Personal blog
Working process of four major components
Four components: Activity, Service, BroadcastReceiver, ContentProvider
Operation status of four major components
In addition to the BroadcastReceiver, the other three components of Android must be registered in the Android manifest. For BroadcastReceiver, you can register either in Android manifest or through code. In terms of calling method, Activity, Service and BroadcastReceiver all need to use Intent, while ContentProvider does not.
Activity is a presentation component. The start of activity is triggered by Intent, which can be divided into display Intent and implicit Intent.
Service is a computational component, which has two states: startup state and binding state. Although the service runs in the background, it itself runs in the main thread.
BroadcastReceiver is a message component. There are two kinds of registration: static registration and dynamic registration.
ContentProvider is a data sharing component. Its internal needs to realize the four operations of adding, deleting, modifying and querying. These four methods need to deal with thread synchronization.
Working process of Activity
Starting from the startActivity method of Activity, there are several overloads of startActivity method, but the startActivityForResult method will be called eventually
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
this.startActivity(intent, null);
}
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}The startActivityForResult method is implemented as follows:
public void startActivityForResult(@RequiresPermission Intent intent, int requestCode,
@Nullable Bundle options) {
if (mParent == null) {
options = transferSpringboardActivityOptions(options);
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode, ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
if (requestCode >= 0) {
// If this start is requesting a result, we can avoid making
// the activity visible until the result is received. Setting
// this code during onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) or onResume() will keep the
// activity hidden during this time, to avoid flickering.
// This can only be done when a result is requested because
// that guarantees we will get information back when the
// activity is finished, no matter what happens to it.
mStartedActivity = true;
}
cancelInputsAndStartExitTransition(options);
// TODO Consider clearing/flushing other event sources and events for child windows.
} else {
if (options != null) {
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this method for compatibility with
// existing applications that may have overridden it.
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode);
}
}
}In the branch with mParent == null, the execStartActivity method of Instrumentation will be called
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
//...
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);
int result = ActivityManager.getService()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}As you can see, ActivityManager.getService() is a singleton, and it returns a Binder object.
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};The final start Activity is implemented by the startActivity method of the ActivityManagerService.
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, bOptions,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = mUserController.handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(),
userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, "startActivityAsUser");
}The start of Activity is transferred to the startActivityMayWait method of ActivityStarter
final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, WaitResult outResult,
Configuration globalConfig, Bundle bOptions, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, int userId,
TaskRecord inTask, String reason) {
//...
final ActivityRecord[] outRecord = new ActivityRecord[1];
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid,
callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, outRecord, inTask,
reason);
//...
}
}The startActivityMayWait method calls the startActivityLocked method
int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, Intent ephemeralIntent,
String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, ResolveInfo rInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags,
ActivityOptions options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity, TaskRecord inTask, String reason) {
//...
mLastStartActivityResult = startActivity(caller, intent, ephemeralIntent, resolvedType,
aInfo, rInfo, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode,
callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags,
options, ignoreTargetSecurity, componentSpecified, mLastStartActivityRecord,
inTask);
//...
}startActivity method is called in startActivityLocked method, and doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked method is called in startActivity method
final void doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked(boolean doResume) {
while (!mPendingActivityLaunches.isEmpty()) {
final PendingActivityLaunch pal = mPendingActivityLaunches.remove(0);
final boolean resume = doResume && mPendingActivityLaunches.isEmpty();
try {
startActivity(pal.r, pal.sourceRecord, null, null, pal.startFlags, resume, null,
null, null /*outRecords*/);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Exception during pending activity launch pal=" + pal, e);
pal.sendErrorResult(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
private int startActivity(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {
int result = START_CANCELED;
try {
mService.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
result = startActivityUnchecked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor,
startFlags, doResume, options, inTask, outActivity);
} finally {
// If we are not able to proceed, disassociate the activity from the task. Leaving an
// activity in an incomplete state can lead to issues, such as performing operations
// without a window container.
if (!ActivityManager.isStartResultSuccessful(result)
&& mStartActivity.getTask() != null) {
mStartActivity.getTask().removeActivity(mStartActivity);
}
mService.mWindowManager.continueSurfaceLayout();
}
postStartActivityProcessing(r, result, mSupervisor.getLastStack().mStackId, mSourceRecord,
mTargetStack);
return result;
}startActivity calls the startActivityUnchecked method
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask,
ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {
//...
if (dontStart) {
topStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
if (mDoResume) {
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
//...
}
//...
}startActivityUnchecked calls the resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked method in the ActivityStackSupervisor
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked() {
return resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(null, null, null);
}
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target, ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
if (!readyToResume()) {
return false;
}
if (targetStack != null && isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {
return targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
}
final ActivityRecord r = mFocusedStack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (r == null || r.state != RESUMED) {
mFocusedStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(null, null);
} else if (r.state == RESUMED) {
// Kick off any lingering app transitions form the MoveTaskToFront operation.
mFocusedStack.executeAppTransition(targetOptions);
}
return false;
}resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked called resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked method of ActivityStack
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
if (mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = true;
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
} finally {
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = false;
}
// When resuming the top activity, it may be necessary to pause the top activity (for
// example, returning to the lock screen. We suppress the normal pause logic in
// {@link #resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked}, since the top activity is resumed at the end.
// We call the {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#checkReadyForSleepLocked} again here to ensure
// any necessary pause logic occurs. In the case where the Activity will be shown regardless
// of the lock screen, the call to {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#checkReadyForSleepLocked}
// is skipped.
final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(true /* focusableOnly */);
if (next == null || !next.canTurnScreenOn()) {
checkReadyForSleep();
}
return result;
}resumeTopActivityInnerLocked method finally calls startSpecificActivityLocked method in ActivityStackSupervisor
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options) {
//...
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
//...
}resumeTopActivityInnerLocked method calls realStartActivityLocked method
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.getStack().setLaunchTime(r);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS) == 0
|| !"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it is a platform component that is marked
// to run in multiple processes, because this is actually
// part of the framework so doesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in the process.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}In the realStartActivityLocked method, start the Activity through the thread of ProcessRecord. Thread is an iaapplicationthread type object, which is implemented as the internal class ApplicationThread in ActivityThread.
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {
//...
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global
// and override configs.
mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),
mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,
r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
//...
}public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState,
List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<ReferrerIntent> pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) {
updateProcessState(procState, false);
ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
r.token = token;
r.ident = ident;
r.intent = intent;
r.referrer = referrer;
r.voiceInteractor = voiceInteractor;
r.activityInfo = info;
r.compatInfo = compatInfo;
r.state = state;
r.persistentState = persistentState;
r.pendingResults = pendingResults;
r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents;
r.startsNotResumed = notResumed;
r.isForward = isForward;
r.profilerInfo = profilerInfo;
r.overrideConfig = overrideConfig;
updatePendingConfiguration(curConfig);
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}So far, the start of activity has been transferred to ApplicationThread. In the scheduleLaunchActivity method, a launch message, launch? Activity, is sent out.
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null, "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY");
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
//...
}
//...
}In Handler, the handleLaunchActivity method of ActivityThread is called
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) {
//...
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
reportSizeConfigurations(r);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason);
if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) {
// The activity manager actually wants this one to start out paused, because it
// needs to be visible but isn't in the foreground. We accomplish this by going
// through the normal startup (because activities expect to go through onResume()
// the first time they run, before their window is displayed), and then pausing it.
// However, in this case we do -not- need to do the full pause cycle (of freezing
// and such) because the activity manager assumes it can just retain the current
// state it has.
performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason);
// We need to keep around the original state, in case we need to be created again.
// But we only do this for pre-Honeycomb apps, which always save their state when
// pausing, so we can not have them save their state when restarting from a paused
// state. For HC and later, we want to (and can) let the state be saved as the
// normal part of stopping the activity.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
r.state = oldState;
}
}
} else {
// If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity manager to stop us.
try {
ActivityManager.getService()
.finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}In performLaunchActivity method, the creation and startup of Activity object are completed.
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
//...
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
//...
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//...
if (activity != null) {
//...
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback);
//...
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
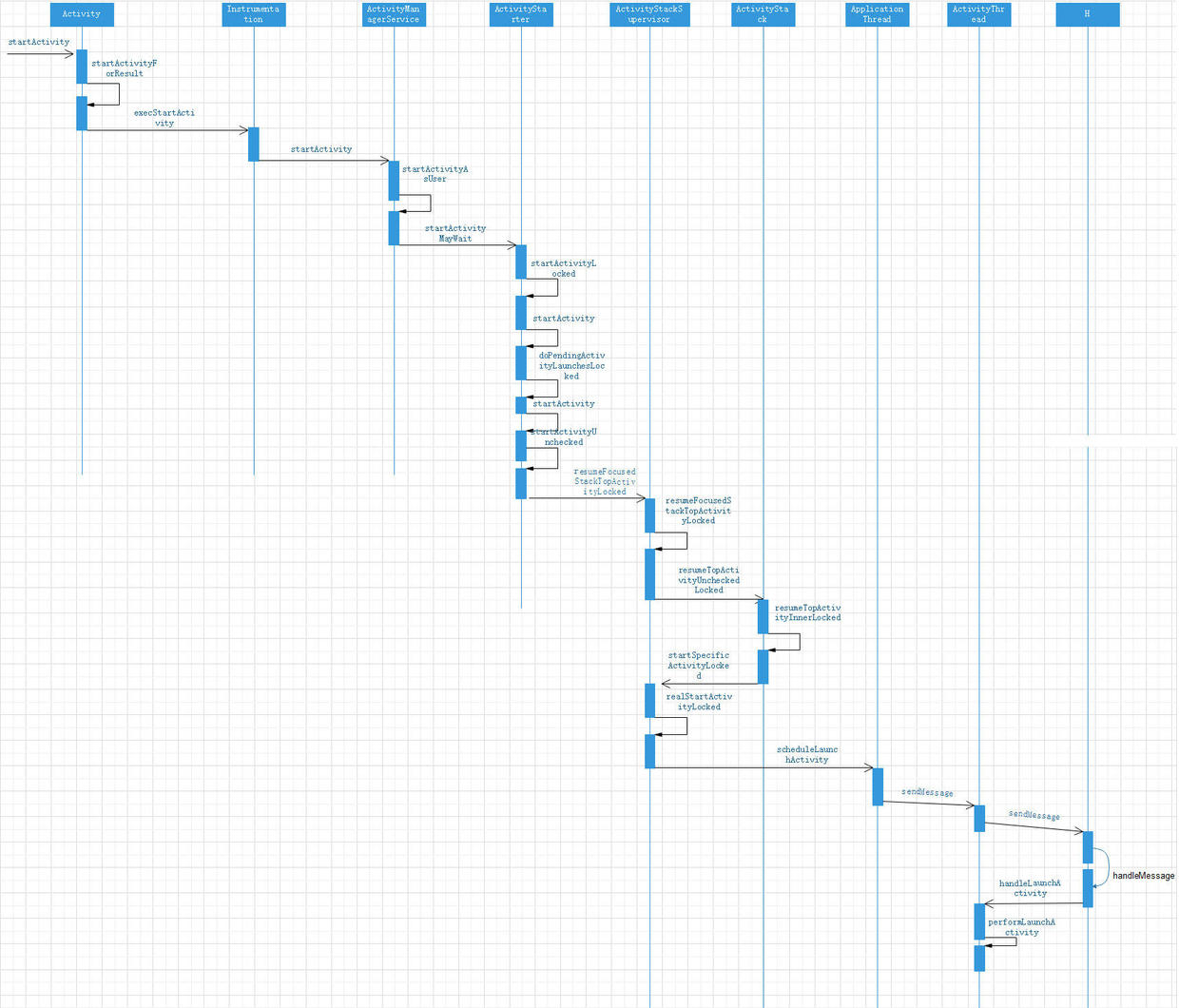
}Activity start sequence diagram
Working process of Service
Service startup process
The start of Service starts from the startService of ContextWrapper
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
return mBase.startService(service);
}The concrete type of mBase is ContextImpl. When an activity is created, it will associate a ContextImpl object through attach. The startService method calls the startServiceCommon method.
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
}The startServiceCommon object calls the startService method of ActivityManagerService, which is a remote calling process.
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
//...
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
//...
}startService method of ActivityManagerService
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
//...
}The startService method calls the startServiceLocked method of ActiveServices
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}The startServiceInnerLocked method is called in the startServiceLocked method
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
if (error != null) {
return new ComponentName("!!", error);
}
//...
}The bringUpServiceLocked method is called in startServiceInnerLocked
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
//...
}Call realStartServiceLocked method in bringUpServiceLocked
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//...
//Create Service
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
//...
//Call the start method of the Service
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
//...
}realStartServiceLocked calls the scheduleCreateService method in ApplicationThread
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}In the scheduleCreateService method, a message is sent to create the Service. The Handler processes the message of create Service and starts the Service through the handleCreateService method of ActivityThread.
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
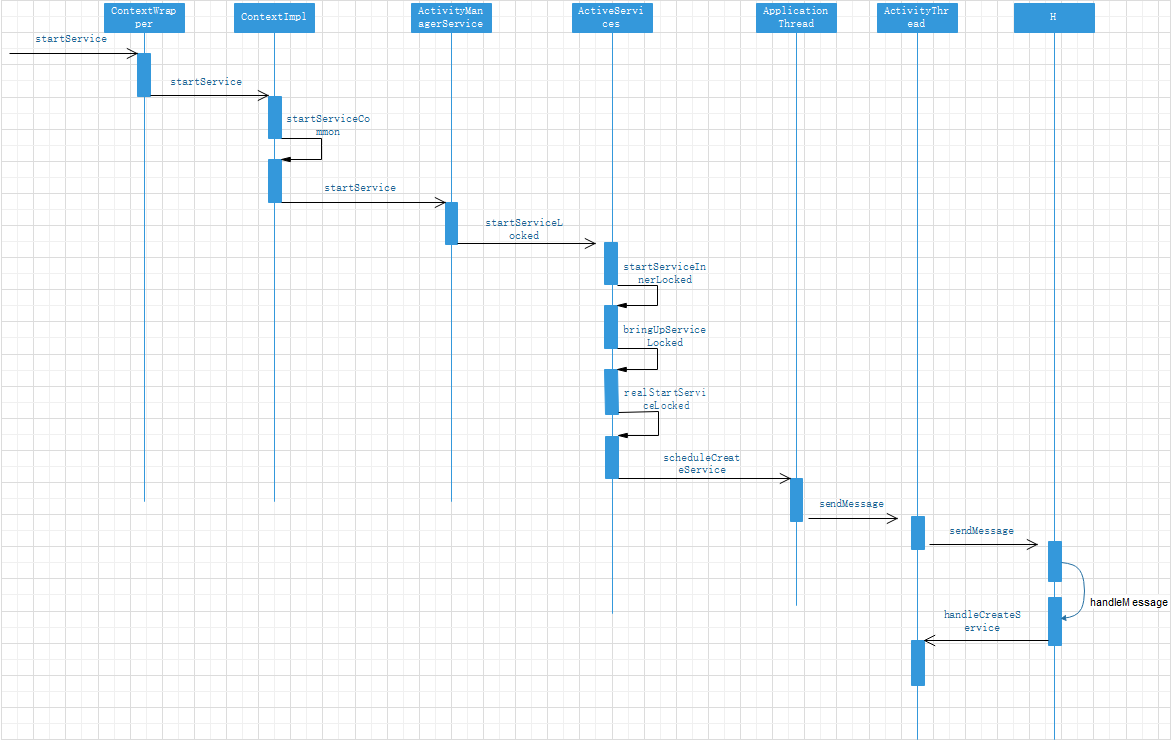
}Sequence diagram of Service startup
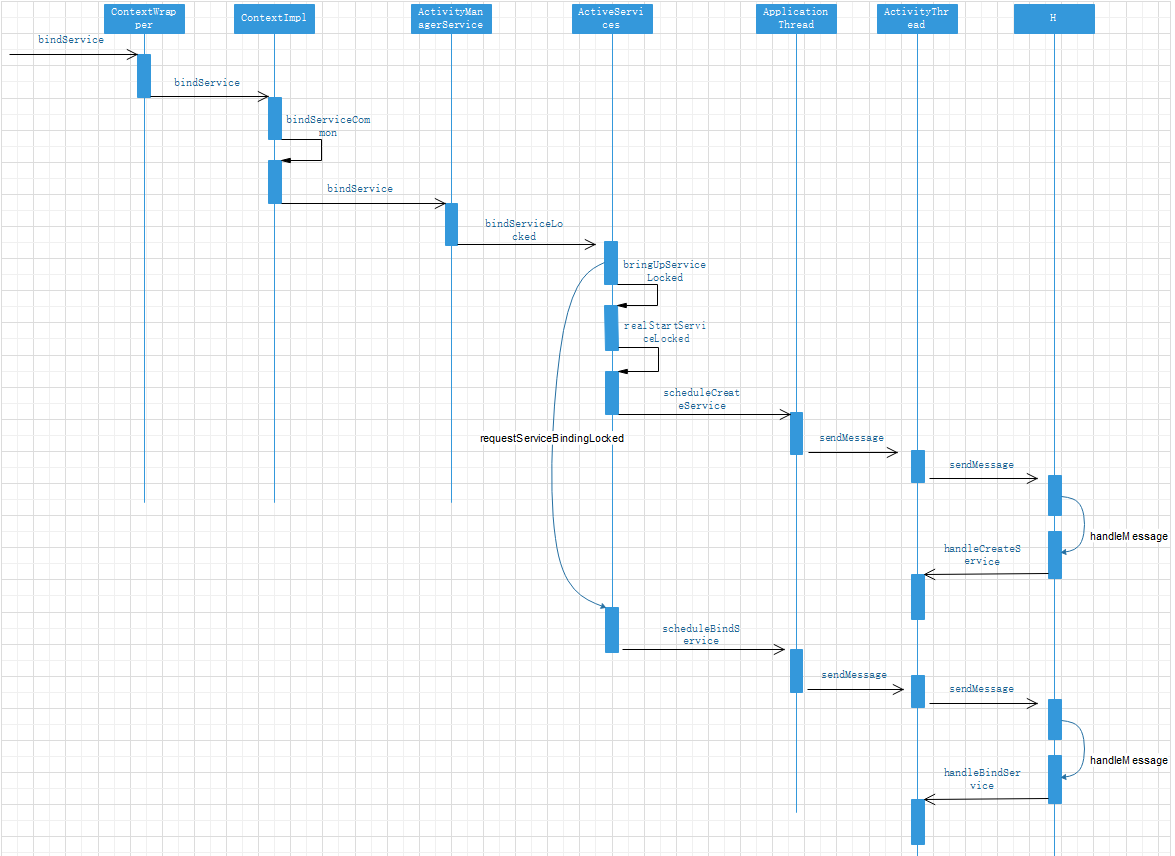
Binding process of Service
The binding of Service starts from the bindService method of ContextWrapper
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}Then call the bindService method of ContextImpl.
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(),
Process.myUserHandle());
}bindService calls bindServiceCommon method
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
//...
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
//...
}bindServiceCommon calls bindService method of ActivityManagerService
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}bindService calls bindServiceLocked method in ActiveServices
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
bringUpServiceLocked(serviceRecord,serviceIntent.getFlags(),callerFg, false, false);
//...
}bindServiceLocked calls the bringUpServiceLocked method
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
//...
}bringUpServiceLocked calls the realStartServiceLocked method. This process is the same as the previous startup process. The difference is that the Service binding process also calls the scheduleBindService method of ApplicationThread, which is in the requestServiceBindingLocked method of ActiveServices
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can't yet bind.
return false;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.d(TAG_SERVICE, "requestBind " + i + ": requested=" + i.requested
+ " rebind=" + rebind);
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r, e);
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r);
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}In the scheduleBindService method, send a message to bind the service. Call handlebindinservice method in ActivityThread
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}Binding sequence diagram of services:
Working process of BroadcastReceiver
Registration process of broadcast
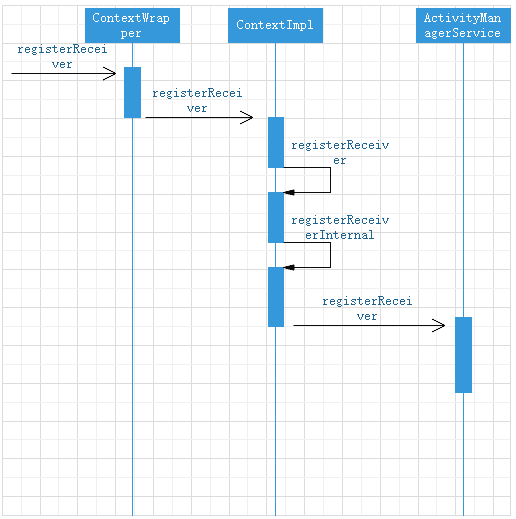
The registration of broadcast can be divided into static registration and dynamic registration, in which the system automatically completes the registration when the application is installed. Only the dynamic registration process of broadcast is analyzed here. Dynamic registration starts with the registerReceiver method of ContextWrapper
public Intent registerReceiver(
BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter) {
return mBase.registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
}registerReceiver calls registerReceiver method in ContextImpl
public Intent registerReceiver(BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter) {
return registerReceiver(receiver, filter, null, null);
}registerReceiver calls the internal registerReceiver method again
public Intent registerReceiver(BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter,
String broadcastPermission, Handler scheduler) {
return registerReceiverInternal(receiver, getUserId(),
filter, broadcastPermission, scheduler, getOuterContext(), 0);
}registerReceiver calls the registerReceiverInternal method
private Intent registerReceiverInternal(BroadcastReceiver receiver, int userId,
IntentFilter filter, String broadcastPermission,
Handler scheduler, Context context, int flags) {
//...
try {
final Intent intent = ActivityManager.getService().registerReceiver(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mBasePackageName, rd, filter,
broadcastPermission, userId, flags);
if (intent != null) {
intent.setExtrasClassLoader(getClassLoader());
intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
}
return intent;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}registerReceiverInternal called the registerReceiver method of AMS
public Intent registerReceiver(IApplicationThread caller, String callerPackage,
IIntentReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter, String permission, int userId,
int flags) {
//...
synchronized (this) {
//...
BroadcastFilter bf = new BroadcastFilter(filter, rl, callerPackage,
permission, callingUid, userId, instantApp, visibleToInstantApps);
rl.add(bf);
if (!bf.debugCheck()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "==> For Dynamic broadcast");
}
mReceiverResolver.addFilter(bf);
//...
return sticky;
}
}Broadcast sending and receiving process
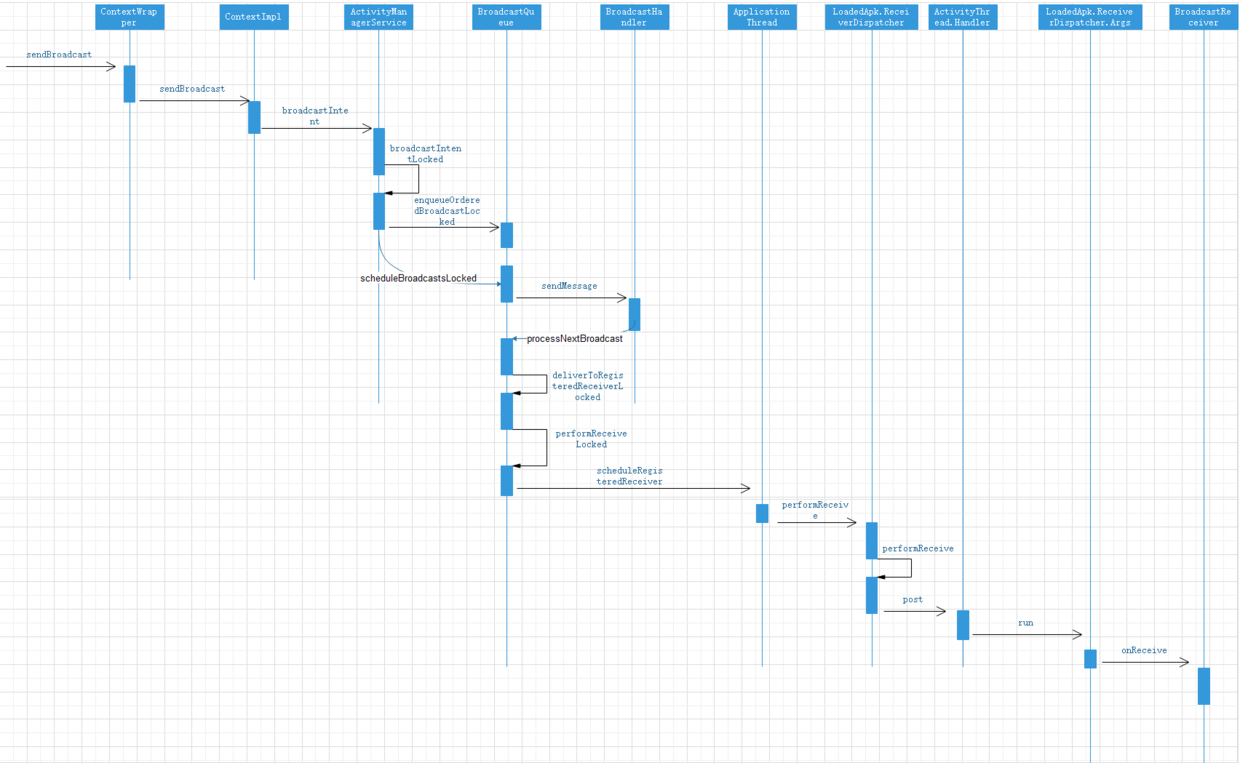
The broadcast is sent through the sendBroadcast method of ContextWrapper
public void sendBroadcast(Intent intent) {
mBase.sendBroadcast(intent);
}sendBroadcast called sendBroadcast method in ContextImpl
public void sendBroadcast(Intent intent) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
String resolvedType = intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver());
try {
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ActivityManager.getService().broadcastIntent(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), intent, resolvedType, null,
Activity.RESULT_OK, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false, false,
getUserId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}sendBroadcast called the broadcastent method of AMS
public final int broadcastIntent(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IIntentReceiver resultTo,
int resultCode, String resultData, Bundle resultExtras,
String[] requiredPermissions, int appOp, Bundle bOptions,
boolean serialized, boolean sticky, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("broadcastIntent");
synchronized(this) {
intent = verifyBroadcastLocked(intent);
final ProcessRecord callerApp = getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
int res = broadcastIntentLocked(callerApp,
callerApp != null ? callerApp.info.packageName : null,
intent, resolvedType, resultTo, resultCode, resultData, resultExtras,
requiredPermissions, appOp, bOptions, serialized, sticky,
callingPid, callingUid, userId);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return res;
}
}Broadcastentent calls the broadcastententlocked method
final int broadcastIntentLocked(ProcessRecord callerApp,
String callerPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IIntentReceiver resultTo, int resultCode, String resultData,
Bundle resultExtras, String[] requiredPermissions, int appOp, Bundle bOptions,
boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int callingPid, int callingUid, int userId) {
//...
queue.enqueueOrderedBroadcastLocked(r);
queue.scheduleBroadcastsLocked();
//...
}broadcastIntentLocked calls enqueueOrderedBroadcastLocked of BroadcastQueue to add the broadcast to the queue, and processes the broadcast in the queue through schedulebroadcastlocked of BroadcastQueue.
public void scheduleBroadcastsLocked() {
if (DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.v(TAG_BROADCAST, "Schedule broadcasts ["
+ mQueueName + "]: current="
+ mBroadcastsScheduled);
if (mBroadcastsScheduled) {
return;
}
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(BROADCAST_INTENT_MSG, this));
mBroadcastsScheduled = true;
}In the scheduleroadcastlocked method, a message of Breadcast "intent" MSG is sent through the Handler
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case BROADCAST_INTENT_MSG: {
if (DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.v(
TAG_BROADCAST, "Received BROADCAST_INTENT_MSG");
processNextBroadcast(true);
} break;
case BROADCAST_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
synchronized (mService) {
broadcastTimeoutLocked(true);
}
} break;
}
}Handle the message in the handleMessage method of the Handler, and call the processNextBroadcast method
final void processNextBroadcast(boolean fromMsg) {
//...
deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked(r, filter, r.ordered, recIdx);
//...
}processNextBroadcast method call deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked
private void deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked(BroadcastRecord r,
BroadcastFilter filter, boolean ordered, int index) {
//...
performReceiveLocked(filter.receiverList.app, filter.receiverList.receiver,
new Intent(r.intent), r.resultCode, r.resultData,
r.resultExtras, r.ordered, r.initialSticky, r.userId);
//...
}deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked calls performReceiveLocked
void performReceiveLocked(ProcessRecord app, IIntentReceiver receiver,
Intent intent, int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras,
boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser) throws RemoteException {
// Send the intent to the receiver asynchronously using one-way binder calls.
if (app != null) {
if (app.thread != null) {
// If we have an app thread, do the call through that so it is
// correctly ordered with other one-way calls.
try {
app.thread.scheduleRegisteredReceiver(receiver, intent, resultCode,
data, extras, ordered, sticky, sendingUser, app.repProcState);
// TODO: Uncomment this when (b/28322359) is fixed and we aren't getting
// DeadObjectException when the process isn't actually dead.
//} catch (DeadObjectException ex) {
// Failed to call into the process. It's dying so just let it die and move on.
// throw ex;
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Failed to call into the process. It's either dying or wedged. Kill it gently.
synchronized (mService) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Can't deliver broadcast to " + app.processName
+ " (pid " + app.pid + "). Crashing it.");
app.scheduleCrash("can't deliver broadcast");
}
throw ex;
}
} else {
// Application has died. Receiver doesn't exist.
throw new RemoteException("app.thread must not be null");
}
} else {
receiver.performReceive(intent, resultCode, data, extras, ordered,
sticky, sendingUser);
}
}performReceiveLocked calls the scheduleRegisteredReceiver method of ApplicationThread
public void scheduleRegisteredReceiver(IIntentReceiver receiver, Intent intent,
int resultCode, String dataStr, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
boolean sticky, int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
receiver.performReceive(intent, resultCode, dataStr, extras, ordered,
sticky, sendingUser);
}In the scheduleRegisteredReceiver, call the performReceive method in the ReceiverDispatcher internal class of LoadedApk
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {
LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher rd;
if (intent == null) {
Log.wtf("LoadedApk", "Null intent received");
rd = null;
} else {
rd = (LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher)this.mDispatcher.get();
}
if (rd != null) {
rd.performReceive(intent, resultCode, data, extras, ordered, sticky, sendingUser);
} else {
IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
if (extras != null) {
extras.setAllowFds(false);
}
mgr.finishReceiver(this, resultCode, data, extras, false, intent.getFlags());
} catch (RemoteException var11) {
throw var11.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}Overload of performReceive call performReceive
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data, Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {
LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher.Args args = new LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher.Args(intent, resultCode, data, extras, ordered, sticky, sendingUser);
if (intent == null) {
Log.wtf("LoadedApk", "Null intent received");
}
if ((intent == null || !this.mActivityThread.post(args)) && this.mRegistered && ordered) {
IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
args.sendFinished(mgr);
}
}performReceive calls the post method of Handler, the internal class of ActivityThread, to send the Args, which is a Runnable interface. When the Handler processes the message, it will call back the run method of Args
public void run() {
//...
receiver.onReceive(ReceiverDispatcher.this.mContext, intent);
//...
}The onReceiver method to call back the receiver in run
Timing chart of broadcast registration
Timing chart of broadcast transmission and reception
The working process of ContentProvider
When the process of ContentProvider starts, ContentProvider will start and be published to AMS at the same time. At this time, onCreate of ContentProvider will execute before onCreate of Application.
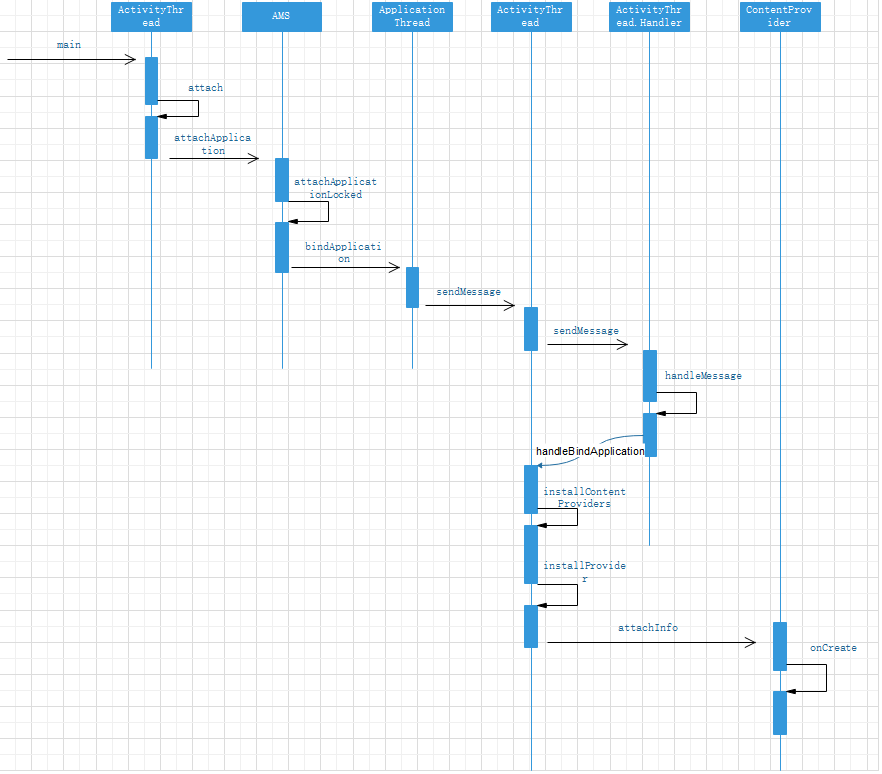
main method with ActivityThread as the entry when the application starts
public static void main(String[] args) {
//...
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}In the main method, an instance of ActivityThread is created, the attach method is called, and the Looper.loop method is called. This paper mainly analyzes the attach method.
private void attach(boolean system) {
//...
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
//...
}In attach, call the attachApplication method of AMS
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}attachApplication calls the attachApplicationLocked method
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
//...
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
//...
}attachApplicationLocked calls the bindApplication method of ApplicationThread
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial) {
if (services != null) {
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
data.buildSerial = buildSerial;
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}bindApplication sends a message to Handler
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
//...
}
}The handleBindApplication method in ActivityThread is invoked in handleMessage.
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
//...
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) {
installContentProviders(app, data.providers);
// For process that contains content providers, we want to
// ensure that the JIT is enabled "at some point".
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10*1000);
}
}
//...
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
//...
}The application instance and ContentProvider are created in handlebindinapplication, and the onCreate callback of application is after ContentProvider.
Let's look at the installContentProviders method
private void installContentProviders(
Context context, List<ProviderInfo> providers) {
final ArrayList<ContentProviderHolder> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (ProviderInfo cpi : providers) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(128);
buf.append("Pub ");
buf.append(cpi.authority);
buf.append(": ");
buf.append(cpi.name);
Log.i(TAG, buf.toString());
}
//1
ContentProviderHolder cph = installProvider(context, null, cpi,
false /*noisy*/, true /*noReleaseNeeded*/, true /*stable*/);
if (cph != null) {
cph.noReleaseNeeded = true;
results.add(cph);
}
}
try {
//2
ActivityManager.getService().publishContentProviders(
getApplicationThread(), results);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}Call the installProvider method at comment 1. Call the publishContentProviders method of AMS at annotation 2
private ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context,
ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) {
//...
localProvider = (ContentProvider)cl.
loadClass(info.name).newInstance();
provider = localProvider.getIContentProvider();
if (provider == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to instantiate class " +
info.name + " from sourceDir " +
info.applicationInfo.sourceDir);
return null;
}
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(
TAG, "Instantiating local provider " + info.name);
// XXX Need to create the correct context for this provider.
localProvider.attachInfo(c, info);
//...
}Created provider in installProvider and called attachInfo method
private void attachInfo(Context context, ProviderInfo info, boolean testing) {
mNoPerms = testing;
/*
* Only allow it to be set once, so after the content service gives
* this to us clients can't change it.
*/
if (mContext == null) {
mContext = context;
if (context != null) {
mTransport.mAppOpsManager = (AppOpsManager) context.getSystemService(
Context.APP_OPS_SERVICE);
}
mMyUid = Process.myUid();
if (info != null) {
setReadPermission(info.readPermission);
setWritePermission(info.writePermission);
setPathPermissions(info.pathPermissions);
mExported = info.exported;
mSingleUser = (info.flags & ProviderInfo.FLAG_SINGLE_USER) != 0;
setAuthorities(info.authority);
}
ContentProvider.this.onCreate();
}
}The onCreate method was invoked in attchInfo.
Look again at AMS's publishContentProviders method
public final void publishContentProviders(IApplicationThread caller,
List<ContentProviderHolder> providers) {
//...
ComponentName comp = new ComponentName(dst.info.packageName, dst.info.name);
mProviderMap.putProviderByClass(comp, dst);
String names[] = dst.info.authority.split(";");
for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) {
mProviderMap.putProviderByName(names[j], dst);
}
//...
if (wasInLaunchingProviders) {
mHandler.removeMessages(CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
}
//...
}In the publishContentProviders method, the main task is to save the provider information to the Map and remove the content provider publish timeout MSG message. Because a content? Provider? Publish? Timeout? MSG message is sent in the attachApplicationLocked method of AMS, so that the corresponding processing can be made in case of timeout.
Start sequence diagram of ContentProvider
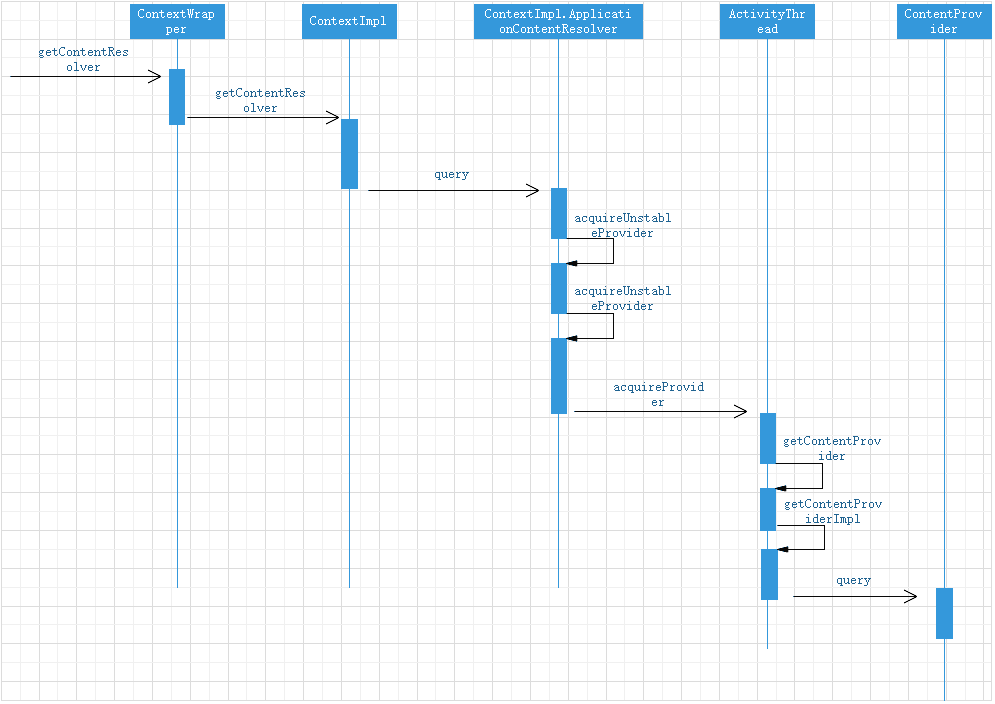
To access the ContentProvider, you need to use ContentResolver, which is an abstract class. The ContentResolver obtained through Context is actually an instance of the internal class ApplicationContentResolver in ContextImpl. When the process of ContentProvider is not started, the first access to it will trigger the creation of ContentProvider, and the process of ContentProvider will also start. Any method of adding, deleting, modifying and querying content provider will trigger the start of content provider. Here, select the query method to analyze.
The usage of ContentProvider is generally as follows:
context.getContentResolver().query()
The implementation class of context is ContextWrapper. See the getContentResolver method of ContextWrapper
public ContentResolver getContentResolver() {
return mBase.getContentResolver();
}getContentResolver calls the getContentResolver method of ContextImpl
public ContentResolver getContentResolver() {
return mContentResolver;
}mContentResolver is initialized in the constructor of ContextImpl
private ContextImpl(@Nullable ContextImpl container, @NonNull ActivityThread mainThread,
@NonNull LoadedApk packageInfo, @Nullable String splitName,
@Nullable IBinder activityToken, @Nullable UserHandle user, int flags,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//...
mContentResolver = new ApplicationContentResolver(this, mainThread, user);
//...
}ApplicationContentResolver is an internal class of ContextImpl. After instantiating ContentResolver, call query method
public final @Nullable Cursor query(final @RequiresPermission.Read @NonNull Uri uri,
@Nullable String[] projection, @Nullable Bundle queryArgs,
@Nullable CancellationSignal cancellationSignal) {
//...
IContentProvider unstableProvider = acquireUnstableProvider(uri);
//...
}In the query method, first obtain the ContentProvider through acquirenstableprovider
public final IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Uri uri) {
if (!SCHEME_CONTENT.equals(uri.getScheme())) {
return null;
}
String auth = uri.getAuthority();
if (auth != null) {
return acquireUnstableProvider(mContext, uri.getAuthority());
}
return null;
}Acquirenstableprovider calls its overloaded method acquirenstableprovider
protected IContentProvider acquireUnstableProvider(Context c, String auth) {
return this.mMainThread.acquireProvider(c, ContentProvider.getAuthorityWithoutUserId(auth), this.resolveUserIdFromAuthority(auth), false);
}Acquirenstableprovider method calls acquireProvider method of ActivityThread
public final IContentProvider acquireProvider(
Context c, String auth, int userId, boolean stable) {
final IContentProvider provider = acquireExistingProvider(c, auth, userId, stable);
if (provider != null) {
return provider;
}
// There is a possible race here. Another thread may try to acquire
// the same provider at the same time. When this happens, we want to ensure
// that the first one wins.
// Note that we cannot hold the lock while acquiring and installing the
// provider since it might take a long time to run and it could also potentially
// be re-entrant in the case where the provider is in the same process.
ContentProviderHolder holder = null;
try {
holder = ActivityManager.getService().getContentProvider(
getApplicationThread(), auth, userId, stable);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
if (holder == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to find provider info for " + auth);
return null;
}
// Install provider will increment the reference count for us, and break
// any ties in the race.
holder = installProvider(c, holder, holder.info,
true /*noisy*/, holder.noReleaseNeeded, stable);
return holder.provider;
}If the ContentProvider has been cached, the return is obtained directly. If there is no cache, get it through the getContentProvider method of AMS
public final ContentProviderHolder getContentProvider(
IApplicationThread caller, String name, int userId, boolean stable) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("getContentProvider");
if (caller == null) {
String msg = "null IApplicationThread when getting content provider "
+ name;
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
throw new SecurityException(msg);
}
// The incoming user check is now handled in checkContentProviderPermissionLocked() to deal
// with cross-user grant.
return getContentProviderImpl(caller, name, null, stable, userId);
}ContentProviderHolder calls getContentProviderImpl method to get contentrecoverholder
After obtaining the Provider, the query method of ContentProvider will be called. This method needs to be implemented when we customize ContentProvider. The code switches to the ContentProvider we defined.
Query sequence diagram of ContentProvider