Static Web server - return fixed page data
Learning objectives
- Be able to write the response message of assembling fixed page data
1. Develop your own static Web server
Implementation steps:
- Write a TCP server program
- Obtain the http request message data sent by the browser
- Read the fixed page data, assemble the page data into HTTP response message data and send it to the browser.
- After sending the HTTP response message data, close the socket serving the client.
2. Static Web server - sample code for returning fixed page data
import socket
# Determine whether it is the code of the main module
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create tcp server socket
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Set the port number reuse, and the port number will be released immediately after the program exits
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, True)
# Binding port number
tcp_server_socket.bind(("", 8000))
# Set listening
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
# Cycle waiting to accept the connection request from the client
while True:
# Waiting to accept the connection request from the client
new_socket, ip_port = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# When the code is executed to this point, the connection is established successfully
# Receive request information from the client
recv_data = new_socket.recv(4096)
print(recv_data)
# Open the file and read the data in the file
with open("static/index.html", "r") as file: # The file here represents the object to open the file
file_data = file.read()
# Tip: the operation of closing the file with open does not need to be completed by the programmer. The system helps us to complete it
# Response line
response_line = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
# Response header
response_header = "Server: PWS/1.0\r\n"
# Responder
response_body = file_data
# Encapsulate the data into data in the format of http response message
response = response_line + response_header + "\r\n" + response_body
# Encode a string into binary
response_data = response.encode("utf-8")
# Response message data sent to browser
new_socket.send(response_data)
# Close the socket serving the client
new_socket.close()
3. Summary
- Write a TCP server program
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) # Cyclic acceptance of client connection requests while True: conn_socket, ip_port = tcp_server_socket.accept()
- Obtain the http request message data sent by the browser
client_request_data = conn_socket.recv(4096)
- Read the fixed page data, assemble the page data into HTTP response message data and send it to the browser.
response_data = (response_line + response_header + "\r\n").encode("utf-8") + response_body
conn_socket.send(response_data)
- After sending the HTTP response message data, close the socket serving the client.
conn_socket.close()
Static Web server - returns the specified page data
Learning objectives
- Be able to write the response message of assembling the specified page data
1. Problems with static Web server
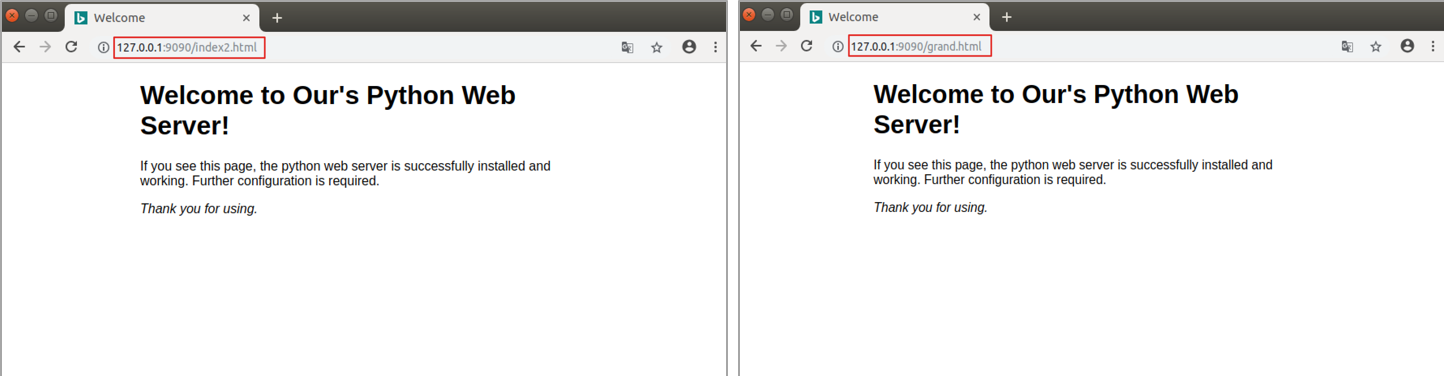
The current Web server, no matter what page the user visits, returns the data of the fixed page. Next, it needs to return the data of the specified page according to the user's request
Implementation steps for returning the specified page data:
- Gets the path to the resource requested by the user
- Read the data of the specified file according to the path of the requested resource
- Assemble the response message of the specified file data and send it to the browser
- Judge that the requested file does not exist at the server, assemble the response message in 404 status and send it to the browser
2. Static Web server - return the sample code of the specified page data
import socket
import os
def main():
# Create tcp server socket
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Set the port number reuse, and the port number will be released immediately after the program exits
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, True)
# Binding port number
tcp_server_socket.bind(("", 8000))
# Set listening
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
# Cycle waiting to accept the connection request from the client
while True:
# Waiting to accept the connection request from the client
new_socket, ip_port = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# When the code is executed to this point, the connection is established successfully
# Receive request information from the client
recv_data = new_socket.recv(4096)
# Judge whether the received data length is 0
if len(recv_data) == 0:
new_socket.close()
return
# Decoding binary data
recv_content = recv_data.decode("utf-8")
print(recv_content)
# Divide the data by spaces
request_list = recv_content.split(" ", maxsplit=2)
# Gets the requested resource path
request_path = request_list[1]
print(request_path)
# Judge whether the requested is the root directory. If it is the root directory, set the returned information
if request_path == "/":
request_path = "/index.html"
# 1. os.path.exits
# os.path.exists("static/" + request_path)
# 2. try-except
# Open the file and read the data in the file. Prompt: rb mode is used here, which is compatible with opening picture files
with open("static" + request_path, "rb") as file: # The file here represents the object to open the file
file_data = file.read()
# Tip: the operation of closing the file with open does not need to be completed by the programmer. The system helps us to complete it
# When the code is executed to this point, it indicates that the file exists and returns 200 status information
# Response line
response_line = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
# Response header
response_header = "Server: PWS/1.0\r\n"
# Responder
response_body = file_data
# Encapsulate the data into data in the format of http response message
response = (response_line +
response_header +
"\r\n").encode("utf-8") + response_body
# Response message data sent to browser
new_socket.send(response)
# Close the socket serving the client
new_socket.close()
# Determine whether it is the code of the main module
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3. Summary
- Gets the path to the resource requested by the user
request_list = client_request_conent.split(" ", maxsplit=2)
request_path = request_list[1]
- Read the data of the specified file according to the path of the requested resource
with open("static" + request_path, "rb") as file:
file_data = file.read()
- Assemble the response message of the specified file data and send it to the browser
response_data = (response_line + response_header + "\r\n").encode("utf-8") + response_body
conn_socket.send(response_data)
- Judge that the requested file does not exist at the server, assemble the response message in 404 status and send it to the browser
try: # Open the specified file and omit the code except Exception as e: conn_socket.send(404 Response message data)
Static Web server - return 404 page data
import socket
import os
def main():
# Create tcp server socket
tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Set the port number reuse, and the port number will be released immediately after the program exits
tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, True)
# Binding port number
tcp_server_socket.bind(("", 8000))
# Set listening
tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
# Cycle waiting to accept the connection request from the client
while True:
# Waiting to accept the connection request from the client
new_socket, ip_port = tcp_server_socket.accept()
# When the code is executed to this point, the connection is established successfully
# Receive request information from the client
recv_data = new_socket.recv(4096)
# Judge whether the received data length is 0
if len(recv_data) == 0:
new_socket.close()
return
# Decoding binary data
recv_content = recv_data.decode("utf-8")
print(recv_content)
# Divide the data by spaces
request_list = recv_content.split(" ", maxsplit=2)
# Gets the requested resource path
request_path = request_list[1]
print(request_path)
# Judge whether the requested is the root directory. If it is the root directory, set the returned information
if request_path == "/":
request_path = "/index.html"
# 1. os.path.exits
# os.path.exists("static/" + request_path)
# 2. try-except
try:
# Open the file and read the data in the file. Prompt: rb mode is used here, which is compatible with opening picture files
with open("static" + request_path, "rb") as file: # The file here represents the object to open the file
file_data = file.read()
# Tip: the operation of closing the file with open does not need to be completed by the programmer. The system helps us to complete it
except Exception as e:
# The code executes here, indicating that there is no requested file, and 404 status information is returned
# Response line
response_line = "HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n"
# Response header
response_header = "Server: PWS/1.0\r\n"
# Read 404 page data
with open("static/error.html", "rb") as file:
file_data = file.read()
# Responder
response_body = file_data
# Encapsulate the data into data in the format of http response message
response = (response_line +
response_header +
"\r\n").encode("utf-8") + response_body
# Response message data sent to browser
new_socket.send(response)
else:
# When the code is executed to this point, it indicates that the file exists and returns 200 status information
# Response line
response_line = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
# Response header
response_header = "Server: PWS/1.0\r\n"
# Responder
response_body = file_data
# Encapsulate the data into data in the format of http response message
response = (response_line +
response_header +
"\r\n").encode("utf-8") + response_body
# Response message data sent to browser
new_socket.send(response)
finally:
# Close the socket serving the client
new_socket.close()
# Determine whether it is the code of the main module
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
come on.
thank!
strive!