- system platform
win10 64bit - Software version
Visual Studio: VS2017
MATLAB: MATLAB R2018b
Note: the version of MATLAB is not lower than VS, otherwise the call fails. - Set up MATLAB external interface
(1) select compiler
>>mbuild -setup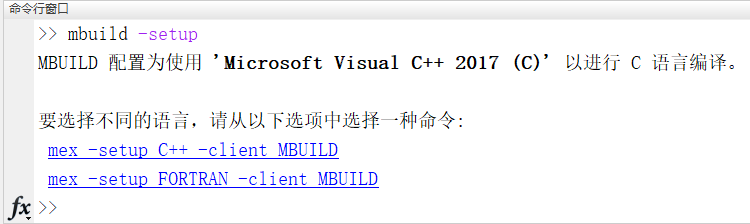
(2) generate DLL file
Method 1:
>>deploytool
Select Library Compiler: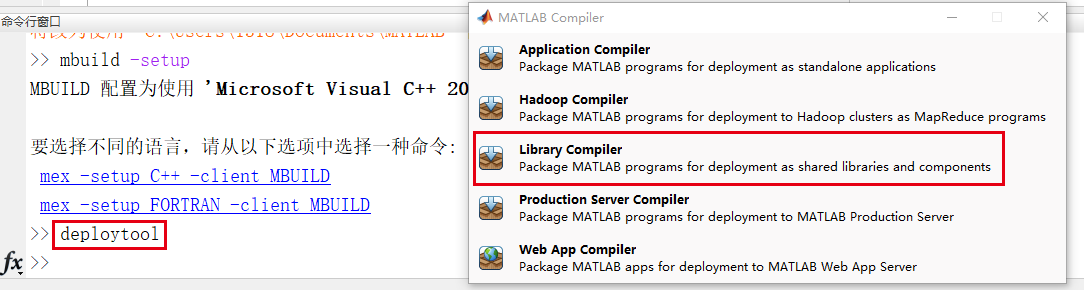
Method 2:
Select directly from the above APP, Library Compiler: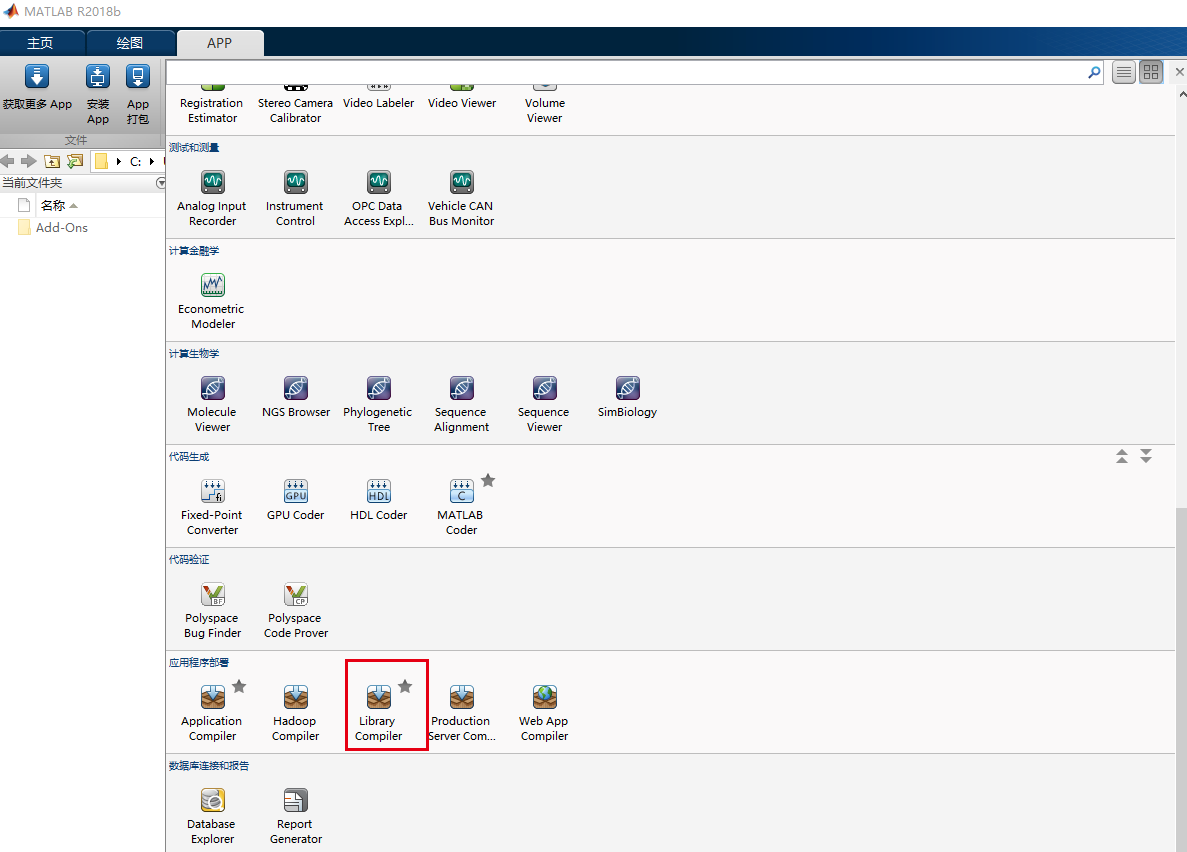
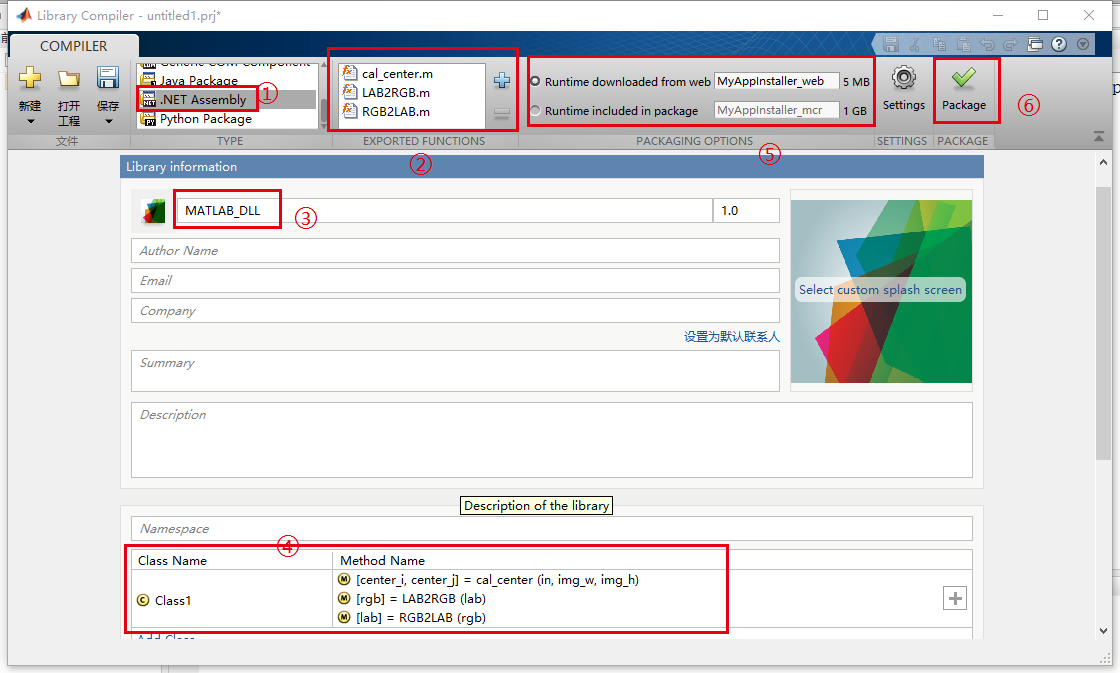
①: C call selection:. NET Assembly
②: click the plus sign to select one or more m files (at this time, multiple M files are integrated into one dll);
③: the name of the generated DLL, which is the name of the first m file by default, can be modified to another name;
④: Class Name is the Class1 used in the call, which can also be modified;
⑤: it has been proved that MCR needs to be installed when running on other computers;
⑥: click Package to generate the file.
Generate the following files and select the dll file in the second folder.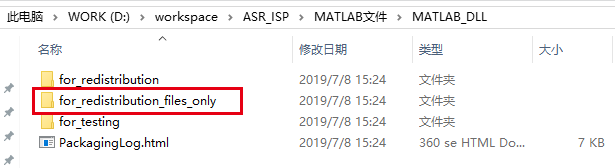
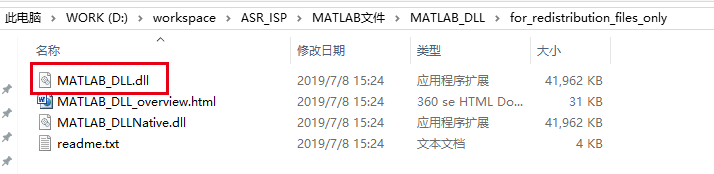
(3) prepare C-program:
Add two dependent libraries: MWArray.dll and MATLAB dll.dll.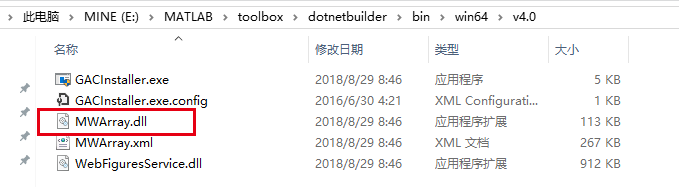
Add reference → browse → select the two files respectively → OK.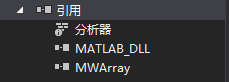
Add namespace:
using MathWorks; using MathWorks.MATLAB; using MathWorks.MATLAB.NET; using MathWorks.MATLAB.NET.Arrays; using MathWorks.MATLAB.NET.Utility; using MATLAB_DLL;
Programming: (since the MATLAB version is 64bit, x64 is selected as the compiling platform)
① when outputting a parameter:
function result=myadd(a,b) result=a+b; end
② when multiple parameters are output:
function [res_add,res_sub,res_mul,res_div]=cal(a,b) res_add=a+b; res_sub=a-b; res_mul=a*b; res_div=a./b; end
The specific procedures are as follows:
using System;
using MathWorks.MATLAB.NET.Arrays;
using Matlab_dll;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Load Class1 in MATLAB DLL
Matlab_dll.Class1 matdll = new Matlab_dll.Class1();
//When the output parameter is one
MWArray a = 1, b = 2, c;//When MWArray is calling MATLAB, the parameter type is MWArray.
c = matdll.myadd(a, b);//Call myadd
Console.WriteLine("When outputting a parameter:");
Console.WriteLine("a + b = ");
Console.WriteLine(c);
//When the output parameters are multiple
MWArray[] input = new MWArray[] { a, b };//Put the input parameter in a MWArray [].
MWArray[] output = new MWArray[4];//Set the number of output parameters
matdll.cal(4, ref output, input);//The first parameter indicates the number of outputs
Console.WriteLine("When multiple parameters are output:");
Console.WriteLine("a + b = ");
Console.WriteLine(output[0]);//Output first result
Console.WriteLine("a - b = ");
Console.WriteLine(output[1]);//The second
Console.WriteLine("a * b = ");
Console.WriteLine(output[2]);//Third
Console.WriteLine("a / b = ");
Console.WriteLine(output[3]);//Fourth
//If you need to use the call result for other calculations
MWNumericArray re_tmp = (MWNumericArray)output[0];
double[,] re = new double[1, 1];//MATLAB deals with matrix. The defined array to be assigned cannot be one-dimensional
re = (double[,])re_tmp.ToArray();
double xx = 10;
xx += re[0, 0];
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("xx:{0:2f}", xx);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
The results are as follows: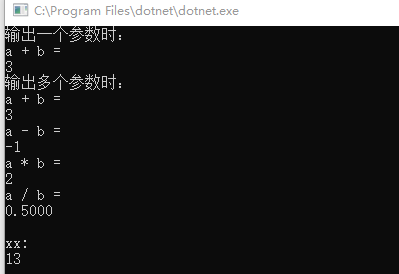
Note:
1. Loading Class1 of MATLAB DLL is slow;
2. The compilation platform is consistent with MATLAB;
3. Call MATLAB function operation is very fast.