Queue is a first in first out ordered list, which can be realized by array or linked list (for example, Bank Queuing System)
prerequisite:
maxSize: queue capacity (length of array)
arr: array of simulated queues
front: points to the previous element of the queue header element, with an initial value of - 1
rear: refers to the element at the end of the queue. The initial value is - 1
First judge:
Empty queue: front == rear
The queue is full: rear == (maxSize - 1), that is, whether the rear has pointed to the last position of the array
Number of queue elements: rear - front
Queue join: join only when the queue is not satisfied, arr[++rear] = value
Queue exit: only when the queue is not empty can you exit the queue, return arr[front + +]
First, let's implement a one-time array simulation queue, that is, we add data to the array until it reaches rear=maxSize-1. At this time, we take out the data. Although there is space in front of the array, rear is always equal to maxSize-1, and we still can't add data to it. This is false overflow, resulting in a waste of resources. The specific code is as follows:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Queue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue queue=new ArrayQueue(3);
char key=' ';//Receive user input
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop=true;
while (loop){
System.out.println("s(show): Show queue");
System.out.println("e(exit): Exit program");
System.out.println("a(add): Add data to queue");
System.out.println("g(get): Fetch data from queue");
System.out.println("h(head): View data of queue header");
System.out.println();
key=scanner.next().charAt(0);//Receive a character
switch (key){
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("Output a number");
int value=scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res=queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("The data removed is%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res=queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("The head of the queue is%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
loop=false;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Program exit");
}
static class ArrayQueue{
private int maxSize;//Represents the maximum capacity of the array
private int front;//The queue header is the previous position of the first node
private int rear;//Queue tail
private int[] arr;//Simulated queue
public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize=arrMaxSize;
arr=new int[maxSize];
front=-1;//Point to the queue header and analyze that front is the previous position pointing to the queue header
rear=-1;//Point to the end of the queue Point to the last data in the queue
}
//Determine whether the queue is full
public boolean isFull(){
return rear==maxSize-1;
}
//Determine whether the queue is empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front==rear;
}
//Add data to queue
public void addQueue(int n){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("The queue is full,Data cannot be added");
return;
}
rear++;
arr[rear]=n;
}
//Get the data of the queue and get out of the queue
public int getQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty,Data cannot be removed");
}
front++;
return arr[front];
}
//Displays all data for the queue
public void showQueue(){
//ergodic
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("The queue is empty,no data");
return;
}
for (int i = front+1; i <=rear ; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
// Displays the header data of the queue Note that the data is not taken out
public int headQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queue empty,no data");
}
return arr[front+1];
}
}
}
Then we can consider "upgrading" this version, that is, we can use arrays to simulate circular queues, so that we can use queues to a greater extent, optimize the previous queues and transform them into ring queues (by taking modules)
prerequisite
maxSize: queue capacity (length of array)
arr: array of simulated queues
front: points to the queue header element, with an initial value of 0
rear: refers to the last element at the end of the queue. The initial value is 0
First judge:
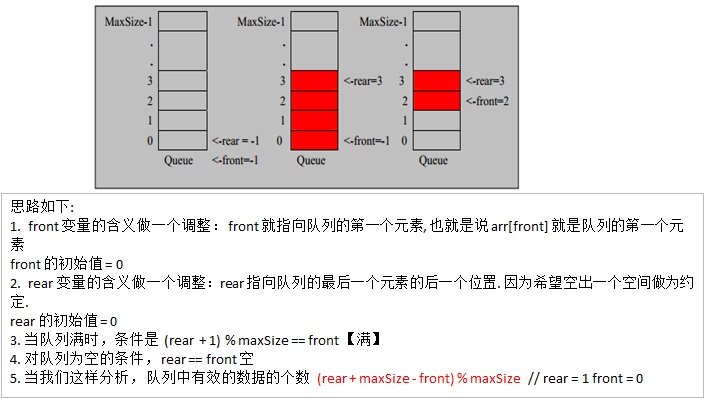
The code is as follows:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CircleQueueArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle queue=new Circle(4);
char key=' ';//Receive user input
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop=true;
while (loop){
System.out.println("s(show): Show queue");
System.out.println("e(exit): Exit program");
System.out.println("a(add): Add data to queue");
System.out.println("g(get): Fetch data from queue");
System.out.println("h(head): View data of queue header");
System.out.println();
key=scanner.next().charAt(0);//Receive a character
switch (key){
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("Output a number");
int value=scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res=queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("The data removed is%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res=queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("The head of the queue is%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
loop=false;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Program exit");
}
static class Circle {
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public Circle(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
//Determine whether the queue is full
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)%maxSize==front;
}
//Determine whether the queue is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear==front;
}
//Add data to queue
public void addQueue(int n) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("The queue is full,Data cannot be added");
return;
}
arr[rear]=n;
rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;
}
//Get the data of the queue and get out of the queue
public int getQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty,Data cannot be removed");
}
// Here, we need to analyze that front is the first element pointing to the queue
// 1. First keep the value corresponding to front to a temporary variable
// 2. Move the front backward and consider taking the mold
// 3. Return temporarily saved variables
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
//Displays all data for the queue
public void showQueue() {
//ergodic
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("The queue is empty,no data");
return;
}
for (int i = front ; i <front+((rear-front+maxSize)%maxSize); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", (i+maxSize)%maxSize, arr[i%maxSize]);
}
}
// Displays the header data of the queue Note that the data is not taken out
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue empty,no data");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
}
reference resources: Shang Silicon Valley Java data structure and Java algorithm (Java data structure and algorithm)_ Beep beep beep_ bilibili