catalogue
Example 3-7 enter two integers and sum the squares
For example, calculate 4! The two phases of the project:
Nested calls to functions
Nested Call
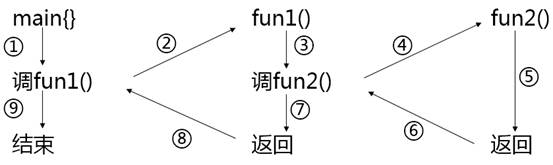
Example 3-7 enter two integers and sum the squares
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fun2(int m) {
return m * m;
}
int fun1(int x,int y) {
return fun2(x) + fun2(y);
}
int main() {
int a, b;
cout<<"Please enter two integers (a and b): ";
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "The sum of square of a and b: "
<< fun1(a, b) << endl;
return 0;
}Recursive call of function
definition
l} functions that call themselves directly or indirectly are called recursive calls.
Example: calculate n!
l) formula 1: n= n × (n-1) × (n-2) × (n-3) ×...× two × one
l) formula 2:
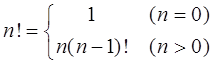
For example, calculate 4! The two phases of the project:
l) recurrence:
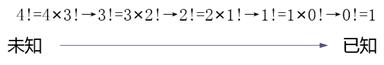
l) regression:
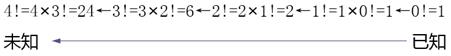
Example 3-8 find n!

Source code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
unsigned fac(int n){
unsigned f;
if (n == 0)
f = 1;
else
f = fac(n - 1) * n;
return f;
}
int main() {
unsigned n;
cout << "Enter a positive integer:";
cin >> n;
unsigned y = fac(n);
cout << n << "! = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}
Operation results:
Enter a positive integer:8 8! = 40320
Example 3-9 calculate the number of different combinations of k people selected from n people to form a committee by recursive method.
analysis
number of combinations selected from n individuals = number of combinations selected from n-1 individuals + number of combinations selected from n-1 individuals;
• when n = k or k = 0, the number of combinations is 1.
Source code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int comm(int n, int k)
{
if (k > n) return 0;
else if (n == k || k == 0)
return 1;
else return comm(n - 1, k) + comm(n - 1, k - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
cout << "C(n, k) = " << comm(n, k) << endl;
return 0;
}Operation results:
18 5 8568
Example 3-10 Hanoi Tower
There are three needles A, B and C. There are n plates on needle A, the large one is lower and the small one is upper. It is required to move the N plates from needle A to needle C. during the movement, needle B can be used to move only one plate at A time, and the large plate is lower and the small plate is upper on the three needles during the movement.
l) moving n plates from pin A to pin C can be divided into three steps:
N. move n-1 plates on A to pin B (with the help of pin C);
n. move the remaining plate on pin A to pin C;
N. move n-1 plates from pin B to pin C (with the help of pin A).
Source code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//Move the top plate of src needle to dest needle
void move(char src, char dest) {
cout << src << " --> " << dest << endl;
}
//Move n plates from src needle to dest needle, and use medium needle as transfer
void hanoi(int n, char src, char medium, char dest)
{
if (n == 1)
move(src, dest);
else {
hanoi(n - 1, src, dest, medium);
move(src, dest);
hanoi(n - 1, medium, src, dest);
}
}
int main() {
int m;
cout << "Enter the number of diskes: ";
cin >> m;
cout << "the steps to moving " << m << " diskes:" << endl;
hanoi(m, 'A', 'B', 'C');
return 0;
}Operation results:
Enter the number of diskes:3 the steps to moving 3 diskes: A --> C A --> B C --> B A --> C B --> A B --> C A --> C
Parameter passing of function
- The storage unit of the formal parameter is allocated only when the function is called
- Arguments can be constants, variables, or expressions
- Argument type must match formal parameter
- Value transfer is the transfer of parameter values, that is, one-way transfer
- Reference passing can achieve two-way passing
- Constant reference as a parameter can ensure the security of argument data