Socket plays a very important role in Android network programming.
Basic Concept of Socket
Socket is the middle software abstraction layer of communication between application layer and TCP/IP protocol family, which is represented as a programming interface (API) encapsulating TCP/IP protocol family.
From the point of view of design pattern, Socket is actually a facade pattern. It hides the complex TCP/IP protocol family behind Socket interface. For users, a simple set of interfaces is all, allowing Socket to organize data to conform to the specified protocol.
Borrowed from the following online structure chart: 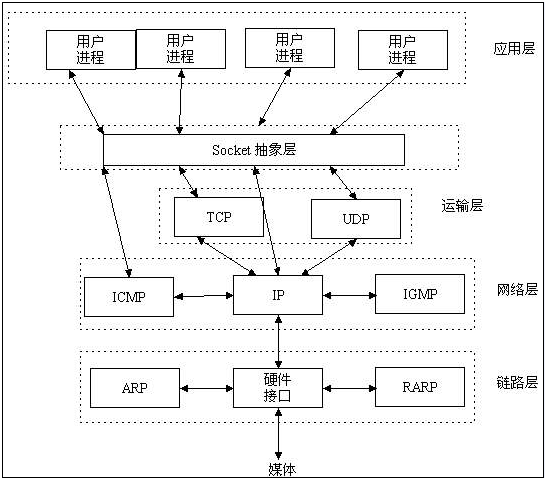
IP addresses and port numbers make up Socket s, which appear in pairs.
Socket ={(IP address 1:PORT port number), (IP address 2:PORT port number)}Single Socke does not have any effect. Data transmission can only be carried out by Socket programming based on a certain protocol (TCP or UDP).
Socket workflow

The server initializes the Socket first, then binds with the port, listens on the port, calls accept to block, and waits for the client to connect.
The client initializes a socket and connects to the server. If the connection is successful, the connection between the client and the server is established.
The client sends the data request, the server receives the request and processes the request, then sends the response data to the client, the client reads the data, finally closes the data, and the interaction ends.
classification
There are two types of Socket usage:
- Based on TCP protocol and stream socket, reliable byte stream service is provided by stream mode.
- Based on UDP protocol and data packet socket, data packet is used to provide data package and send service.
Socket Programming Based on TCP
Main API
Socket
Construction method
public Socket(String host, int port) throws UnknownHostException, IOException
Create a stream socket and connect it to the specified port number on the specified host.
- host: host address
- Port: port number
getInputStream
Returns the input stream of Socket, and the user accepts the data.
getOutputStream
Returns the output stream of Socket for sending data.
ServerSocket
Server-side Implementation of Socket
Constructor
public ServerSocket(int port) throws IOException
Create the server Socket and bind it to the specified port.
- Port: port number
accept
public Socket accept() throws IOException
Listen for and accept connections to this socket. This method will block until the connection is established.
Example
Server side
public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1. Create ServerSocket ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888); //2. monitoring Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("server start listen"); //3. input stream InputStream is = socket.getInputStream(); InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(is); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); String content = null; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); while ((content = br.readLine()) != null) { sb.append(content); } System.out.println("server receiver: " + sb.toString()); socket.shutdownInput(); br.close(); reader.close(); is.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); } }
A very simple Socket server, receiving data from the client, closes the current connection. This example just shows a complete process.
If you need complex server-side implementations, you can use Netty, Mina, or other Socket frameworks.
Client
//1. Create Client Socket socket = new Socket("your ip", 8888); //2. output stream OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream(); //3. Send data os.write("Hello world".getBytes()); System.out.println("send message"); os.flush(); socket.shutdownOutput(); os.close(); socket.close();
After the client connects, it sends a piece of data and closes the connection.
In this way, the communication between client and server is realized.
Socket programming based on UDP
Main API
DatagramPacket
Used to package data received and sent.
- Constructing Received Packets
public DatagramPacket(byte[] buf,int length)
It is used to receive packets of length.
- Constructing Send Packet
DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length,SocketAddress address) DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port)
Used to send a package of length to the specified port number on the specified host.
DatagramSocket
A socket used to send and receive data packets.
Construction method
//Create a datagram socket and bind it to a specified port on the local host DatagramSocket(int port) //Create a datagram socket and bind it to the specified local address DatagramSocket(int port, InetAddress laddr)
send data
void send(DatagramPacket p)
The Datagram Packet contains information indicating the data to be sent, its length, the IP address of the remote host and the port number of the remote host.
receive data
void receive(DatagramPacket p)
When this method returns, the buffer of Datagram Packet fills in the received data.
Example
Server side
public class UDPServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; // receive // 1.create DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); // 2.create udp socket DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(8888); // 3. receive start socket.receive(packet); // 4. receive data System.out.println("sever: " + new String(buf, 0, buf.length)); // send DatagramPacket p = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, packet.getAddress(), packet.getPort()); socket.send(p); socket.close(); } }
Client
// send InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("your ip"); //1.create packet DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, address, 8888); //2.create socket DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(); //3.send data socket.send(packet); // receive //1.create packet final byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket receiverPacket = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length); socket.receive(receiverPacket); System.out.println("client: " + new String(bytes, 0, bytes.length)); socket.close();
The implementation of both client and server is relatively simple.
About Socket programming, I will introduce it. This article is just the beginning. The most important thing is to practice in the project.
Reference resources
This article is based on a multi-article platform. ArtiPub Automatic publishing