Bidirectional linked list, also known as double linked list, is a kind of linked list. There are two pointers in each data node, pointing to the direct precursor and direct successor respectively. Therefore, starting from any node in the two-way linked list, it is convenient to directly access its predecessor node and successor node with address.
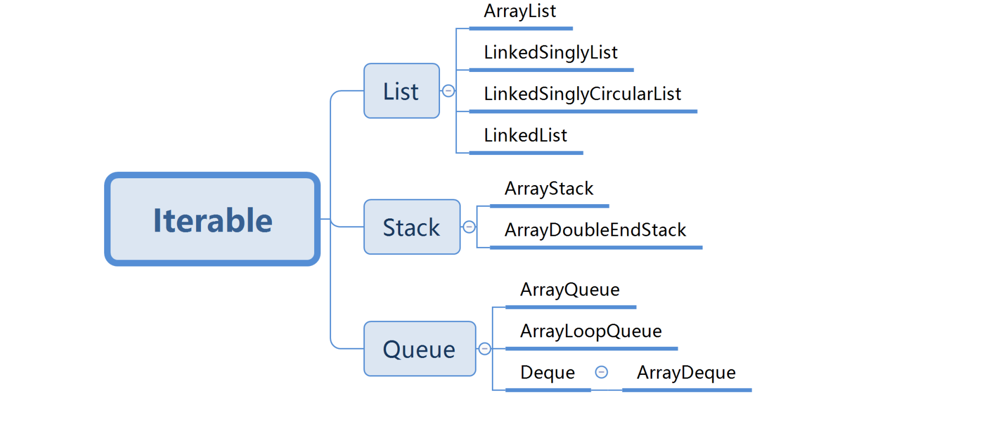
Here, we define the bidirectional circular linked List as the LinkedList class and implement the List, Deque and Stack interfaces
Here we mainly talk about the principles of several aspects,
1, Add node
If you are adding element node objects directly, you can add them directly
public void add(E element) {
add(size,element);
}
If it is added through index, four situations should be considered:
First, judge whether the index of the linked list is out of bounds. If it is out of bounds, throw an out of bounds exception
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index outof range");
}
First case When the linked list is empty If empty, head The header pointer points to the added node, tail The tail pointer points to the newly added node, Because it is a two-way circular linked list tail Successor to next point head,head Precursor of pre point tail

The code is as follows
if (isEmpty()) {
head = node;
tail = node;
tail.next = head;
head.pre = tail;
}
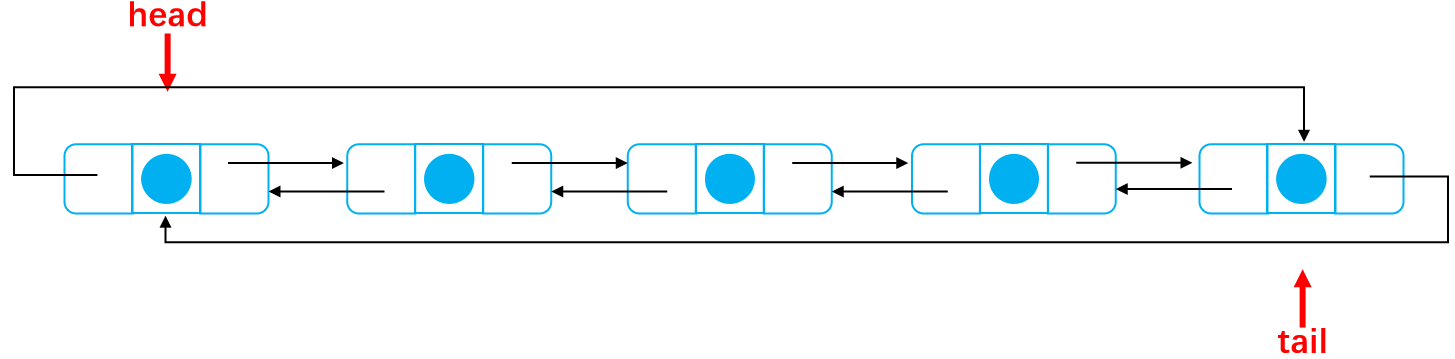
The second case Add from the head node of the linked list Nodes to be added node.pre point head.pre node.next point head head.pre point node take node Defined as a new header node Again tail.next point head The linked list after successful addition is shown as follows:

The code is as follows:
else if (index == 0) {
node.pre = head.pre;
node.next = head;
head.pre = node;
head = node;
tail.next = head;
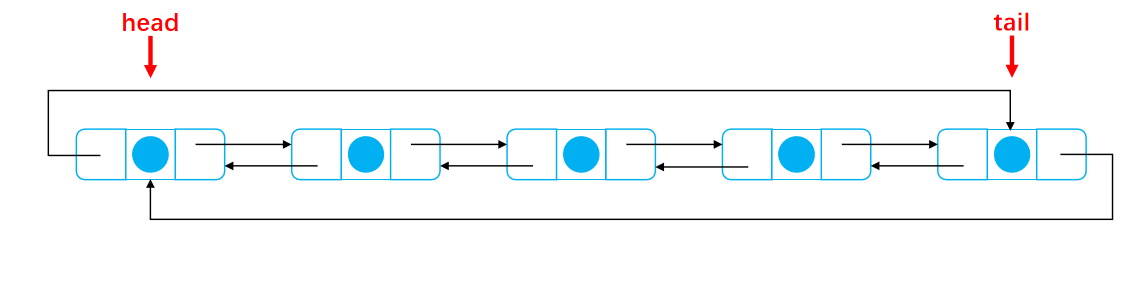
The third case Add from the tail node of the linked list take node.next point tail.next tail.next point node node.pre point tail take node Define as new tail Tail node Finally head.pre point tail The linked list after successful addition at the end is as follows:
Before adding:

After adding:
The code is as follows:
else if (index == size) {
node.next = tail.next;
tail.next = node;
node.pre = tail;
tail = node;
head.pre = tail;
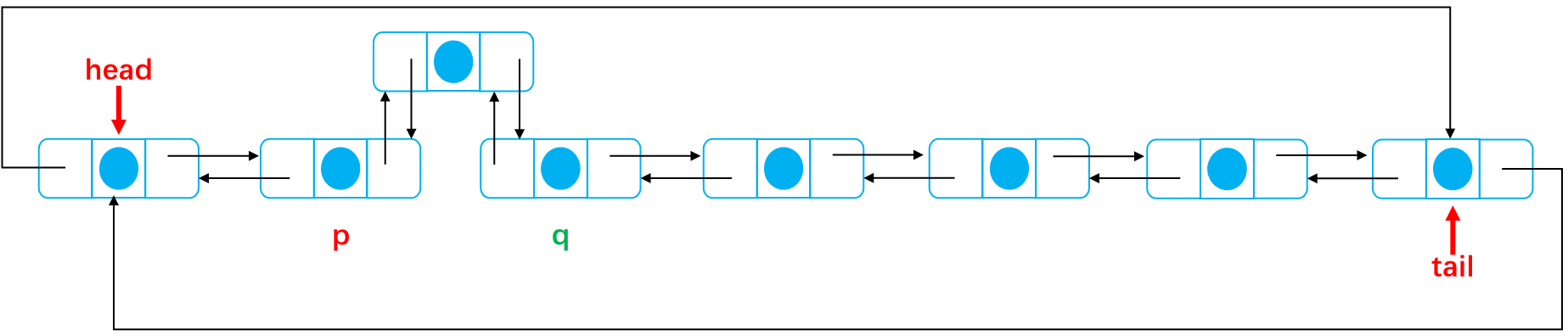
The fourth case Add from the middle of the linked list First, we need to define two pointers, p The node is the precursor of the added node, q The node is a node next The next hop is also the next hop for adding nodes First of all, the location of the added node should be considered. If the inserted node is in size/2 The default position is on the left, from head Start pointing back Define two nodes p,q p point p.next q point p.next p.next point node node.pre point p node.next point q last q.pre point node
The node addition is completed as shown in the figure below:
The code is as follows:
Node p,q;
if (index <= size / 2) {
p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
q = p.next;
p.next = node;
node.pre = p;
node.next = q;
q.pre = node;
Then the added position is close to the tail node
First, point p to the tail node of tai
Then p=p.pre
q points to p.pre
q.next points to node
p.pre points to node
Finally, node Next points to p
After adding nodes, see the figure below:
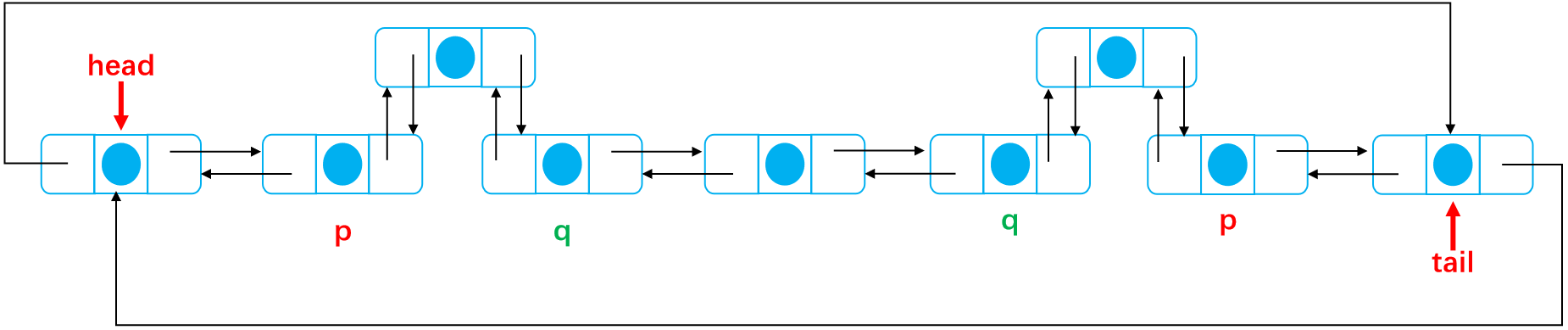
The code is as follows:
else {
p = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
p = p.pre;
}
q = p.pre;
q.next = node;
node.pre = q;
p.pre = node;
node.next = p;
}
Add nodes in any case; After adding, size the length of the linked list++
2, Delete node
The first thing is to delete the element directly
Find the location of the element to be deleted through the indexOf method
As long as the position is not - 1, it will be deleted directly
public void remove(E element) {
int index = indexOf(element);
if (index != -1) {
remove(index);
}
}
If it is deleted through index
Like adding, first judge whether the index is out of bounds, and then consider the location of deletion
There are four major situations:
Only one node
First, define a ret to store the deleted node
Directly set the head to null
Set tail to null
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index outof range");
}
E ret = null;
if (size == 1) {
ret = head.data;
head = null;
tail = null;
}
Delete from scratch node
First point node to head next;
Set RET = head data
head.next empty
node.pre points to head pre
head.pre empty
head points to node
tail.next points to head;
As shown below:
Define a node node
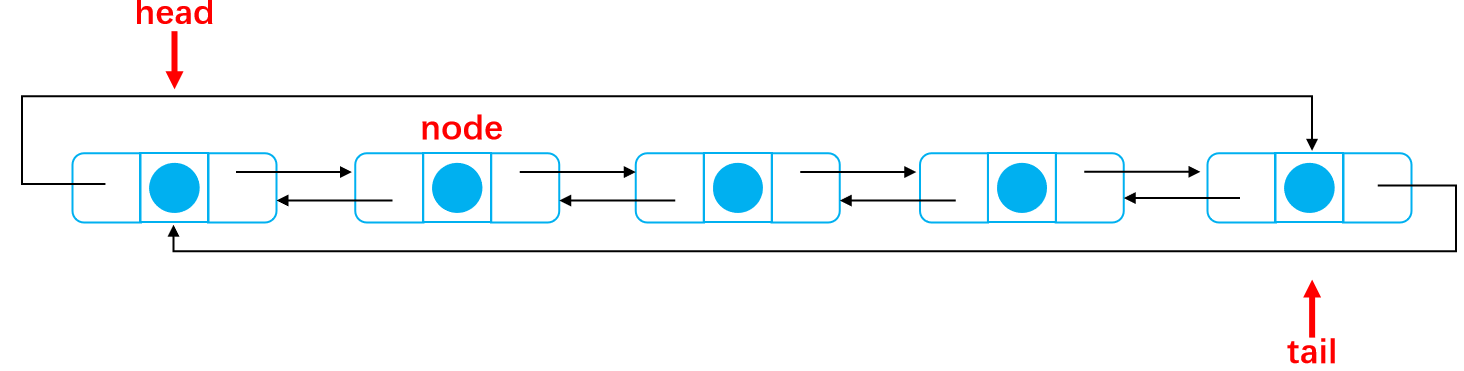
Disconnect all connections of the beginning node
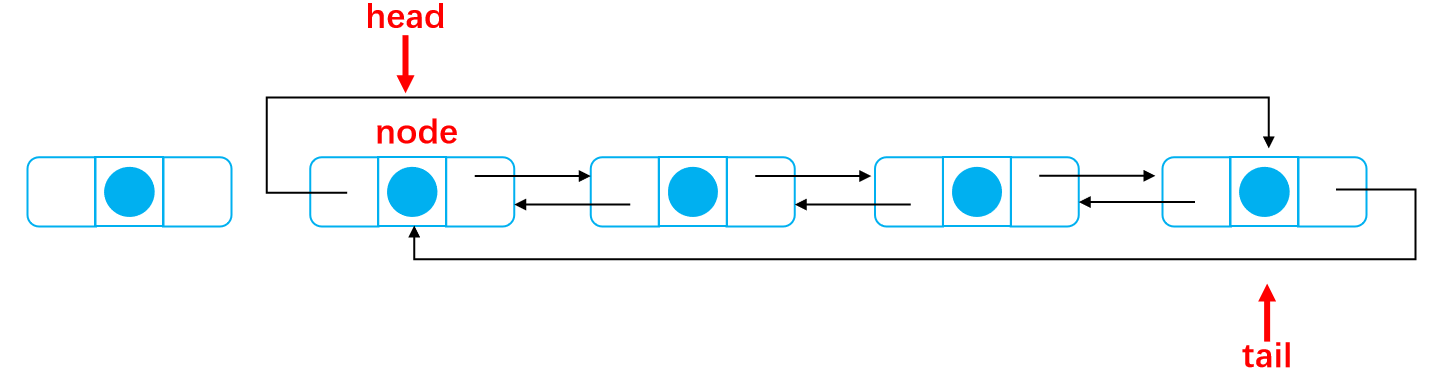
This is the case after complete deletion
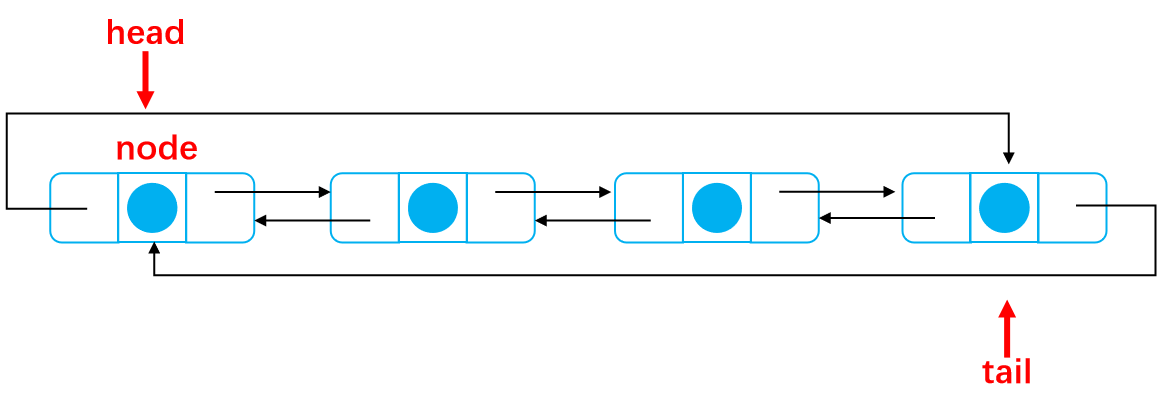
The code is as follows:
else if (index == 0) {
Node node = head.next;
ret = head.data;
head.next = null;
node.pre = head.pre;
head.pre = null;
head = node;
tail.next = head;
}
Delete from tail node
node points to tail pre
ret=tail.data
tail.pre set null
node.next points to tail next
tail.next empty
tail points to node
Finally, head Pre points to tail
As shown below:
Before deletion:
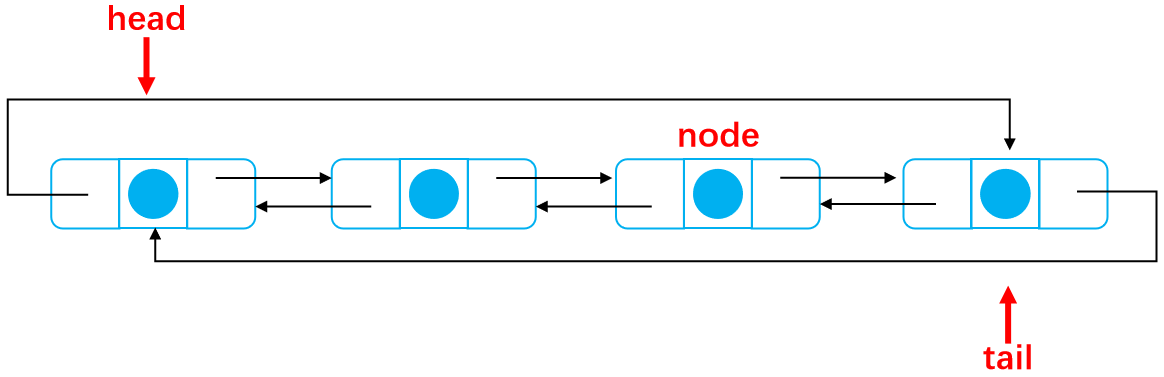
Disconnect all contacts:
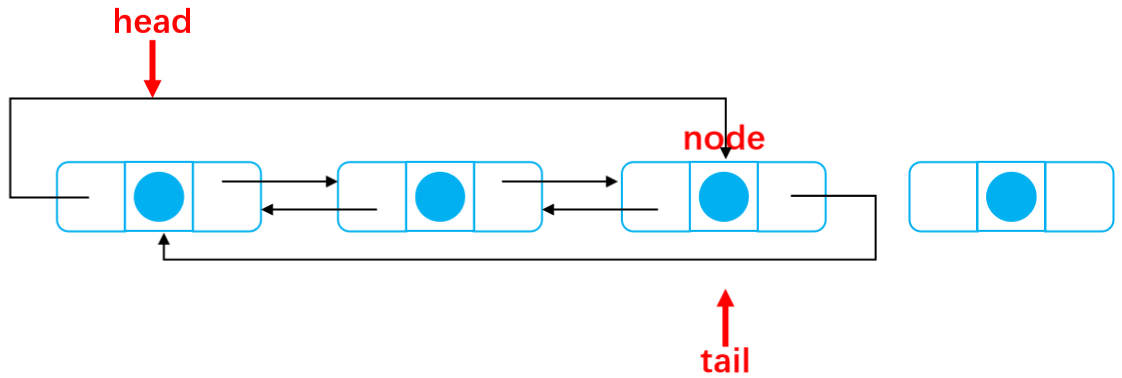
After deletion:
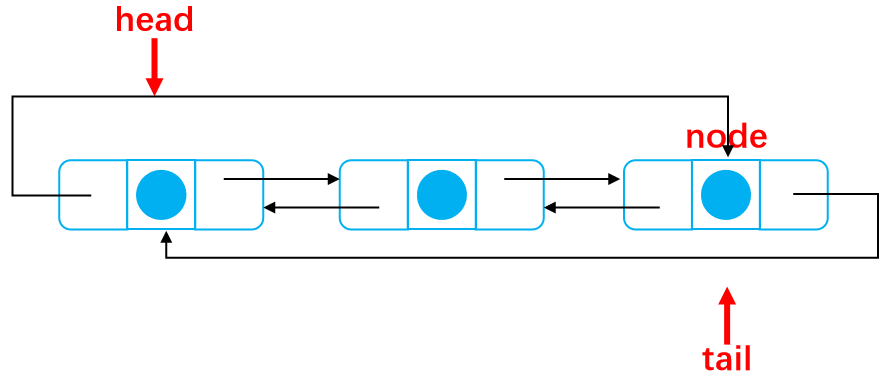
The code is as follows:
else if (index == size - 1) {
Node node = tail.pre;
ret = tail.data;
tail.pre = null;
node.next = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
tail = node;
head.pre = tail;
}
Delete from middle
If you delete from the middle, you have to consider the approximate location of the deleted node as you add
Define three nodes p,q,r
p is the previous node to delete
q is the node to be deleted
r is the last node to be deleted
When the node to be deleted is on the left
p points to head
Then move to p.next
Then point q to p.next
Give the value of q.data to ret
r points to q.next
p.next points to r
r.pre points to p
q.next empty
q.pre empty
As shown below:
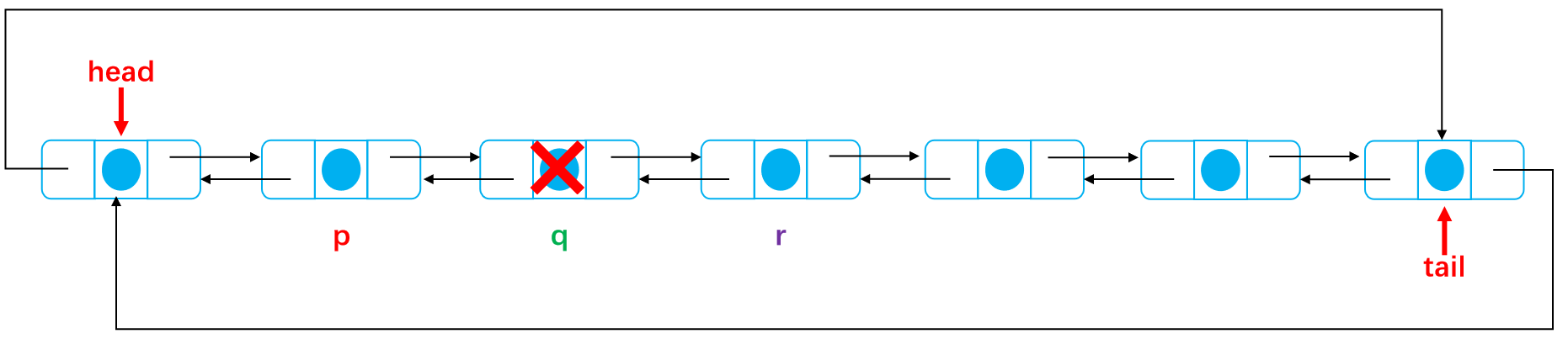
After deletion:
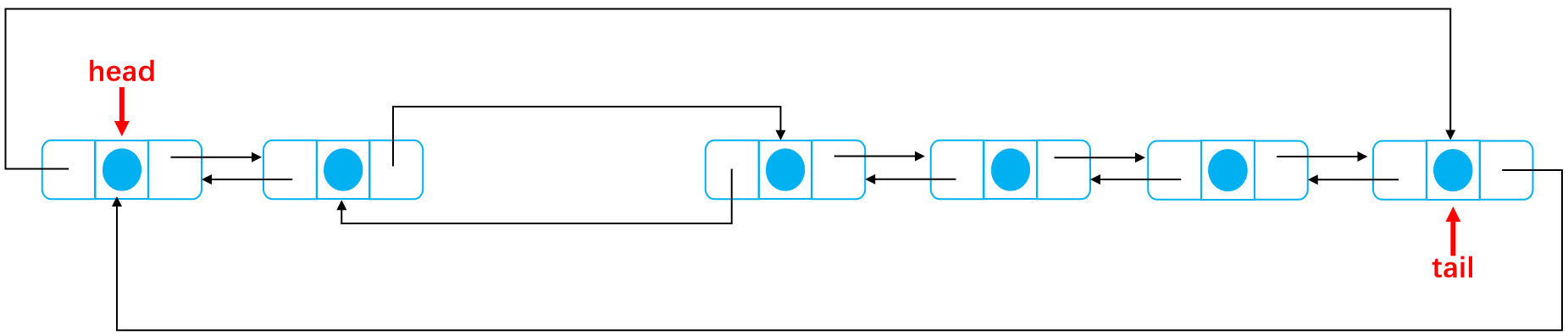
The code is as follows:
else {
Node p,q,r;
if (index <= size / 2) {
p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
q = p.next;
ret = q.data;
r = q.next;
p.next = r;
r.pre = p;
q.next = null;
q.pre = null;
}
Then, the node to be deleted is close to the tail node
p start with tail
P move left p=p.next
q points to p.pre
Give q.data to ret
r points to q.pre
r.next points to p
p.pre points to r
q.next empty
q.pre empty
Just like adding, in any case, if deleted, the overall length of the linked list is - 1, that is, size - and finally ret is returned
As shown in the figure:

After deletion:
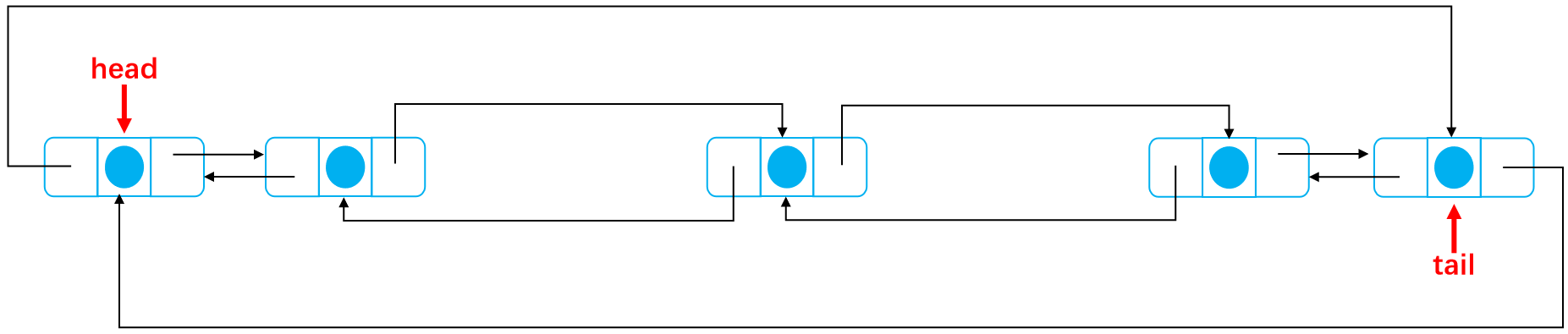
The code is as follows:
else {
p = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
p = p.pre;
}
q = p.pre;
ret = q.data;
r = q.pre;
r.next = p;
p.pre = r;
q.next = null;
q.pre = null;
}
}
size--;
return ret;
}
The whole code is as follows:
public class LinkedList<E> implements List<E>, Stack<E>, Queue<E>, Deque<E> {
private class Node {
E data;
Node pre;
Node next;
public Node(E data) {
this.data = data;
pre = null;
next = null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data.toString();
}
}
private Node head;
private Node tail;
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
@Override
public void add(E element) {
add(size,element);
}
@Override
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index outof range");
}
Node node = new Node(element);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = node;
tail = node;
tail.next = head;
head.pre = tail;
} else if (index == 0) {
node.pre = head.pre;
node.next = head;
head.pre = node;
head = node;
tail.next = head;
} else if (index == size) {
node.next = tail.next;
tail.next = node;
node.pre = tail;
tail = node;
head.pre = tail;
} else {
Node p,q;
if (index <= size / 2) {
p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
q = p.next;
p.next = node;
node.pre = p;
node.next = q;
q.pre = node;
} else {
p = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
p = p.pre;
}
q = p.pre;
q.next = node;
node.pre = q;
p.pre = node;
node.next = p;
}
}
size++;
}
@Override
public void remove(E element) {
int index = indexOf(element);
if (index != -1) {
remove(index);
}
}
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index outof range");
}
E ret = null;
if (size == 1) {
ret = head.data;
head = null;
tail = null;
} else if (index == 0) {
Node node = head.next;
ret = head.data;
head.next = null;
node.pre = head.pre;
head.pre = null;
head = node;
tail.next = head;
} else if (index == size - 1) {
Node node = tail.pre;
ret = tail.data;
tail.pre = null;
node.next = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
tail = node;
head.pre = tail;
} else {
Node p,q,r;
if (index <= size / 2) {
p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
q = p.next;
ret = q.data;
r = q.next;
p.next = r;
r.pre = p;
q.next = null;
q.pre = null;
} else {
p = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
p = p.pre;
}
q = p.pre;
ret = q.data;
r = q.pre;
r.next = p;
p.pre = r;
q.next = null;
q.pre = null;
}
}
size--;
return ret;
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (index == 0) {
return head.data;
} else if (index == size - 1) {
return tail.data;
} else {
Node p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
return p.data;
}
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index outof range");
}
E ret = null;
if (index == 0) {
ret = head.data;
head.data = element;
} else if (index == size - 1) {
ret = tail.data;
tail.data = element;
} else {
Node p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
ret = p.data;
p.data = element;
}
return ret;
}
@Override
public void addFirst(E element) {
add(0,element);
}
@Override
public void addLast(E element) {
add(size,element);
}
@Override
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
@Override
public E removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
@Override
public E getFirst() {
return get(0);
}
@Override
public E getLast() {
return get(size - 1);
}
@Override
public void offer(E element) {
add(size,element);
}
@Override
public E poll() {
return remove(0);
}
@Override
public E element() {
return get(0);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(E element) {
int index = 0;
Node p = head;
while (!p.data.equals(element)) {
index++;
p = p.next;
if (p == head) {
return -1;
}
}
return index;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(E element) {
return indexOf(element) != -1;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0 && head == null && tail == null;
}
@Override
public void push(E element) {
add(size,element);
}
@Override
public E pop() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
@Override
public E peek() {
return get(size - 1);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
@Override
public void sort(Comparator<E> comparator) {
if (comparator == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("comparator can not be null");
}
if (size < 2) {
return;
}
Node i = head.next;
Node j = null;
Node k = null;
E e = null;
while (i != head) {
e = i.data;
j = i;
k = j.pre;
while (k != tail && comparator.compare(k.data, e) > 0) {
j.data = k.data;
j = j.pre;
k = j.pre;
}
j.data = e;
i = i.next;
}
}
@Override
public List<E> sublist(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex < 0 || toIndex >= size || fromIndex >= toIndex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sublist index outof range");
}
Node nodeA = head;
for (int i = 0; i < fromIndex; i++) {
nodeA = nodeA.next;
}
Node nodeB = head;
for (int i = 0; i < toIndex - 1; i++) {
nodeB = nodeB.next;
}
Node p = nodeA;
LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<>();
while (true) {
list.add(p.data);
if (p == nodeB) {
break;
}
p = p.next;
}
return list;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
if (isEmpty()) {
sb.append(']');
} else {
Node p = head;
while (true) {
sb.append(p.data);
if (p == tail) {
sb.append(']');
break;
}
sb.append(',');
p = p.next;
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
if (obj == this) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof LinkedList) {
LinkedList other = (LinkedList) obj;
if (this.size == other.size) {
if (this.size == 0) {
return true;
}
Node p1 = this.head;
Node p2 = other.head;
while (true) {
if (!p1.data.equals(p2.data)) {
return false;
}
if (p1 == this.tail) {
return true;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new LinkedListIterator();
}
private class LinkedListIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private Node cur = head;
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
return flag;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E ret = cur.data;
cur = cur.next;
if (cur == head) {
flag = false;
}
return ret;
}
}