Experimental report on 0-1 knapsack problem realized by ant colony algorithm
[experiment content]
The 0-1 knapsack problem is solved by ant colony algorithm.
[experimental environment]
Microsoft Visual C++ 6.0
[basic theory]
Ant colony algorithm is a bionic algorithm based on the simulation of the foraging and path finding methods of ants in nature. First briefly introduce the specific process of ants searching for food. The research shows that during the foraging process, the ant colony will leave a volatile secretion pheromone in the path, and can perceive its existence and intensity, moving towards the direction of high pheromone concentration. At the same time, pheromones related to the path length are released. The longer the path, the lower the concentration of the released kink. The higher the concentration of the path, the more ants choose it, and the more pheromone concentration on the path, which attracts more ants, thus forming a positive feedback. Eventually, ants can always find the best path from food to nest. The concentration of excitation cable on the optimal path is increasing. The hormone concentration in other pathways will decrease with the passage of time. Eventually, the whole ant colony will find the best way to find food.
Artificial ants imitate natural ants and leave pheromones on the path, which provides a new method to solve various optimization problems. The algorithm has been successfully applied to many complex combinatorial optimization problems. Dorigo first used this method to solve TSP problem, and then many scholars successively used this algorithm to solve quadratic assignment problem, queen problem and so on. The problems solved are mainly TSP problems, in addition to function optimization problems and knapsack problems, which are extended from discrete space to continuous space. Compared with the traditional optimization algorithm, ant optimization algorithm shows good performance in solving these problems.


#include "iostream"
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
#define M 8 / / number of ants
#define P 0.2 / / pheromone volatilization rate
#define MAX 70
int BRoute[MAX];//Optimal solution
int BValue=0;//Total value of optimal solution
int BWeight;//Total weight of optimal solution
int max_circle=500;//Maximum times of external circulation
int antRoute[9][MAX];
int antValue[9];
void main(){
int n;//Number of items
int w_limit;//Backpack weight limit
int value[MAX];//Value of each item
int weight[MAX];//Weight of each item
float inf[MAX][MAX];//Pheromone matrix
int i,j;
// **************Read data*************************//
string filestring;
cout<<"Please enter a test file name: ";
cin>>filestring;
ifstream inFile(filestring.c_str());
//Report error
if(!inFile)
{
cerr<<"Cannot open test file:"<<filestring<<endl;
exit(-1);
}
inFile>>n;
inFile>>w_limit;
value[0]=0;
weight[0]=0;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
inFile >> weight[i];
}
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
inFile >> value[i];
}
//*************************Pheromone matrix initialization********************//
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
inf[i][0]=0;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++){
for(j=1;j<=n;j++){
inf[i][j]=1;
}
}
//************************Data output****************************//
cout<<"The total number of items is:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"The weight of the backpack is limited to:"<<w_limit<<endl;
cout<<"The weight of each article is:"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
cout<< weight[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"The value of each item is:"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
cout<< value[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
srand((int)time(0)); //Initialize random seed
bool mark[MAX];
int no_modify=0;
for(int k=1;k<=max_circle && no_modify<100 ;k++){//External circulation
// For (int k = 1; K < = max_circle; K + +) {/ / outer loop
for(i=1;i<=M;i++){
antRoute[i][0]=0;
int Cur_n=0; //Number of selected items
int Cur_w=0; //Total weight of selected items
int Cur_v=0; //Total value of selected items
int Cur_ps=0; //Record the label of the currently selected item
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
mark[j]=false; //As a sign of whether the item is selected or not
bool finish=false;
int ok[MAX];
while(finish==false){
if(Cur_n==n){
antRoute[i][++Cur_n]=0;
antValue[i]=Cur_v;
finish=true;
}
else{
int ok_n=0;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(mark[j]==false &&(Cur_w+weight[j])<=w_limit){
ok[ok_n++]=j; //This array is used to store the labels of items that meet the conditions
}
}
if(ok_n==0){ //There are no items that meet the conditions
antRoute[i][++Cur_n]=0;
antValue[i]=Cur_v;
finish=true;
}
else{
//Items that meet the conditions: randomly select according to pheromones
float total=0;
float rate[MAX];
for(j=0;j<ok_n;j++){
float total=total+inf[Cur_ps][ok[j]];
}
for(j=0;j<ok_n;j++)
rate[j]=(inf[Cur_ps][ok[j]]/total);
bool choose=false;
while(choose==false){
double r=(double)(rand() % 1001) * 0.001f;
int u=(int)(rand()%ok_n);
if(rate[u]>r){
antRoute[i][++Cur_n]=ok[u];
Cur_ps=ok[u];
Cur_w+=weight[ok[u]];
Cur_v+=value[ok[u]];
mark[ok[u]]=true;
choose=true;
break;
}
/*
for(j=0;j<ok_n;j++)
if(leiji[j]>r){
antRoute[i][++Cur_n]=ok[j];
Cur_ps=ok[j];
Cur_w+=weight[ok[j]];
Cur_v+=value[ok[j]];
mark[ok[j]]=true;
// cout<<endl<<"Select "< < OK [J] < < endl";
choose=true;
break;
}*/
}
}//else
}//else
}//while
}//for: inner loop
//Comparison with the current optimal solution
int temp=0;
for(i=1;i<=M;i++){
if(antValue[i]>BValue){
BValue=antValue[i];
temp=i;
}
}
if(temp==0)
no_modify++; //Record the number of times that do not change continuously, and stop the external circulation when it reaches a certain value
if(temp!=0){
no_modify=0;
for(int s=0;s<MAX;s++){
BRoute[s]=antRoute[temp][s];
}
}
//Pheromone update/
//volatilization
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
for(j=0;j<=n;j++){
inf[i][j]*=(1-P);
}
//The optimal solution is then enhanced by pheromone
inf[BRoute[0]][BRoute[1]]+=P/n;
for(int s=1; s<MAX && BRoute[s]!=0;s++){
inf[BRoute[s]][BRoute[s+1]]+=P/n;
}
}//External circulation
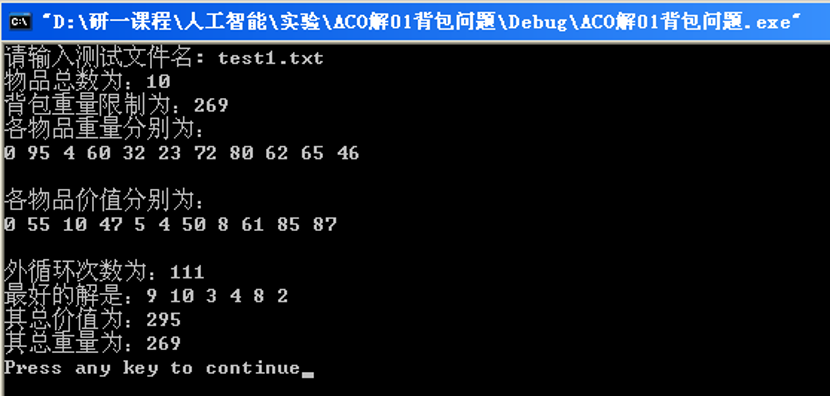
cout<<"The number of external cycles is:"<<k<<endl;
cout<<"The best solution is:";
for( k=1;k<MAX && BRoute[k]!=0;k++)
cout<<BRoute[k]<<" " ;
cout<<endl<<"Its total value is:"<<BValue<<endl;
BWeight=0;
for(int s=1;s<MAX && BRoute[s]!=0;s++)
BWeight=BWeight+weight[BRoute[s]];
cout<<"Its total weight is:"<<BWeight<<endl;
}