Android references external database (1)
There is a ready-made database, which needs to be directly introduced into the project.
Prepare for preparation
Before we start, we need to confirm the table structure and field information of the existing database. (pay attention to the size of the database, which is useful later)
First step
Copy the external database to the assets folder in the project, as shown in the figure
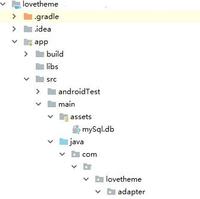
Second steps
Copy the database to the / data/data / package name / databases / directory before you use the database.
Code
public static void copyDbFile(Context context, String db_name) {
InputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
//String path = "/data/data/" + context.getPackageName() + "/databases/";
File filePath = context.getDatabasePath(db_name);
//spUtils is to prevent multiple copies
if (!SharePreferenceUtils.getBoolean(GlobalContent.COPE_SUCCESS,false)){
try {
in = context.getAssets().open(db_name); // Copy from assets directory
out = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
int length = -1;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((length = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, length);
}
out.flush();
SharePreferenceUtils.putBoolean(GlobalContent.COPE_SUCCESS,true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (in != null) in.close();
if (out != null) out.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Third steps
Then we can start to check the library
SqlLiteHelper sqlLiteHelper = new SqlLiteHelper(getContext(), "mySql.db", null, 1);
SQLiteDatabase readableDatabase = sqlLiteHelper.getReadableDatabase();
try {
Cursor query = readableDatabase.query("message", new String[]{"_id", "message"}, null, null, null, null, null, limit);
boolean b = query.moveToFirst();
while (!query.isLast()) {
int id = query.getInt(query.getColumnIndex("_id"));
String message = query.getString(query.getColumnIndex("message"));
mDataList.add(new LoveMessageBean(id, message));
query.moveToNext();
}
query.close();
Logger.i("mDataList : "+ mDataList.size());
}catch (Exception e){
UiUtils.showToast(getContext(),"error");
}
So far, we have successfully copied the external database into the project and started CRUD.
The above method is the most simple and original method. Later, we will try to use a third-party tool to query, such as GreenDao LitePal.
Using database for storage query and other operations in Android development is a basic skill. The following articles are recommended:
Guo Shen's LitePal series of articles, the secret script of Android database expert http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/38556989
Android database comparison https://blog.csdn.net/u010134293/article/details/58590092