Binary tree
1. What is a binary tree
Binary tree is a kind of tree. Each node can have at most two subtrees, that is, the maximum degree of the node is 2 (node degree: node degree)
Some subtrees).

2. Binary tree species
Binary search tree:
The left side of the current root node is smaller than the root node, and the right side of the current root node is larger than the root node.
Oblique tree:
All nodes have only left subtree or right subtree.
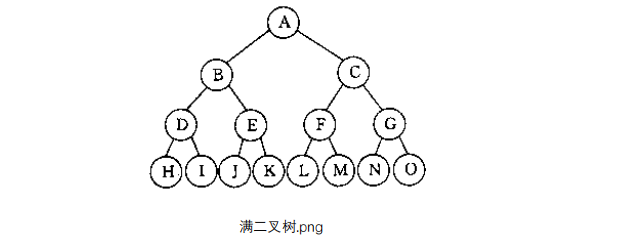
Full binary tree
All branch nodes have left and right nodes.
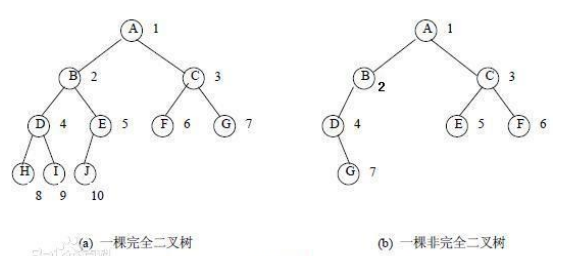
Complete binary tree
If the depth of the binary tree is h, the number of nodes in all other layers (1 ~ h-1) reaches the maximum, H
All nodes in the layer are continuously concentrated on the left, which is a complete binary tree.
3. Some properties of binary tree
The maximum number of nodes on layer I of binary tree is 2^(i-1) (i ≥ 1)
A binary tree with depth h has at most 2^h-1 nodes (H ≥ 1)
The height of a binary tree containing N nodes is at least log2 (n+1)
In any binary tree, if the number of terminal nodes is n0 and the number of nodes with degree 2 is n2, then n0=n2+1
4. Traversal of binary tree
Preorder traversal
First access the root node, then the left node, and then the right node
Medium order traversal
Access the left node first, then the root node, and then the right node
Postorder traversal
First access the left node, then the right node, and then the root node
Tip: the traversal method is named according to the location of the root node. The access order of left and right nodes will not change

Preorder traversal (root left right): 1-2-4-8-9-5-10-3-6-7
Middle order traversal: (left root right): 8-4-9-2-10-5-1-6-3-7
Post order traversal (left right root): 8-9-4-10-5-2-6-7-3-1
5. Code implementation
Tree structure
public class TreeNode<T> {
private T data;
private TreeNode left;
private TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public TreeNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(TreeNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public TreeNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(TreeNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
Manual construction of binary tree + traversal
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode<String> root = new TreeNode<>("1");
TreeNode<String> node2 = new TreeNode<>("2");
TreeNode<String> node3 = new TreeNode<>("3");
TreeNode<String> node4 = new TreeNode<>("4");
TreeNode<String> node5 = new TreeNode<>("5");
TreeNode<String> node6 = new TreeNode<>("6");
TreeNode<String> node7 = new TreeNode<>("7");
// Build binary tree manually
root.setLeft(node2);
node2.setLeft(node4);
node2.setRight(node5);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setLeft(node6);
node3.setRight(node7);
System.out.println("Breadth traversal:");
printByLayer(root);
System.out.println("\n Preorder traversal:");
pre_print(root);
System.out.println("\n Middle order traversal:");
mid_print(root);
System.out.println("\n Post order traversal:");
last_print(root);
}
/**
* Traverse by breadth
* @param root
*/
public static void printByLayer(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
// When the queue is not empty
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
if (temp.getLeft()!=null){
// Enter queue
queue.add(temp.getLeft());
} if (temp.getRight() != null){
// Enter queue
queue.add(temp.getRight());
}
System.out.print(temp.getData()+"\t");
}
}
/**
* Preorder traversal: left and right roots
* @param root
*/
public static void pre_print(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
// root
System.out.print(root.getData()+"\t");
// Left
pre_print(root.getLeft());
// right
pre_print(root.getRight());
}
}
/**
* Middle order traversal: left root right
* @param root
*/
public static void mid_print(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
// Left
mid_print(root.getLeft());
// root
System.out.print(root.getData()+"\t");
// right
mid_print(root.getRight());
}
}
/**
* Postorder traversal: left and right roots
* @param root
*/
public static void last_print(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
// Left
last_print(root.getLeft());
// right
last_print(root.getRight());
// root
System.out.print(root.getData()+"\t");
}
}
}
Operation results
Breadth traversal: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Preorder traversal: 1 2 4 5 3 6 7 Middle order traversal: 4 2 5 1 6 3 7 Post order traversal: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
Sorted binary tree
/**
* Binary sort tree
*/
public class BinarySortTree<T> {
private TreeNode<T> root; // Root node
public TreeNode<T> getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(TreeNode<T> root) {
this.root = root;
}
/**
* Get node
* @param data
* @return
*/
public TreeNode get(T data){
if (this.root == null) return null;
TreeNode temp = root;
while (temp != null){
String currentData = String.valueOf(temp.getData());
String nodeData = String.valueOf(data);
if (currentData.compareTo(nodeData) > 0){
//The root node goes to the left
temp = temp.getLeft();
} else if (currentData.compareTo(nodeData) < 0){
//The root node is small. Go to the right
temp = temp.getRight();
} else {
return temp;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Insert according to node size
* @param data treeNode node
* @return
*/
public boolean add(TreeNode<T> data) {
if (root == null) {
this.root = data;
return true;
} else {
TreeNode<T> current = root;
TreeNode<T> parentNode = null;
while(current != null) {
parentNode = current;
String currentData = (String)parentNode.getData();
String nodeData = (String)data.getData();
//Convert to string comparison
if (currentData.compareTo(nodeData) > 0) {
// Large root node
if (parentNode.getLeft() == null){
// Insert left subtree
parentNode.setLeft(data);
return true;
}
// Continue to look at the left subtree
current = parentNode.getLeft();
} else {
// Small root node
if (parentNode.getRight() == null){
// Insert right subtree
parentNode.setRight(data);
return true;
}
// Continue to look at the right subtree
current = parentNode.getRight();
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
test
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode<String> root = new TreeNode<>("a14");
TreeNode<String> node2 = new TreeNode<>("b25");
TreeNode<String> node3 = new TreeNode<>("c10");
TreeNode<String> node4 = new TreeNode<>("d18");
TreeNode<String> node5 = new TreeNode<>("d13");
//Sorted binary tree
BinarySortTree<String> btree = new BinarySortTree<String>();
btree.add(root);
btree.add(node2);
btree.add(node3);
btree.add(node4);
btree.add(node5);
System.out.println("\n Middle order traversal:");
mid_print(btree.getRoot());
TreeNode d13 = btree.get("d13");
System.out.println("\n" + d13.getData());
}
/**
* Middle order traversal: left root right
* @param root
*/
public static void mid_print(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
// Left
mid_print(root.getLeft());
// root
System.out.print(root.getData()+"\t");
// right
mid_print(root.getRight());
}
}
}
Operation results
Middle order traversal: a14 b25 c10 d13 d18 d13