//Index of the picture to be displayed in the picture array
private int pictutureIndex;
//X-coordinate of finger press while sliding left and right
private float touchDownX;
//X-coordinate of finger release when sliding left and right
private float touchUpX;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);//Set Full Screen Display
imageSwitcher = (ImageSwitcher) findViewById(R.id.imageswitcher); // Get Image Switcher
//Set up a Factory for ImageSwicher to make ImageView for ImageSwicher
imageSwitcher.setFactory(new ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory() {
@Override
public View makeView() {
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(MainActivity.this); // Instantiate an object of the ImageView class
imageView.setImageResource(arrayPictures[pictutureIndex]);//Load default display pictures based on id
return imageView; // Return imageView object
}
});
imageSwitcher.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
//Get the X-coordinate of your finger as you slide left and right
touchDownX = event.getX();
return true;
} else if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
//Get the X coordinate of your finger as you slide left and right
touchUpX = event.getX();
//From left to right, look at the next one
if (touchUpX - touchDownX > 100) {
//Get the index of the current picture you want to see
pictutureIndex = pictutureIndex == 0 ? arrayPictures.length - 1 : pictutureIndex - 1;
//Set animation for picture switching
imageSwitcher.setInAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.slide_in_left));
imageSwitcher.setOutAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.slide_out_right));
//Set the current picture to see
imageSwitcher.setImageResource(arrayPictures[pictutureIndex]);
//From right to left, look at the previous one
} else if (touchDownX - touchUpX > 100) {
//Get the current image index to see
pictutureIndex = pictutureIndex == arrayPictures.length - 1 ? 0 : pictutureIndex + 1;
//Set toggle animation
imageSwitcher.setOutAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.slide_out_left));
imageSwitcher.setInAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.slide_in_right));
//Set Pictures to View
imageSwitcher.setImageResource(arrayPictures[pictutureIndex]);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
});
}
}
6. GridView component GridView
GridView , which displays components in a grid, where data is passed to the UI interface through the Adapter, and styles are configured through a separate layout file
Adapter: An adapter is an important bridge between back-end data and UI interfaces, complex to set up a View for each data in a dataset.
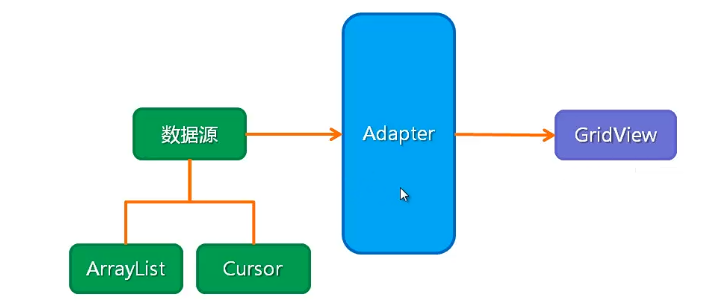
Common Adapter s:
-
ArrayAdapter
Array adapter that wraps multiple values of an array into multiple list items and displays only one line of text
-
SmipleAdapter
A simple adapter that wraps multiple values of a List into a list item to customize effects
-
SimpleCursorAdapter
Package data from a database into a list item
-
BaseAdapter
Base adapter, powerful customization
GirdView main properties:
| attribute | Explain |
|---|---|
| android:columnWidth | Column Width |
| android:gravity | Placement within each cell |
| android:horizontalSpacing | Horizontal spacing |
| android:numColumns | Number of columns |
| android:verticalSpacing | Vertical spacing |
| android:stretchMode | Extension Method |
Examples of use:
<!--Grid Layout-->
<GridView
android:id="@+id/gridView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:columnWidth="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:numColumns="auto_fit"
android:stretchMode="columnWidth"
android:verticalSpacing="5dp">
- <GridView>. SetAdapter (<Adapter adapter>): Set Adapter
Give an example:
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.GridView;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
//Picture Array Displayed
private Integer[] picture = {R.mipmap.img01, R.mipmap.img02, R.mipmap.img03,
R.mipmap.img04, R.mipmap.img05, R.mipmap.img06, R.mipmap.img07,
R.mipmap.img08, R.mipmap.img09, R.mipmap.img10, R.mipmap.img11,
R.mipmap.img12,};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
GridView gridView= (GridView) findViewById(R.id.gridView); //Get the GridView component in the layout file
gridView.setAdapter(new ImageAdapter(this)); //Call ImageAdapter
}
//Create ImageAdapter
public class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private Context mContext; //Get Context
public ImageAdapter(Context c){
mContext=c;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return picture.length;//Length of picture array
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ImageView imageView;
if(convertView==null){ //Determine if the value passed in is empty
imageView=new ImageView(mContext); //Create ImageView Component
imageView.setLayoutParams(new GridView.LayoutParams(100, 90)); //Set width and height for components
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER_CROP); //Select Picture Layout
}else{
imageView= (ImageView) convertView;
}
imageView.setImageResource(picture[position]); //Place the captured pictures in the ImageView component
return imageView; //Return to ImageView
}
}
}
7. Drop-down list box Spinner
Spinner To display a drop-down list.
Examples of use:
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/planets_spinner"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
You can use the array resource file xml to define the data to populate in this drop-down list. Create a new array under res/values. An xml file with the following examples:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string-array name="planets_array">
<item>Mercury</item>
<item>Venus</item>
<item>Earth</item>
<item>Mars</item>
<item>Jupiter</item>
<item>Saturn</item>
<item>Uranus</item>
<item>Neptune</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
Then set the property android:entries to array/planets_arra is fine.
You can also set it in Java code through the Adapter
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.Spinner;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Spinner spinner = (Spinner) findViewById(R.id.spinner); //Get drop-down list
/****************Specify list items for the selection list box by specifying an adapter**************/
// Method One
// String[] ctype=new String[]{All','Movie','Book','Record','Minor','User','Group','Group Chat','Game','Activity'}
// ArrayAdapter<String> adapter=new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item,ctype);
// Method 2
// ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(
// This, R.array. Ctype, android. R.layout. Simple_ Dropdown_ Item_ 1line; // Create an adapter
//
// adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); // Set the option style for the adapter when the list box drops down
// Spinner. SetAdapter; // Associate the adapter with the selection list box
/***************************************************************************/
//Create listening events for the drop-down list
spinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
String result = parent.getItemAtPosition(position).toString(); //Get the value of the selection
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,result,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); //Show selected values
}
@Override
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) {
}
});
}
}
8. List View ListView
ListView , list display.
Examples of use:
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
-
List items can be specified through the andoroid:entries property
-
You can also use the adapter: <ListView>. SetAdapter()
Give an example:
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ListView listview = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview); // Get List View
int[] imageId = new int[]{R.mipmap.img01, R.mipmap.img02, R.mipmap.img03,
R.mipmap.img04, R.mipmap.img05, R.mipmap.img06,
R.mipmap.img07, R.mipmap.img08, R.mipmap.img09,
}; // Define and initialize an array to save the picture id
String[] title = new String[]{"Liu Yi", "Chen Er", "Zhang San", "Li Si", "King Five",
"Zhao Six", "Sun Qi", "Week Eighth", "Wu Jiu"}; // Define and initialize an array to hold list item text
List<Map<String, Object>> listItems = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>(); // Create a list collection
// Put the picture id and list item text into the Map through a for loop and add them to the list collection
for (int i = 0; i < imageId.length; i++) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // Instantiate Map Objects
map.put("image", imageId[i]);
map.put("Name", title[i]);
listItems.add(map); // Add a map object to the List collection
}
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, listItems,
R.layout.main, new String[] { "Name", "image" }, new int[] {
R.id.title, R.id.image }); // Create SimpleAdapter
listview.setAdapter(adapter); // Associate Adapter with ListView
listview.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
Map<String, Object> map = ( Map<String, Object> )parent.getItemAtPosition(position); //Get the value of the selection
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,map.get("Name").toString(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
9. ScrollView ScrollView
ScrollVView , scroll view, scroll vertically (horizontal use: HorizontalScrollView).
Examples of use:
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
andorid:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ScrollView>
- There can only be one subtag inside, so when multiple components are needed, they need to be nested using the layout Layout.
Give an example:
package com.mingrisoft;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
LinearLayout linearLayout, linearLayout2;//Define linearLayout as the default layout manager and linearLayout 2 as the new layout manager
ScrollView scrollView;//Define Scroll View Components
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
linearLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll);//Get Layout Manager
linearLayout2 = new LinearLayout(MainActivity.this);//Create a new layout manager
linearLayout2.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);//Set to Vertical Arrangement
scrollView = new ScrollView(MainActivity.this);//Create Scroll View Component
scrollView.addView(linearLayout2);//Add New Layout to Scroll View Component
linearLayout.addView(scrollView);//Add Scroll View Component to Default Layout
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(MainActivity.this);//Create ImageView Component
imageView.setImageResource(R.mipmap.cidian);//ImagView Add Picture
TextView textView = new TextView(MainActivity.this);//Create TextView Component
textView.setText(R.string.cidian);//TextView Add Text
linearLayout2.addView(imageView);//Add ImageView component to new layout
linearLayout2.addView(textView);//Add TextView Component to New Layout
}
}
- <ScrollView>. AddView(): Add Layout
10. Tabs
More tabs.
Add steps:
-
Add TabHost, TabWidget, TabContent (using FrameLayout) components to the layout file.
-
TabHost's ID uses a fixed value: @android:id/tabhost
-
Add LinearLayout Layout Layout Manager to <TabHost> to add TabWidget, TabContent.
-
In LinearLayout Layout Layout management, add a TabWidget with a fixed value for id: @android:id/tabs
-
In LinearLayout Layout Layout Layout Management, add the FrameLayout Layout Layout Manager with a fixed value for id: @android:id/tabcontent
Examples of use:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@android:id/tabhost" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.mingrisoft.MainActivity"> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TabWidget android:id="@android:id/tabs" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <FrameLayout android:id="@android:id/tabcontent" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> </FrameLayout> </LinearLayout> </TabHost>
-
-
Write layout files for each tab.
-
Gets and initializes the TabHost component.
-
Get TabHost:
tabHost = (TabHost) findViewById(android.R.id.tabhost);//Get TabHost Object
-
Initialize TabHost:
tabHost.setup();//Initialize TabHost component
-
-
Add a tab to the TabHost object.
-
Declare the LayoutInflater object and load the layout resources:
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this); // Declare and instantiate a LayoutInflater object inflater.inflate(<Layout Resources id,as R.layout.tab1>, tabHost.getTabContentView());
-
Add Tab
<tabHost>.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("<tab Normalized name, not empty, such as t>") .setIndicator("<Label Name>") .setContent(<layout id,as R.id.liL1>));
-