brief introduction
When doing UI automation, a large part of energy is to locate elements. If the element positioning is not accurate, it will directly affect the success or failure and efficiency of automation
environment
- Appium server : v1.20.2
- Appium-Python-Client : 2.1.2
- selenium 4.1.0
Common element positioning methods
- id location element
- class_name locate element
- Content desc locating element
- Name locating element (appium1.5 and later versions have abandoned the name attribute)
- xpath positioning element
- uiautomator positioning element, unique to Android
id location
-
usage method
find_element(AppiumBy.ID, "")
driver.find_element_by_id() is obsolete -
Resource ID of element
-
The value that uniquely identifies the element (id is sometimes not unique)
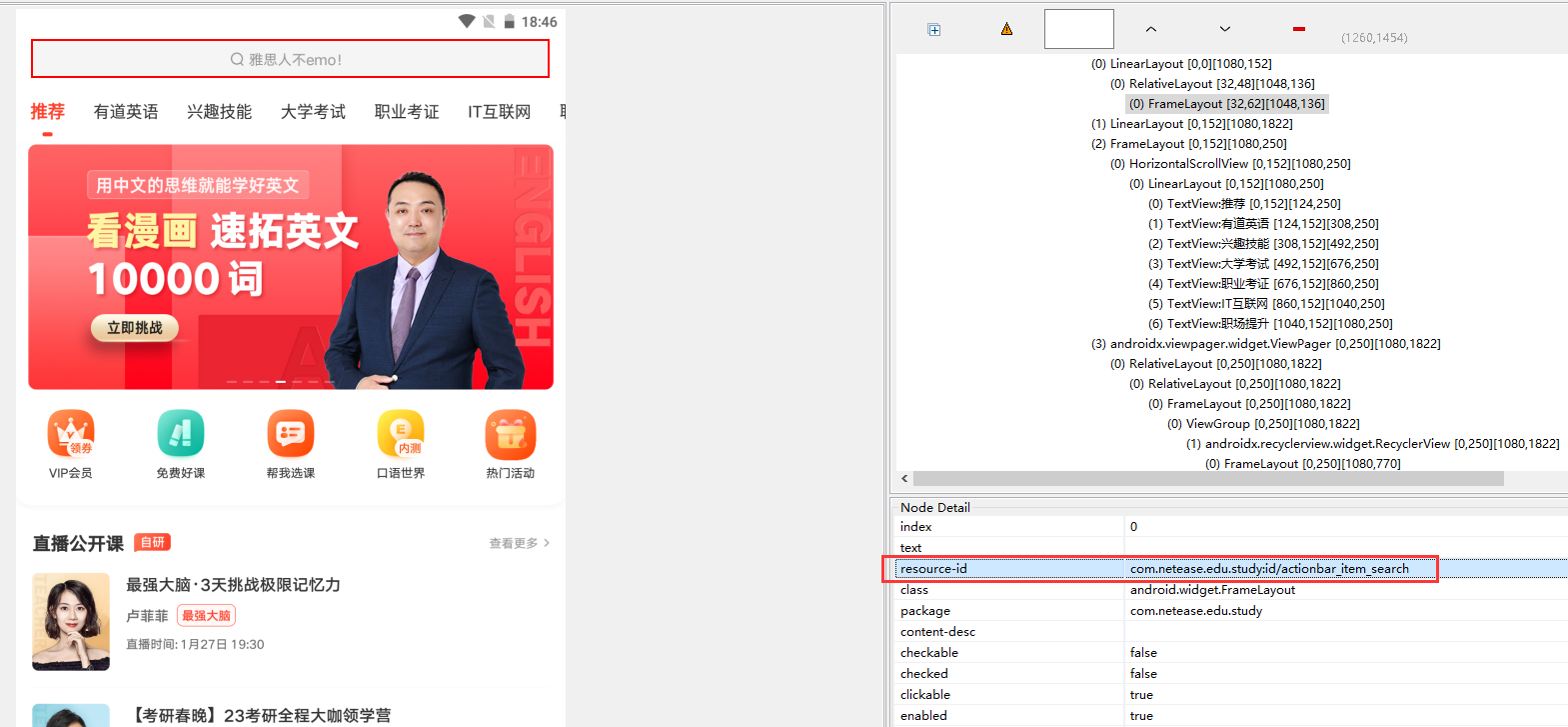
-
Example: this method is generally preferred for positioning
driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ID, "com.netease.edu.study:id/actionbar_item_search")
class_name positioning
- usage method
find_element(AppiumBy.CLASS_NAME, "") - This method is generally not used. Because the class repetition of interface elements is too high, there is basically no unique value
- class attribute of element
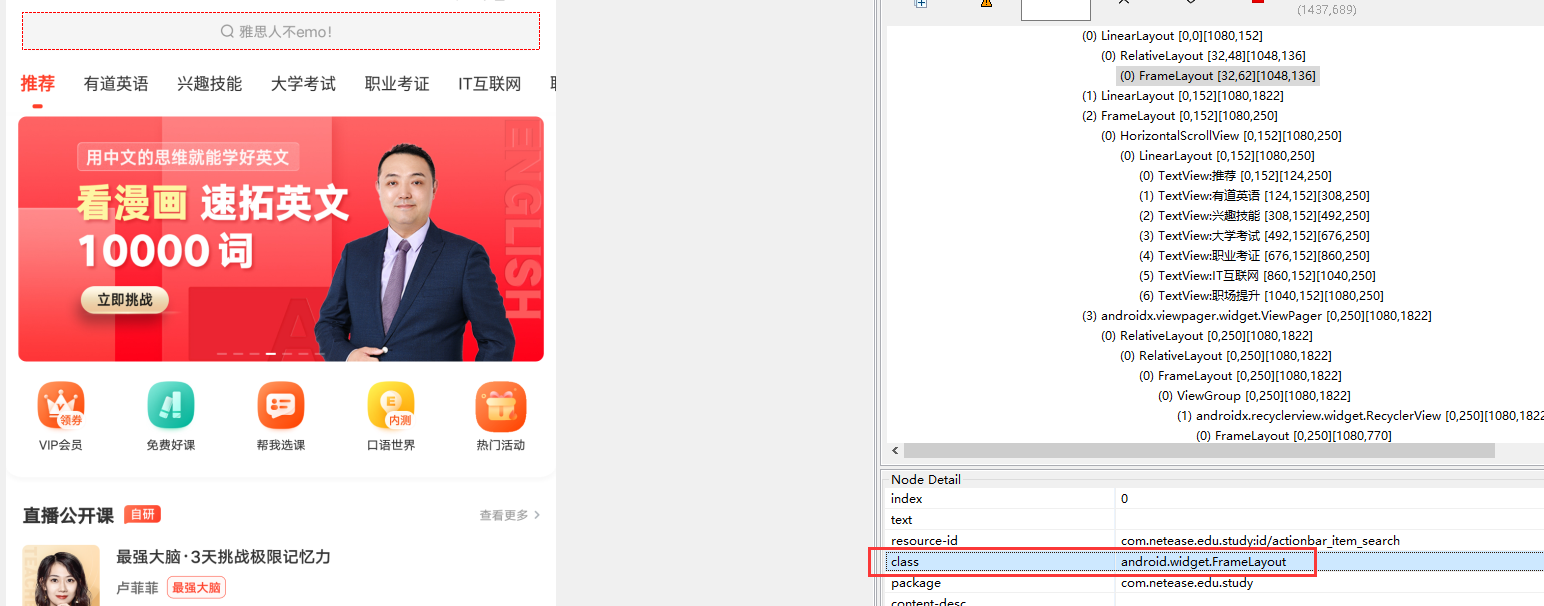
- Example:
driver.find_element(AppiumBy.CLASS_NAME, "android.widget.LinearLayout")
Content desc location
- usage method
find_element(AppiumBy.ACCESSIBILITY_ID, "") - Content desc attribute of element
The content desc attribute is used to describe the function of the element, which is generally empty

- Examples
find_element(AppiumBy.ACCESSIBILITY_ID, "")
name positioning
- This method is in appium1 5 and later versions abandoned the name attribute
xpath positioning
Single element positioning
-
Locate by id attribute
Expression: / / * [@ resource id = 'ID attribute'] -
Locate according to text attribute
Expression: / / * [@ text = 'text attribute'] -
Locate according to class attribute
Expression: / / * [@ class = 'class attribute'] -
Locate through content desc attribute
Expression: / / * [@ content desc = 'text of desc'] -
Examples
driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, "//*[@resource-id='com.netease.edu.study:id/look_more']").click() driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, "//*[@ text = 'view more'] "). click() driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, "//*[@class='android.widget.TextView']").click() driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, "//*[@ content desc = 'more buttons'] "). click()
Fuzzy location
-
contains is the location method of fuzzy matching. The attributes of some elements are variable, but some are fixed. This method can be used for fuzzy matching
//[contains(@text, 'view')]
//[contains(@content-desc, '')]
//[contains (@ resource id, 'id attribute')]
//[contains(@clsss, 'class attribute')]
Combined positioning
When a single element location is not unique, we can use multiple attribute combination location
-
If an element has multiple attributes, you can also match two attributes at the same time through xpath. Text, resource ID, class, index and content desc can be located in any combination
id_class = '//android.widget.TextView[@resource-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/look_more"]'
desc_class = '/ / * [@ text = "view more" and @index = "2"]'
Hierarchical positioning
Sometimes, when we see that the element attribute is empty except the class attribute, and the class attribute is not unique, the general method cannot locate it
- Father positioning son
'//[@resoure-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/composite_item_list_recyclerview"]/android.widget.TextView'
'//[@resoure-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/composite_item_list_recyclerview"]/com.netease.edu.study:id/item_kingkong_area_image[2]' - Son positioning father
'//[@resource-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/composite_item_list_recyclerview"]/...'
'//[@resource-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/composite_item_list_recyclerview"]/parent::'
'//[@resource-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/composite_item_list_recyclerview"]/parent::android.widget.LinearLayout' - Sibling element positioning
'//*[@resource-id="com.netease.edu.study:id/composite_item_list_recyclerview"]/.../android.widget.RelativeLayout'
uiautomator positioning
explain
Appium encapsulates the uiautomator framework of android, so some positioning methods of uiautomator can be used normally
Official website address: https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/test/uiautomator/UiSelector
usage method
driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ANDROID_UIAUTOMATOR, "new UiSelector().resourceId(\"com.netease.edu.study:id/look_more\")")
You can omit: new UiSelector()
driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ANDROID_UIAUTOMATOR,"resourceId(\"com.netease.edu.study:id/look_more\")")
resourceId
1.adopt resourceId location
new UiSelector().resourceId("id")
2.adopt resourceIdMatches regular expression
new UiSelector().resourceIdMatches("regular expression ")
className
1.adopt className location
new UiSelector().className("className")
2.adopt classNameMatches regular expression
new UiSelector().classNameMatches("regular expression ")
text
1.adopt text Text location syntax
new UiSelector().text("text text")
2.The text is long or variable and can be used textContains Fuzzy matching,As long as the text contains a match.
new UiSelector().textContains("contain text text")
3.textStartsWith Is a match that begins with a text
new UiSelector().textStartsWith("with text Beginning of text")
4.Regular matching textMatches,This requires a regular expression.
new UiSelector().textMatches("regular expression ")
content-des
1.adopt content-des Text location syntax
new UiSelector().description("content-des attribute")
2.The text is long or variable and can be used descriptionContains Fuzzy matching,As long as the text contains a match.
new UiSelector().descriptionContains("contain content-des Attribute text")
3.descriptionStartsWith Is a match that begins with a text
new UiSelector().descriptionStartsWith("with content-des Start of attribute text")
4.Regular matching descriptionMatches,This requires a regular expression.
new UiSelector().descriptionMatches("regular expression ")
Combined positioning
1.Most of them are used id,class,text These three attributes are combined, followed by description This attribute can also be combined in pairs
new UiSelector().resourceId("id").text("text text")
2.Parent-child positioning childSelector
new UiSelector().resourceId("id").childSelector(text("text text"))
3.Brother positioning fromParent
new UiSelector().resourceId("id").fromParent(text("text text"))
The above content is purely personal understanding. If there are deficiencies, you are welcome to correct!
If you feel that the article is good, welcome to WeChat official account, WeChat official account regularly push test related technical articles.
