Background:
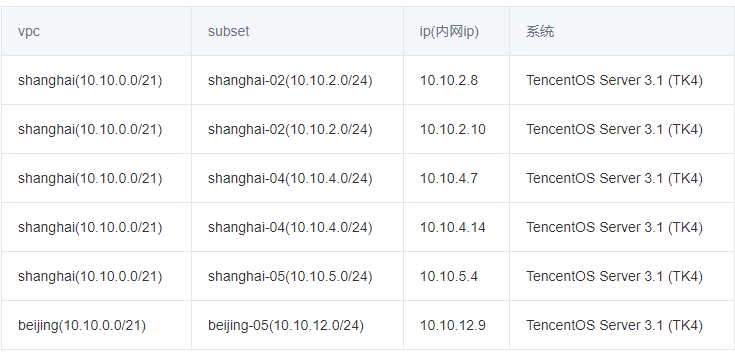
Network environment reference: Cloud networking experience Two vpc networks in Shanghai and Beijing. The servers are distributed as follows:
Let's talk about why we use TencentOS Server 3.1 (TK4) system. It's not because CentOS 8 doesn't provide long-term maintenance.... by the way, experience Tencent cloud's open source Tencent OS. For details, see Tencent cloud's official website: https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/213/38027 . Compare the process of installing CentOS 8 compatible with CentOS 8. Build kubernetes to experience whether it is feasible to cross regions!
Basic planning:
Note: Well, multi area dispersion comparison can also be highly available!
ip | hostname | Area | |
|---|---|---|---|
10.10.2.8 | sh-master-01 | Shanghai zone 2 | |
10.10.2.10 | sh-master-02 | Shanghai zone 2 | |
10.10.5.4 | sh-master-03 | Shanghai District 5 | |
10.10.4.7 | sh-work-01 | Shanghai District 4 | |
10.10.4.14 | sh-work-02 | Shanghai District 4 | |
10.10.12.9 | bj-work-01 | Beijing District 5 |
Create an intranet load balancing slb and make apiserver's vip. The traditional type used in the past is now only applied load balancing
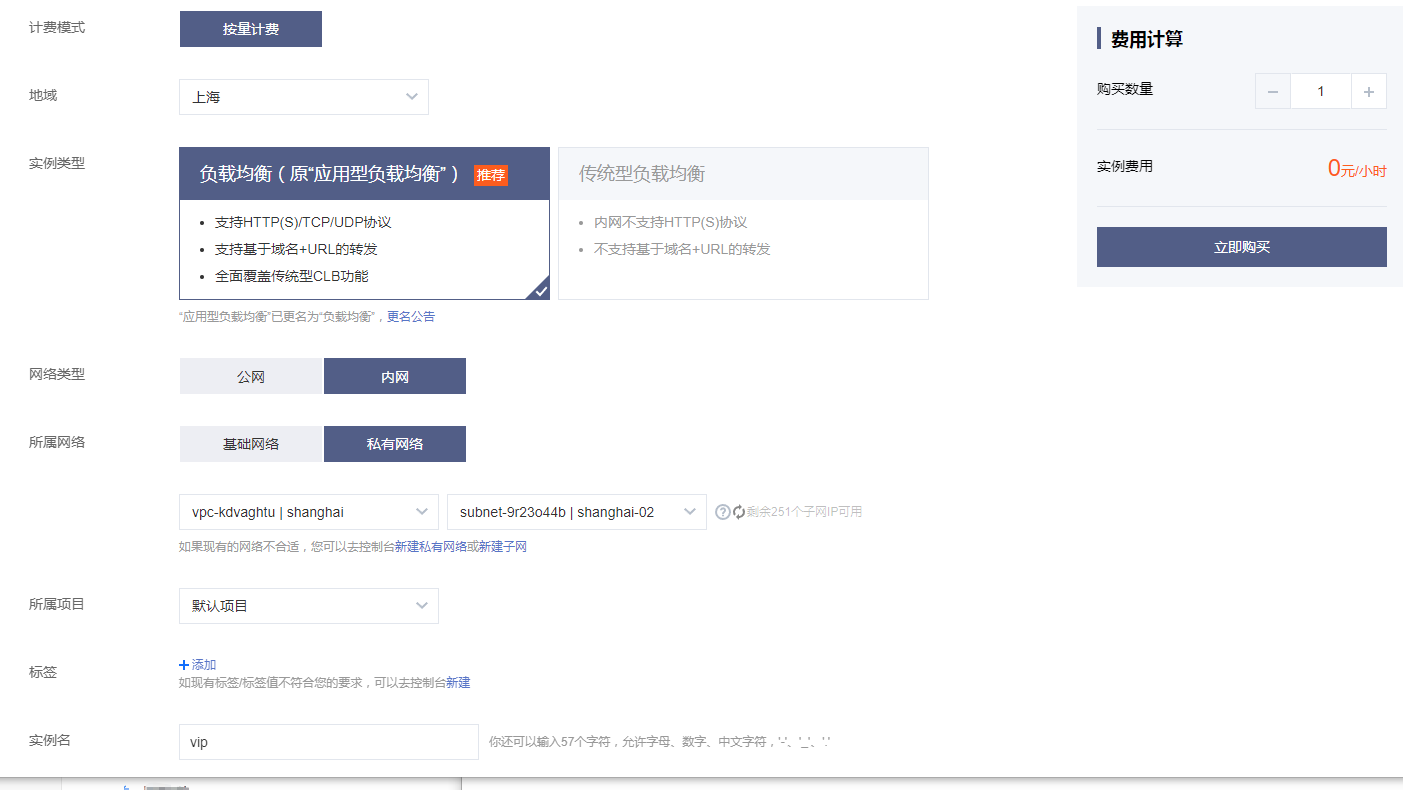
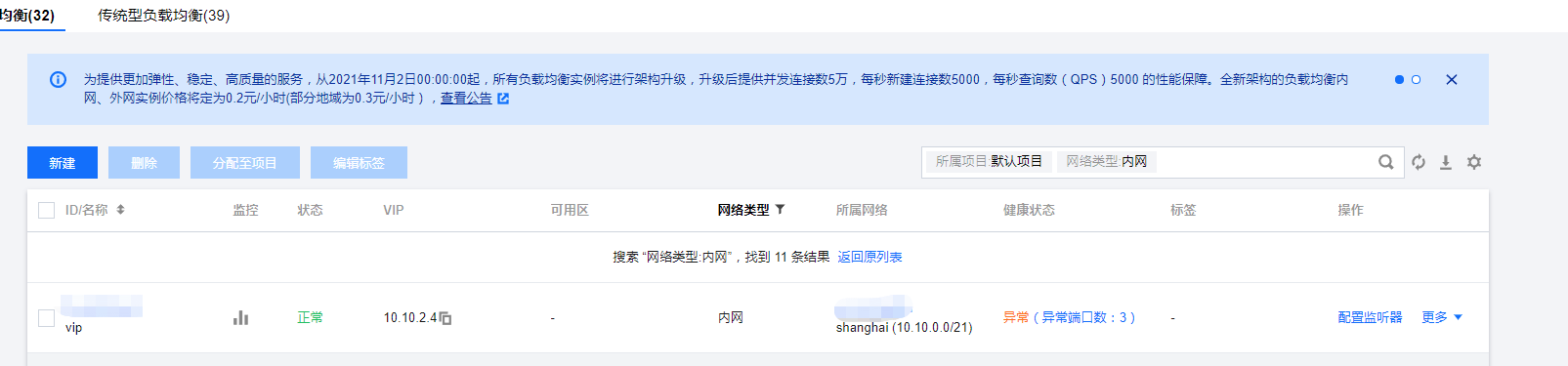
System initialization
Note: 1-12 is executed for all nodes
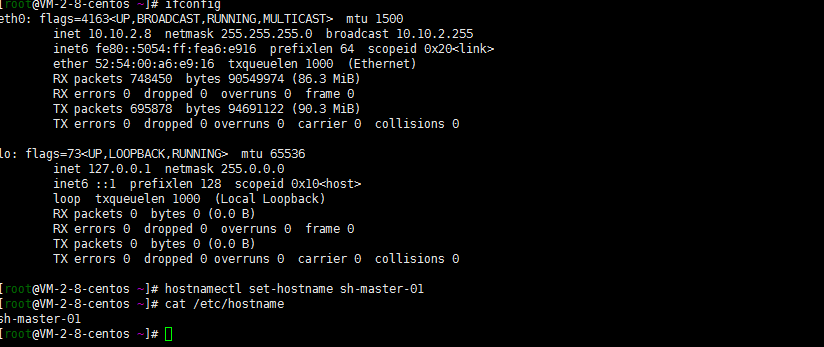
1. Change host name
Note: if the hostname is not initialized, modify the hostname
[root@VM-2-8-centos ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname sh-master-01 [root@VM-2-8-centos ~]# cat /etc/hostname sh-master-01
The other ones are the same way
2. Close swap partition
swapoff -a sed -i 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab
3. Close selinux
[root@sh-master-01 ~]# setenforce 0 ssive/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/configsetenforce: SELinux is disabled [root@sh-master-01 ~]# sed -i "s/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/sysconfig/selinux [root@sh-master-01 ~]# sed -i "s/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config [root@sh-master-01 ~]# sed -i "s/^SELINUX=permissive/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/sysconfig/selinux [root@sh-master-01 ~]# sed -i "s/^SELINUX=permissive/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config
4. Turn off the firewall
systemctl disable --now firewalld chkconfig firewalld off
Note: firewalld and iptables are not installed and can be ignored
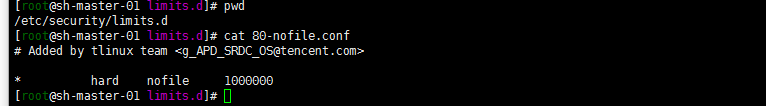
5. Adjust the file opening number and other configurations
cat> /etc/security/limits.conf <<EOF * soft nproc 1000000 * hard nproc 1000000 * soft nofile 1000000 * hard nofile 1000000 * soft memlock unlimited * hard memlock unlimited EOF
Of course, it seems that there is an 80-nofile.conf in the tencentos limits.d directory. The modified configuration files can be placed here. This avoids modifying the master file
6. yum update
yum update yum -y install gcc bc gcc-c++ ncurses ncurses-devel cmake elfutils-libelf-devel openssl-devel flex* bison* autoconf automake zlib* fiex* libxml* ncurses-devel libmcrypt* libtool-ltdl-devel* make cmake pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel jemalloc-devel tlc libtool vim unzip wget lrzsz bash-comp* ipvsadm ipset jq sysstat conntrack libseccomp conntrack-tools socat curl wget git conntrack-tools psmisc nfs-utils tree bash-completion conntrack libseccomp net-tools crontabs sysstat iftop nload strace bind-utils tcpdump htop telnet lsof
Of course, I ignored it here... I usually use oneinstack script to initialize cvm
7. Add IPVS
The system kernel of tencentos is 5.4.119
:> /etc/modules-load.d/ipvs.conf
module=(
ip_vs
ip_vs_rr
ip_vs_wrr
ip_vs_sh
nf_conntrack
br_netfilter
)
for kernel_module in ${module[@]};do
/sbin/modinfo -F filename $kernel_module |& grep -qv ERROR && echo $kernel_module >> /etc/modules-load.d/ipvs.conf || :
donesystemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable --now systemd-modules-load.service
Verify that ipvs is loaded successfully
# lsmod | grep ip_vs ip_vs_sh 16384 0 ip_vs_wrr 16384 0 ip_vs_rr 16384 5 ip_vs 151552 11 ip_vs_rr,ip_vs_sh,ip_vs_wrr nf_conntrack 114688 5 xt_conntrack,nf_nat,nf_conntrack_netlink,xt_MASQUERADE,ip_vs nf_defrag_ipv6 20480 2 nf_conntrack,ip_vs
8. Optimize system parameters (not necessarily optimal, take all)
Oneinstall is the default initialization installation. Don't change it first. Take your time. Wait a minute. There's a problem. Find a problem
cat /etc/sysctl.d/99-sysctl.conf
fs.file-max=1000000 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 6000 net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 4194304 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 16384 4194304 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 32768 net.core.somaxconn = 32768 net.core.wmem_default = 8388608 net.core.rmem_default = 8388608 net.core.rmem_max = 16777216 net.core.wmem_max = 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 20 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 #net.ipv4.tcp_tw_len = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 94500000 915000000 927000000 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 3276800 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 net.nf_conntrack_max = 6553500 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 6553500 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 3600
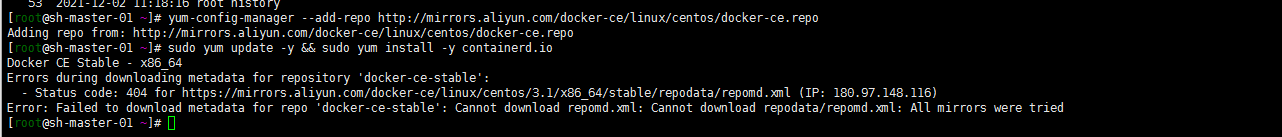
9. containerd installation
The changes of dnf and Yum centos8 have been seen by yourself. Almost... I'm used to adding Alibaba cloud sources as follows:
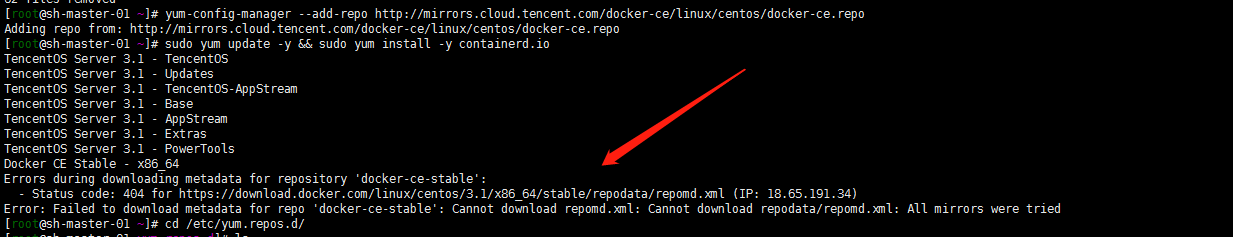
dnf install dnf-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sudo yum update -y && sudo yum install -y containerd.io containerd config default > /etc/containerd/config.toml # Replace the default sand of containerd_ Box image, edit / etc/containerd/config.toml sandbox_image = "registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.2" # Restart containerd $ systemctl daemon-reload $ systemctl restart containerd
It seems that I'm still not sure... The matching version is wrong. Hahaha, how to fix it?
Try Tencent's source. Of course, delete Alibaba's source first:
rm -rf /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo yum clean all
https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/
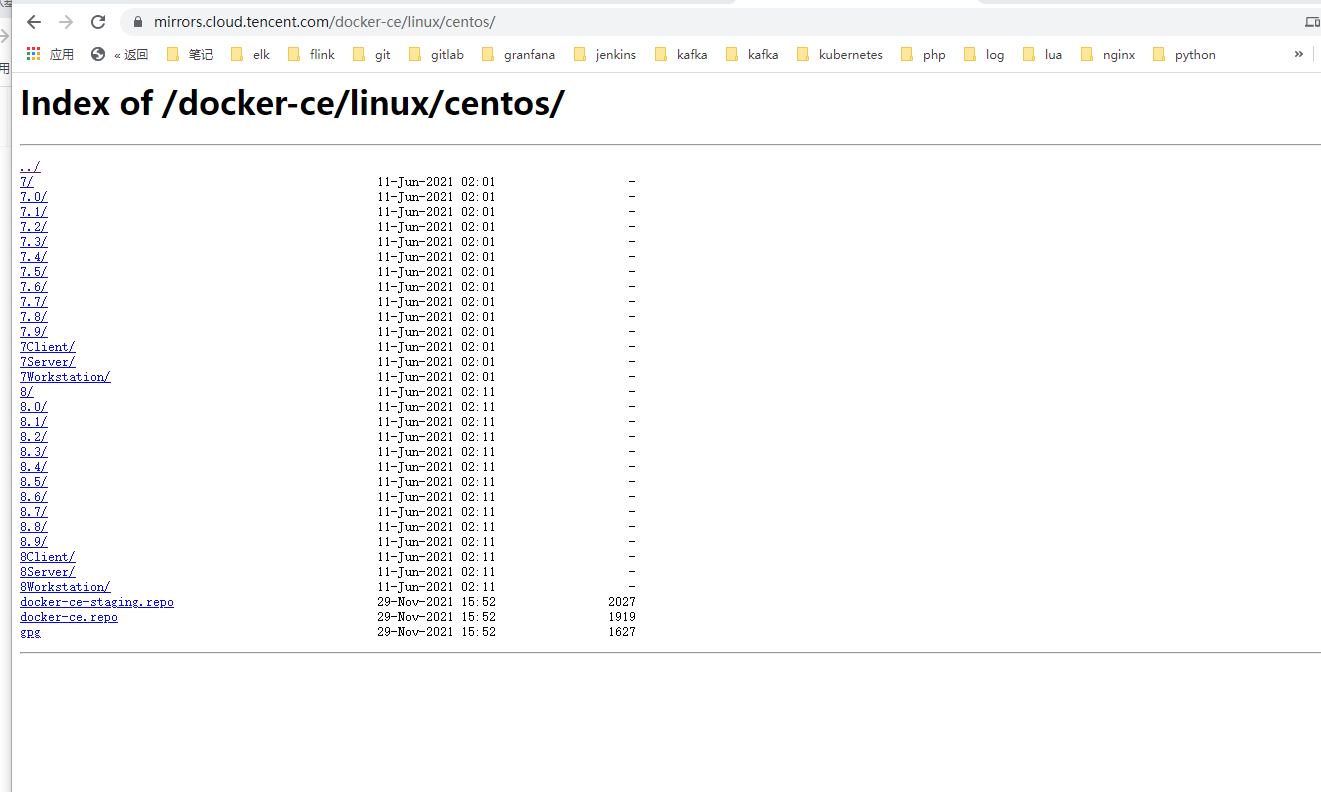
dnf install dnf-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sudo yum update -y && sudo yum install -y containerd.io containerd config default > /etc/containerd/config.toml # Replace the default sand of containerd_ Box image, edit / etc/containerd/config.toml sandbox_image = "registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.2" # Restart containerd $ systemctl daemon-reload $ systemctl restart containerd
Still... I didn't match the system... How? Manual modification?
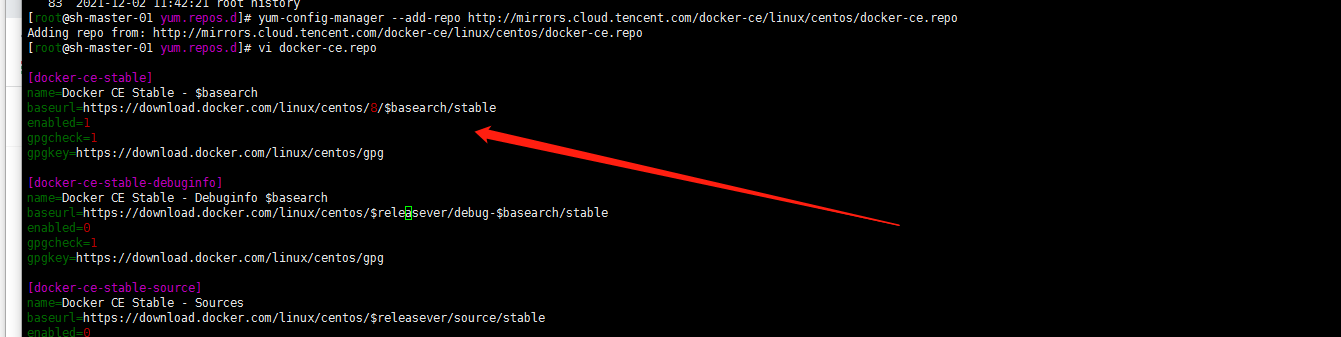
Yes, I hope tencentos can support the commonly used yum source... Don't let me convert it manually
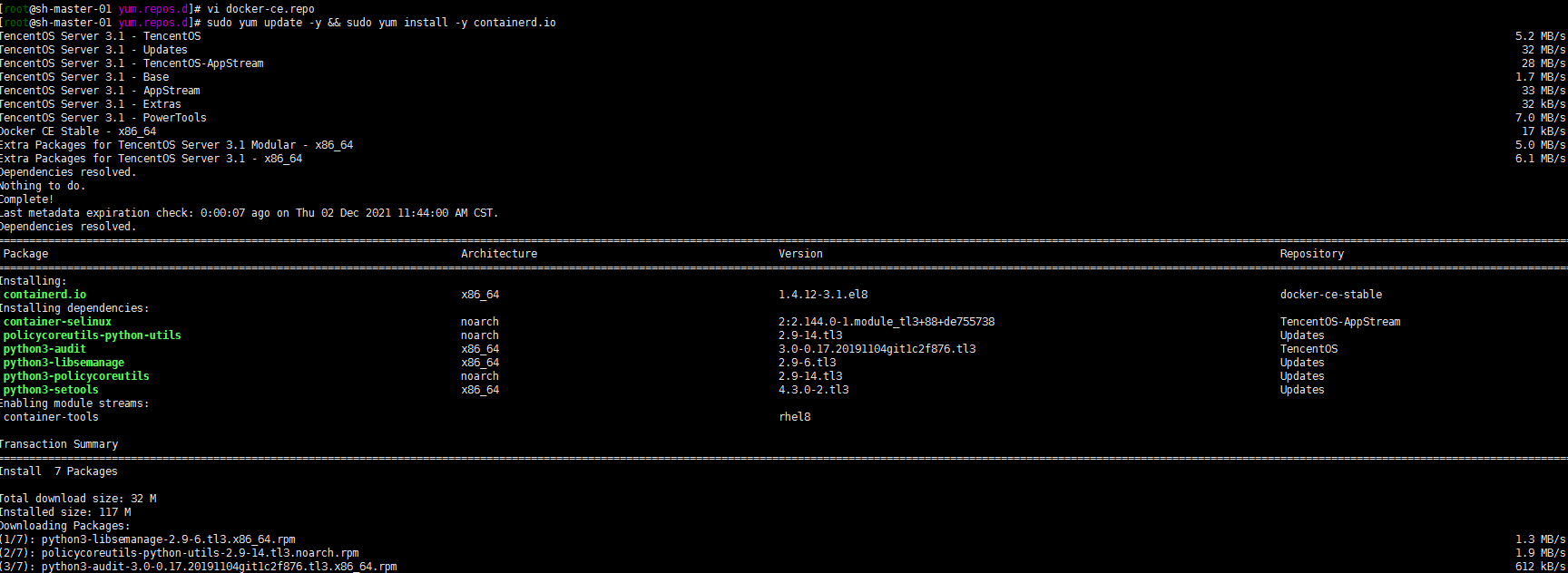
containerd config default > /etc/containerd/config.toml
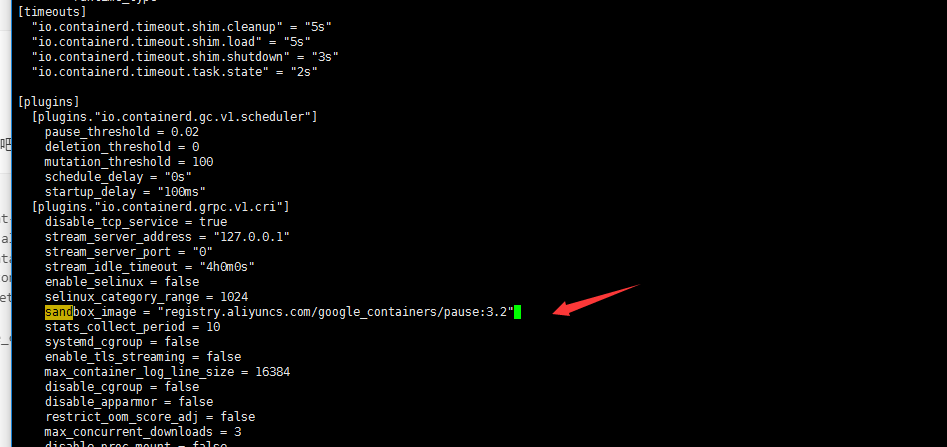
# Restart containerd systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart containerd systemctl status containerd
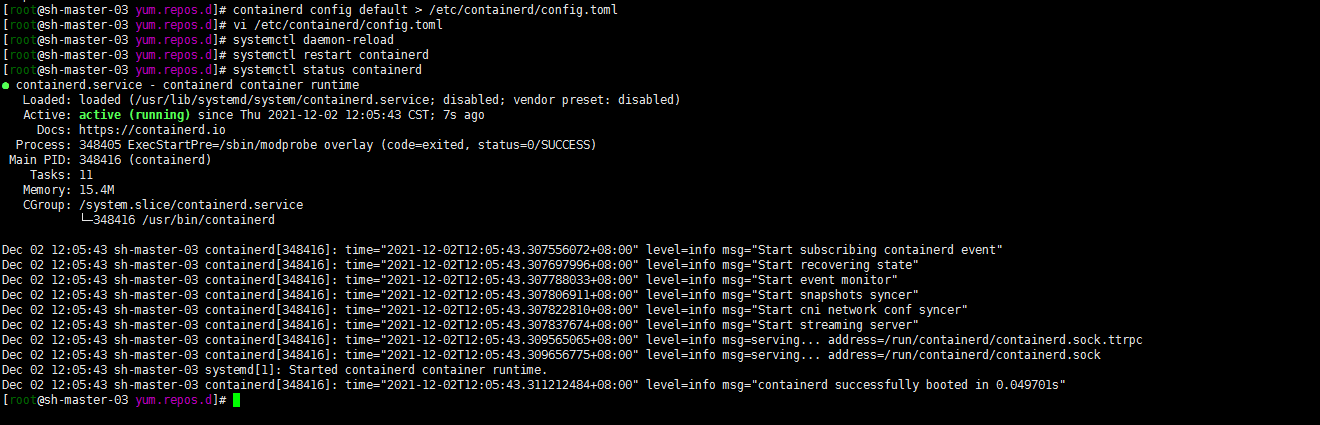
10. Configure CRI client crictl
Note: there seems to be version matching
VERSION="v1.22.0" wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools/releases/download/$VERSION/crictl-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz sudo tar zxvf crictl-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin rm -f crictl-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
You may not be able to download github to the desktop and upload it manually
cat <<EOF > /etc/crictl.yaml runtime-endpoint: unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock image-endpoint: unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock timeout: 10 debug: false EOF # Verify whether it is available (you can verify the private warehouse by the way) crictl pull nginx:alpine crictl rmi nginx:alpine crictl images
Well, modify the plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."docker.io" in / etc/containerd/config.toml. The endpoint is the accelerator address of Alibaba cloud (of course, it can also be the address of other accelerators). In addition, the plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options also add SystemdCgroup = true
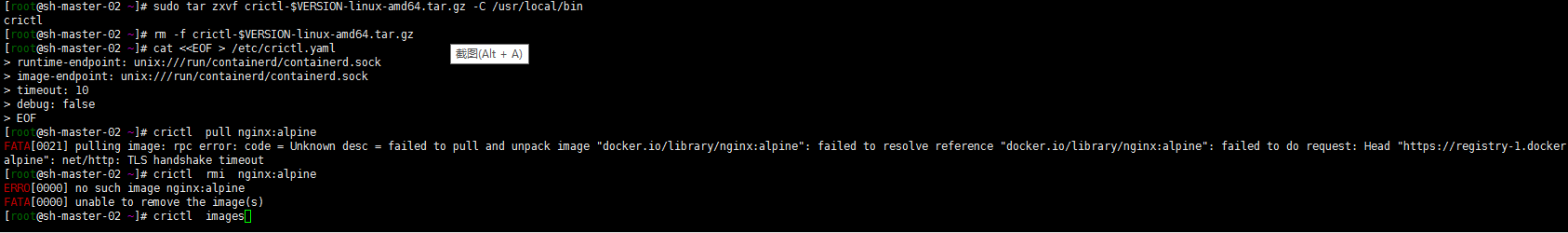
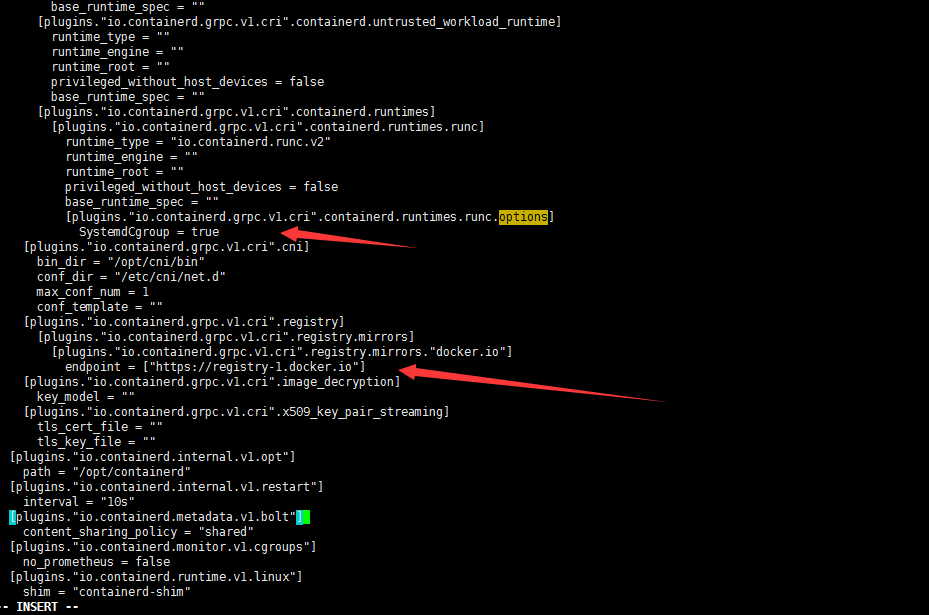
Change the endpoint to Alibaba cloud accelerator address: https://2lefsjdg.mirror.aliyuncs.com
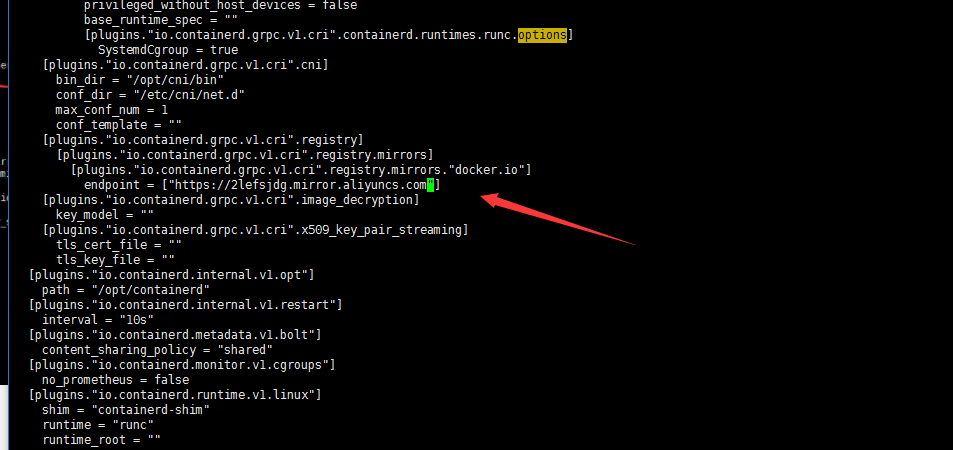
Restart the containerd service to re download the image verification:
systemctl restart containerd.service crictl pull nginx:alpine
OK
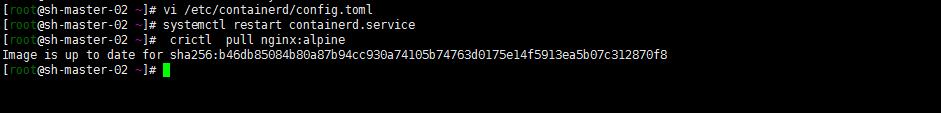
11. Install kubedm (centos8 does not have a corresponding yum source. Use the Alibaba cloud yum source of centos7)
Note: why install version 1.21.3? Because my online version is also version 1.21.3. Just in time to test the upgrade
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF # Remove the old version if installed yum remove kubeadm kubectl kubelet kubernetes-cni cri-tools socat # Check all installable versions. The following two are OK # yum list --showduplicates kubeadm --disableexcludes=kubernetes # Install the specified version with the following command # yum -y install kubeadm-1.21.3 kubectl-1.21.3 kubelet-1.21.3 or # Install the latest stable version by default. The current version is 1.22.4 #yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes # Startup and self start systemctl enable kubelet.service
Of course, you can also directly use the source of Tencent cloud here... The same reason.
12. Modify kubelet configuration
vi /etc/sysconfig/kubelet KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS= --cgroup-driver=systemd --container-runtime=remote --container-runtime-endpoint=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Additional operations on the master node:
1. Install haproxy
Note: the three master nodes must be installed with haproxy and related configurations
yum install haproxy
cat <<EOF > /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example configuration for a possible web application. See the
# full configuration options online.
#
# http://haproxy.1wt.eu/download/1.4/doc/configuration.txt
#
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Global settings
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
global
# to have these messages end up in /var/log/haproxy.log you will
# need to:
#
# 1) configure syslog to accept network log events. This is done
# by adding the '-r' option to the SYSLOGD_OPTIONS in
# /etc/sysconfig/syslog
#
# 2) configure local2 events to go to the /var/log/haproxy.log
# file. A line like the following can be added to
# /etc/sysconfig/syslog
#
# local2.* /var/log/haproxy.log
#
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will
# use if not designated in their block
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
defaults
mode tcp
log global
option tcplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# main frontend which proxys to the backends
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
frontend kubernetes
bind *:8443 #The configuration port is 8443
mode tcp
default_backend kubernetes
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# static backend for serving up images, stylesheets and such
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend kubernetes #The back-end server, that is, accessing 10.3.2.12:6443 will forward the request to the three back-end servers, so as to achieve load balancing
balance roundrobin
server master1 10.10.2.8:6443 check maxconn 2000
server master2 10.10.2.10:6443 check maxconn 2000
server master3 10.10.5.4:6443 check maxconn 2000
EOF
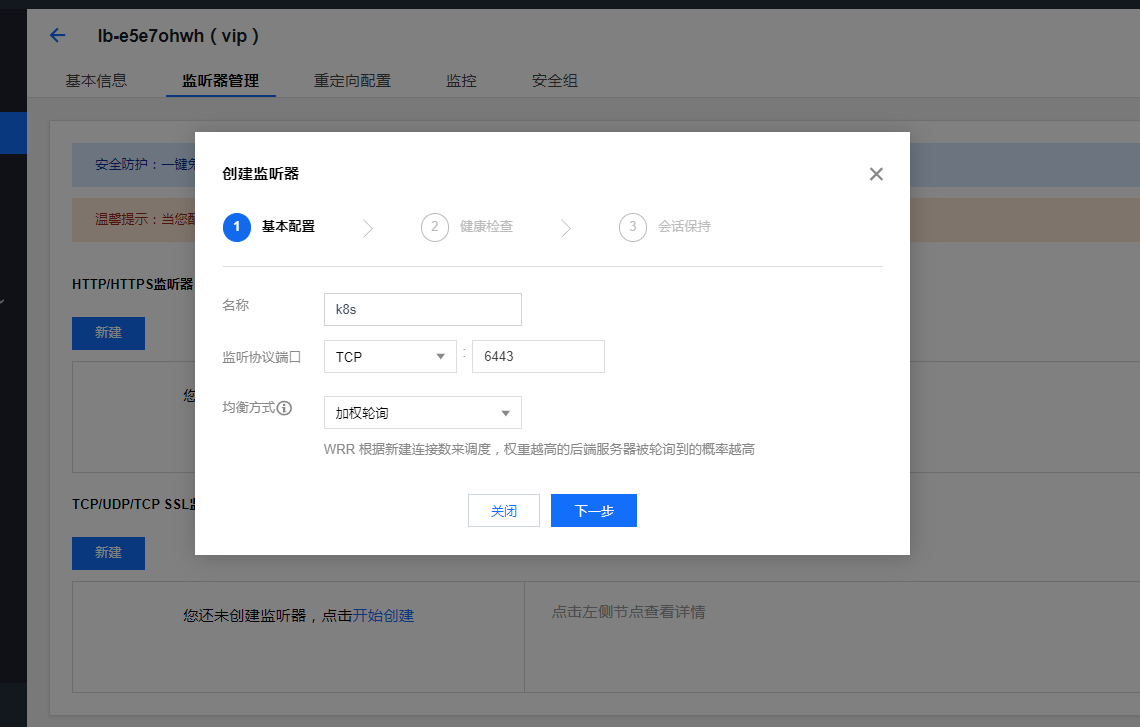
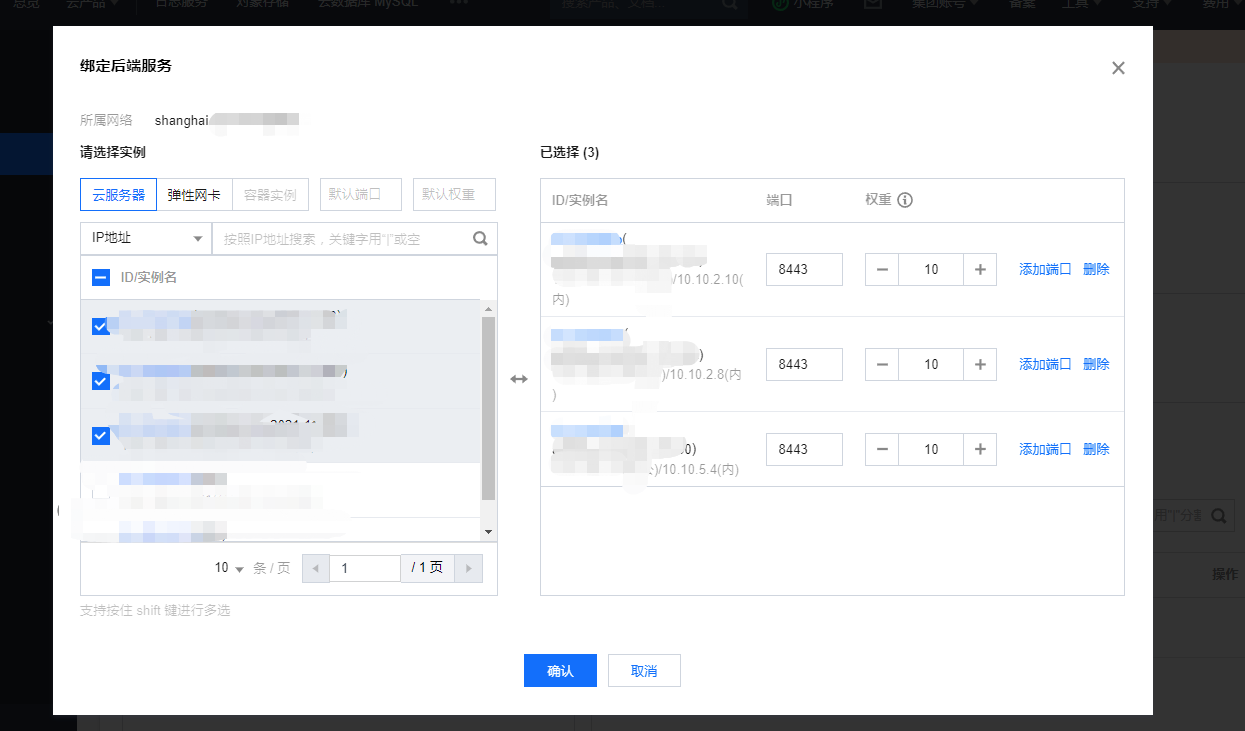
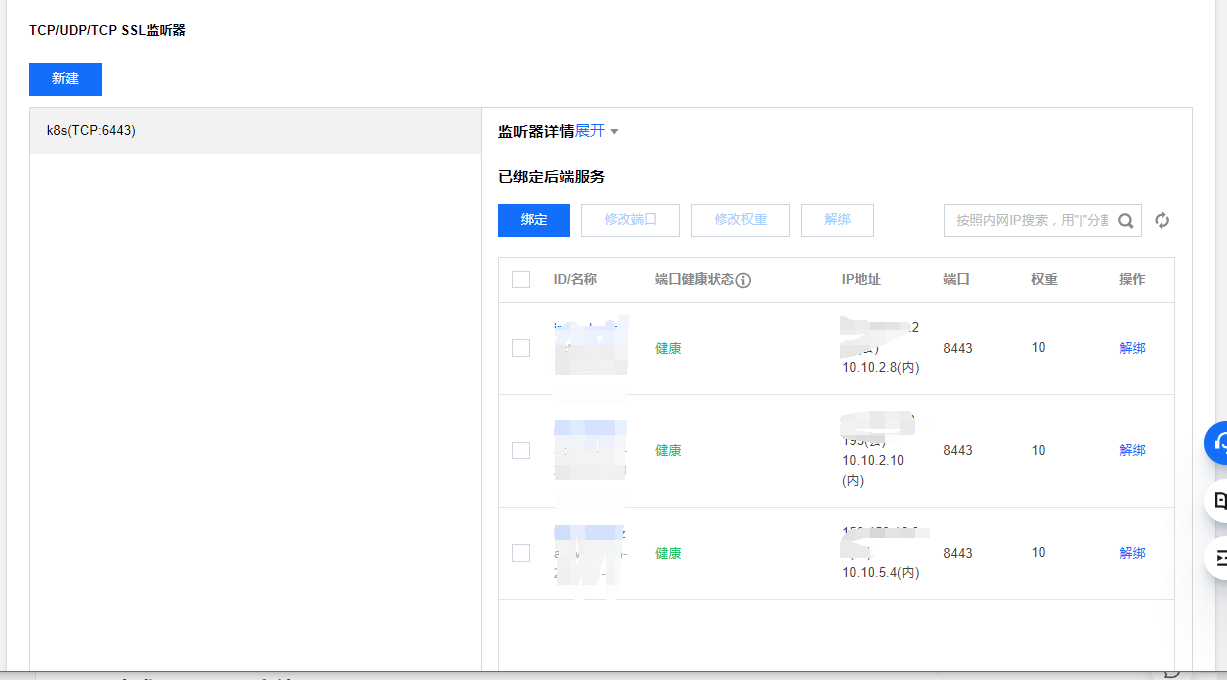
systemctl enable haproxy && systemctl start haproxy && systemctl status haproxyLog in to Tencent cloud load balancing management background: https://console.cloud.tencent.com/clb , create a TCP listener named k8s listening port 6443. The back-end service is bound to port 8443 of three master nodes. The weight is 10 by default and has not been modified.
2. The sh-master-01 node generates a configuration file
Note: of course, it can also be a sh-master-02 or sh-master-03 node
kubeadm config print init-defaults > config.yaml
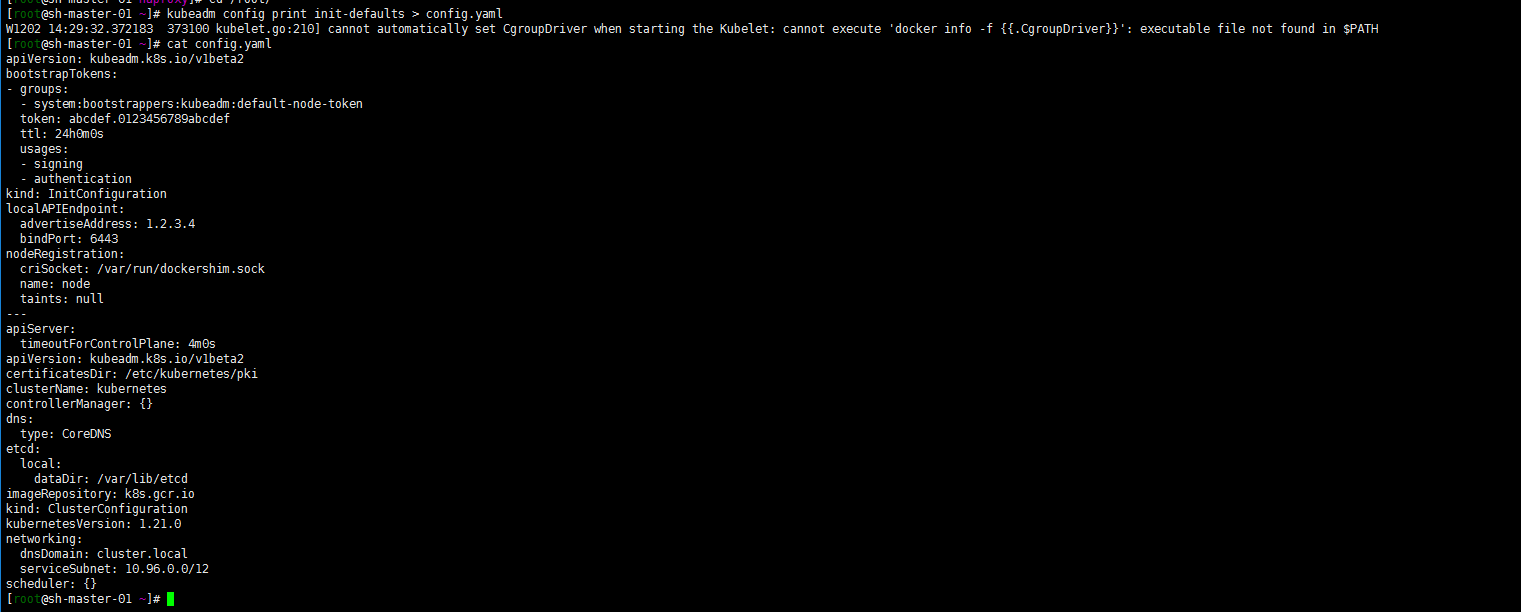
Modify the configuration file as follows:
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
bootstrapTokens:
- groups:
- system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token
token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef
ttl: 24h0m0s
usages:
- signing
- authentication
kind: InitConfiguration
localAPIEndpoint:
advertiseAddress: 10.10.2.8
bindPort: 6443
nodeRegistration:
criSocket: /run/containerd/containerd.sock
name: sh-master-01
taints:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
---
apiServer:
timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s
certSANs:
- sh-master-01
- sh-master-02
- sh-master-03
- sh-master.k8s.io
- localhost
- 127.0.0.1
- 10.10.2.8
- 10.10.2.10
- 10.10.5.4
- 10.10.2.4
- xx.xx.xx.xx
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2
certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki
clusterName: kubernetes
controlPlaneEndpoint: "10.10.2.4:6443"
controllerManager: {}
dns:
type: CoreDNS
etcd:
local:
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
imageRepository: registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
kind: ClusterConfiguration
kubernetesVersion: 1.21.3
networking:
dnsDomain: cluster.local
serviceSubnet: 172.31.0.0/16
scheduler: {}
---
apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubeProxyConfiguration
mode: ipvs
ipvs:
excludeCIDRs: null
minSyncPeriod: 0s
scheduler: "rr"
strictARP: false
syncPeriod: 15s
iptables:
masqueradeAll: true
masqueradeBit: 14
minSyncPeriod: 0s
syncPeriod: 30sThe configuration of ipvs is added, the subnet of service is specified, and the domestic image warehouse is also specified. Xx.xx.xx is that I reserved an ip (ip can be reserved to facilitate future expansion of the primary node)
3. Kubedm master-01 node initialization
kubeadm init --config /root/config.yaml
Note: the following screenshot does not match the above command, because I started to want to install cilium... It failed. Hahaha, I'd better start calico first
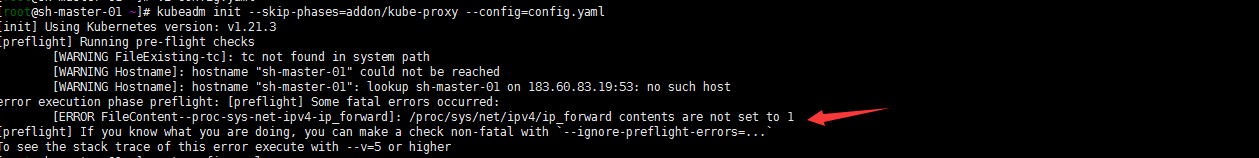
Well, net.ipv4.ip was not used when optimizing system parameters_ Forward emphasize that sysctl -w is temporary
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
For a long time, add it to the configuration file:
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/99-sysctl.conf fs.file-max=1000000 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 6000 net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 4194304 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 16384 4194304 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 32768 net.core.somaxconn = 32768 net.core.wmem_default = 8388608 net.core.rmem_default = 8388608 net.core.rmem_max = 16777216 net.core.wmem_max = 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 20 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 #net.ipv4.tcp_tw_len = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 94500000 915000000 927000000 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 3276800 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 net.nf_conntrack_max = 6553500 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 6553500 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 3600 EOF sysctl --system
Note: all nodes execute
kubeadm init --config /root/config.yaml
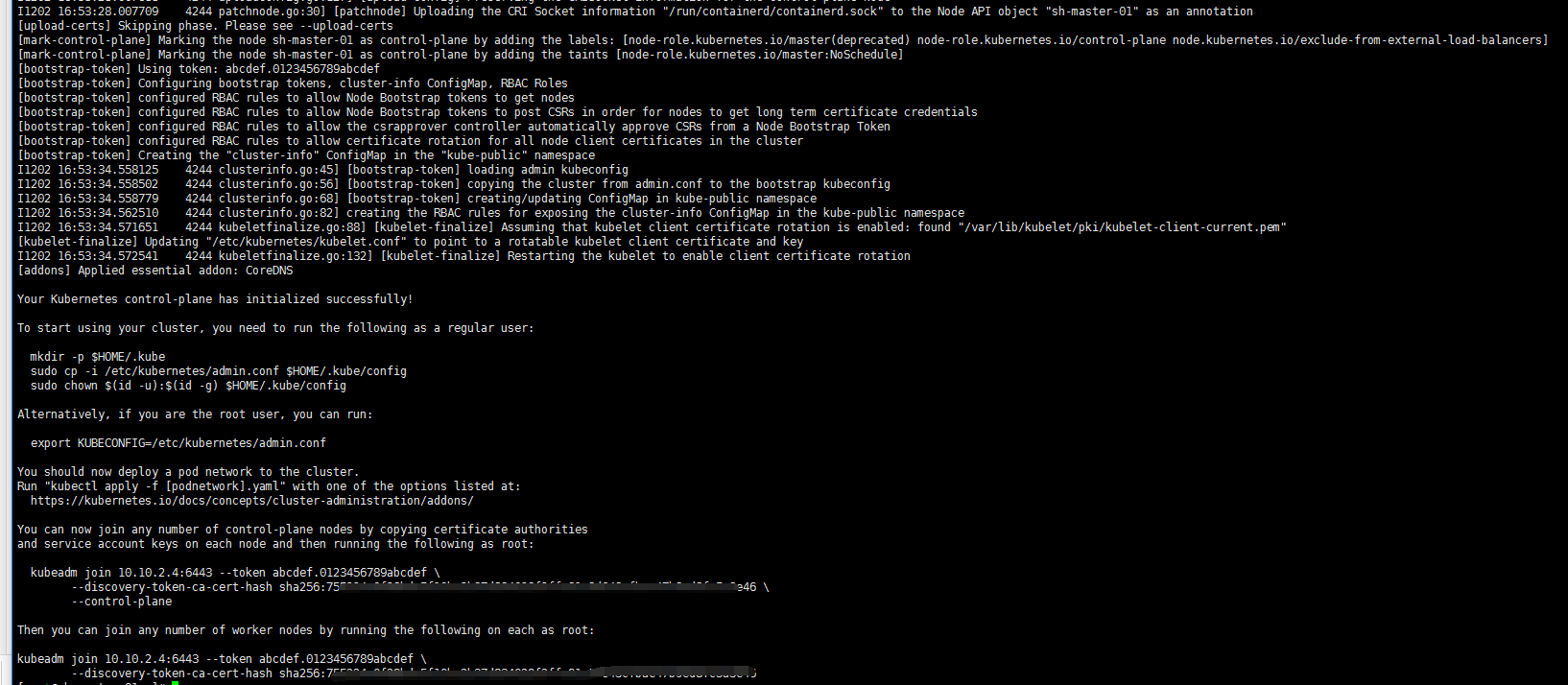
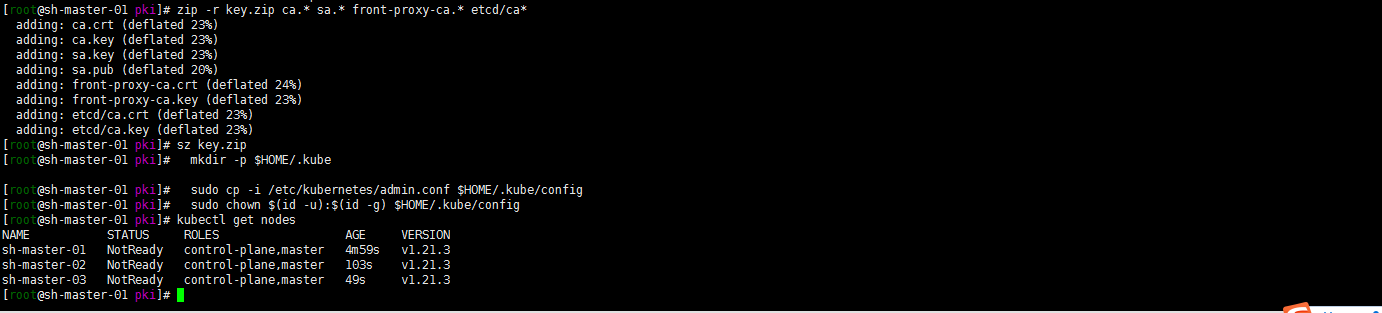
4. Sh-master-02 and sh-master-03 control plane nodes join the cluster
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config According to output sh-master-02 ,sh-master-03 Nodes join the cluster take sh-master-01 /etc/kubernetes/pki Directory ca.* sa.* front-proxy-ca.* etcd/ca* Package and distribute to sh-master-02,sh-master-03 /etc/kubernetes/pki Directory kubeadm join 10.10.2.4:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:ccfd4e2b85a6a07fde8580422769c9e14113e8f05e95272e51cca2f13b0eb8c3 --control-plan Then the same sh-master-01 Execute the following command again: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo \cp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
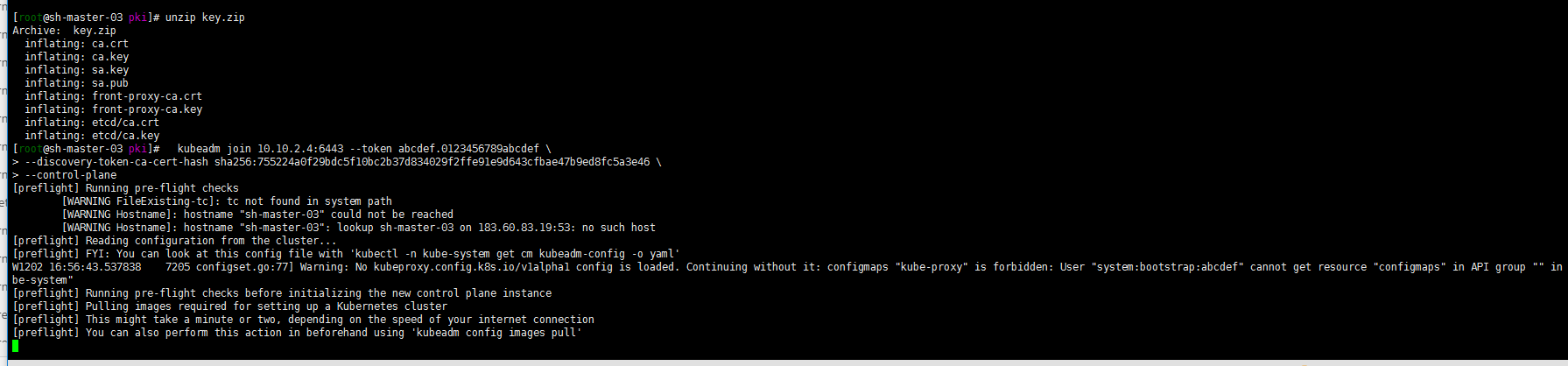
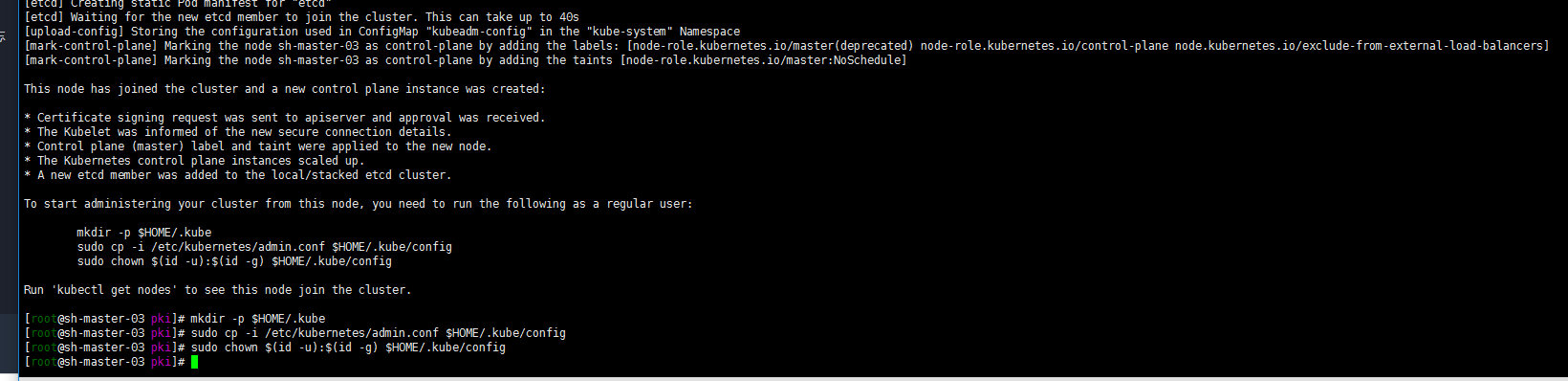
kubectl get nodes
Well, because cni network plug-ins are not installed, they are not ready.
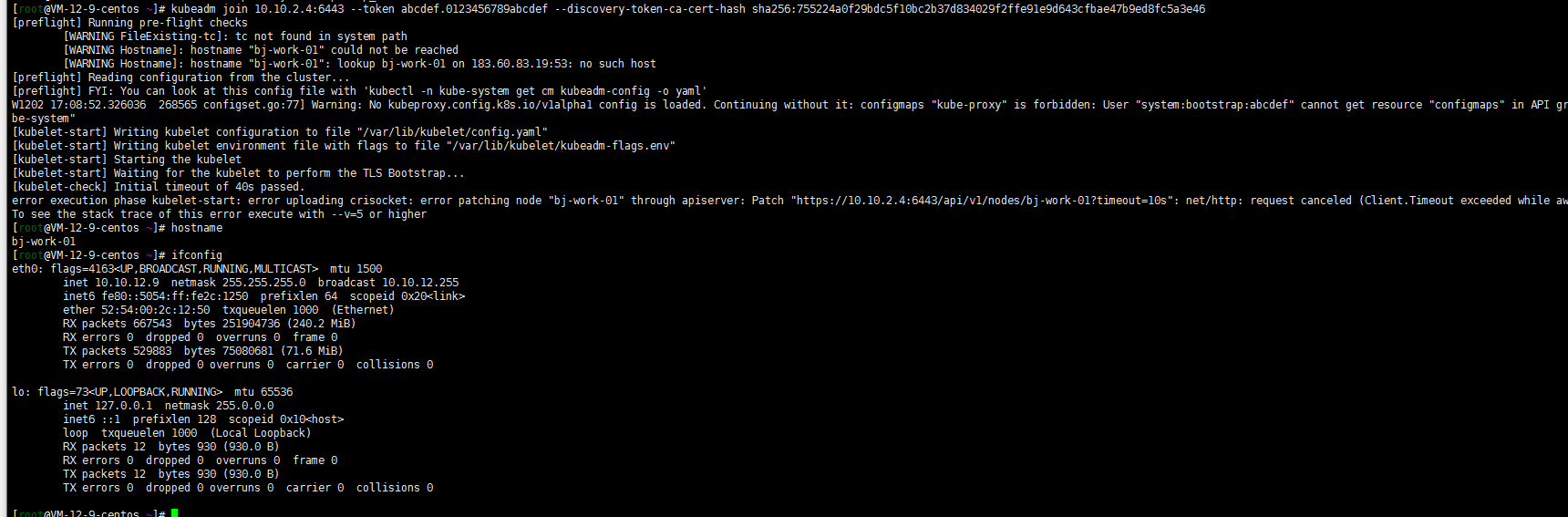
work nodes join the cluster
kubeadm join 10.10.2.4:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:ccfd4e2b85a6a07fde8580422769c9e14113e8f05e95272e51cca2f13b0eb8c3

first cnn management console First, I purchased 1Mbps bandwidth. After all, I did the following tests:
Install cni network plug-in
Let's start with a simple calico (we didn't start with the whole flannel city. We'll calculate one by one first. We'll learn to optimize the others later)
curl https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.11/manifests/calico.yaml -O
sed -i -e "s?192.168.0.0/16?172.31.0.0/16?g" calico.yaml
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml kubectl get pods -o kube-system -o wide
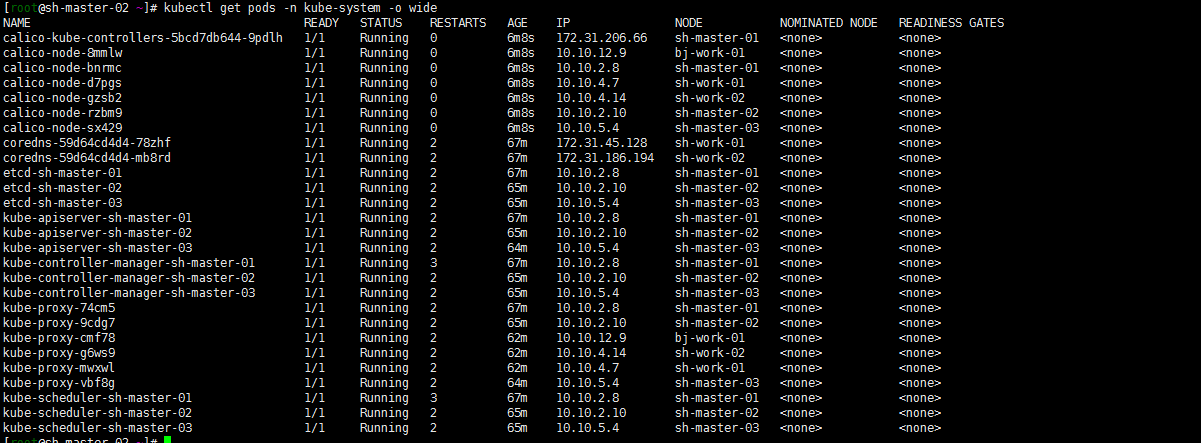
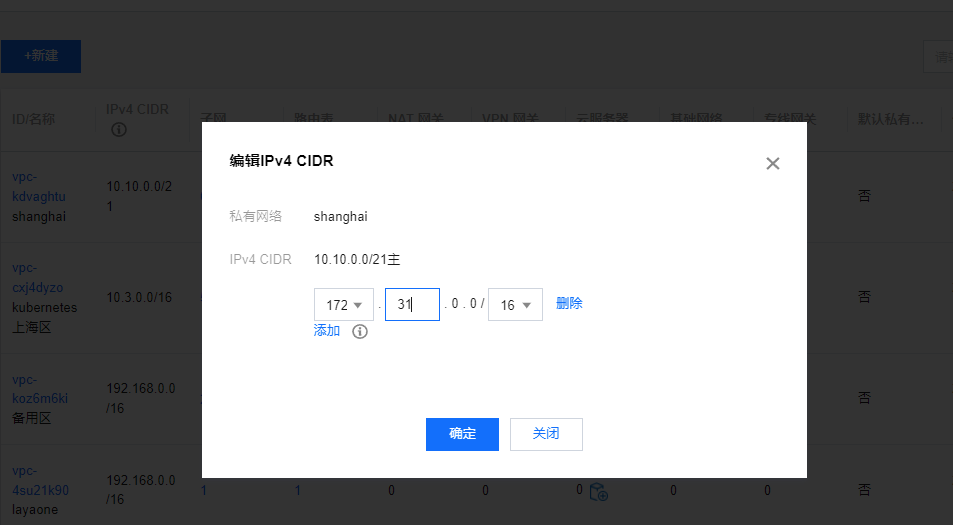
Note: I'm also in Tencent cloud Private network console Add an auxiliary cidr. I wonder if I can also communicate with container networks in other regions? Not tested yet... Just remember to add:
[
](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/vpc/vpc?rid=4)
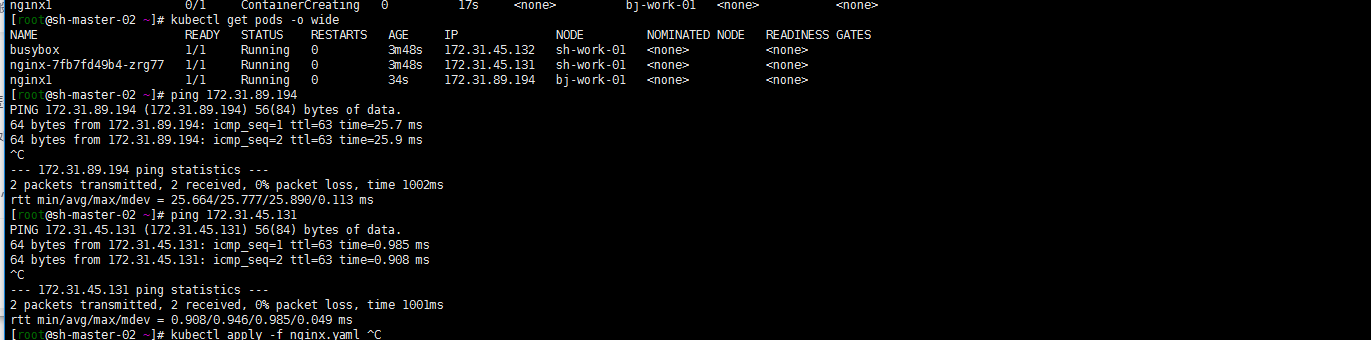
Do a simple ping test:
1. Deploy two pod s in Shanghai
cat<<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:alpine
name: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busybox
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox:1.28.4
command:
- sleep
- "3600"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always
EOFWell, they all run in Shanghai
[root@sh-master-01 ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES busybox 1/1 Running 14 14h 172.31.45.132 sh-work-01 <none> <none> nginx-7fb7fd49b4-zrg77 1/1 Running 0 14h 172.31.45.131 sh-work-01 <none> <none>
2. nodeSelector dispatcher starts a pod in Beijing
Then I want to start a pod running in Beijing. What's the matter? Steal a lazy tag and schedule nodeSelector!
kubectl label node bj-work-01 zone=beijing
cat nginx1.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
run: nginx1
name: nginx1
spec:
nodeSelector: #Deploy the pod to the node with the specified label of zone and beijing
zone: "beijing"
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx1
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
status: {}kubectl apply -f nginx1.yaml
[root@sh-master-01 ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES busybox 1/1 Running 14 14h 172.31.45.132 sh-work-01 <none> <none> nginx-7fb7fd49b4-zrg77 1/1 Running 0 14h 172.31.45.131 sh-work-01 <none> <none> nginx1 1/1 Running 0 14h 172.31.89.194 bj-work-01 <none> <none>
3. ping test
ping the Beijing pod and Shanghai pod at the sh-master-02 node
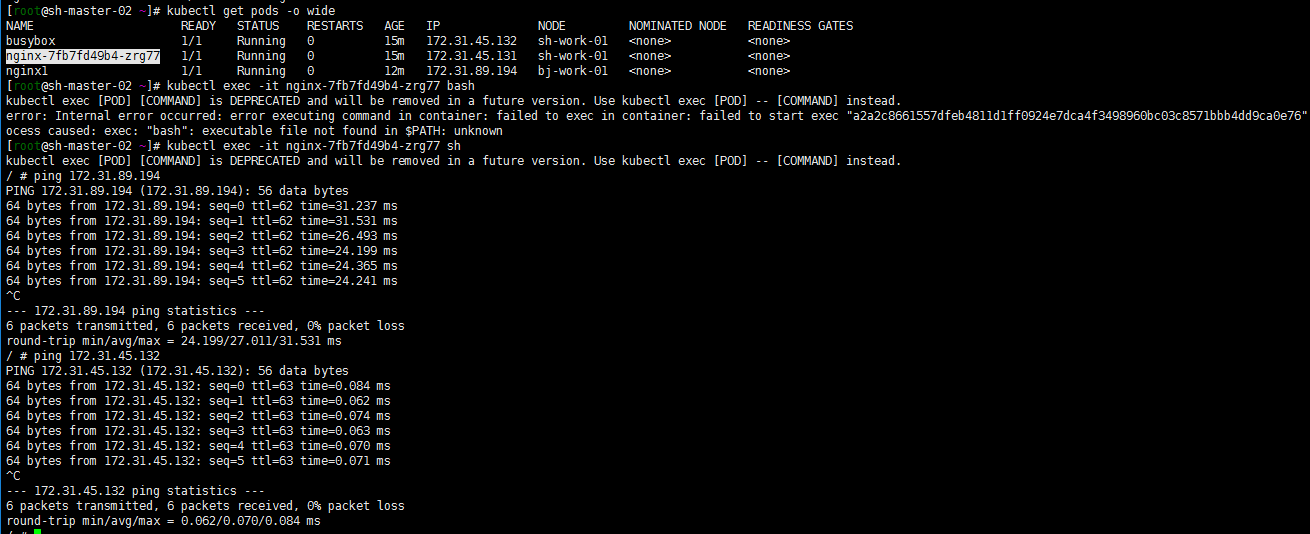
It's basically the same. The main purpose is to verify the feasibility of building kubernetes clusters across regional VPCs. I haven't figured out how to test the network quality. Just throwing a brick to attract jade. The clouds are very big, and there are many above Chengdu. At least bgp configuration is relatively omitted. If there are cross regional kubernetes clusters on the cloud, you can refer to it.