How to generate a table
<com.bin.david.form.core.SmartTable
android:id="@+id/table"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
/>
You can annotate the @ SmartColumn field with the annotation @ SmartTable table
@SmartTable(name="User information list")
public class UserInfo {
@SmartColumn(id =1,name = "full name")
private String name;
@SmartColumn(id=2,name="Age")
private int age;
...
}
List<UserInfo> list = new ArrayList<>();
...
table = (SmartTable<UserInfo>) findViewById(R.id.table);
table.setData(list);
OK, this is the simplest annotation version. Let's take a look at the powerful ordinary version. Just create the columns to be displayed and set the fields to be parsed. Suppose it needs to be parsed to userinfo parent.name, just parent Name.

final Column<String> nameColumn = new Column<>("full name", "name");
final Column<Integer> ageColumn = new Column<>("Age", "age");
...
tableData = new TableData<>("test",list,nameColumn,ageColumn...);
table.setTableData(tableData);
beautify
Someone must say that this function, ha ha. Come on, let's sit down and start showing the rich features. The interface is not beautiful. Here, format the content background:
table.getConfig().setContentBackgroundFormat(new BaseBackgroundFormat<CellInfo>() {
@Override
public int getBackGroundColor() {
return ContextCompat.getColor(AnnotationModeActivity.this,R.color.content_bg);
}
@Override
public boolean isDraw(CellInfo cellInfo) {
return cellInfo.position%2 ==0;
}
});
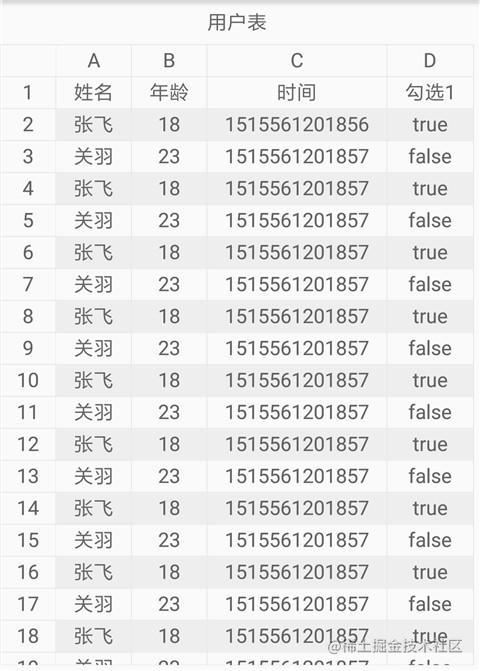
Format data
It is found that the time column is not beautiful. We want to format the time column
final IFormat<Long> format = new IFormat<Long>() {
@Override
public String format(Long aLong) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTimeInMillis(aLong);
return calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR)+"-"+(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1)+"-"+calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
}
};
final Column<Long> timeColumn = new Column<>("time", "time",format);
It also supports the formatting of table text, serial number and column title; The table consists of background, text, grid, padding and other configurations. You can refer to the demo;
Check this column and we want to show the checked icon
int size = DensityUtils.dp2px(this,15); //Specify icon size
Column<Boolean> checkColumn = new Column<>("Tick", "isCheck",new ImageResDrawFormat<Boolean>(size,size) {
@Override
protected Context getContext() {
return AnnotationModeActivity.this;
}
@Override
protected int getResourceID(Boolean isCheck, String value, int position) {
if(isCheck){
return R.mipmap.check;
}
return 0;
}
});

Support text, multiline text, text and icon combination (up, down, left and right)
Tables can generally have statistics function. We can turn on the statistics function setShowCount(true), which column needs statistics, and turn on setAutoCount. If statistics is the addition of numbers, the text takes the longest size
tableData.setShowCount(true); nameColumn.setAutoCount(true);
However, this does not meet the real needs, and the needs are often pitiful. Therefore, a statistical interface is provided. The following is an example of statistical maximum time:
timeColumn.setAutoCount(true);
timeColumn.setCountFormat(new ICountFormat<Long, Long>() {
private long maxTime;
@Override
public void count(Long aLong) {
if(aLong > maxTime){
maxTime = aLong;
}
}
@Override
public Long getCount() {
return maxTime;
}
@Override
public String getCountString() {
return format.format(maxTime);
}
@Override
public void clearCount() {
maxTime =0;
}
});
Sometimes we need a title combination, which can be played like this:
Column groupColumn = new Column("combination",nameColumn,ageColumn);
TableData<UserInfo> tableData = new TableData<>("User table",userInfos,groupColumn,timeColumn,checkColumn);

Dynamic effect
Fixed specified column, X sequence number column, Y sequence number column, column title, and statistics row. You can open it according to your needs. The combination effect is really great
//Fixed specified column timeColumn.setFixed(true); //Y sequence number column table.getConfig().setFixedYSequence(true); //X sequence number column table.getConfig().setFixedXSequence(true); //Column header table.getConfig().setFixedCountRow(true); //Statistical line table.getConfig().setFixedTitle(true);

zoom
Of course, there must be zooming in and out
table.setZoom(true); //You can set the maximum and minimum magnification values setZoom(boolean zoom,float maxZoom,float minZoom);

event
Comments and click events
table.setOnColumnClickListener();
MultiLineBubbleTip<Column> tip = new MultiLineBubbleTip<Column>(this,R.mipmap.round_rect,R.mipmap.triangle,fontStyle) {
@Override
public boolean isShowTip(Column column, int position) {
if(column == nameColumn){
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String[] format(Column column, int position) {
UserInfo data = testData.get(position);
String[] strings = {"Annotation","full name:"+data.getName(),"Age:"+data.getAge()};
return strings;
}
};

sort
You can sort by setting columns and then column criteria.
//Set the sorting sequence and whether to reverse the sequence table.setSortColumn(ageColumn,false);
If you still feel dissatisfied, you can define your own sorting rules
ageColumn.setComparator(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1- o2;
}
});
Support 2D array
You can use ArrayTableData instead of TableData. You can use a two-dimensional array happily, and you don't even need to set column headings. In this way, you can realize some similar voting and seat selection app requirements.
String[] week = {"day","one","two","three","four","five","six"};
Integer[][] infos = {{0,1,2,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,2,3}, {4,2,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,2,2,3},
{2,2,0,1,2,4,1,0,1,3,0,1,1},{2,1,1,0,1,4,0,1,1,2,2,0,3},
{0,1,2,4,1,0,1,4,0,1,1,2,2}, {1,0,1,3,2,2,0,1,2,1,1,0,4},
{3,1,2,4,0,1,2,1,1,0,1,1,0}};
ArrayTableData<Integer> tableData = ArrayTableData.create("calendar",week,infos,new IDrawFormat<Integer>(){
@Override
public int measureWidth(Column<Integer> column, TableConfig config) {
return DensityUtils.dp2px(ArrayModeActivity.this,50);
}
@Override
public int measureHeight(Column<Integer> column, int position, TableConfig config) {
return DensityUtils.dp2px(ArrayModeActivity.this,50);
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas c, Column<Integer> column, Integer integer, String value, Rect rect, int position, TableConfig config) {
Paint paint = config.getPaint();
int color;
switch (integer){
case 1:
color =R.color.github_con_1;
break;
case 2:
color =R.color.github_con_2;
break;
case 3:
color =R.color.github_con_3;
break;
case 4:
color =R.color.github_con_4;
break;
default:
color =R.color.github_con_0;
break;
}
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(ContextCompat.getColor(ArrayModeActivity.this, color));
c.drawRect(rect.left+5,rect.top+5,rect.right-5,rect.bottom-5,paint);
}
});

other
There are also many function points, including dynamic addition of header and footer data, pagination, formatting font, background, etc. I won't introduce them one by one here.
- Support dynamic data addition from beginning to end
Add data smarttable dynamically from beginning to end Adddata (list < T > t, Boolean isfoot) to add data

- Set a single grid background
Referring to the html table on the Internet, it is found that the style is much better. According to this idea, SmartTable adds support for different backgrounds of a single grid. There are five IBackgroundFormat styles in TableConfig. You can judge whether to draw the background drawBackground according to the data returned by boolean isDraw(T t), and draw the whole background by default, Of course, you can define IBackgroundFormat and use other shapes.
- Set single grid font
Because it supports the support of a single grid background, the font color also needs to be adjusted according to the background, so it supports the font setting of a single grid. There is int getTextColor(T t) in IBackgroundFormat. You just need to rewrite it and set different colors according to your needs.
- paging
There is too much data on the client and the experience is not good, so the paging mode is developed. Without annotations, you only need to use the PageTableData paging table data class to replace the previous TableData table data class, and use the setPageSize method of PageTableData to set the number of pages per page. Paging is complete. If you use annotation, please add pageSize attribute to @ SmartTable annotation element. setData will return PageTableData object, which you can use to complete other settings later.
- other
The notifyDataChanged method is added to SmartTable to re parse and calculate the layout;
Provide the back method to fly to the origin.

Related tutorials
Android Foundation Series tutorials:
Android foundation course U-summary_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
Android foundation course UI layout_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
Android basic course UI control_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
Android foundation course UI animation_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
Android basic course - use of activity_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
Android basic course - Fragment usage_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
Android basic course - Principles of hot repair / hot update technology_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili
This article is transferred from https://juejin.cn/post/6844903549109813255 , in case of infringement, please contact to delete.