brief introduction
Awk is an excellent text processing tool and one of the most powerful data processing engines in Linux and Unix environments. The greatest function of this programming and data manipulation language (whose name comes from the initials of the surnames of its founders Alfred aihou, Peter Weinberg and Brian collinhan) depends on one's knowledge. Awk is a new version of nawk and gawk generated after improvement. Now gawk is used by default under Linux system. You can check the source of the awk being applied with the command (ls -l /bin/awk)
A simple example
#Create a file
vim awk.txt
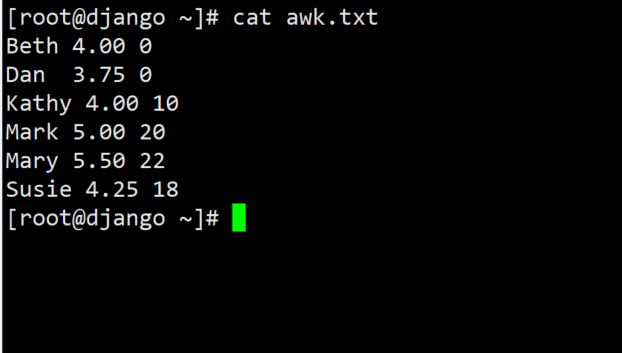
Beth 4.00 0
Dan 3.75 0
Kathy 4.00 10
Mark 5.00 20
Mary 5.50 22
Susie 4.25 18
Explain field: Name hourly wage working hours
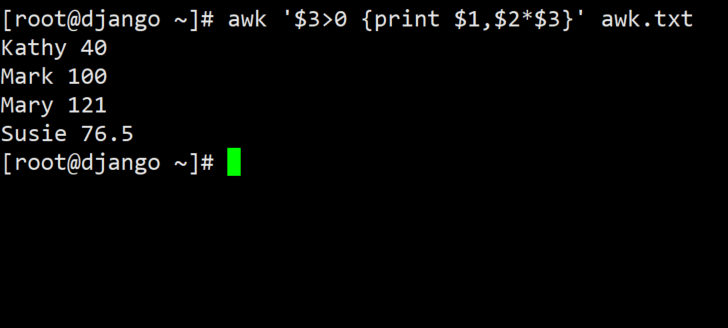
#Print the name and remuneration of each employee
awk '$3>0 {print $1,$2*$3}' awk.txt
$3>0 It's a pattern
print $1,$2*$3 It's action
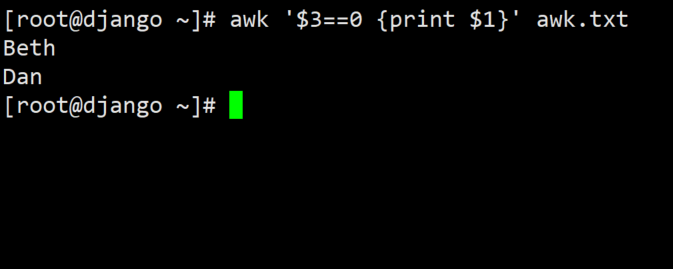
#Want to know which employees are lazy
awk '$3==0 {print $1}' awk.txtExecution result diagram:
AWK program structure
- AWK program execution process
awk The basic operation of is in a sequence composed of input lines, Scan each line one after another, Search can be"pattern"matching(match) Line of.Execute if match"action",Continue until all inputs are read
- Mode action analysis
(1)pattern-All actions exist awk '$3==0 {print $1}' awk.txt
(2)Mode exists, action does not exist awk '$3==0' awk.txt
(3)Mode does not exist, action exists awk '{print $1}' awk.txt
(4)No, neither exists(Cannot run)Operation format of AWK command
#Followed by documents
awk '$3==0 {print $1}' awk.txt Followed by a file
awk '$3==0 {print $1}' awk.txt awk02.txt Followed by two files
#Waiting for input
awk '$3==0 {print $1}' There is no file after it. Wait for input before judging
#Put the awk program into a file
cat program
$3==0 {print $1}
Execute command: awk -f program awk.txtOutput format of AWK
- Data type
-
Numbers and strings
- Rows and fields
awk Read one line at a time from its input,Decompose rows into fields(By default, fields are treated as a sequence of non whitespace characters). The first field of the current input line is called $1,The second is $2,And so on,A whole line is recorded as $0,The number of fields in each row may be different.
- Case
#Print each line
awk '{print}' awk.txt or awk '{print $0}' awk.txt
#Print some fields
awk '{print $1,$3}' awk.txt
#Print the number of fields per line (built-in variable NF)
awk '{print NF}' awk.txt
#Print the first and last fields
awk '{print $1,$NF}' awk.txt
#Calculation and printing
awk '{print $1,$2 * $3}' awk.txt
#Print line number (NR)
awk '{print NR,$0}' awk.txt
#Splice strings and fields
awk '{print $1,"Today's income is",$2 * $3}' awk.txt
#Format output
awk '{ printf("%s Today's income is $%.2f\n",$1,$2*$3) }' awk.txt
Fixed width output
awk '{ printf("%-8s Today's income is $%6.2f\n",$1,$2*$3) }' awk.txt
Output sorting
awk '{ printf("%6.2f,%-8s Today's income is $%6.2f\n",$2*$3,$1,$2*$3) }' awk.txt |sort -nk3 -t,AWK pattern matching
- Single mode
#Records with hourly wage greater than 5
awk '$2>5 {print $0}' awk.txt
#Employees paid more than 50
awk '$2*$3>50 {print $1,$2*$3}' awk.txt
#Query the record named Mark
awk '$1=="Mark" {print $0}' awk.txt
#Regular expressions match records with names with Mar
awk '/Mar/ {print $0}' awk.txt- Pattern combination
#Print lines where $2 is at least 4, or $3 is at least 20
awk '$2>=4||$3>=20 {print $0}' awk.txt
awk '!($2<4&&$3<20) {print $0}' awk.txt
#Print lines where $2 is at least 4 and $3 is at least 20
awk '$2>=4 && $3>=20 {print $0}' awk.txt- BEGIN and END
Special mode BEGIN Is matched before the first line of the first input file, END Match after the last line of the last input file is processed.
awk 'BEGIN {*********} END{***********}'
awk 'BEGIN {print "NAME RATE HOURS"} {print} END{print "END"}' awk.txt
awk 'BEGIN {print "NAME RATE HOURS";print "------"} {print} END{print "------";print "END"}' awk.txtCalculated with AWK
- Calculate sum
Total number of employees # working more than 15 hours
Awk '$3 > 15 {EMP = EMP + 1} end {print EMP, "number of employees working more than 15 hours"}' awk txt
- Calculate average
# calculate the average salary of employees
awk '{pay=pay+,*} END{print NR, "total number of employees"; print "total salary", pay; print "average salary", pay / NR}' awk txt
- Find maximum
# find the employee with the highest hourly wage
Awk '$2 > maxrate {maxrate = $2; maxemp = $1} end {print "the employee with the highest hourly salary is:", maxemp, "salary is:", maxrate}' awk txt
- Print last line
awk '{last=$0} END{print last}' awk.txt
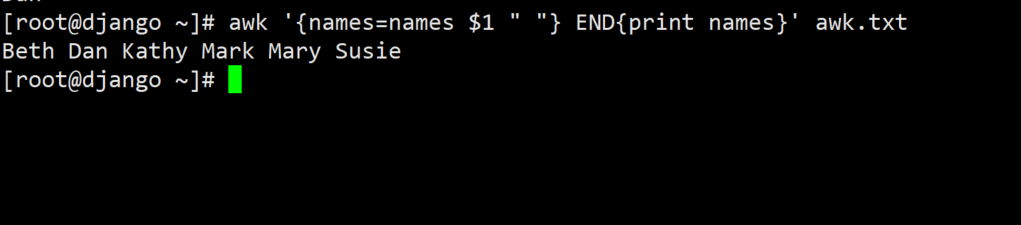
String splicing
#Add a space between name s
awk '{names=names $1 " "} END{print names}' awk.txt
Built in function
#length find the length of the string
Calculate the length of the name
awk '{print $1,length($1)}' awk.txt
#Calculate the number of lines, total fields and total bytes of text
awk '{nc=nc+length($0)+1;nw=nw+NF} END{print NR,"lines,",nw,"words,",nc,"characters"}' awk.txt
Process control statement
- If else statement
# find total and average compensation for employees who earn more than $6.00 per hour
awk '$2>6 {n=n+1;pay=pay+$2*$3} END{if(n>0) print n,"employees,total pay is",pay,"average pay is",pay/n;else print "not exit"}' awk.txt
- while statement
Calculate the sum of 1 to 100
awk 'BEGIN{ test=100; total=0; while(i<=test) { total+=i; i++; } print total; }' 5050
#shell script
#!/bin/bash
total=0
i=0
while [ $i -le 100 ]
do
let total+=$i
let i++
done
echo $total
- for statement
# calculate the sum of 1 to 100
awk 'BEGIN{ total=0; for(i=0;i<=100;i++) { total+=i; } print total; }'
- Array
# print each line of record upside down
awk '{line[NR] = $0} END {i=NR; while (i>0){ print line[i];i=i-1}}' awk.txt
awk '{line[NR] = $0} END{for(i=NR;i>0;i--){print line[i]}}' awk.txt
AWK production case
# enter the total number of rows
awk 'END{print NR}' awk.txt
#Print line 2
awk 'NR==2 {print $0}' awk.txt
#Print the last field of each line
awk '{print $NF}' awk.txt
#Print the last field of the last line
awk '{field=$NF} END{print field}' awk.txt
#Print input lines with more than 2 fields
awk 'NF>2 {print $0}' awk.txt
#Print the last input line with a field value greater than 4
awk '$NF>4{print $0}' awk.txt