1. (1): write a program to establish a single linked list and output all data elements in the single linked list one by one.
Implementation code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}linklist;
linklist *CreateLinklist(){
linklist *head,*p,*s;
head = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
p = head;
printf("Please enter the data elements in the single linked list (input)-1 Do not process when entering (end):\n");
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
while (x != -1){
s = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
s->data = x;
p->next = s;
p = s;
scanf("%d",&x);
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
};
void PrintLinklist(linklist *head){
linklist *t = head->next;
if (t == NULL){
printf("The single linked table is empty!\n");
}
while(t != NULL){
printf("%d ",t->data);
t = t->next;
}
}
int main(){
linklist *l = CreateLinklist();
printf("All elements in the single linked list are:");
PrintLinklist(l);
return 0;
}
Operation results:
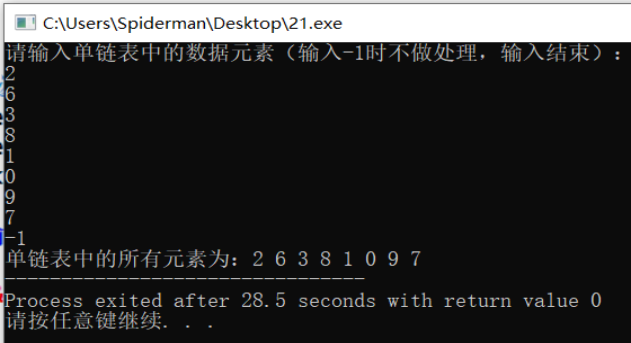
analysis:
The time complexity and space complexity of the functions used to output all elements in the single linked list of the leading node in the program are linear order O (n).
(2) : insert a new node x into the incrementally ordered single linked list to maintain the order of the single linked list.
Problem solving ideas: first find the insertion position, and then perform the insertion operation; Starting from the first node, find the first node greater than the value of the new node, that is, the insertion position; Then insert a new node before the found node; Note that the insertion operation can be completed only when the pointer of the node is reserved before the insertion position.
Implementation code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}linklist;
linklist *CreateLinklist(){
linklist *head,*p,*s;
head = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
p = head;
printf("Please enter the data elements in the single linked list (input)-1 Do not process when entering (end):\n");
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
while (x != -1){
s = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
s->data = x;
p->next = s;
p = s;
scanf("%d",&x);
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
};
void PrintLinklist(linklist *head){
linklist *t = head->next;
if (t == NULL){
printf("The single linked table is empty!\n");
}
while(t != NULL){
printf("%d ",t->data);
t = t->next;
}
}
linklist *SearchAndInsert(linklist *head,int x){
linklist *p,*q;
p = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
p->data = x;
if (head->next == NULL || head->next->data > x){
p->next = head->next;
head->next = p;
return head;
}
q = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
q = head->next;
while (q != NULL && q->next != NULL){
if (x >= q->data && x < q->next->data){
p->next = q->next;
q->next = p;
return head;
}
q = q->next;
}
q->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return head;
}
int main(){
linklist *l = CreateLinklist();
printf("All elements in the single linked list are:");
PrintLinklist(l);
printf("\n Please enter the data field of the new node you want to insert:");
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("After inserting a new node, all elements in the single linked list are:");
SearchAndInsert(l,x);
PrintLinklist(l);
return 0;
}
Operation results:
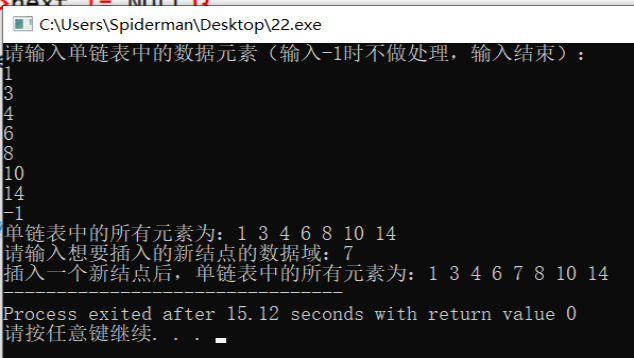
analysis:
The time complexity and space complexity of the SearchAndInsert function used to insert according to the problem-solving idea in the program are linear order O (n).
(3) : write the sub function to realize the local inversion of the leading node single linked list, and write the main function test results.
Let's talk about how I implement inversion:
(the method is not the only one. If there are good methods, please add them.)
/*
The basic idea is to put one node at a time behind the head node in order
If the elements in the input single linked list are 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, that is:
The original single linked list is: head - > 3 - > 4 - > 5 - > 6 - > 7 - > 0 - > null, then:
After the first cycle, the single linked list becomes: head - > 4 - > 3 - > 5 - > 6 - > 7 - > 0 - > null
After the second cycle, the single linked list becomes: head - > 5 - > 4 - > 3 - > 6 - > 7 - > 0 - > null
After the third cycle, the single linked list becomes: head - > 6 - > 5 - > 4 - > 3 - > 7 - > 0 - > null
After the fourth cycle, the single linked list becomes: head - > 7 - > 6 - > 5 - > 4 - > 3 - > 0 - > null
After the fifth cycle, the single linked list becomes: head - > 0 - > 7 - > 6 - > 5 - > 4 - > 3 - > null
To sum up, inversion is successfully realized.
*/
Implementation code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}linklist;
linklist *CreateLinklist(){
linklist *head,*p,*s;
head = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
p = head;
printf("Please enter the data elements in the single linked list (input)-1 Do not process when entering (end):\n");
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
while (x != -1){
s = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
s->data = x;
p->next = s;
p = s;
scanf("%d",&x);
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
};
void PrintLinklist(linklist *head){
linklist *t = head->next;
if (t == NULL){
printf("The single linked table is empty!\n");
}
while(t != NULL){
printf("%d ",t->data);
t = t->next;
}
}
linklist *ReverseLinklist(linklist *head){
linklist *p,*q;
p = head->next;
if (p == NULL){
return head;
}
q = p->next;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p->next = q->next;
q->next = head->next;
head->next = q;
do{
q = q->next;
}while(q != p->next);
}
return head;
}
int main(){
linklist *l = CreateLinklist();
printf("Before inversion,All elements in the single linked list are:");
PrintLinklist(l);
printf("\n After inversion,All elements in the single linked list are:");
ReverseLinklist(l);
PrintLinklist(l);
return 0;
}
Operation results:

analysis:
In this program, the time complexity of the local inverse sub function of the leading node single linked list is square order O (n) ²), The space complexity is linear order O (n).
2. It is known that the pointers LA and LB respectively point to the first element of the two headless single linked lists. It is required to compile an algorithm to delete a total of len elements from the i-th element in the table LA and insert them before the j-th element in the table lb.
Implementation code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}linklist;
linklist *CreateLinklist(){
linklist *head,*p,*s;
head = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
p = head;
printf("Please enter the data elements in the single linked list (input)-1 Do not process when entering (end):\n");
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
if (x != -1){
p->data = x;
}else{
p = NULL;
return head;
}
scanf("%d",&x);
while (x != -1){
s = (linklist *)malloc(sizeof(linklist));
s->data = x;
p->next = s;
p = s;
scanf("%d",&x);
}
p->next = NULL;
return head;
};
void PrintLinklist(linklist *head){
linklist *t = head;
if (t == NULL){
printf("The single linked table is empty!\n");
}
while(t != NULL){
printf("%d ",t->data);
t = t->next;
}
}
linklist *Get(linklist *head,int i){
int j = 1;
linklist *p = head;
while ((p->next != NULL)&&(j < i)){
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if (j == i){
return p;
}else{
return NULL;
}
}
linklist *DeleteAndInsert(linklist *LA,linklist *LB,int i,int j,int len){
linklist *p = LA,*q = LB,*m = NULL,*r = NULL,*s = NULL,*t = NULL;
if (i <= 0 || j <= 0 || len <= 0){
printf("Unable to delete and insert!");
return NULL;
}
m = Get(p,i-1);
if (m != NULL){
while (len > 0){
s = m->next;
m->next = s->next;
free(s);
len--;
}
}else{
printf("Single linked list LA Section in i Nodes do not exist!");
return NULL;
}
while (m->next != NULL){
m = m->next;
}
t = Get(q,j-1);
if (t != NULL){
m->next = t->next;
t->next = LA;
}else{
printf("Single linked list LB Section in j Nodes do not exist!");
return NULL;
}
return LB;
}
int main(){
int i,j,len;
printf("Create single linked list LA\n");
linklist *LA = CreateLinklist();
printf("Create single linked list LB\n");
linklist *LB = CreateLinklist();
printf("Single linked list LA All elements in are:");
PrintLinklist(LA);
printf("\n Single linked list LB All elements in are:");
PrintLinklist(LB);
printf("\n Please enter i,j and len Value of:\n");
scanf("%d %d %d",&i,&j,&len);
printf("From single linked list LA Deleted from page%d Elements in total%d Elements,Insert into single linked list LB pass the civil examinations%d Before the first element.",i,len,j);
LB = DeleteAndInsert(LA,LB,i,j,len);
printf("\n After the delete and insert operations are completed, the single linked list LB All elements in are:");
PrintLinklist(LB);
return 0;
}
Operation results:

analysis:
In this program, the time complexity and spatial complexity of the function used to obtain the pointer to the ith node in the headless node single linked list are linear order O (n). The time complexity of the function used to complete the deletion and insertion operations in this program is linear order O (n). Assuming that there are n elements in the single linked list LA and single linked list LB, the spatial complexity of the function is linear order O (n).