catalogue
3.# Identifier constant defined by define
1. static can modify local variables
2. static can modify global variables
3. static can modify functions
1, What is C language?
C language is a general computer programming language, which is widely used in Bottom development. The design goal of C language is to provide a programming language that can compile and process low-level memory in a simple way, generate a small amount of machine code and run without any running environment support. Although C language provides many low-level processing functions, it still maintains good cross platform characteristics. C language programs written in a standard specification can be compiled on many computer platforms, even including some embedded processors (single chip microcomputer or MCU) and supercomputers. In the 1980s, in order to avoid differences in C language syntax used by various developers, the American National Bureau of standards formulated a complete set of American national standard syntax for C language, called ANSI C, as the original standard of C language. [1] At present, the C11 standard issued by the international organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on December 8, 2011 is the third official standard of C language and the latest standard of C language. The standard better supports Chinese function name and Chinese identifier, and realizes Chinese character programming to a certain extent. C language is a process oriented computer programming language, which is different from object-oriented programming languages such as C + +, Java and so on. Its compilers mainly include Clang, GCC, WIN-TC, SUBLIME, MSVC, Turbo C, etc.
2, Common keywords
auto break case char const continue default do
double else enum extern float for goto if
int long register return short signed sizeof static
struct switch typedef union unsigned void volatile while
1. Keyword typedef
typedef, as the name suggests, is a type definition, which should be understood here as type renaming.
//Rename unsigned int uint_32, so uint_32 is also a type name
typedef unsigned int uint_32;
int main()
{
//Look at num1 and num2. These two variables are of the same type
unsigned int num1 = 0;
uint_32 num2 = 0;
return 0;
}2. Keyword register
Register variables can't get addresses. Why?
Register serves as a recommendation. It is recommended to put the value of num in the register, which is finally determined by the compiler
int main()
{
register int num = 10;
return 0;
}Simply record how the CPU processor works
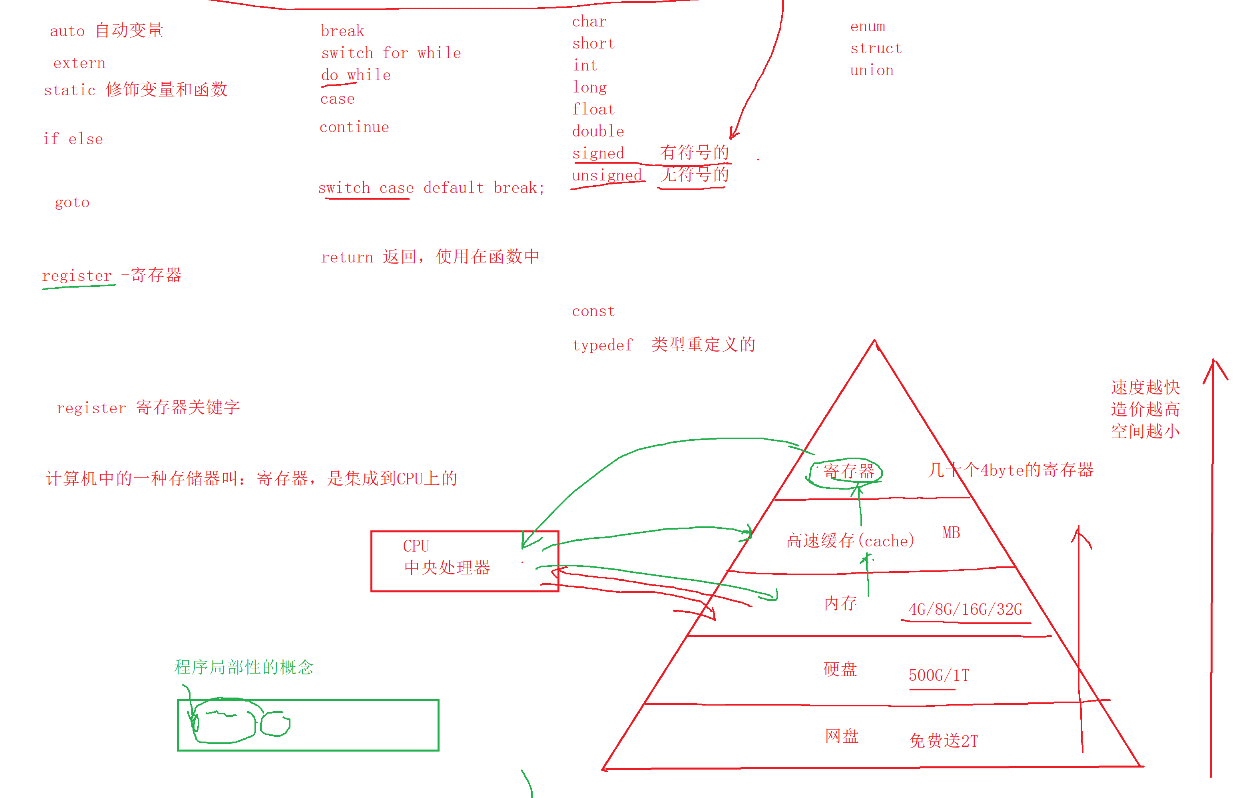
3, Data type
char short int long
long long float double
When using char type, you need to use '' when the object is a single character and '' when the object is a string
Eg:1.'w' 2."linqinyan"
#include <stdio.h>
//sizeof is an operator that calculates the size of types and variables
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(char));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(short));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(int));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(long));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(long long));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(float));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(double));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(long double));
return 0;
}IV. ASCII code table
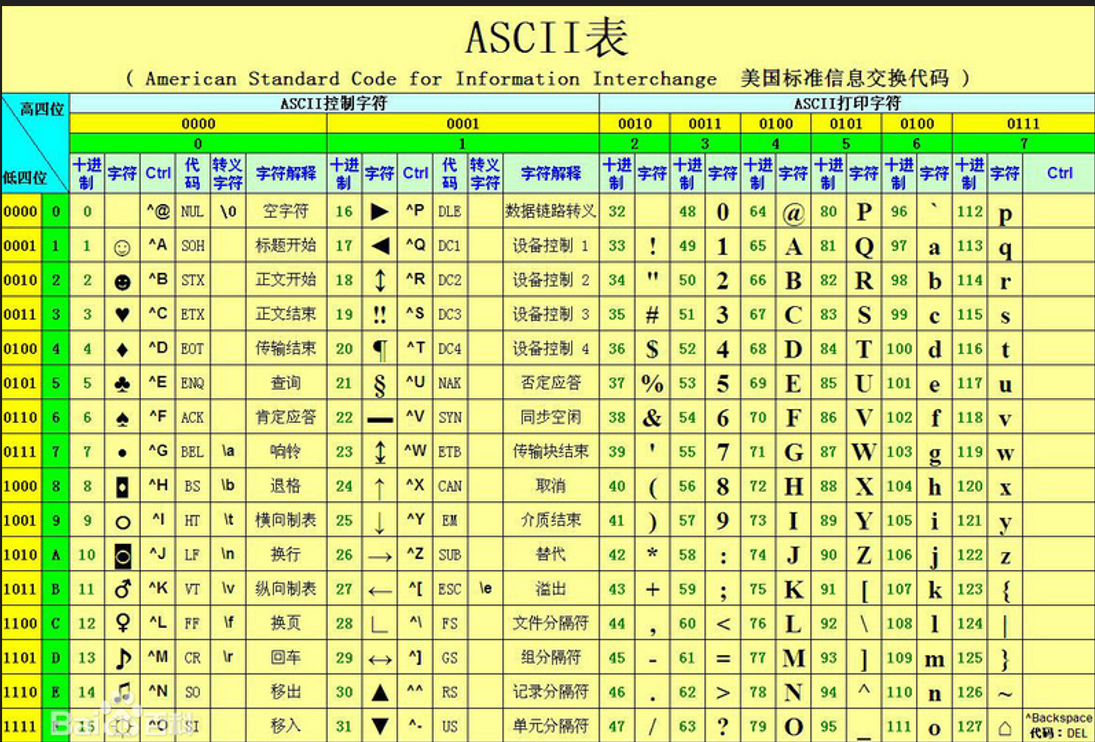
5, Variable type
1. Global variables
If a global variable is not initialized, it will be initialized to 0 by default
2. Local variables
If a local variable is not initialized, it defaults to a random value
#include <stdio.h>
int global = 2019;//global variable
int main()
{
int local = 2018;//local variable
//Is there a problem with the global defined below?
int global = 2020;//local variable
printf("global = %d\n", global);
return 0;
}Ext can also introduce variables in header files or other cpp sub files
extern int g_val; //Declare external symbols, such as those in the header file
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
}Corresponding header file
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 int g_val = 2022;//global variable
6, Constants in C language
1. Literal constant
int main()
{
3.14;//Literal constant
1000;//Literal constant
return 0;
}2.const modified constant
const int n = 10;
printf("n=%d\n", n);//10
n = 20;
printf("n=%d\n", n);//20
const int n = 10;//Here n has a constant property, but it is essentially a variable
3.# Identifier constant defined by define
#define MAX 100
int main()
{
//MAX = 101;//err error reporting
int m = MAX;
printf("%d\n", m);
printf("%d\n", MAX);
return 0;
}4. Enumeration constants
Enumerating constants are enumerations one by one. They are a custom type method provided by C language
eg: Gender: male, female, three primary colors: red green blue
enum Sex
{
MALE,//The contents are sorted from 0, 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
FEMALE,
SECRET
};
enum COLOR
{
RED,
GREEN,
BLUE
};
int main()
{
//MALE = 5;//err
enum Sex s = MALE;
printf("%d\n", MALE); //0
printf("%d\n", FEMALE); //1
printf("%d\n", SECRET); //2
return 0;
}
7, Escape character
Suppose we want to print a directory on the screen: C: \ code \ test c
How do we write code? Is it like this?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("c:\code\test.c\n");
return 0;
}In fact, the result of the program is as follows:
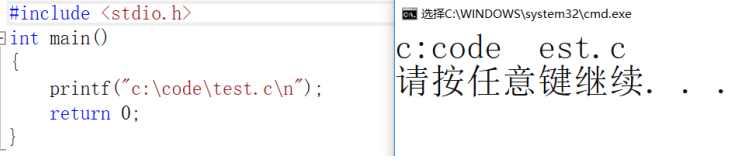 It's different from what we expected.
It's different from what we expected.
I have to mention the escape character here.
Escape character table
| Escape character | interpretation |
|---|---|
| \? | Used when writing consecutive question marks to prevent them from being parsed into three letter words |
| \' | Used to represent character constants' |
| \" | Double quotation marks used to represent the inside of a string |
| \\ | Used to represent a backslash to prevent it from being interpreted as an escape sequence character. |
| \a | Warning character, beep |
| \b | Backspace character |
| \f | Feed character |
| \n | Line feed |
| \r | enter |
| \t | Horizontal tab |
| \v | vertical tab |
| \ddd | ddd represents 1 ~ 3 octal digits. For example: \ 130 X |
| \xdd | dd represents 2 hexadecimal digits. For example: \ x30 |
Program verification:
int main()
{
printf("c:\\test\\test.c");
printf("abcndef");
printf("abc\ndef");
//Three letter word:?) Will be transformed into]
printf("(are you ok\?\?)");//(are you ok]
printf("%c\n", 'a');
printf("%c\n", '\'');
printf("%s\n", "abc");
printf("%s\n", "a");
printf("%s\n", "\"");
printf("\a\a\a\a\a");
printf("%c\n", '\135');
//The number converted to decimal is 64 + 24 + 5 = 93
printf("%c\n", '\x42');
return 0;
}What will the following program output?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", strlen("abcdef")); //6
// \62 is parsed into an escape character
printf("%d\n", strlen("c:\test\628\test.c")); //14
return 0;
}VIII. Comma expression
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = 3;
int c = 4;
int d = (a = b - 3, b = a * 2, c = a - b); //Comma expression d takes the last value
printf("%d %d %d %d\n", a,b,c,d);
return 0;
}9, The essence of scanf
int main()
{
int iq = 0;
while (scanf("%d", &iq) != EOF)
{
if (iq >= 140)
printf("Genius\n");
}
return 0;
}int main()
{
int iq = 0;
while(scanf("%d", &iq) == 1)
{
if(iq>=140)
printf("Genius\n");
}
return 0;
}10, Static - static
1. static can modify local variables
#include <stdio.h>
void test()
{
static int n = 1;
n++;
printf("%d ", n);
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
while (i < 10)
{
test();
i++;
}
return 0;
}
2. static can modify global variables
extern int g_val;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
}Header file
static int g_val = 2022;
3. static can modify functions
extern int Add(int, int); //Declare functions from outside
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
int sum = Add(a, b);
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}Header file
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
int z = x + y;
return z;
}11, define macro
#define defines constants and macros
#define constant
#define NUM 100
#define STR "hehe"
#Define add (x, y) ((x) + (y) / / define macro - macro has parameters
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", NUM);
printf("%s\n", STR);
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int sum = ADD(a, b);
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}