introduction
nothing
[De1CTF2019]xorz
The encryption code is as follows:
from itertools import *
from data import flag,plain
key=flag.strip("de1ctf{").strip("}")
assert(len(key)<38)
salt="WeAreDe1taTeam"
ki=cycle(key)
si=cycle(salt)
cipher = ''.join([hex(ord(p) ^ ord(next(ki)) ^ ord(next(si)))[2:].zfill(2) for p in plain])
print cipher
# output:
# 49380d773440222d1b421b3060380c3f403c3844791b202651306721135b6229294a3c3222357e766b2f15561b35305e3c3b670e49382c295c6c170553577d3a2b791470406318315d753f03637f2b614a4f2e1c4f21027e227a4122757b446037786a7b0e37635024246d60136f7802543e4d36265c3e035a725c6322700d626b345d1d6464283a016f35714d434124281b607d315f66212d671428026a4f4f79657e34153f3467097e4e135f187a21767f02125b375563517a3742597b6c394e78742c4a725069606576777c314429264f6e330d7530453f22537f5e3034560d22146831456b1b72725f30676d0d5c71617d48753e26667e2f7a334c731c22630a242c7140457a42324629064441036c7e646208630e745531436b7c51743a36674c4f352a5575407b767a5c747176016c0676386e403a2b42356a727a04662b4446375f36265f3f124b724c6e346544706277641025063420016629225b43432428036f29341a2338627c47650b264c477c653a67043e6766152a485c7f33617264780656537e5468143f305f4537722352303c3d4379043d69797e6f3922527b24536e310d653d4c33696c635474637d0326516f745e610d773340306621105a7361654e3e392970687c2e335f3015677d4b3a724a4659767c2f5b7c16055a126820306c14315d6b59224a27311f747f336f4d5974321a22507b22705a226c6d446a37375761423a2b5c29247163046d7e47032244377508300751727126326f117f7a38670c2b23203d4f27046a5c5e1532601126292f577776606f0c6d0126474b2a73737a41316362146e581d7c1228717664091c
There are plain and key, which can't help but remind people of the Virginia password and the one they have done before [NCTF2019]Sore
So he referred to Virginia's blasting method to solve the problem Sample code
The first is Kasiski experiment:
def GCD(step):
gcd_list = []
buf = []
if not len(step):
return "None has ben found"
else: # find GCD
step_min = max(step) // 2
for con in range(2, step_min + 1):
flag = True
for each_step in step:
if each_step % con:
flag = False
break
if flag:
gcd_list.append(con)
if len(gcd_list):
return gcd_list
else: # find GCD list
for con in range(2, step_min + 1):
gcd_list.append([con, len(step)])
for each_step in step:
if each_step % con:
gcd_list[con - 2][1] -= 1
for each in gcd_list:
if each[1]:
buf.append(each)
for i in range(1, len(buf)):
j = i
while j > 0:
if buf[j][1] < buf[j - 1][1]:
tem = buf[j - 1]
buf[j - 1] = buf[j]
buf[j] = tem
j -= 1
return buf
def find(string1, string2):
k, t = 0, 0
for t in range(len(string1)):
if string1[t] == string2[0] and t+len(string2) <= len(string1):
for k in range(len(string2)):
if string1[t+k] != string2[k]:
k -= 1
break
if k == len(string2)-1:
break
if t == len(string1)-1 or string1 == '':
return -1
else:
return t
def kasiski(cipher):
sec_msg = cipher
step = []
flag = False
lenth = len(sec_msg)
for i in range(lenth - 5):
flag_tem = 0
i_tem = i
while True:
print(sec_msg[i_tem + 3:], sec_msg[i_tem:i_tem + 3])
flag_tem = find(sec_msg[i_tem + 3:], sec_msg[i_tem:i_tem + 3])
# flag_tem = sec_msg[i_tem + 3:].find(sec_msg[i_tem:i_tem + 3])
print(flag_tem)
if flag_tem == -1:
break
flag_tem += 3
step.append(flag_tem)
i_tem += flag_tem
# print('step:', step)
print(GCD(step))
return GCD(step)
if __name__ == '__main__':
cipher = 'nsfAIHFrMuLynuCApeEstxJOzniQuyBVfAChDEznppfAiEIDcyNFBsCjsLvGlDtqztuaHvHbCmuyGNsIMhGlDtbotCoDzDjhyBzHGfHGfoHsuhlssIMvwlixBHHGfDRjoCKrapNIwqNyuxIBACQhtMwCmMCfEBpsrzEuiLGBoMipTkxrznoHfAkqwzvxuzCzDbLyApCGvjpqxkuwpgsLrqsVfCRwzlFmtlyrhuyEiivruFRpCRjkEDrqEqthyGwgsLnQvHmtzwDEznopBpsDOxvgBGIKzurFQxwQxkptutxzmfeLFQoRpJRvrpHxilwqeqMeiiIGBsQpCCvrptAlHsDnuRltmHuCGFpsBcwnsEblsswEPwerNpIADpJRCvwQxrntJltNpfAuFBwRstytoyvcepwtwqNlmmNGFsJjsQvkyvrkrstxJOzniQvNvzdDUdyJzjqzsErqxEjguyFMNwtPjsDwjoDfCdxzvftNGyzKjCEjsDxjqsjGMqFpimGpIADpJRFkovHJlpthyHnpqyBOHhmDMmoosClwiehEzmffOGMvDxDSnnyLuXFlwYEPvosQxCrRxwCpDswHopxDruvEzsOgBsXxDLvvlMpezwpnOOsjrANzHDsLCnoqLCepgtaHNHfpysNHGfOMqkyvlozxHetJGfvNuCGKjIRnoDLAbpyxnJCpqeLxuBCuwCpGpOnkEywrEPrisHrItSiDQgvtLCipyJnDzwtxBnNoKxpWuCxwuiqwDmIJxffIqSGSbzGpqlDnXvNIwqNzoxBrQoXuDRjonsAozzHeBjweTBBypDtIGnvHGDiosItqGvusGrIFzoNRjsyykrExweMvDtsLGItVbAIkxrFnuEyDmuIzxMNBIyziDJfyqLqbmjAtqOEiivnwyNgwCtmzsCgFxIfEMEiiBrFzNgxRdEEKqbHtJltIEmiNzygGfHyknVwnmJtJrxvyewNBSCTsHCnptxHlFiDnJHtohmuyKztHRkvwKxopfImuWFurIGuGRpGCcCDzntlxqevJCfEHLQoXxtIgzEynqEnCgsGztiLnHrBmDQgBEGCephprHJFtiFnHrXpJAqEwvBqlwItECpbvNuuHMvIRAwFKrZtyplMvJttFnSGhuLyuzwsHfyldhcvCjicGJzzztBvrlLBXxjHoDBlcsOGzwEuNWgkCKjdzBweDdHbwuyCHSmtIknezjqDtCeDDnfxBvHuzcDSvmlJAlFxtlIOsfCuyQoXtEJcIEznplrtsEIrtMNuIIFiIRjonsAozzHeBRltgFBMsCjCRjoHAwqpwIiCzzmhjuIsAfHyknTLFXDywevDCtxNvGsRitNtknLrZlqAyIvteeHLNvHovqjoAJxYlgAyvJChsNFBsVbHQwzAGBboyDbuNzsiuGGslbNzglpujrDjxtIvCpyHqWvQjHRokDaBXtihhuyterNFuMzoNRjsyyFepsXsqDouluGmvDqGMdkmDHoprtmrzCfhMuyKztHSrzzKnaEtqeIJCfeNzyRNzDSykyLClrtuoHvCjhyBHwSJHyknTCwbHxweFMzcevySrHelFgxDzntlxptyIJmmNGFsJjsypnLDufpfCdTWlohcHMsCuDEqDzLqbAfGkMDEilyEMvDxpQokosklFyIhuxlsvIHMsKZDSeyFDmkElttxzCpjzGBsFpsBcwEzrkrNBtEJmjkMuyGzjsgvrzMpeExweMvDoxABCBFuDypCHwAjpgJtICpemxaIMNvGCpyEYxlyNAlMvtujIESofpDLKClAmTpBtruMthlNGBsQfIFgxeznopBtruvqfAEvxGQjsGpqzFrqxtHtBTGfvSyCHSmtIknDswalktwFvCfrNFQsQfLykDtFpXCtJntJFuwCqyGHuIGpqzFCepgtnsCpteHquzKXwyvSoAmtlxXwuIEvtNBNvDxxLfyHOqbCjIhuTDfpFGBsSjrIgDDswamtJgxOzmhjuIsAfpRkmvwCQsjCIwvGfmNGIvDshFgGlKBqlssiDBCjkBGHsWuIMooSwAbTxpitrljxuFyqNosRcupLqbCjHtEAJpyLqIIFiIMqSDLjoEjsgyQtokBrLHGfGCuDzxCepiDuwCDiixyyBSntwqEvwnmtyZeuKtujIEGsRitQcsolqbyxweIvtevCtBHzgICtGlJmMwjpsuosbxMqyDQfHQkxrOqbyxDmuwzeCMnSGOmtyuoEGHlFNBeqItgmNFjvNfqCqBDGvbmtsyjCluhyCLsRttBvrpzniwtJtEAxfFOGcDTuIFgnzMpemfrkyIxztIpEsSBGCpDJGDdzsCaHDofxIBMvDbHIgnxwbepBpsBJzlmHtuHLfHMtDzxorysNYEPnpyFqNsKmHFgGlKwqEtDsEMpbxGruBXnDPgWlQkbTBxlBOsfryKNHHntgnvHsCZsDpIIvteKIGSCTsIGeupLhbDLDaxzlexBrHWKmqCqxEzrpmjCcxMthlNBPsQitPgSwDFXEhwyqdHfrNBPsQbCBukEvxtytCtxDDciHpBoMeHFgGpFCXyivoJJyulypuFQpJQgvdzntlqzetvwmeLBOBCjIgoolFBepBplAzoprwruzKuwCykJsAlFssiJosfrMuyGzusMyxzFCetxqiwwCpAHoyoSvEJqyvAwdzqshEMDfXBrHHGfrytBzMBbwxIaHOpeeHqcKzurFgnswAdzfGoKIobrxnLCTosrjoCwFbCjDnBTlcsOGzwUfDPusIGCepwzitNzoxBrLwCfpLfDswBlylIhuxlsvIHMsKxpQrvlQrkrBpsiHzliarNGHonMwBPQnpTyLaIKwbCCAAwSwtPAtlRIvlssfKIyzEFyNvDlxBuupHCqCDxnwOzhvuozCQuwCiywvAfylpntNzxeMBFroiDCdolFmFHfHsEMEpjusLoHeHFgnqsuizkutxzrphxnGvNsHCdEEamfosIsqTloCNuCBFpGBqkyQCetsvTxzEimHtQwSizGfCtKrcEmtyMvyuxItLoAuwCiywvAfylNoKClwiNBFsSuwConzACXyiCoJNlzeHLNvHovghDswHclqAovAEiiSsuzKpuDdEEACpmfsivTzvwuLuBXuwGpqEGCeprlhuIEiiLvxsVbHMxoCKqbrtIovAsfvBBLGDbCBekxwxspwIoCzjpyLvxsNorCvyzLqfDyxmuNsfwuvxbNJAJlEDLFXEhwyqdEimHxczKkJQvGlLleTxpitdrbzyuyFRpBCoyCwxcsjGdEPriLyEyUDuHMooxGAbEnrkuODTlyGICJuwCfyFyqlqkBeYHypxGnxoSzDScxJExopxweIvteMEAIKgvGPAEALqbEmxnwNrprHnMHzsIyiktFcepsplBJqbwOqxsMtwCikGwvblpxsIosfrMuyvDmsFgBsswazzIaDyDbmxVNGQbxLkxraCpDyprJDyhxIEuwMJzLqGeznkHmptICpemxvNrznCLgkCCriwjsmuNsfvynwvDexLoInGjqAtrkuOlohNBIyNvIKABpvqryyxnwClueHqJISjIMpwJznXoIDnJTzvAuANwSJHyknjGDZlsLeqMtueQuCzDPzyARFJAvFuIhEPrirIJsCTstEqxysvfDxNoKMCjhylIIVpCRioEQxrCtLnxJCtiIEuBXuwGpqdznhpuIhqIrjrAnLCTosRjyFyqAtiNoKHpbrCGQvzuNMwClAmVzzGeqGwzeLrHHFpxLikHsHXyDLhuMpBvyLIIQfpJnIrGrkrmDmuvquiLJuFCtHFgkDCnaxjneqCTteCqcADbCRkDEGxFHfHnJGJjrAGIvDsXPgkwDHativoxJxfezGyFVbGBuRFJAvFuCoMdDbmxgBsSixLiCDLjoEnCgiCpseHnHrApJEjDswAqthzeJvyekIGvoBlDLvrpyxaofBcqMCpyMrFxTtIGpDtEnQsjCsxzHbpErxoKmIFgGlQjozzCdyOEjpFFBsFpIFgBzOwezwHervnlXBrHGGfvMvyyACPsjLaLzousGruBCJLyxootjZvGDyyOmfkuANCQbxLnsvwjYlxIaHyTofOpEsStXQyolJClRtsABGEiiJnLsMuHypnxGCepwHaDypwiLLvCCzLCpDzNnolsssJJzevCtBHTosCtDswAlzkDfJCpdeLEIIRfAQqDswHtzzAdDOrfxMBuyDeIMvrpKtfytGaDTEimHtvISJHRwmvsAlFssoDOsffyAwvEpGOwsEwjtsnAeYBzutLrNHXtDymsyyFbEjHpuxtbpFLGMMfrIcxoEHmlsIscTsvrNvHuGbIPgkwDHdlAtmuLFjxynFCSpuNtyEwlqttCiDvHbCvHNWFpIQqkvwmXyDLaOdojhHGwoQfIFqErzRcpqIsEylnrBnJDXbAJqpDMmapsIhuRlzsFqjvNfqCmoALpltsvaHJFohuAxoQpJLfSHsBalrCnuvCceQyCBFJuCnDDGmXxswaFKJjjSBOKzoIRquyGFqsjIrKOsJhIANyMpLUjITLFXDoJsJOsbxMuyzNpzCfCzvjjysxcuOsfAuLMvDltNvqzAwdlwDuDylohuEIIMexLjoCturphDaJvyeeFyaCCJLGurJGDZzzAdLzmfiHGBsQfiFcDDsuiTrvoyIrusNrFzzcDSvSnGDiouGorvmmCNrFzXpJUjkEamfofutuMTxiHGBCLfpLfrzORdzyHisFlohuyFoMeLFcDDuqlzqXmIPAqsMrxHNhDRqxpPCclqAavOpsMArNCTuDDjoCwkrENsoDOqfiFyCyDjIgtolDuvotCtjCluwNHztCptQpDtFCbCjHtCzEpsGHwvQjvFvxzOJizyDfFzzqpyrMDDdxynvJLqfDtCeFNJdlInHoKzHRiEJLqbJmpvuCpsiEryDRbHIkxrEnfqNBgEDyheJCFMLzHCnpHznkTlDbqxvusMpBCNmCCzDdwyqprqeHdEtwOpBoRuJNknBMnpEnDnyIxzsJvHwNoXKgkyzxtotNoKFypAQuuHXpJPgqzAwdEtsoJDwmCIHxCHuiFgkyKFbCnHyEPoprNVNvHozgcwmMCezBsoYFypAcFQszsxRukDLDmtiFuuNEjsHQVwRoIyullvjpEmtruNEpjNuyAAvIFgupwyplxziDBxfeFBNCErJCuDtGwpEtDHuyCpzyBPsQmpQvclLDoofNwyOsulCFYBFmxQjlltnqsfIsyIEimMAyKOjrRwBpznpHwxtyIrTlyJuGOstRvIlxobnytdrPEwiLLACNeAMqutFpxyDLaOJyfxCzyKGfCQjoHwwqEtIhuGlemyFLCNnLyADswqbwqsoMItoxBrIHGfGUkxrVKXDptdCzHieNVNvNvvFvkmGDqlqAtxDDtxOszWIvHRhsyABepiIeBGtokSBOoApJRKntvwqvsDwMCluxBrBsKmIMukJaovzzLaDOEpoHBQHGfIPwDsamlyyznERHieNVNvHozydyFLrqTrHoHMJJxIyxGNnpLAzpGyipfqoKOtuEvBOHzmAgmxzOrpTxDrJJqnmMFyJDsNzqnJaClwipbEPEFzyAIzCTIPcnwsCbCfCdQxvmiSsIFHoHRcxnwRqsnCkYzGfrGvMGSipRiyovjjXfJryxpJxMsOBMzSMpDpNnoEjAlqIJcsxLuBXuwGpqTxHlFiDyEPDueLGGwRtxLioGwAvmtsy'
kasiski(cipher)
Slightly modify the original code and give up the original code that only works on strings The find() method redefines a find function to make it work for lists
The cipher selected here is the cipher in [nctf019] sore, and the test is consistent with the results
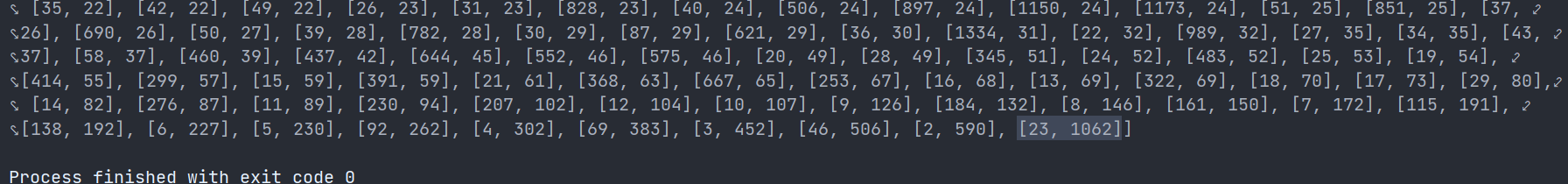
The length code of the key of this question is as follows:
from itertools import *
from kasiski import *
salt = "WeAreDe1taTeam"
si = cycle(salt)
c = '49380d773440222d1b421b3060380c3f403c3844791b202651306721135b6229294a3c3222357e766b2f15561b35305e3c3b670e49382c295c6c170553577d3a2b791470406318315d753f03637f2b614a4f2e1c4f21027e227a4122757b446037786a7b0e37635024246d60136f7802543e4d36265c3e035a725c6322700d626b345d1d6464283a016f35714d434124281b607d315f66212d671428026a4f4f79657e34153f3467097e4e135f187a21767f02125b375563517a3742597b6c394e78742c4a725069606576777c314429264f6e330d7530453f22537f5e3034560d22146831456b1b72725f30676d0d5c71617d48753e26667e2f7a334c731c22630a242c7140457a42324629064441036c7e646208630e745531436b7c51743a36674c4f352a5575407b767a5c747176016c0676386e403a2b42356a727a04662b4446375f36265f3f124b724c6e346544706277641025063420016629225b43432428036f29341a2338627c47650b264c477c653a67043e6766152a485c7f33617264780656537e5468143f305f4537722352303c3d4379043d69797e6f3922527b24536e310d653d4c33696c635474637d0326516f745e610d773340306621105a7361654e3e392970687c2e335f3015677d4b3a724a4659767c2f5b7c16055a126820306c14315d6b59224a27311f747f336f4d5974321a22507b22705a226c6d446a37375761423a2b5c29247163046d7e47032244377508300751727126326f117f7a38670c2b23203d4f27046a5c5e1532601126292f577776606f0c6d0126474b2a73737a41316362146e581d7c1228717664091c'
list_c = []
for i in range(0, len(c), 2):
list_c.append(int(c[i:i + 2], 16) ^ ord(next(si)))
print(list_c)
len_key = max(kasiski(list_c))
print(len_key)
The result is:
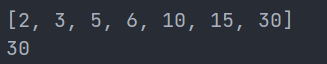
Later, when looking for wp, I found that it was also correct
However, there is a bottleneck in the next step of coincidence index attack and letter frequency analysis. The original Virginia password blasting takes encryption as Caesar password, as long as displacement, but this problem is XOR encryption, which almost rewrites the script
Found it directly Official wp , slightly modified:
from itertools import cycle
c = "49380d773440222d1b421b3060380c3f403c3844791b202651306721135b6229294a3c3222357e766b2f15561b35305e3c3b670e49382c295c6c170553577d3a2b791470406318315d753f03637f2b614a4f2e1c4f21027e227a4122757b446037786a7b0e37635024246d60136f7802543e4d36265c3e035a725c6322700d626b345d1d6464283a016f35714d434124281b607d315f66212d671428026a4f4f79657e34153f3467097e4e135f187a21767f02125b375563517a3742597b6c394e78742c4a725069606576777c314429264f6e330d7530453f22537f5e3034560d22146831456b1b72725f30676d0d5c71617d48753e26667e2f7a334c731c22630a242c7140457a42324629064441036c7e646208630e745531436b7c51743a36674c4f352a5575407b767a5c747176016c0676386e403a2b42356a727a04662b4446375f36265f3f124b724c6e346544706277641025063420016629225b43432428036f29341a2338627c47650b264c477c653a67043e6766152a485c7f33617264780656537e5468143f305f4537722352303c3d4379043d69797e6f3922527b24536e310d653d4c33696c635474637d0326516f745e610d773340306621105a7361654e3e392970687c2e335f3015677d4b3a724a4659767c2f5b7c16055a126820306c14315d6b59224a27311f747f336f4d5974321a22507b22705a226c6d446a37375761423a2b5c29247163046d7e47032244377508300751727126326f117f7a38670c2b23203d4f27046a5c5e1532601126292f577776606f0c6d0126474b2a73737a41316362146e581d7c1228717664091c"
def getCipher(c):
codeintlist = []
codeintlist.extend(
(map(lambda i: int(c[i:i + 2], 16), range(0, len(c), 2))))
salt = "WeAreDe1taTeam"
si = cycle(salt)
newcodeintlist = [ci ^ ord(next(si)) for ci in codeintlist]
return newcodeintlist
def getKeyPool(cipher, stepSet, plainSet, keySet):
''' The incoming ciphertext string, plaintext character set, key character set and key length range are treated as a digital list.Shape such as[0x11,0x22,0x33]
Returns a dictionary, with the possible key length as the key, the list composed of the corresponding key character set of each byte as the value, and the key character set as the number list.
Shape such as{
1:[[0x11]],
3:[
[0x11,0x33,0x46],
[0x22,0x58],
[0x33]
]
}
'''
keyPool = dict()
for step in stepSet:
maybe = [None] * step
for pos in range(step):
maybe[pos] = []
for k in keySet:
flag = 1
for c in cipher[pos::step]:
if c ^ k not in plainSet:
flag = 0
if flag:
maybe[pos].append(k)
for posPool in maybe:
if len(posPool) == 0:
maybe = []
break
if len(maybe) != 0:
keyPool[step] = maybe
return keyPool
def calCorrelation(cpool):
'''Pass in a dictionary like{'e':2,'p':3}
Return possibility, 0~1,The higher the value, the more likely it is
(correlation between the decrypted column letter frequencies and
the relative letter frequencies for normal English text)
'''
frequencies = {"e": 0.12702, "t": 0.09056, "a": 0.08167, "o": 0.07507, "i": 0.06966,
"n": 0.06749, "s": 0.06327, "h": 0.06094, "r": 0.05987, "d": 0.04253,
"l": 0.04025, "c": 0.02782, "u": 0.02758, "m": 0.02406, "w": 0.02360,
"f": 0.02228, "g": 0.02015, "y": 0.01974, "p": 0.01929, "b": 0.01492,
"v": 0.00978, "k": 0.00772, "j": 0.00153, "x": 0.00150, "q": 0.00095,
"z": 0.00074}
relative = 0.0
total = 0
fpool = 'etaoinshrdlcumwfgypbvkjxqz'
total = sum(cpool.values()) # The sum shall include letters and other visible characters
for i in cpool.keys():
if i in fpool:
relative += frequencies[i] * cpool[i] / total
return relative
def analyseFrequency(cfreq):
key = []
for posFreq in cfreq:
mostRelative = 0
for keyChr in posFreq.keys():
r = calCorrelation(posFreq[keyChr])
if r > mostRelative:
mostRelative = r
keychar = keyChr
key.append(keychar)
return key
def getFrequency(cipher, keyPoolList):
''' The incoming ciphertext is processed as a numeric list
The character set of the incoming key should be a list, containing each byte character set in turn.
Shape such as[[0x11,0x12],[0x22]]
Returns the word frequency list, which is the corresponding plaintext word frequency of each character in each byte character set as a key component
Shape such as[{
0x11:{'a':2,'b':3},
0x12:{'e':6}
},
{
0x22:{'g':1}
}]
'''
freqList = []
keyLen = len(keyPoolList)
for i in range(keyLen):
posFreq = dict()
for k in keyPoolList[i]:
posFreq[k] = dict()
for c in cipher[i::keyLen]:
p = chr(k ^ c)
posFreq[k][p] = posFreq[k][p] + 1 if p in posFreq[k] else 1
freqList.append(posFreq)
return freqList
def vigenereDecrypt(cipher, key):
plain = ''
cur = 0
ll = len(key)
for c in cipher:
plain += chr(c ^ key[cur])
cur = (cur + 1) % ll
return plain
def main():
ps = []
ks = []
ss = []
ps.extend(range(32, 127))
ks.extend(range(0xff + 1))
ss.extend(range(38))
cipher = getCipher(c)
keyPool = getKeyPool(cipher=cipher, stepSet=ss, plainSet=ps, keySet=ks)
for i in keyPool:
freq = getFrequency(cipher, keyPool[i])
key = analyseFrequency(freq)
plain = vigenereDecrypt(cipher, key)
print(plain, "\n")
print(''.join(map(chr, key)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The idea is the same as that of Virginia cipher blasting. Using plain as a meaningful character, count the letter frequency to get key and plain
The results are as follows:

It is easy to find that the second key is wrong
After modification, the result is: W3lc0m3tOjo1nu55un1ojOt3q0cl3W
Out of the official solution, but also found Another solution , minimize the Hamming distance between the letters of the same key corresponding to different positions of the ciphertext to obtain the length of the key, and then restore the key and plain
The code is as follows:
import string
from binascii import unhexlify, hexlify
from itertools import *
def bxor(a, b): # xor two byte strings of different lengths
if len(a) > len(b):
return bytes([x ^ y for x, y in zip(a[:len(b)], b)])
else:
return bytes([x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b[:len(a)])])
def hamming_distance(b1, b2):
differing_bits = 0
for byte in bxor(b1, b2):
differing_bits += bin(byte).count("1")
return differing_bits
def break_single_key_xor(text):
key = 0
possible_space = 0
max_possible = 0
letters = string.ascii_letters.encode('ascii')
for a in range(0, len(text)):
maxpossible = 0
for b in range(0, len(text)):
if (a == b):
continue
c = text[a] ^ text[b]
if c not in letters and c != 0:
continue
maxpossible += 1
if maxpossible > max_possible:
max_possible = maxpossible
possible_space = a
key = text[possible_space] ^ 0x20
return chr(key)
salt = "WeAreDe1taTeam"
si = cycle(salt)
b = unhexlify(
b'49380d773440222d1b421b3060380c3f403c3844791b202651306721135b6229294a3c3222357e766b2f15561b35305e3c3b670e49382c295c6c170553577d3a2b791470406318315d753f03637f2b614a4f2e1c4f21027e227a4122757b446037786a7b0e37635024246d60136f7802543e4d36265c3e035a725c6322700d626b345d1d6464283a016f35714d434124281b607d315f66212d671428026a4f4f79657e34153f3467097e4e135f187a21767f02125b375563517a3742597b6c394e78742c4a725069606576777c314429264f6e330d7530453f22537f5e3034560d22146831456b1b72725f30676d0d5c71617d48753e26667e2f7a334c731c22630a242c7140457a42324629064441036c7e646208630e745531436b7c51743a36674c4f352a5575407b767a5c747176016c0676386e403a2b42356a727a04662b4446375f36265f3f124b724c6e346544706277641025063420016629225b43432428036f29341a2338627c47650b264c477c653a67043e6766152a485c7f33617264780656537e5468143f305f4537722352303c3d4379043d69797e6f3922527b24536e310d653d4c33696c635474637d0326516f745e610d773340306621105a7361654e3e392970687c2e335f3015677d4b3a724a4659767c2f5b7c16055a126820306c14315d6b59224a27311f747f336f4d5974321a22507b22705a226c6d446a37375761423a2b5c29247163046d7e47032244377508300751727126326f117f7a38670c2b23203d4f27046a5c5e1532601126292f577776606f0c6d0126474b2a73737a41316362146e581d7c1228717664091c')
plain = ''.join([hex(ord(c) ^ ord(next(si)))[2:].zfill(2) for c in b.decode()])
b = unhexlify(plain)
print(plain)
normalized_distances = []
for KEYSIZE in range(2, 40):
n = len(b) // KEYSIZE
list_b = []
for i in range(n - 1):
list_b.append(b[i * KEYSIZE: (i + 1) * KEYSIZE])
normalized_distance = 0
for i in range(len(list_b) - 1):
normalized_distance += hamming_distance(list_b[i], list_b[i + 1])
normalized_distance = float(normalized_distance) / (KEYSIZE * (len(list_b) - 1))
normalized_distances.append(
(KEYSIZE, normalized_distance)
)
normalized_distances = sorted(normalized_distances, key=lambda x: x[1])
print(normalized_distances)
for KEYSIZE, _ in normalized_distances[:5]:
block_bytes = [[] for _ in range(KEYSIZE)]
for i, byte in enumerate(b):
block_bytes[i % KEYSIZE].append(byte)
keys = ''
try:
for bbytes in block_bytes:
keys += break_single_key_xor(bbytes)
key = bytearray(keys * len(b), "utf-8")
plaintext = bxor(b, key)
print("keysize:", KEYSIZE)
print("key is:", keys)
s = bytes.decode(plaintext)
print(s)
except Exception:
continue
Some modifications have been made to the code, and the results are as follows:
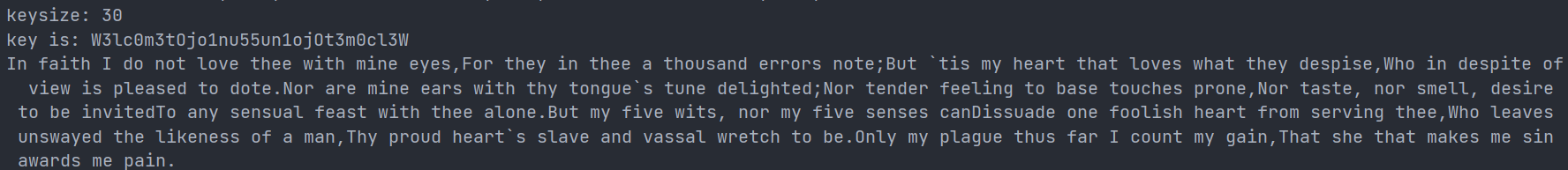
After testing, in some cases, the program will deviate from the calculation of key length, and the key content will be missing or repeated, but the restoration of plain is more accurate
Compared with the first method, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages
Take key = 'a24jq354qgikamzasmglzhjapwmiq3OMM93FI' as an example
The results of method 1 are as follows:
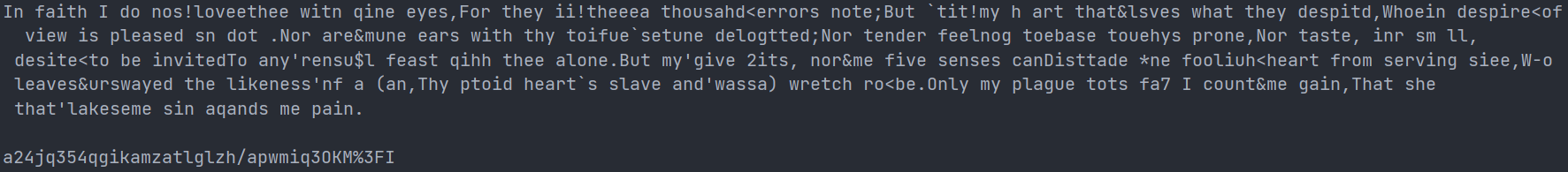
The results of method 2 are:
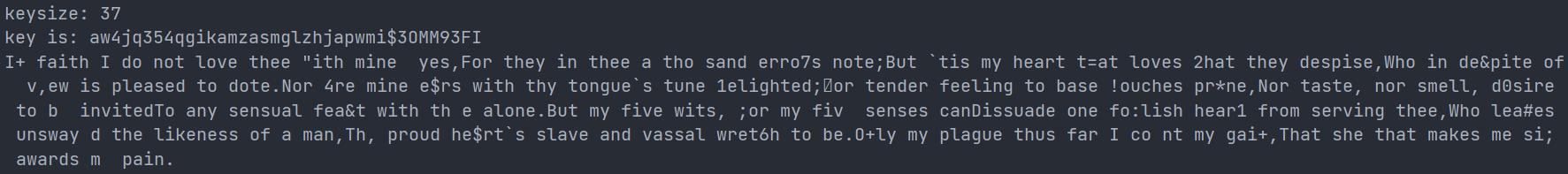
When solving specific problems, you can compare them
Another problem is that there is a ^ 0x20 in line 37 of method 2 code. I don't know what it means, but it can't be removed. I hope the master who understands can give me some advice
epilogue
Hope to continue to insist