Android Gradle plug-in development - release and integration
This article describes how to package and publish third-party libraries together
In some cases, we need to merge the jar package that the project depends on into the jar package of our own project. The jar that comes out is called fat jar. The method I use requires the shadow plug-in
shadow plug-in documentation: https://imperceptiblethoughts.com/shadow/introduction/
I downloaded apktool for convenience here_ 2.5.0. Jar is ready to be merged into the final released plug-in jar package
1. Integrate the shadow plug-in into the plugin module
Please find the corresponding relationship between shadow version and gradle version here https://github.com/johnrengelman/shadow/releases
The following is the build of the plugin module Gradle configuration
import com.github.jengelman.gradle.plugins.shadow.tasks.ConfigureShadowRelocation
plugins {
id 'groovy'
id 'java'
id 'maven-publish'
//shadow corresponds to gradle
//My gradle 6.5, so I use shadow 6.1.0
id 'com.github.johnrengelman.shadow' version '6.1.0'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: "libs", include: ["*.jar", "*.aar"])
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.6.0'
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.7.0'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.7.0'
//kotlin
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:$kotlin_version"
//In order to prevent the problem of inconsistent groovy versions, you can change to the following to let gradle automatically obtain the local groovy version
implementation localGroovy()
//Because the gradle dependency is used, it needs to be in the project build Add a dependency of gradle to the gradle script file:
implementation gradleApi()
//Reference android gradle extension library
implementation 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.0.1'
}
publishing {
//Configure POM
publications {
maven(MavenPublication) {
groupId = 'com.test'
artifactId = 'plugin'
version = '1.0.2-SNAPSHOT'
artifact shadowJar
}
}
//Publish to local e disk
repositories {
maven {
name = "file"
url = "E://reps"
}
}
}
task relocateShadowJar(type: ConfigureShadowRelocation) {
target = tasks.shadowJar
}
tasks.shadowJar.dependsOn tasks.relocateShadowJar
shadowJar {
//Use default classification
archiveClassifier.set(null)
//Configure dependencies that need to be packaged together
Configuration configuration = project.configurations.create("apktoolDependcy")
configuration.defaultDependencies { dependencies ->
dependencies.add(project.dependencies.create(fileTree(dir: "libs", include: ["*.jar", "*.aar"])))
}
configurations = [configuration]
//Allows you to build zip files containing more than 65535 files or larger than 4GB
zip64 true
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}be careful
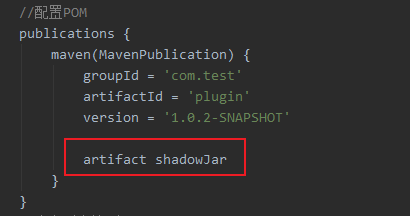
artifact shadowJar # means that publishing those artifacts is controlled by the shadowJar task
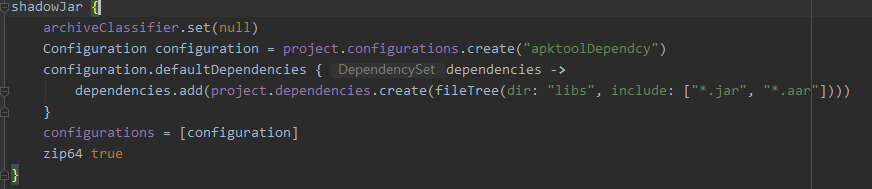
archiveClassifier.set(null) indicates that the default classification is used
Default category reference
classpath "com.test:plugin:1.0.1-SNAPSHOT"
Other category references
archiveClassifier.set("xxx")
classpath "com.test:plugin:1.0.1-SNAPSHOT:xxx"
Configure dependencies that need to be packaged together
Configuration configuration = project.configurations.create("apktoolDependcy")
configuration.defaultDependencies { dependencies ->
dependencies.add(project.dependencies.create(fileTree(dir: "libs", include: ["*.jar", "*.aar"])))
}
configurations = [configuration]3. Configuration relocation of gradle plug-in
In some cases, writing a Gradle plug-in may cause problems because your plug-in may conflict with the version of the same dependency provided by the Gradle runtime. If this is the case, you can use Shadow to relocate your dependencies to different package names to avoid conflicts. It may not be well understood. Look at the picture below
Non emphasis bit

Relocation added
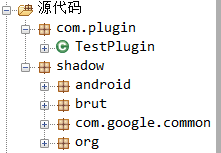
Therefore, the emphasis positioning will put the jar package under your libs under the shadow package, so that it will not conflict with the dependencies introduced by gradle
Relocation needs to be introduced in three places
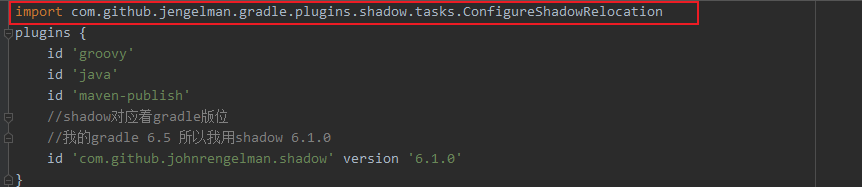
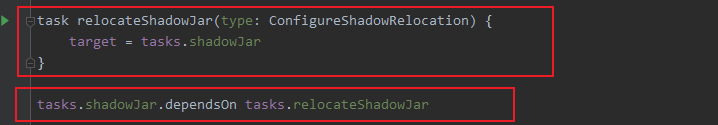
4. Publish fat jar
After configuration, we modify the TestPlugin class to print apktool_ 2.5.0. Androlib class under jar package
package com.plugin
import brut.androlib.Androlib
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
/**
* Plug in entry
*/
class TestPlugin implements Plugin<Project> {
@Override
void apply(Project project) {
println "${Androlib.class.name} find apktool class"
println "Test Plugin Start"
}
}Click the gradle button in the right column of Android studio
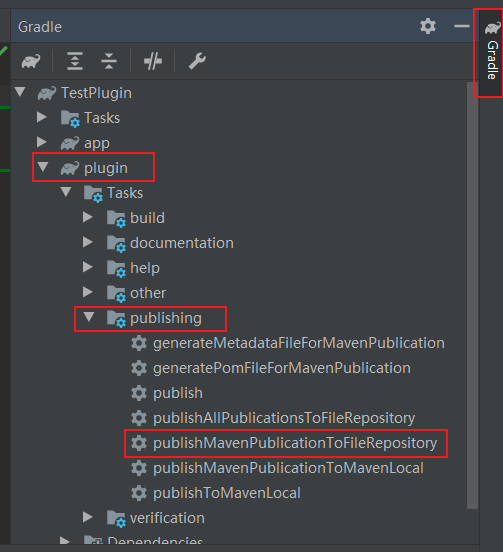
Click publish maven publicatintofilerepository to publish the plug-in to the local disk
5. Test fat jar
Integrate the plug-in according to the method in the previous article, and click the synchronize gradle button to output the log
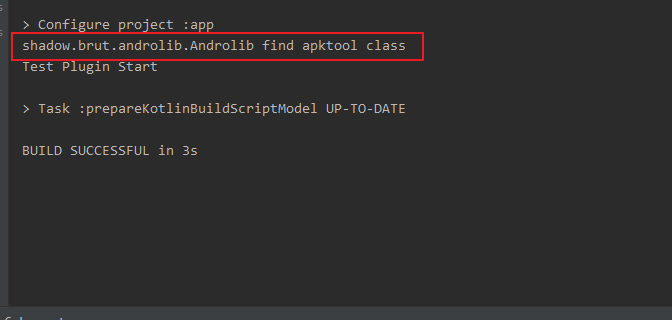
At this point, fat jar release and testing are complete