Audio and video development route:
demo address:
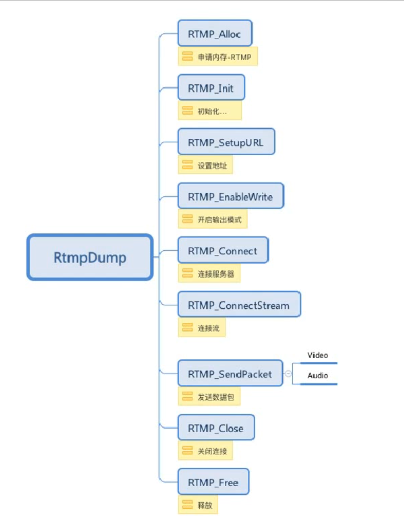
I RTMP usage process
The api calling sequence of rtmp protocol is as follows:
II Initialize RTMP and connect to the server
There are two ways to build RTMP servers. We use the server of station B. to use the server of station B, you have to authenticate it. The audit will take about a day. In addition, we can build RTMP servers ourselves. You can spend tens of dollars to buy a cloud server such as Alibaba cloud and pre install a Linux system. RTMP servers are generally installed on Linux, He needs to cooperate with ngix and other proxy frameworks. If he doesn't want to configure himself, he will apply for a live broadcast of station B. I am a windows computer, and then ran an Ubuntu virtual machine on his computer and ran the RTMP server in the virtual machine. For specific configuration, please refer to:
Easy install nginx RTMP module for Ubuntu 16.04_ Android / Linux column - CSDN blog
Because I am not familiar with the Linux system, I may encounter various problems during installation. Sometimes I get stuck in one place, and then I have to check all kinds of data, such as VIM editing text. It took me a long time to know that VIM was originally used to edit documents directly in the command box. If I get stuck, You don't have to drill a bull's horn, place it for a while, or leave a message. If I see it, I'll look at it and study it. The blogger is also a climbing developer. If possible, I hope it can help you.
Next, we initialize the RTMP server. Here, we define a structure to save RTMP, sps, pps and other data for video
//Used to save SPS and PPS structures
typedef struct {
RTMP *rtmp;
int8_t *sps;//sps array
int8_t *pps;//pps array
int16_t sps_len;//sps array length
int16_t pps_len;//pps array length
} Live;Initialize the rtmp server, configure rtmp, and then link the rtmp address passed in from our java layer. If our rtmp server is configured normally and turned on, rtmp_ The connectstream function will return success
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL
Java_com_example_rtmpdemo_mediacodec_ScreenLive_connect(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring url_) {
//Link rtmp server
int ret = 0;
const char *url = env->GetStringUTFChars(url_, 0);
//Keep retrying, link server
do {
//Initialize live data
live = (Live *) malloc(sizeof(Live));
//Clear live data
memset(live, 0, sizeof(Live));
//Initialize RTMP and request memory
live->rtmp = RTMP_Alloc();
RTMP_Init(live->rtmp);
//Set timeout
live->rtmp->Link.timeout = 10;
LOGI("connect %s", url);
//Set address
if (!(ret = RTMP_SetupURL(live->rtmp, (char *) url))) break;
//Set output mode
RTMP_EnableWrite(live->rtmp);
LOGI("connect Connect");
//connect
if (!(ret = RTMP_Connect(live->rtmp, 0))) break;
LOGI("connect ConnectStream");
//Connection flow
if (!(ret = RTMP_ConnectStream(live->rtmp, 0))) break;
LOGI("connect success");
} while (0);
//Connection failed, free memory
if (!ret && live) {
free(live);
live = nullptr;
}
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(url_, url);
return ret;
}III Send data to rtmp server
In the java layer, we use Camera2 to obtain video data, AudioRecord to record, and then use MediaCodec to realize coding. The api call of cameara2 is cumbersome. You can go to my github project to check the specific use methods. In short, we convert the collected video drama into nv12, and use MediaCodec to encode yuv data into h264 code stream, Then transfer h264 data to our Native layer through jni method. Now let's take a look at the operation after receiving data in Native:
//Send data to rtmp server
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL
Java_com_example_rtmpdemo2_mediacodec_ScreenLive_sendData(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz,
jbyteArray data_, jint len,
jlong tms, jint type) {
// Ensure that empty RTMP packets are not fetched
if (!data_) {
return 0;
}
int ret;
int8_t *data = env->GetByteArrayElements(data_, NULL);
if (type == 1) {//video
LOGI("Start sending video %d", len);
ret = sendVideo(data, len, tms);
} else {//audio frequency
LOGI("Start sending audio %d", len);
ret = sendAudio(data, len, tms, type);
}
env->ReleaseByteArrayElements(data_, data, 0);
return ret;
}
After receiving the video data, you need to judge whether it is sps and pps data. If so, cache them in the structure. When subsequent I frames enter, we will add sps and pps to the header, because users entering at any time in the live broadcast must first analyze the sps/pps configuration data before they want to play
/**
*Send frame data to rtmp server
*Cache pps and sps in front of each I frame,
*/
int sendVideo(int8_t *buf, int len, long tms) {
int ret = 0;
//At the current time, cache sps and pps to global variables
if (buf[4] == 0x67) {
//Judge whether live has been cached. If liv has been cached, it will not be cached
if (live && (!live->sps || !live->pps)) {
saveSPSPPS(buf, len, live);
}
return ret;
}
//I frame, key frame, non key frame, direct push frame data
if (buf[4] == 0x65) {
LOGI("Find keys,Send first sps data %d", len);
//Push sps and pps first
RTMPPacket *SPpacket = createSPSPPSPacket(live);
sendPacket(SPpacket);
}
//Push frame data
RTMPPacket *packet = createVideoPacket(buf, len, tms, live);
ret = sendPacket(packet);
return ret;
}
RTMP protocol sends RTMPPacket packets, in which sps and pps packets are:
/**
* Create rtmppackets for sps and pps
*/
RTMPPacket *createSPSPPSPacket(Live *live) {
//packet of sps and pps
int body_size = 16 + live->sps_len + live->pps_len;
LOGI("establish sps Packet ,body_size:%d", body_size);
RTMPPacket *packet = (RTMPPacket *) malloc(sizeof(RTMPPacket));
//Initialize packet data and apply for array
RTMPPacket_Alloc(packet, body_size);
int i = 0;
//Fixed protocol byte ID
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x17;
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x00;
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x00;
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x00;
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x00;
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x01;
//sps configuration information
packet->m_body[i++] = live->sps[1];
packet->m_body[i++] = live->sps[2];
packet->m_body[i++] = live->sps[3];
//fixed
packet->m_body[i++] = 0xFF;
packet->m_body[i++] = 0xE1;
//Two bytes to store sps length
packet->m_body[i++] = (live->sps_len >> 8) & 0xFF;
packet->m_body[i++] = (live->sps_len) & 0xFF;
//sps content writing
memcpy(&packet->m_body[i], live->sps, live->sps_len);
i += live->sps_len;
//pps start writing
packet->m_body[i++] = 0x01;
//pps length
packet->m_body[i++] = (live->pps_len >> 8) & 0xFF;
packet->m_body[i++] = (live->pps_len) & 0xFF;
memcpy(&packet->m_body[i], live->pps, live->pps_len);
//Set video type
packet->m_packetType = RTMP_PACKET_TYPE_VIDEO;
packet->m_nBodySize = body_size;
//Channel value, audio and video cannot be the same
packet->m_nChannel = 0x04;
packet->m_nTimeStamp = 0;
packet->m_hasAbsTimestamp = 0;
packet->m_headerType = RTMP_PACKET_SIZE_LARGE;
packet->m_nInfoField2 = live->rtmp->m_stream_id;
return packet;
}For the construction method of ordinary frame data, note that the starting byte of RTMPPacket is different between I frame and non I frame
/**
* Create rtmppackets for intra frame data, where I frames and non key frames synthesize rtmppackets
*/
RTMPPacket *createVideoPacket(int8_t *buf, int len, long tms, Live *live) {
buf += 4;
len -= 4;
RTMPPacket *packet = (RTMPPacket *) malloc(sizeof(RTMPPacket));
int body_size = len + 9;
LOGI("Create frame data Packet ,body_size:%d", body_size);
//Initialize internal body array
RTMPPacket_Alloc(packet, body_size);
packet->m_body[0] = 0x27;//Non key frame
if (buf[0] == 0x65) {//Key frame
packet->m_body[0] = 0x17;
}
//fixed
packet->m_body[1] = 0x01;
packet->m_body[2] = 0x00;
packet->m_body[3] = 0x00;
packet->m_body[4] = 0x00;
//Frame length, 4 bytes storage
packet->m_body[5] = (len >> 24) & 0xFF;
packet->m_body[6] = (len >> 16) & 0xFF;
packet->m_body[7] = (len >> 8) & 0xFF;
packet->m_body[8] = (len) & 0xFF;
//copy frame data
memcpy(&packet->m_body[9], buf, len);
//Set video type
packet->m_packetType = RTMP_PACKET_TYPE_VIDEO;
packet->m_nBodySize = body_size;
//Channel value, audio and video cannot be the same
packet->m_nChannel = 0x04;
packet->m_nTimeStamp = tms;
packet->m_hasAbsTimestamp = 0;
packet->m_headerType = RTMP_PACKET_SIZE_LARGE;
packet->m_nInfoField2 = live->rtmp->m_stream_id;
return packet;
}Send the code so that we can send the video data
//Send rtmp packet
int sendPacket(RTMPPacket *packet) {
int r = RTMP_SendPacket(live->rtmp, packet, 0);
RTMPPacket_Free(packet);
free(packet);
LOGI("send out packet: %d ", r);
return r;
}IV Send audio data to server
AudioRecord is used for audio recording. MediaCodec is also used to encode pcm original audio data into AAC format data and push it to the server. The specific code has also been written in the early stage. Check the demo code. It should be noted that rtmp protocol sends a fixed audio format header: 0x12, 0x08 before sending audio data
The java layer sends the audio header before coding:
//Send audio header
RTMPPacket rtmpPacket = new RTMPPacket();
byte[] audioHeadInfo = {0x12, 0x08};
rtmpPacket.setBuffer(audioHeadInfo);
rtmpPacket.setType(AUDIO_HEAD_TYPE);
screenLive.addPacket(rtmpPacket);In native, it is judged according to the type passed by the java layer. The second byte of RTMPPacket data of the audio header is 0x00 and that of ordinary audio is 0x01
//Create audio package
RTMPPacket *createAudioPacket(int8_t *buf, int len, long tms, int type, Live *live) {
int body_size = len + 2;
RTMPPacket *packet = (RTMPPacket *) malloc(sizeof(RTMPPacket));
RTMPPacket_Alloc(packet, body_size);
packet->m_body[0] = 0xAF;
if (type == 2) {//Audio head
packet->m_body[1] = 0x00;
} else {//Normal data
packet->m_body[1] = 0x01;
}
memcpy(&packet->m_body[2], buf, len);
//Set audio type
packet->m_packetType = RTMP_PACKET_TYPE_AUDIO;
packet->m_nBodySize = body_size;
//Channel value, audio and video cannot be the same
packet->m_nChannel = 0x05;
packet->m_nTimeStamp = tms;
packet->m_hasAbsTimestamp = 0;
packet->m_headerType = RTMP_PACKET_SIZE_LARGE;
packet->m_nInfoField2 = live->rtmp->m_stream_id;
return packet;
}We have finished writing the overall calling process, and you can go to github to see the specific code details