1. Personal information can be stored in the address book
Such as: name, gender, telephone number, address, etc.
2. Modify the information of the designated person;
3. Delete the information of the designated person;
4. Find the information of the designated person;
5. Add information;
What is advanced edition
The so-called advanced address book is to increase the dynamic memory development and the storage of address book content;
Now let's implement the address book
First, the macro and header files are displayed to make it easy for readers to understand when reading
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define MAX_NAME 10 #define MAX_ADD 20 #define MAX_SEX 5 #define MAX_NUM 15 #define VALUE 2 #define DOUBLE_SZ 3
Considering that there are many contents in the address book, we now use structures to put them together for easy operation
#define MAX_NAME 10
#define MAX_ADD 20
#define MAX_SEX 5
#define MAX_NUM 15
typedef struct PeopleInfor
{
char name[MAX_NAME];//name
char add[MAX_ADD];//address
char sex[MAX_SEX];//Gender
char num[MAX_NUM];//Telephone number
int age;
}PeopleInfor;Considering the number of people in the address book, we create the following structure
//Collection
typedef struct PeopleColl
{
PeopleInfor* date;//Everyone's information
int sz;//Number of contacts stored in
int capacity;//Address book capacity
}PeopleColl;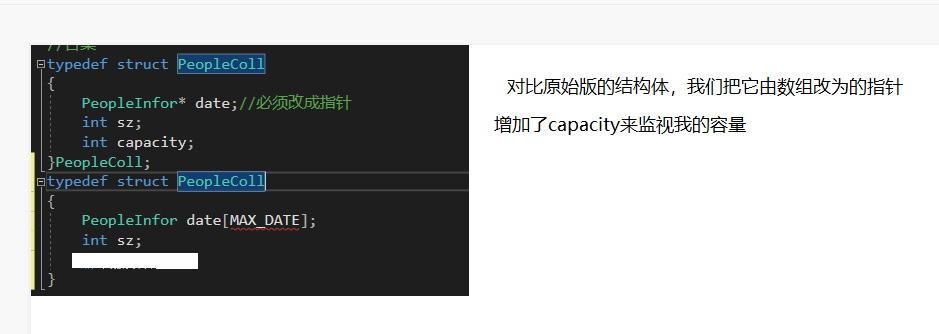
The following is the creation of the main function:
The function name can be set according to people's preferences
int main()
{
int a = 0;
PeopleColl con;
Initial(&con);//initialization
do {
menu();
printf("Please select:");
scanf("%d", &a);
switch (a)
{
case 1:
ADDITION(&con);//Add a contact
Check(con);
break;
case 2:
Delete(&con);//Delete information
break;
case 3:
SEEK(&con);//Find information about the specified person
break;
case 4:
Revise(&con);//Modify information
break;
case 5:
Check(con);//View contacts
break;
case 0: StoreIfor(&con);
Freed(&con);//Release address book
break;
default:
printf("Selection error, re-enter\n");
break;
}
} while (a);
return 0;
}Let's implement the function from top to bottom
1. Initialization
 In initialization, we need to change the structure, so we use &;
In initialization, we need to change the structure, so we use &;
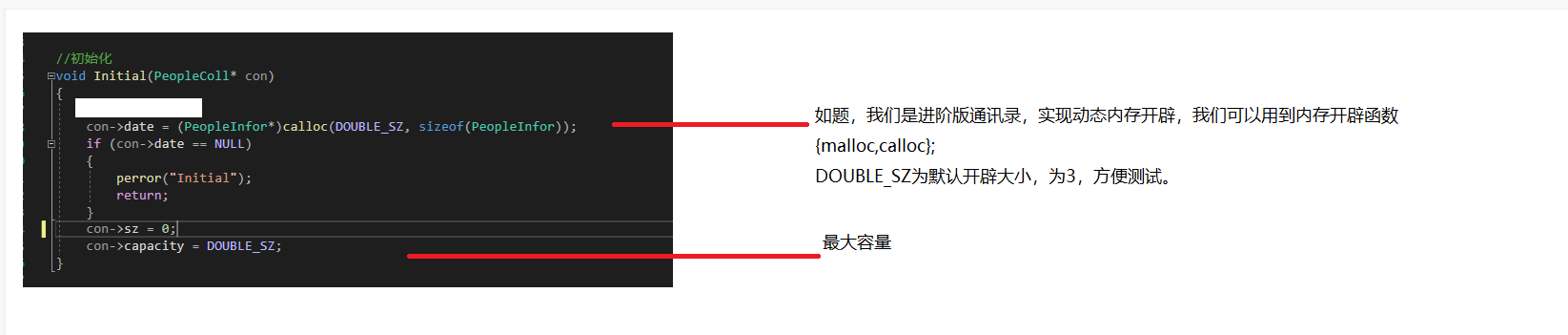
void Initial(PeopleColl* con)
{
con->date = (PeopleInfor*)calloc(DOUBLE_SZ, sizeof(PeopleInfor));
if (con->date == NULL)
{
perror("Initial");
return;
}
con->sz = 0;
con->capacity = DOUBLE_SZ;
ReadIfor(con);
}
ReadIfor(); Functions are interpreted separately
It is easy to understand that when opening the address book, you need to read the previously stored content
//Read information
void ReadIfor(PeopleColl* con)
{
FILE* ptr = fopen("AddBook.dat", "rb");
if (ptr == NULL)
{
perror("ReadIfor");
printf("read failure\n");
return;
}
else {
PeopleInfor mat = { 0 };
while (fread(&mat, sizeof(PeopleInfor), 1, ptr))
{
Congestion(con);
con->date[con->sz] = mat;
con->sz++;
}
}
} 
2 add contact
void ADDITION(PeopleColl* con)
{
Congestion(con);
printf("Please enter your name:\n");
scanf("%s", con->date[con->sz].name);
printf("Please enter gender:\n");
scanf("%s", con->date[con->sz].sex);
printf("Please enter the address:\n");
scanf("%s", con->date[con->sz].add);
printf("Please enter the number:\n");
scanf("%s", &(con->date[con->sz].num));
printf("Please enter age:\n");
scanf("%d", &(con->date[con->sz].age));
con->sz++;
printf("Entered successfully\n");
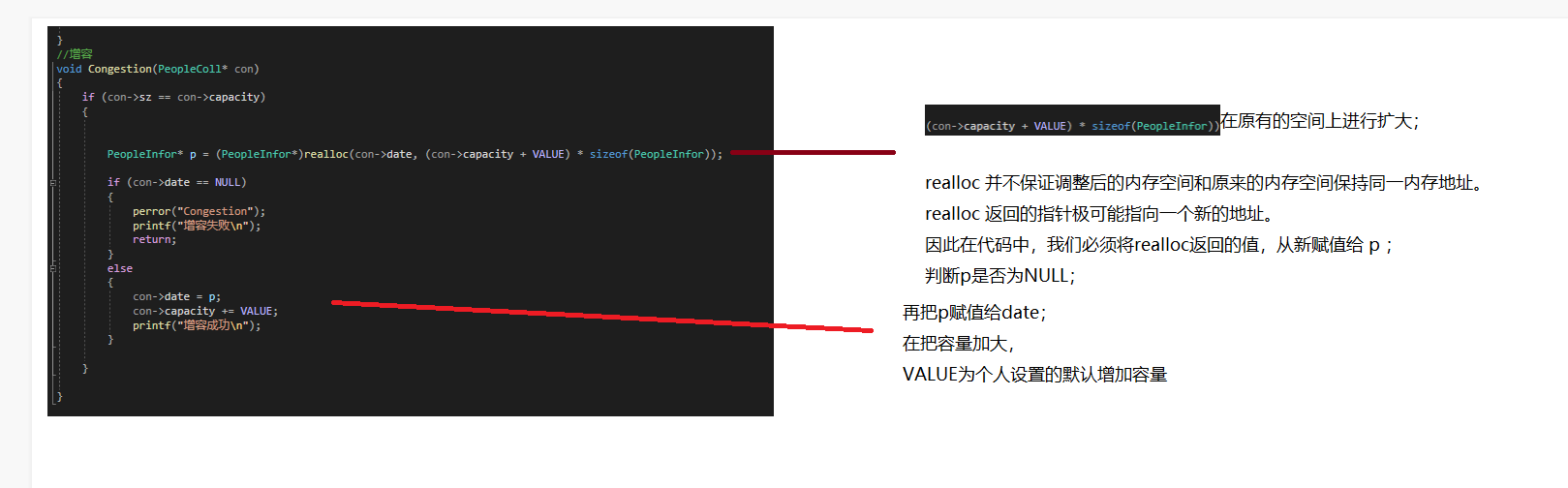
}Before adding contacts, first consider whether the address book is full; Therefore, a condensation () is created here; Compatibilization function;
Convergence() is implemented as follows:
void Congestion(PeopleColl* con)
{
if (con->sz == con->capacity)
{
PeopleInfor* p = (PeopleInfor*)realloc(con->date, (con->capacity + VALUE) * sizeof(PeopleInfor));
if (con->date == NULL)
{
perror("Congestion");
printf("Capacity increase failed\n");
return;
}
else
{
con->date = p;
con->capacity += VALUE;
printf("Successful capacity increase\n");
}
}
}
3 delete contact
//Delete information
void Delete(PeopleColl* con)
{
if (con->sz == 0) {
printf("Address book is empty\n");
return;
}
char arr[MAX_NAME] = { 0 };
printf("Please enter the name of the person to delete:\n");
scanf("%s", arr);
int p = Seek(con, arr);
if (p == -1) {
printf("The deleted person does not exist\n");
}
else
{
int i = 0;
for (i = p; i < con->sz - 1; i++) {
con->date[i] = con->date[i + 1];
}
con->sz--;
printf("Delete succeeded\n");
}
}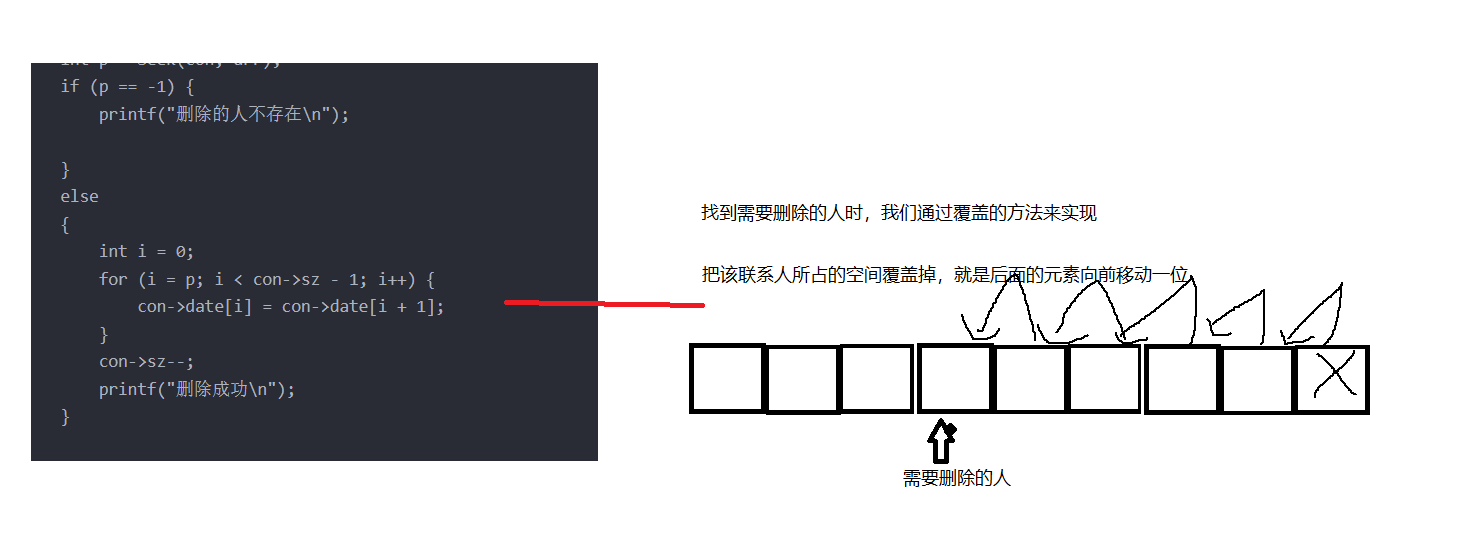
When deleting a contact, a function Seek is used; This function is a search function, which determines whether to find the specified contact according to the return value of this function (this function will also be used in subsequent function implementations);
int Seek(const PeopleColl* con, char arr[MAX_NAME])
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < con->sz; i++)
{
if (strcmp(con->date[i].name, arr) == 0)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
4 find information
The function is an extension of the search function and adds a function of displaying information
//Find information about the specified person
void SEEK(PeopleColl* con)
{
if (con->sz == 0) {
printf("Address book is empty\n");
return;
}
char arr[MAX_NAME] = { 0 };
printf("Please enter the name of the person you want to find:\n");
scanf("%s", arr);
int p = Seek(con, arr);
if (p == -1) {
printf("The person you are looking for does not exist\n");
}
else
{
printf("The information of the finder is:\n");
printf("%-10s %-10s %-20s %-20s %-10s\n", "full name", "Gender", "address", "number", "Age");
printf("%-10s %-10s %-20s %-20s %-10d\n", con->date[p].name,
con->date[p].sex,
con->date[p].add,
con->date[p].num,
con->date[p].age);
}
}5 modify information
//Modify information
void Revise(PeopleColl* con)
{
if (con->sz == 0) {
printf("Address book is empty\n");
return;
}
char arr[MAX_NAME] = { 0 };
printf("Please enter the name of the person to modify:\n");
scanf("%s", arr);
int p = Seek(con, arr);
if (p == -1) {
printf("Modified by does not exist\n");
}
else {
printf("Please enter your name:\n");
scanf("%s", con->date[p].name);
printf("Please enter gender:\n");
scanf("%s", con->date[p].sex);
printf("Please enter the address:\n");
scanf("%s", con->date[p].add);
printf("Please enter the number:\n");
scanf("%s", &(con->date[p].num));
printf("Please enter age:\n");
scanf("%d", &(con->date[p].age));
printf("Modified successfully\n");
}
}Modifying the content of the information is to add a reduced version of the information
6 view address book
This function can be added after each option to achieve the display effect
//see information
void Check(PeopleColl con)
{
if (con.sz == 0) {
printf("Please enter the information first\n");
}
int i = 0;
printf("%-10s %-10s %-20s %-20s %-10s\n", "full name", "Gender", "address", "number", "Age");
for (i = 0; i < con.sz; i++)
{
printf("%-10s %-10s %-20s %-20s %-10d\n", con.date[i].name,
con.date[i].sex,
con.date[i].add,
con.date[i].num,
con.date[i].age);
}
}7 exit and store information
Before we quit, we should store the address book information and destroy the address book
//Save information to file
void StoreIfor(PeopleColl* con)
{
FILE* p = fopen("AddBook.dat", "wb");
if (p == NULL)
{
perror("StoreIfor");
printf("Storage failed\n");
return;
}
//Storage file
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < con->sz; i++)
{
fwrite(con->date + i, sizeof(PeopleInfor), 1, p);
}
printf("Storage successful\n");
//Close file
//Freeing pointers to avoid memory leaks
fclose(p);
p = NULL;
}

Destroy address book
void Freed(PeopleColl* con)
{
free(con->date);
con->date = NULL;
con->capacity = 0;
con->sz = 0;
}