BOM and DOM operations
What are BOM and DOM
-
BOM refers to the object model of the browsing area, which enables js to operate the browser through it
-
DOM refers to the document object model, which enables js to operate the front-end page (that is, all elements of HTML document)
BOM needs to master operation
window.open() - Open a new window window.close() - Close current window history.forward() // Forward one page history.back() // Back one page location.href obtain URL location.href="URL" // Jump to the specified page location.reload() Reload page setTimeout() clearTimeout() setInterval() clearInterval()
windows object
- All browsers support window objects. It represents the browser window
Common window methods include:
-
window.innerHeight - displays the internal height of the browser window
-
window.innerWidth - displays the internal width of the browser window
-
window. [name - url], [open]
window.open()Three parameters,url Yes, it must be the link address of the newly opened page name Is the name of the newly opened window, which can be used to obtain the window object configuration: Some configuration items for the newly opened window, such as whether there is menu bar, scroll bar, length and height, etc ps: window.open("https://www.baidu.com", "newWindow", "width=1024, height=700, top=0, left=0, titlebar=no, menubar=no, scrollbars=yes, resizable=yes, status=yes, , toolbar=no, location=yes"); -
window.close() - closes the current window
Child objects of windows
navigator object (understand)
- Browser object, which can determine the browser used by the user, including the relevant information of the browser
navigator.appName // Full name of Web browser navigator.appVersion // Detailed string of Web browser manufacturer and version navigator.userAgent // Most client information navigator.platform // The operating system on which the browser is running

screen object
Screen object, not commonly used.
Some properties:
- screen.availWidth - available screen width
- screen.availHeight - available screen height
history object
window. The history object contains the history of the browser.
The browsing history object contains the user's browsing history of the current page, but we can't view the specific address. It can be simply used to move forward or backward a page.
history.forward() // Forward one page history.back() // Back one page
location object
window. The location object is used to get the address (URL) of the current page and redirect the browser to a new page.
Common properties and methods:
location.href obtain URL location.href="URL" // Jump to the specified page location.reload() Reload page
Three pop ups
- Three message boxes can be created in JavaScript: warning box, confirmation box and prompt box.
// Warning box alert
alert('Warning content');
// confirm box
confirm('Contents to be confirmed') // If there is a return value, return true or false according to the confirmation
// Prompt box prompt
prompt('Prompt content','Default information') // If there is a return value, return the user input information
Timing correlation
- By using JavaScript, we can execute code after a certain time interval, rather than immediately after the function is called. We call it a timed event.
setTimeout()
var t=setTimeout(command,millisecond) // How many milliseconds to execute JS statement
clearTimeout()
clearTimeout(t) // Cancel timing task above
setInterval()
setInterval(command,time interval) // How often do JS statements execute
clearInterval() Method can be cancelled by setInterval() Set timeout.
// The command can be 'js statement' ps: 'alert("123")' or function ps:
function func1(){}
var t = setTimeout(func1,3000)

BOM needs to master operation
- HTML DOM tree
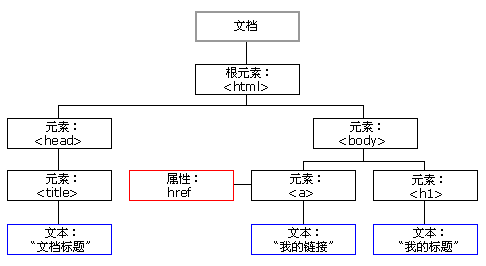
The DOM standard specifies that each component in an HTML document is a node:
- Document node (document object): represents the whole document
- Element node (element object): represents an element (label)
- Text node (text object): represents the text in the element (label)
- Attribute node (attribute object): represents an attribute, and only elements (labels) have attributes
- Comments are comment nodes (comment objects)
JavaScript can create dynamic HTML through DOM:
- JavaScript can change all HTML elements in a page
- JavaScript can change all HTML attributes in a page
- JavaScript can change all CSS styles in a page
- JavaScript can respond to all events in the page
Lookup label of DOM operation
- Keyword document
// Basic search (core) document.getElementById according to ID Get a tag document.getElementsByClassName according to class Property acquisition document.getElementsByTagName Get the tag collection according to the tag name // Indirect search parentElement Parent node label element children All child Tags firstElementChild First child label element lastElementChild Last child tag element nextElementSibling Next sibling tag element previousElementSibling Previous sibling tag element

Node operation
-
Create node
Syntax: createElement (tag name)
ps : var divEle = document.createElement("div")
-
Add node
Append a child node (as the last child node)
- somenode.appendChild(newnode); // Somenode refers to the node obtained
Put the added node in front of a node.
- somenode.insertBefore(newnode, a node);
ps:
var d1Ele = document.getElementById("d1"); d1Ele.appendChild(imgEle); -
Delete node
Syntax: somenode Removechild (node to be deleted)
-
Replace node
Syntax: somenode Replacechild (newnode, a node);
Node attribute and value operation
- Get the value of the text node:
var divEle = document.getElementById("d1")
divEle.innerText // Get text content
divEle.innerText = 'Okay, good' // Set text content
divEle.innerHTML // Gets the label and text within the node
divEle.innerHTML="<p>2</p>" // Set labels and text
innerText
No assignment symbol is used to get the internal text
The assignment symbol is used to set the built-in text
// HTML tags are not recognized
innerHTML
No assignment symbol is used to obtain the internal label+text
The assignment symbol is used to set the built-in label+text
// HTML tags can be recognized
- Set the attribute of the text node (attribute operation)
var divEle = document.getElementById("d1")
divEle.setAttribute("age",18) // set a property
divEle.getAttribute("age") // get attribute
divEle.removeAttribute("age") // Delete attribute
- Get value operation
Syntax:
elementNode.value
Applicable to the following labels:
- .input
- .select
- .textarea
// Ordinary text data acquisition
Label object.value
// Special file data acquisition
Label object.value '''Just get a file address'''
Label object.files[0] '''Get single file data'''
Label object.files '''Get all file data'''

class operation
classList View all classes classList.remove(cls) Delete the specified class classList.add(cls) Add class classList.contains(cls) Existence return true,Otherwise return false classList.toggle(cls) Delete if it exists, otherwise add notes: Only those in this text can be obtained class Property cannot be obtained across text
Specify css operation
obj.style.backgroundColor="red" Label object.style.Attribute name = Attribute value
event
- One of the new features of HTML 4.0 is the ability to enable HTML events to trigger action s in the browser, such as launching a JavaScript when a user clicks on an HTML element.
// Event is to add custom functions to HTML elements
How to bind events 1
<button onclick="func()">Point me</button>
<script>
function func() {
alert(123)
}
</script>
How to bind events 2
<button id="d1">Choose me</button>
<script>
// 1. Find the label first
var btnEle = document.getElementById('d1')
// 2. Binding events
btnEle.onclick = function () {
alert(456)
}
</script>
- The built-in parameter this represents the current element that triggers the event. This is a formal parameter in the function definition process
Used inside the function body code of the event
btnEle.onclick = function () {
alert(456)
console.log(this)
}
Case:
onclick Click event onfocus Focus event onblur Loss of focus event onchange Text field change event onload wait for...Events executed after loading

Timer case
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id = 'd1'>
<button id = 'd2'>start</button>
<button id = 'd3'>suspend</button>
<button id = 'd4'>empty</button>
<script>
// 1. Find the button first
var iEle = document.getElementById('d1')
var but1Ele = document.getElementById('d2')
var but2Ele = document.getElementById('d3')
var but3Ele = document.getElementById('d4')
var t = null
// 3. Construct a function to display the time in the text box
function showTime() {
// Get current time
var cTime = new Date().toLocaleString()
// Displays the time in a text box
iEle.value = cTime
}
// 2. Bind start button
but1Ele.onclick = function () {
// Prevent repetitive scheduled tasks
if (!t){
// Execute cycle timing task
t = setInterval(showTime,999)
}
}
// 4. Bind pause button
function func1() {
// Abort scheduled task
clearInterval(t)
t = null
}
but2Ele.onclick = func1
// 5. Bind empty button
but3Ele.onclick = function () {
func1()
iEle.value = ''
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
- Drop down box linkage
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id = 'd1'>
<button id = 'd2'>start</button>
<button id = 'd3'>suspend</button>
<button id = 'd4'>empty</button>
<script>
// 1. Find the button first
var iEle = document.getElementById('d1')
var but1Ele = document.getElementById('d2')
var but2Ele = document.getElementById('d3')
var but3Ele = document.getElementById('d4')
var t = null
// 3. Construct a function to display the time in the text box
function showTime() {
// Get current time
var cTime = new Date().toLocaleString()
// Displays the time in a text box
iEle.value = cTime
}
// 2. Bind start button
but1Ele.onclick = function () {
// Prevent repetitive scheduled tasks
if (!t){
// Execute cycle timing task
t = setInterval(showTime,999)
}
}
// 4. Bind pause button
function func1() {
// Abort scheduled task
clearInterval(t)
t = null
}
but2Ele.onclick = func1
// 5. Bind empty button
but3Ele.onclick = function () {
func1()
iEle.value = ''
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Supplement:
1. Involve DOM Operational JS The code should be in the documentation body At the back of the label. 2. **window.onload** Internal code executed after waiting for the document to load .onload()Function has coverage.