I. Introduction to docker
Architecture diagram
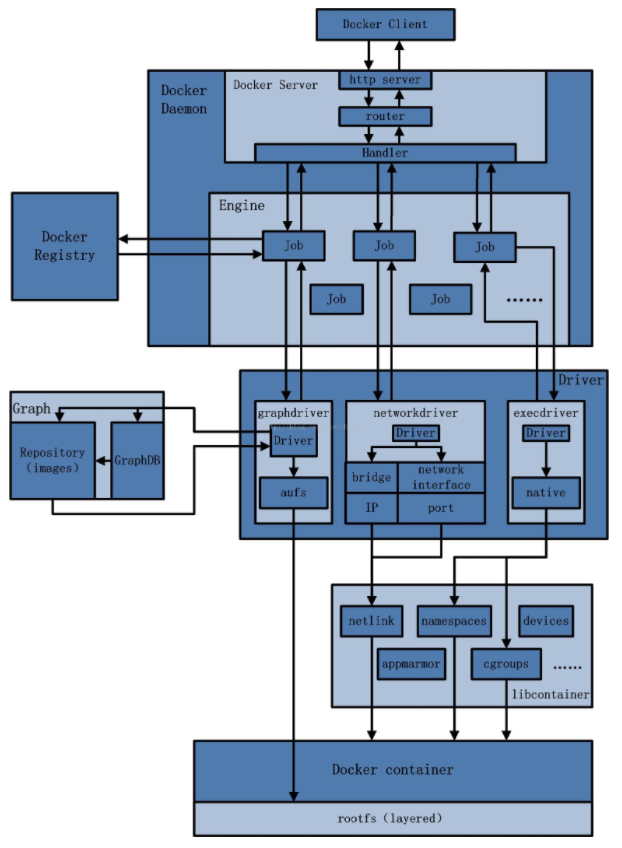
1 what is Docker
- Docker is an open source application container engine, which is based on Go language and complies with Apache 2.0 0 protocol open source;
- Docker allows developers to package their applications and dependency packages into a lightweight and portable container, and then publish them to any popular Linux machine. It can also realize virtualization;
- Containers completely use the sandbox mechanism, and there will be no interface between them. More importantly, the performance overhead of containers is very low;
- Docker is divided into CE (Community Edition) and EE (Enterprise Edition) after version 17.03.
2. Application scenario of docker
- Automatic packaging and publishing of Web applications, automatic testing and continuous integration and publishing;
- Deploy and adjust databases or other background applications in a service-oriented environment;
- Compile or extend the existing OpenShift or Cloud Foundry platform from scratch to build your own PaaS environment.
3 links
II. Installation
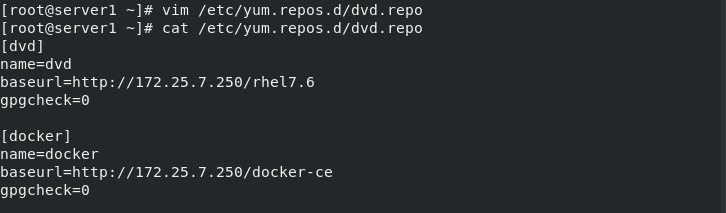
1 Write yum source
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/dvd.repo [root@server1 ~]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/dvd.repo [dvd] name=dvd baseurl=http://172.25.7.250/rhel7.6 gpgcheck=0 [docker] name=docker baseurl=http://172.25.7.250/docker-ce gpgcheck=0
2. Install docker CE
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y docker-ce
 3 start service
3 start service
root@server1 ~]# systemctl enable --now docker Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.

4. View docker information
[root@server1 ~]# docker info Client: Debug Mode: false Server: Containers: 0 Running: 0 Paused: 0 Stopped: 0 Images: 0 Server Version: 19.03.15 Storage Driver: overlay2 Backing Filesystem: xfs Supports d_type: true Native Overlay Diff: true Logging Driver: json-file Cgroup Driver: cgroupfs Plugins: Volume: local Network: bridge host ipvlan macvlan null overlay Log: awslogs fluentd gcplogs gelf journald json-file local logentries splunk syslog Swarm: inactive Runtimes: runc Default Runtime: runc Init Binary: docker-init containerd version: 05f951a3781f4f2c1911b05e61c160e9c30eaa8e runc version: 12644e614e25b05da6fd08a38ffa0cfe1903fdec init version: fec3683 Security Options: seccomp Profile: default Kernel Version: 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 Operating System: Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7.6 (Maipo) OSType: linux Architecture: x86_64 CPUs: 2 Total Memory: 1.795GiB Name: server1 ID: 2FNT:DSJG:7QEX:LGQA:EOGT:KKGC:LNCR:LR6J:YQNV:BJL3:A6K2:N64X Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker Debug Mode: false Registry: https://index.docker.io/v1/ Labels: Experimental: false Insecure Registries: 127.0.0.0/8 Live Restore Enabled: false WARNING: bridge-nf-call-iptables is disabled WARNING: bridge-nf-call-ip6tables is disabled
Warning:

Handling warning issues:
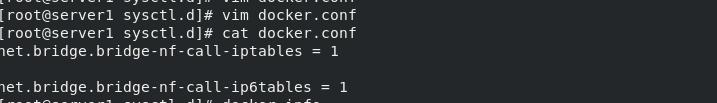
In / etc / sysctl D / edit docker Conf file
[root@server1 sysctl.d]# vim docker.conf [root@server1 sysctl.d]# cat docker.conf net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
Restart service:
[root@server1 sysctl.d]# systemctl restart docker.service [root@server1 sysctl.d]# sysctl --system
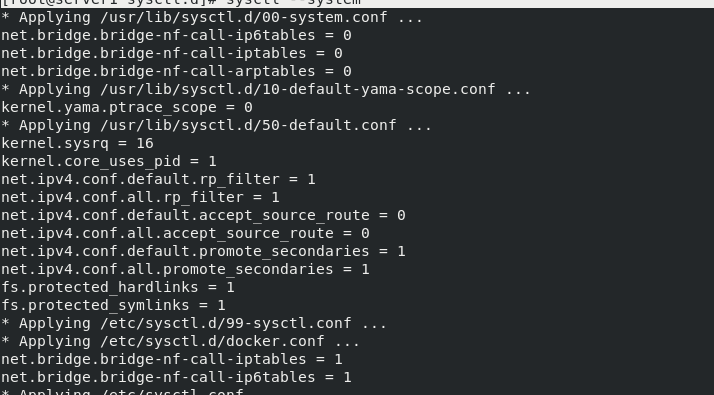
View information again
[root@server1 sysctl.d]# docker info Client: Debug Mode: false Server: Containers: 0 Running: 0 Paused: 0 Stopped: 0 Images: 0 Server Version: 19.03.15 Storage Driver: overlay2 Backing Filesystem: xfs Supports d_type: true Native Overlay Diff: true Logging Driver: json-file Cgroup Driver: cgroupfs Plugins: Volume: local Network: bridge host ipvlan macvlan null overlay Log: awslogs fluentd gcplogs gelf journald json-file local logentries splunk syslog Swarm: inactive Runtimes: runc Default Runtime: runc Init Binary: docker-init containerd version: 05f951a3781f4f2c1911b05e61c160e9c30eaa8e runc version: 12644e614e25b05da6fd08a38ffa0cfe1903fdec init version: fec3683 Security Options: seccomp Profile: default Kernel Version: 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 Operating System: Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7.6 (Maipo) OSType: linux Architecture: x86_64 CPUs: 2 Total Memory: 1.795GiB Name: server1 ID: 2FNT:DSJG:7QEX:LGQA:EOGT:KKGC:LNCR:LR6J:YQNV:BJL3:A6K2:N64X Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker Debug Mode: false Registry: https://index.docker.io/v1/ Labels: Experimental: false Insecure Registries: 127.0.0.0/8 Live Restore Enabled: false
At this point, the warning has been handled
Three tests -- running Mario games with docker
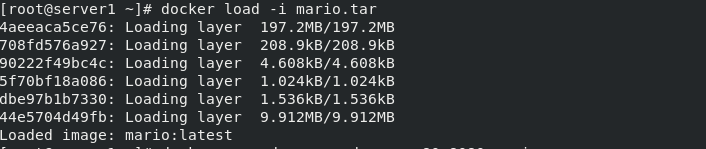
1. Game module
[root@server1 ~]# docker load -i mario.tar 4aeeaca5ce76: Loading layer 197.2MB/197.2MB 708fd576a927: Loading layer 208.9kB/208.9kB 90222f49bc4c: Loading layer 4.608kB/4.608kB 5f70bf18a086: Loading layer 1.024kB/1.024kB dbe97b1b7330: Loading layer 1.536kB/1.536kB 44e5704d49fb: Loading layer 9.912MB/9.912MB Loaded image: mario:latest
2 operation module
[root@server1 ~]# docker run -d --name demo -p 80:8080 mario 3e2efe5e6160d0182e2ea9078e577724cd4d0af6cf7d4f72a5b2a331201ef95e

3 view on Web page
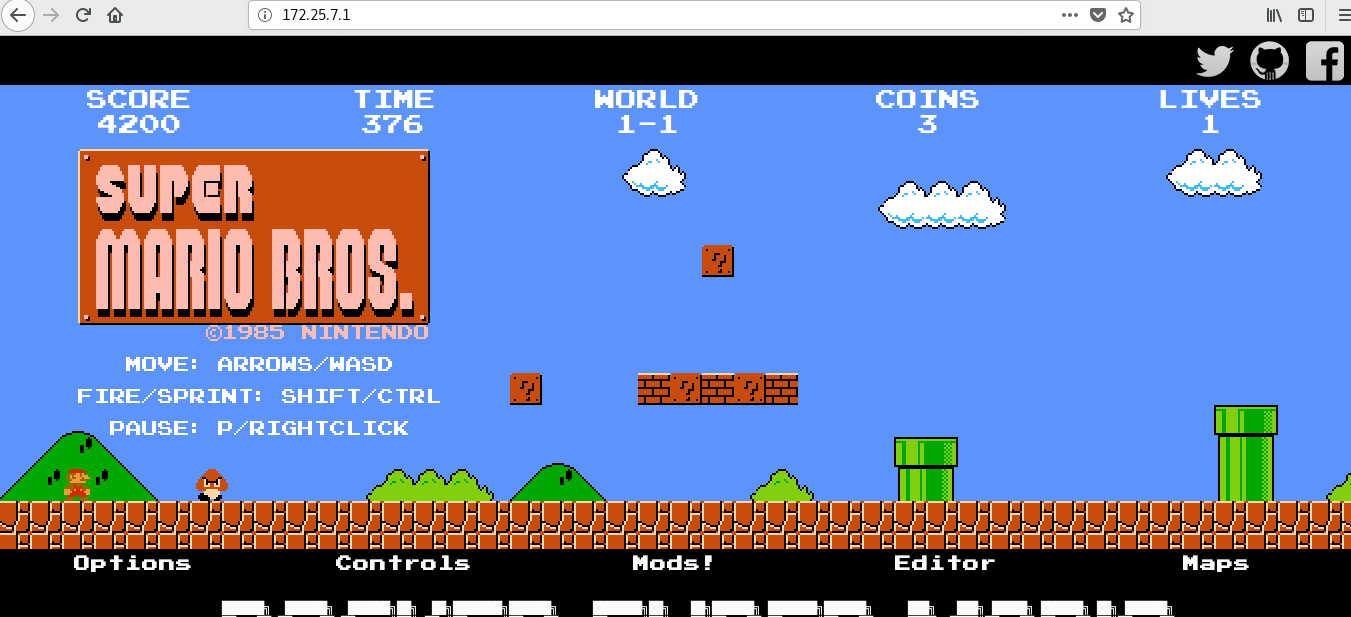
IV. docker command
pull
Pull or update the specified image from the image warehouse. If the image label is not declared, the default label is latest.
Usage: docker pull [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG|@DIGEST]
Options:
-a Pull all versions of an image
--disable-content-trust Skip verification, enabled by defaultrun
Create and start a container
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Options:
-d, --detach Run the container in the background and output the container ID
-e, --env list Sets the environment variable that can be used within the container
-h, --hostname string Specifies the name of the container hostname
-i, --interactive Run the container in interactive mode, usually with-t Simultaneous use
-l, --label list Label containers
--name string Set the container name, otherwise it will be named automatically
--network string Join container to specified network
-p, --publish list Set container mapping port
-P,--publish-all Set container to all exposed Random mapping of ports
--restart string The container restart policy is no restart by default
on-failure[:max-retries]: You can set the number of restarts when the container exits abnormally.
unless-stopped: Always restart unless using stop Stop container
always: Always restart
--rm When the container exits, the container is automatically deleted
-t, --tty Assign a pseudo terminal
-u, --user string Run user or UID
-v, --volume list Data mount
-w, --workdir string Working directory of the container
--privileged Give container privilegesbuild
Build image through Dockerfile
Usage: docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
Options:
-f, --file string appoint Dockerfile,The default is the of the current path Dockerfile
-q, --quiet Quiet mode, output image after successful construction ID
-t, --tag list Setting for mirror tag,name:tagcommit
Create a new image from the container
Usage: docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Options:
-a, --author string author
-m, --message string Submit informationcp
Copy files between container and host
Usage:
docker cp [OPTIONS] CONTAINER:SRC_PATH DEST_PATH|-
docker cp [OPTIONS] SRC_PATH|- CONTAINER:DEST_PATH
Options:
-a, --archive Preserve file permissionsexec
Issue a command to a running container
Usage: docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
Options:
-d, --detach Running commands in the background
-e, --env list Setting environment variables
-i, --interactive Run in interactive mode
-t, --tty Assign a pseudo terminal
-u, --user string User executing the command
-w, --workdir string working directoryexport
Export the container as a tar package
Usage: docker export [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Options:
-o, --output string tar Package nameimages
List mirrors
Usage: docker images [OPTIONS] [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Options:
-a, --all Show all mirrors
-f, --filter filter Filter images using filters
dangling true or false, true List those without labels, false contrary
label (label=<key> or label=<key>=<value>),If the mirror setting is label,You can use label Filter
before (<image-name>[:<tag>], <image id> or <image@digest>) - Mirror before a mirror
since (<image-name>[:<tag>], <image id> or <image@digest>) - Mirror after a mirror
reference (pattern of an image reference) - Fuzzy query,Example:--
filter=reference='busy*:*libc'
--format string Format output
.ID image ID
.Repository Mirror warehouse
.Tag image tag
.Digest Image digest
.CreatedSince How long has it been created
.CreatedAt Image creation time
.Size Mirror size
-q, --quiet Show only mirrors IDimport
Create an image by importing a tar package
Usage: docker kill [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
kill
Kill one or more containers
Usage: docker kill [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
load
Load an image from the tar package
Usage: docker load [OPTIONS] Options: -i, --input string appoint tar package -q, --quiet Show only ID
login
Log in to Docker image warehouse
Usage: docker login [OPTIONS] [SERVER] Options: -p, --password string password -u, --username string account
logout
Exit Docker image warehouse
Usage: docker logout [SERVER]
logs
Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER Options: --details Show detailed log -f, --follow Follow log output --tail string Display rows -t, --timestamps presentation time stamp
ps
List containers
Usage: docker ps [OPTIONS] Options: -a, --all List all containers -f, --filter filter Filter with filter --format string Format output -n, --last int Show last created n Containers -l, --latest Displays the last container created -q, --quiet Show containers only ID -s, --size Display size
push
Push container to mirror warehouse
Usage: docker push [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG]
rename
Rename container
Usage: docker rename CONTAINER NEW_NAME
restart
Restart one or more containers
Usage: docker restart [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
rm
Delete one or more containers
Usage: docker rm [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...] Options: -f, --force Force delete -v, --volumes Delete data volumes at the same time
rmi
Delete one or more mirrors
Usage: docker rmi [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...] Options: -f, --force Force delete
inspect
Gets the metadata of the container or image
Usage: docker inspect [OPTIONS] NAME|ID [NAME|ID...]
V. docker image
1 mirror Tiering
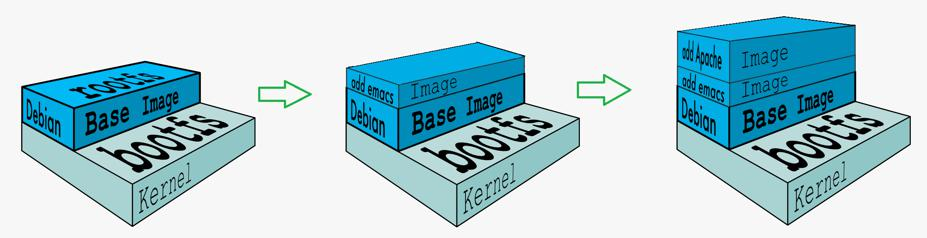
Shared host's kernel
The base image provides the smallest Linux distribution
The same docker host supports running multiple Linux distributions
The biggest advantage of adopting hierarchical structure is to share resources
Copy on write writable container layer
All mirror layers below the container layer are read-only
docker looks for files from top to bottom
The container layer holds the changed part of the image and does not
Any changes are made to the mirror itself
A mirror can have up to 127 layers
2. Construction of image
docker commit build a new image Trilogy
Run the container # modify the container # save the container as a new image
Disadvantages:
Low efficiency, weak repeatability and error prone
The user cannot audit the image, which is a potential security hazard
Dockerfile is a text file used to build an image. The text content contains instructions and instructions required to build an image one by one
ARG
Set a parameter whose value can be received from -- build Arg < Varname > = < value >
FROM
When specifying the underlying image, the FROM must be the first line of the Dockerfile non comment line.
ENV
Setting environment variables
- Suggestion: no matter which writing method is used, in actual use, only one environment variable is written in each line, which is convenient for reading.
- In particular: when using the docker run command to add the parameter -- env, if there are the same environment variables, the run command shall prevail.
ADD
Add files to add files from the host to the container.
COPY
Add files to add files from the host to the container.
USER
Specifies the user who runs the container
WORKDIR
Working directory. After entering the container, take WORKDIR as the current path
EXPOSE
Describe the port exposed by the container. The default protocol is tcp. If it is a udp protocol, you need to add udp later, such as 80/udp
VOLUME
Set the mount point to mount the path in the container to the host. The mounting method is to mount the path in the container to the docker data path
RUN
Execute the command and create a new mirror layer, usually used to update or install software.
CMD
Set the command to be executed by default after the container is started, and the CMD command will be overwritten by the parameter of docker run.
ENTRYPOINT
Like CMD, set the command to be executed by default after the container is started, but the command will not be overwritten by docker run, it will always be executed, and CMD will be overwritten by the command passed in by docker run.
Import mirror
docker load -i busybox.tar
Run container docker run -it --name test busybox Modify container (The following command runs inside the container) echo helloworld > testfile Save the container as a new mirror docker run -it --name test busybox docker commit test test:v1 View mirror docker images test:v1
Create a Dockerfile
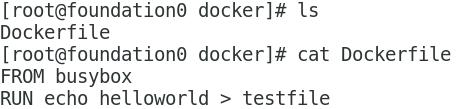
Build mirror
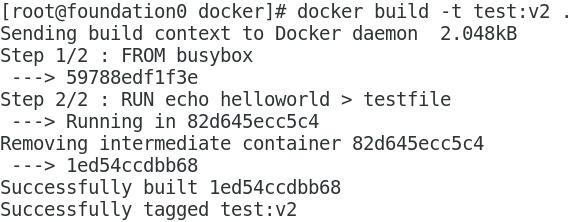
View the hierarchy of mirrors
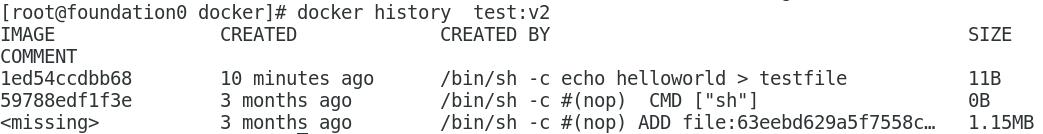
View the hierarchy of mirrors
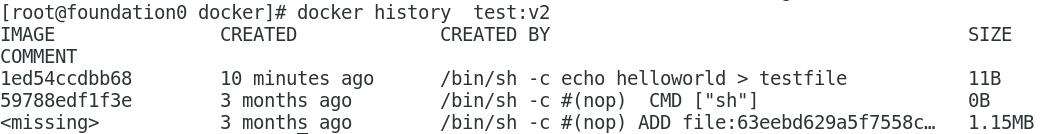
Mirrored cache properties
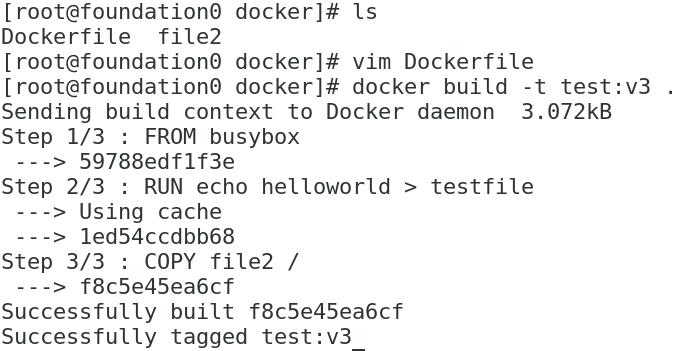
Look at the differences when running the container
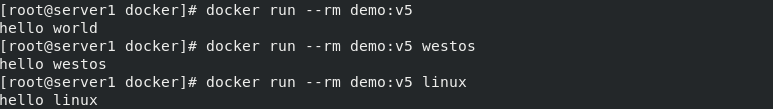
3. Image optimization
/Create a dockerfile in the root/docker directory
FROM rhel7 EXPOSE 80 VOLUME ["/usr/local/nginx/html"] COPY dvd.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/ ADD nginx-1.20.1.tar.gz /mnt RUN rpmdb --rebuilddb RUN yum install -y gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel make WORKDIR /mnt/nginx-1.20.1 RUN ./configure &> /dev/null RUN make &> /dev/null RUN make install &> /dev/null CMD ["/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx","-g","daemon off;"]
Prepare nginx and software warehouse files
mv nginx-1.20.1.tar.gz docker/ cp /etc/yum.repos.d/dvd.repo .
Generate image
docker build -t rhel7:v1 .
Build container
docker run -d --name demo rhel7:v1
View container information
docker inspect demo
Start optimization
Select the thinnest base image
Reduce the number of mirror layers
Clean up the intermediate products of image construction
Pay attention to optimizing network requests
Try to build the cache with
Use multi-stage to build mirrors
[root@server1 docker]# cat Dockerfile FROM rhel7 as build EXPOSE 80 VOLUME ["/usr/local/nginx/html"] COPY dvd.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/ ADD nginx-1.20.1.tar.gz /mnt WORKDIR /mnt/nginx-1.20.1 RUN rpmdb --rebuilddb && yum install -y gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel make && sed -i 's/CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/#CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/g' auto/cc/gcc && ./configure &> /dev/null && make &> /dev/null && make install &> /dev/null && rm -fr /mnt/nginx-1.20.1 /var/cache/* #Reduce the number of image layers and clean up the intermediate products of image construction FROM rhel7 # Use multi-stage to build mirrors COPY --from=build /usr/local/nginx /usr/local/nginx CMD ["/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx","-g","daemon off;"]
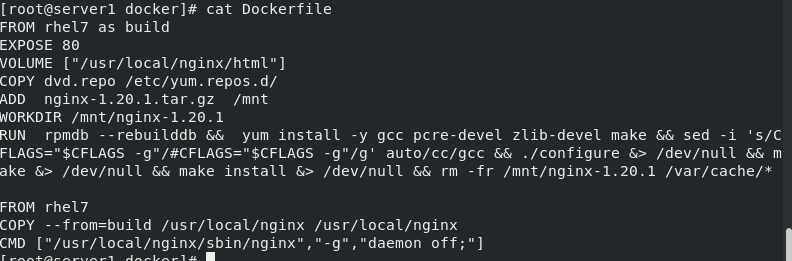
Select the thinnest base image
FROM nginx as base
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones
ARG TIME_ZONE
RUN mkdir -p /opt/var/cache/nginx && \
cp -a --parents /usr/lib/nginx /opt && \
cp -a --parents /usr/share/nginx /opt && \
cp -a --parents /var/log/nginx /opt && \
cp -aL --parents /var/run /opt && \
cp -a --parents /etc/nginx /opt && \
cp -a --parents /etc/passwd /opt && \
cp -a --parents /etc/group /opt && \
cp -a --parents /usr/sbin/nginx /opt && \
cp -a --parents /usr/sbin/nginx-debug /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpcre.so.* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libz.so.* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdl* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcrypt* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libssl.so.* /opt && \
cp -a --parents /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcrypto.so.* /opt && \
cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/${TIME_ZONE:-ROC} /opt/etc/localtime
FROM gcr.io/distroless/base-debian10
COPY --from=base /opt /
VOLUME ["/usr/share/nginx/html"]
EXPOSE 80 443
ENTRYPOINT ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
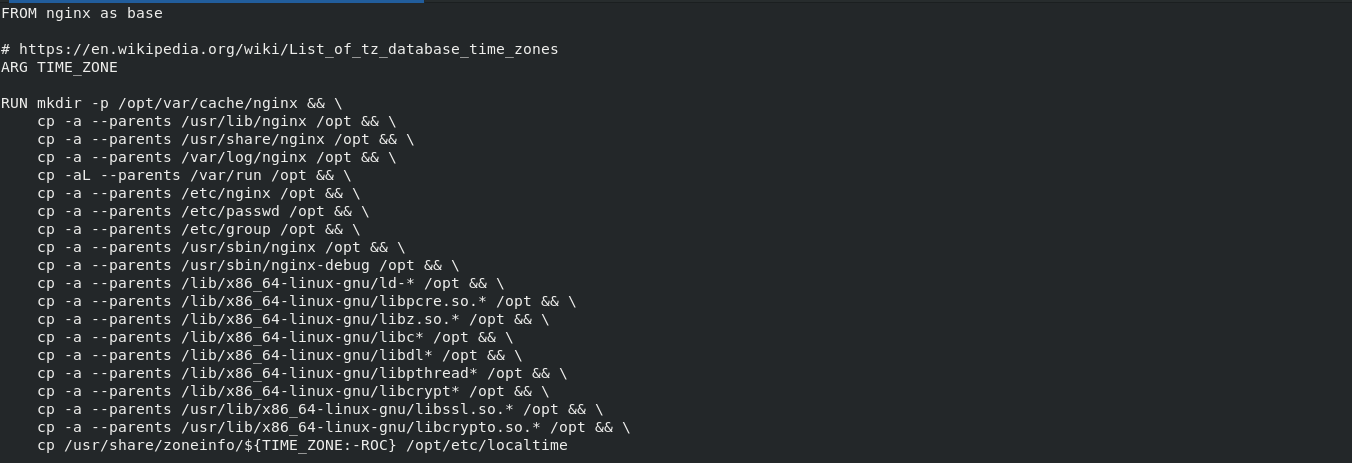

The reconstructed image size is only 31.6MB, so try to select it in the actual construction
Select the thinnest base image.
