Introduction to Ansible
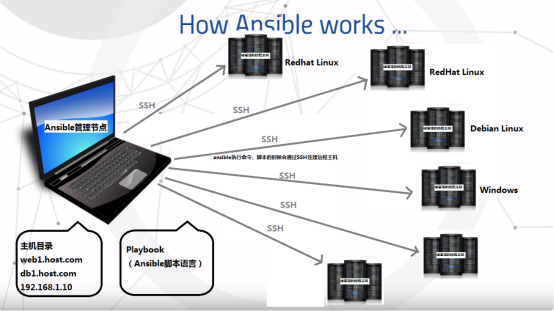
- Ansible can manage both Linux for Redhat s, Linux for Debian, and Windows hosts.The management node only connects to the remote host while executing the script, and there is no special synchronization mechanism, so exceptions such as power outages generally do not affect ansbile.
-
Ansible is a new automated operation and maintenance tool. It is developed based on Python and combines the advantages of many operation and maintenance tools (puppet, cfengine, chef, func, fabric). It realizes the functions of batch system configuration, batch program deployment, batch running commands and so on.Ansible is module-based and does not have the capability to deploy in bulk.What really has a bulk deployment is the modules that ansible runs, and Ansible only provides a framework.Mainly include:
1. connection plugins: responsible and monitored for communication;
2. host inventory: The host for the specified operation is the host for which monitoring is defined in the configuration file;
3. Various module core modules, command modules, custom modules;
4. With the help of plug-in, logging of log messages and other functions can be completed;
5. playbook: When a script performs multiple tasks, it is not necessary for a node to run multiple tasks at once. - Ansible's architecture: connect to other hosts Using ssh protocol by default
Ansible Environment Installation Deployment
| Server Role | IP Address |
|---|---|
| Ansible management side | 192.168.142.120 |
| Ansible Managed End 01 | 192.168.142.121 |
| Ansible Managed End 02 | 192.168.142.122 |
- Install epel source
yum install -y epel-release
- Install Ansible Service
yum install ansible -y
- View the Ansible version
ansible --version
- Install tree Service
yum install tree -y
- Tree structure display folder
tree /etc/ansible/
/etc/ansible/ ├── ansible.cfg #ansible configuration file ├── hosts #ansible's main repository for storing information about remote hosts that need to be managed └── roles
- Switch Ansible working directory
cd /etc/ansible
- Configure host list
vim hosts [webserver] 192.168.142.121 [mysql] 192.168.142.122
- Configure key pair validation
ssh-keygen -t rsa
- Key pair transfer
ssh-copy-id root@192.168.142.121 ssh-copy-id root@192.168.142.122
Ansible command line module
- command module
Command format:
ansible [host] [-m module] [-a args]
#List all installed modules Note: Quit by q ansible-doc -l #-s Lists yum module description information and action ansible-doc -s yum - View the other party's system time #Specify ip execution date ansible 192.168.142.121 -m command -a 'date' #Specify Category Execution date ansible webserver -m command -a 'date' #Exempt from interactive execution date ansible mysql -m command -a 'date' #All hosts host execute date command ansible all -m command -a 'date' #Run command module by default if -m module is not added ansible all -a 'ls /'
- cron module
Two state s: press adds (can be omitted), absent removes
#View cron module information ansible-doc -s cron #Create planned tasks ansible webserver -m cron -a 'minute="*/1" job="/bin/echo heihei" name="test cron job"' #View planned tasks ansible webserver -a 'crontab -l' #Remove the scheduled task, name=None if it is not named ansible webserver -m cron -a 'name="test cron job" state=absent'
- user module
The user module is requesting three instructions: useradd, userdel, usermod
#View user module information ansible-doc -s user #Create user test01 ansible mysql -m user -a 'name="test01"' #View user information ansible mysql -m command -a 'tail /etc/passwd' #Delete user test01 ansible mysql -m user -a 'name="test01" state=absent'
- group module
The group module requests three instructions: groupadd, groupdel, groupmod
#View group module information ansible-doc -s group #Create Group ansible mysql -m group -a 'name=mysql gid=306 system=yes' ansible mysql -a 'tail /etc/group' #Create user and add to group ansible mysql -m user -a 'name=test01 uid=306 system=yes group=mysql' #View user information ansible mysql -a 'tail /etc/passwd' ansible mysql -a 'id test01'
- copy module
#View copy module information ansible-doc -s copy #Copy Files ansible mysql -m copy -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/opt/fstab.back owner=root mode=640' #View opt directory ansible mysql -a 'ls -l /opt' #View fstab.back file ansible mysql -a 'cat /opt/fstab.back' #Write hello heihei! To/opt/fstab.back ansible mysql -m copy -a 'content="hello heihei!" dest=/opt/fstab.back' #View the fstab.back file again ansible mysql -a 'cat /opt/fstab.back'
- file module
#View file module information ansible-doc -s file #Create User ansible mysql -m user -a 'name=mysql system=yes' #Create Group ansible mysql -m user -a 'name=mysql system=yes' #Modify file ownership group permissions, etc. ansible mysql -m file -a 'owner=mysql group=mysql mode=644 path=/opt/fstab.back' #Link file to set/opt/fstab.link to/opt/fstab.back ansible mysql -m file -a 'path=/opt/fstab.link src=/opt/fstab.back state=link' #Delete a file ansible mysql -m file -a "path=/opt/fstab.back state=absent" #Create a file ansible mysql -m file -a "path=/opt/test state=touch"
- ping module
#View ping module information ansible-doc -s ping #Test whether the managed host is online ansible all -m ping - service Modular #View service module information ansible-doc -s service #Install httpd service yum install -y httpd #View the web server httpd status ansible webserver -a 'systemctl status httpd' #service httpd start ansible webserver -m service -a 'enabled=true name=httpd state=started' #Check to see if it's turned on systemctl status httpd
- shell module
#View shell module information ansible-doc -s shell #Create user Password for user using no interactive mode ansible mysql -m shell -a 'echo abc123|passwd --stdin mysql'
- script module
#View script module information ansible-doc -s script #Loop script vim test.sh #!/bin/bash echo "hello ansible from script"> /opt/script.txt #Give Execution Permission chmod +x test.sh #Execute script ansible mysql -m script -a 'test.sh' #View on other hosts cat /opt/script.txt
- yum module
#View yum module information ansible-doc -s yum #yum install zsh ansible mysql -m yum -a 'name=zsh' rpm -q zsh #Uninstall zsh ansible mysql -m yum -a 'name=zsh state=absent' rpm -q zsh
- setup module
#View setup module information ansible-doc -s setup #Get facts information for mysql group host ansible mysql -m setup