catalogue
3, UDP programming server side
1.C # implements the console helloworld
2.C # implementation window helloworld
5, C # using UDP socket to send messages
6, The Form window program uses TCP communication
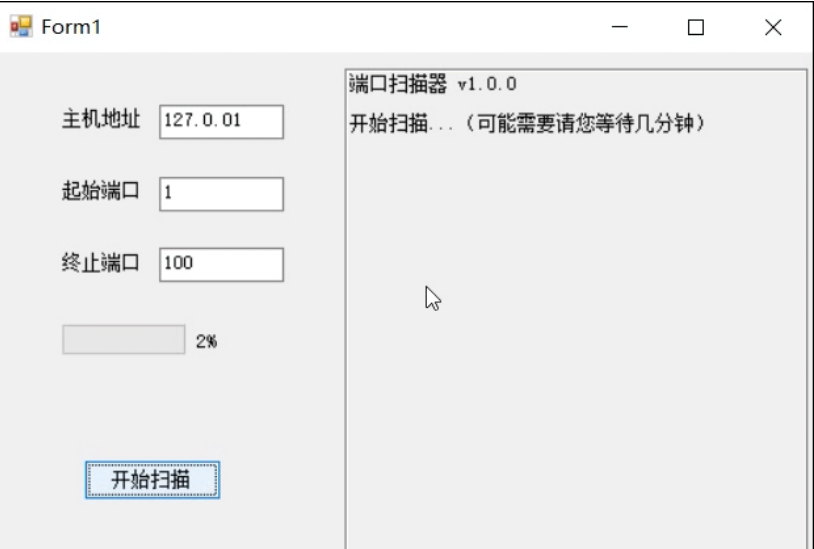
3) Write the port scanner program, and compare the effects of single process and multithreading.
1. The application of single thread creating form is the same as above. Interface design:
8, Capture packets via wireshark
1) Write a simple hello world program of command line / console in C#, Java or python to realize the following functions: continuously output 50 lines of "hello cqjtu! Re handover IOT level 2019" on the screen; At the same time, open a network UDP socket and send these 50 lines of messages to another roommate's computer
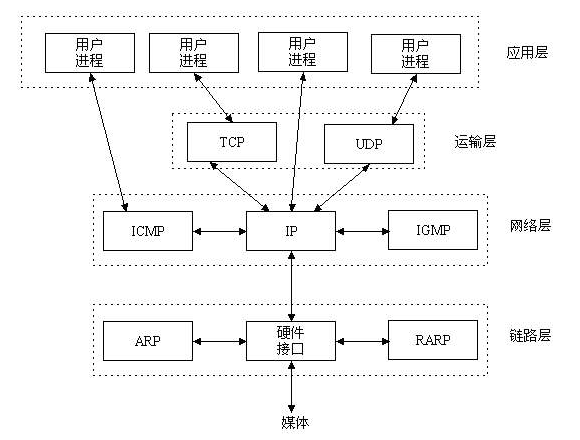
1, UDP
1. Introduction
UDP (User Data Protocol) is a protocol corresponding to TCP. It belongs to the TCP/IP protocol family.
2. Contact
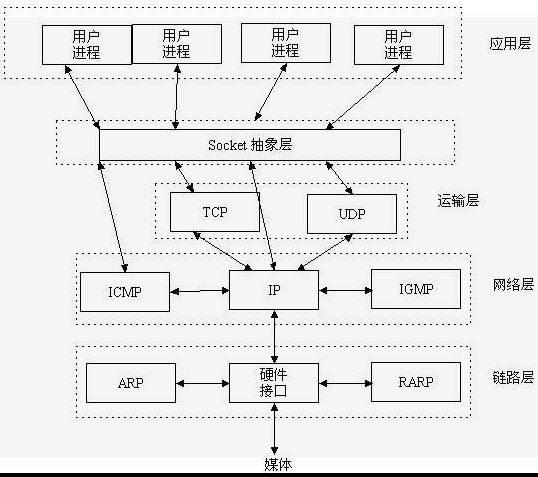
2, Socket
1. Introduction
The first use in networking was published on February 12, 1970 IETF RFC33 The authors are Stephen Carr, Steve Crocker and Vint Cerf. According to the records of the American Museum of computer history, Croker wrote: "all elements of the namespace can be called socket interfaces. A socket interface constitutes one end of a connection, and a connection can be completely specified by a pair of socket interfaces." the Museum of computer history added: "this is about 12 years earlier than the BSD socket interface definition.
Socket is the intermediate software abstraction layer for the communication between the application layer and the TCP/IP protocol family. It is a set of interfaces. In the design mode, socket is actually a facade mode. It hides the complex TCP/IP protocol family behind the socket interface. For users, a set of simple interfaces is all. Let the socket organize data to comply with the specified protocol.
2. Principle
3, UDP programming server side
UDP protocol provides an end-to-end service different from TCP protocol. The end-to-end transmission service provided by UDP protocol is best effort, that is, UDP socket will transmit information as much as possible, but it does not guarantee that the information will successfully reach the destination address, and the order of information arrival is not necessarily consistent with its sending order.
Server side general steps of UDP programming
① Create a socket and use the function socket()
② Bind the IP address, port and other information to the socket, and use the function bind()
③ Receive data circularly, using the function recvfrom()
④ Close network connection
General steps of UDP programming client
① Create a socket and use the function socket()
② Set the IP address, port and other properties of the other party
③ Send data with the function sendto()
④ Close network connection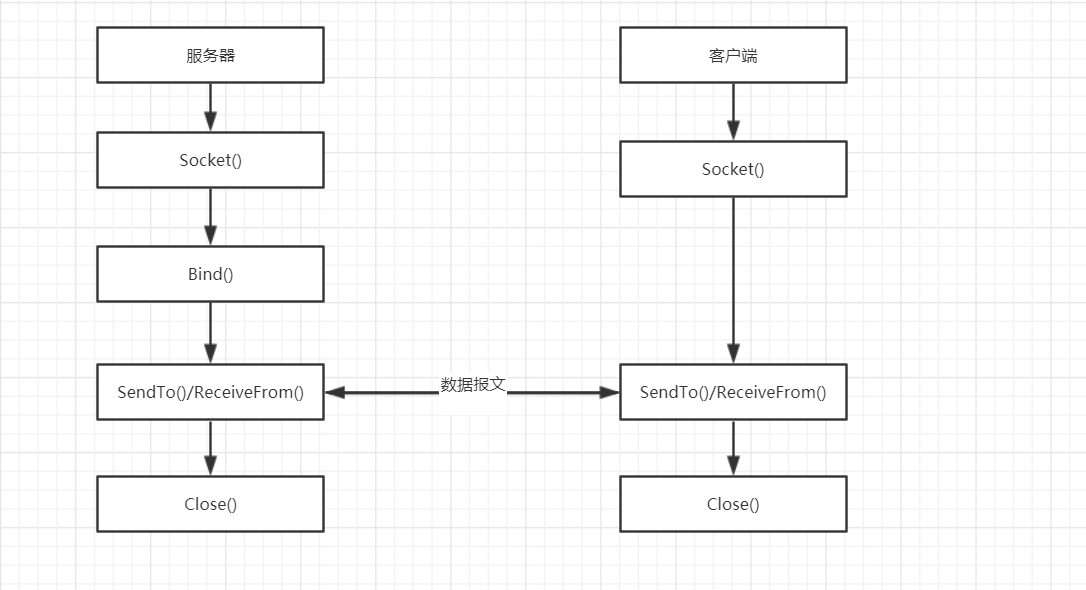
4, C # implements HelloWorld
Visual Studio 2019
1.C # implements the console helloworld
1. Open the software creation project
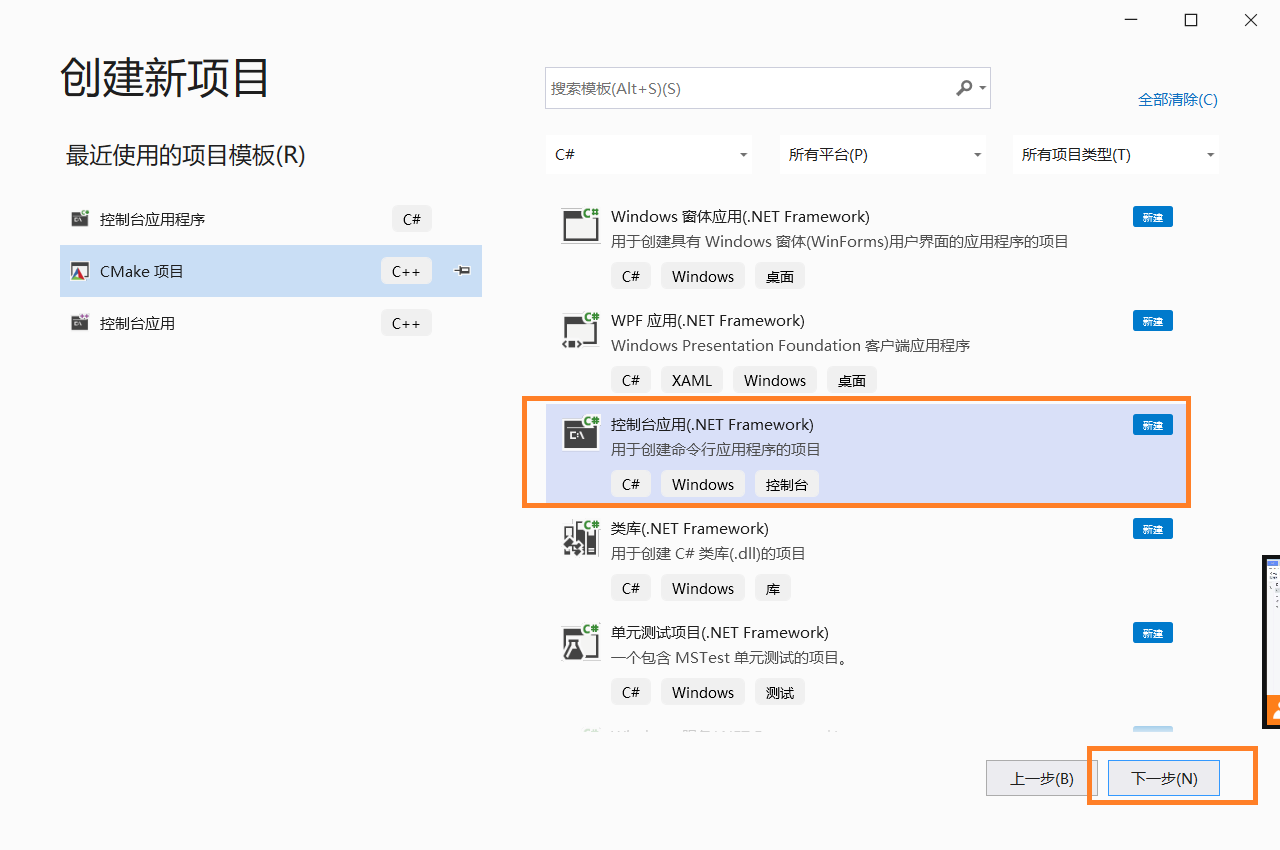
code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HelloWorldConsole
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Realize the output of helloworld statement, which is equivalent to printf in C language
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}
}
effect

2.C # implementation window helloworld
code
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace HelloworldWindow
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Click to add and display the actual data
showMsg();
}
void showMsg()
{
//Add HelloWorld to a text control
textBox1.AppendText("Hello World!" + "\t\n");
}
}
}
2) Use VS2017/2019 C# to write a simple Form window program, with a text box textEdit and a send button. After running the program, you can enter text in the text box, such as "hello cqjtu! Resubmit IOT 2019", click the button to send these text to your roommate's computer, using UDP socket;
5, C # using UDP socket to send messages
1. Create project
2. Server code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace UDP
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int recv;
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
//Get the local IP and set the TCP port number
IPEndPoint ip = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 8001);
Socket newsock = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Dgram, ProtocolType.Udp);
//Bind network address
newsock.Bind(ip);
Console.WriteLine("This is a Server, host name is {0}", Dns.GetHostName());
//Waiting for client connection
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for a client");
//Get client IP
IPEndPoint sender = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 0);
EndPoint Remote = (EndPoint)(sender);
recv = newsock.ReceiveFrom(data, ref Remote);
Console.WriteLine("Message received from {0}: ", Remote.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data, 0, recv));
//After the client connection is successful, send a message
string welcome = "Hello ! ";
//Conversion between string and byte array
data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(welcome);
//Send message
newsock.SendTo(data, data.Length, SocketFlags.None, Remote);
while (true)
{
data = new byte[1024];
//Receive information
recv = newsock.ReceiveFrom(data, ref Remote);
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data, 0, recv));
//newsock.SendTo(data, recv, SocketFlags.None, Remote);
}
}
}
}
3. Client code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace UDPClient
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
string input, stringData;
//Build TCP server
Console.WriteLine("This is a Client, host name is {0}", Dns.GetHostName());
//Set the service IP (this IP address is the IP address of the server) and set the TCP port number
IPEndPoint ip = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("192.168.43.98"), 8001);
//Define network type, data connection type and network protocol UDP
Socket server = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Dgram, ProtocolType.Udp);
string welcome = "Hello! ";
data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(welcome);
server.SendTo(data, data.Length, SocketFlags.None, ip);
IPEndPoint sender = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 0);
EndPoint Remote = (EndPoint)sender;
data = new byte[1024];
//For non-existent IP addresses, add this line of code to remove the blocking mode restriction within the specified time
int recv = server.ReceiveFrom(data, ref Remote);
Console.WriteLine("Message received from {0}: ", Remote.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data, 0, recv));
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
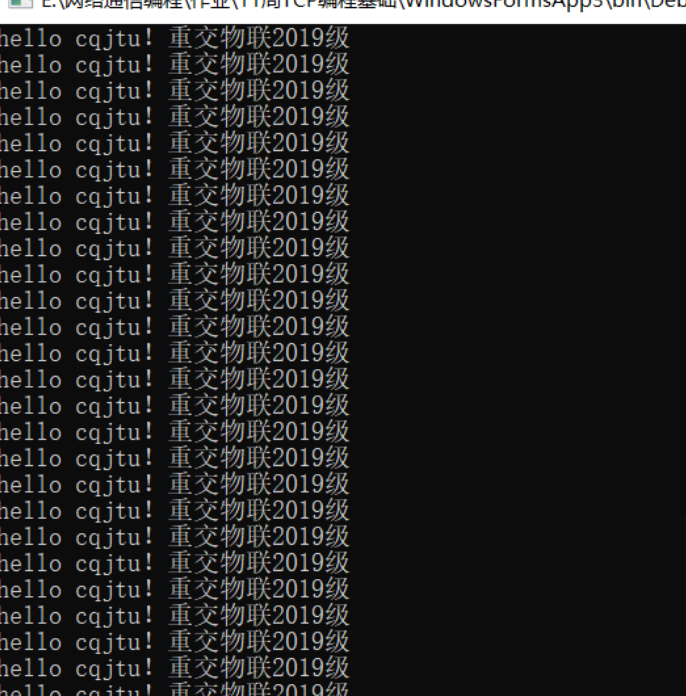
string s = "hello cqjtu!Heavy handed IOT class 2019"+i;
Console.WriteLine(s);
server.SendTo(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(s),Remote);
if(i==50)
{
break;
}
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Stopping Client.");
server.Close();
}
}
}
4. Operation results
6, The Form window program uses TCP communication
1. Create client project
2. Client design interface
Open the toolbox and drag 2 textboxes and 1 Button control from the toolbox
Set input box properties
Set message display interface properties
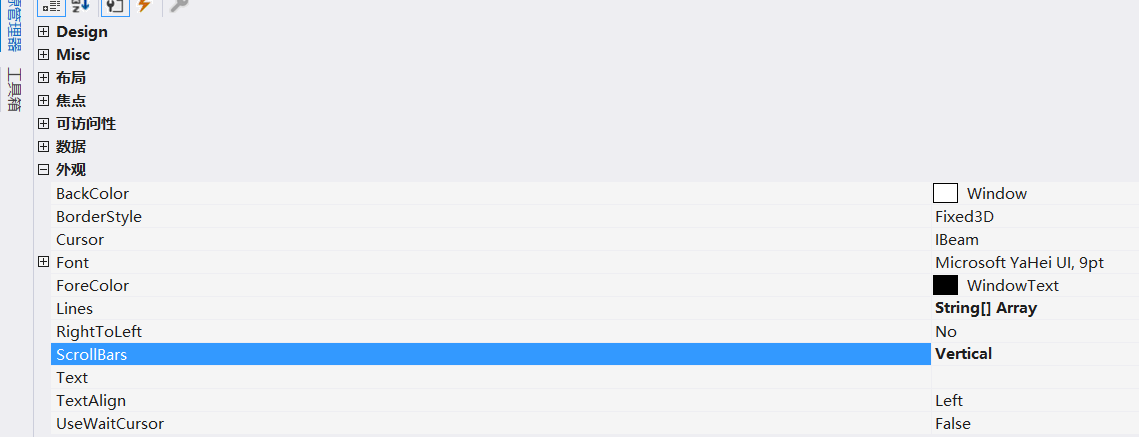
Add Vertical scroll bar: find the ScrollBars property and set the parameter to Vertical
Set send message button properties:
Set form properties
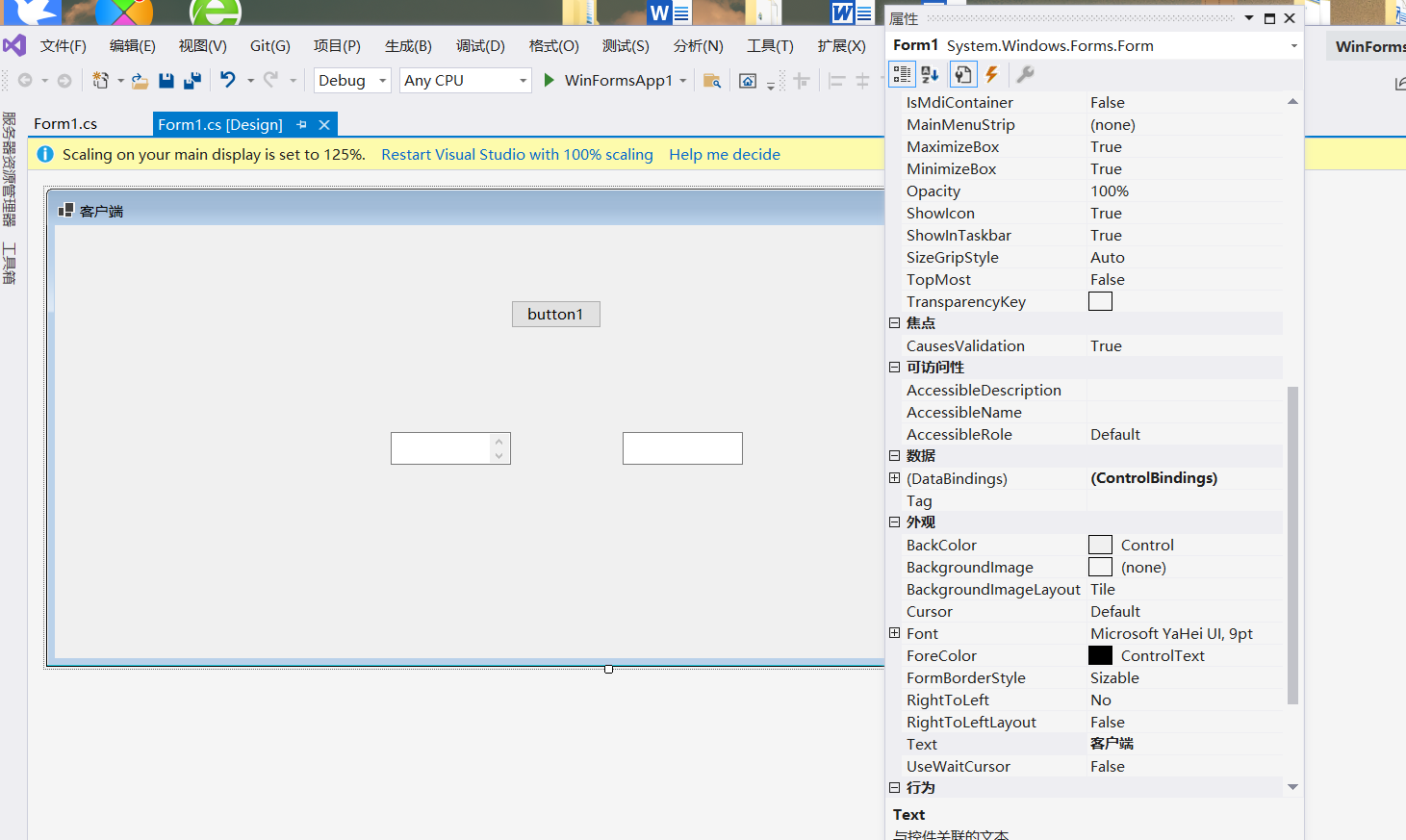
Client code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Form window TCP_signal communication
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
/*
* Displays the current time
*/
string str = "The current time: ";
str += DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
/*
* Prepare for connection
*/
int port = 2000;
string host = "10.61.170.2";//My roommate's IP address
IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse(host);
IPEndPoint ipe = new IPEndPoint(ip, port);//Convert ip and port to IPEndPoint instance
Socket c = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);//Create a Socket
/*
* Start connection
*/
str = "Connect to server...";
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
c.Connect(ipe);//Connect to server
/*
*send message
*/
string sendStr = textBox2.Text;
str = "The message content: " + sendStr;
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
byte[] bs = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(sendStr);
str = "Send the message to the server...";
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
c.Send(bs, bs.Length, 0);//Send message
/*
* Receive feedback from the server
*/
string recvStr = "";
byte[] recvBytes = new byte[1024];
int bytes;
bytes = c.Receive(recvBytes, recvBytes.Length, 0);//Receive the returned information from the server
recvStr += Encoding.UTF8.GetString(recvBytes, 0, bytes);
str = "The server feedback: " + recvStr;//Display server return information
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
/*
* Close socket
*/
c.Close();
}
catch (ArgumentNullException f)
{
string str = "ArgumentNullException: " + f.ToString();
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
}
catch (SocketException f)
{
string str = "ArgumentNullException: " + f.ToString();
textBox1.AppendText(str + Environment.NewLine);
}
textBox1.AppendText("" + Environment.NewLine);
textBox2.Text = "";
}
}
}
Server side code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp3
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*
* Prepare for connection
*/
int i = 0;
int port = 2000;
string host = "10.61.170.2";
IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse(host);
IPEndPoint ipe = new IPEndPoint(ip, port);
Socket s = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);//Create a Socket class
s.Bind(ipe);//Bind 2000 port
/*
* Loop listening and processing messages
*/
while (true)
{
i++;
try
{
Console.WriteLine("\t-----------------------------------------------");
Console.Write("Perform operations {0} :", i);
s.Listen(0);//Start listening
Console.WriteLine("1. Wait for connect...");
/*
* Instance a new socket port
*/
Socket temp = s.Accept();//Create a new Socket for the new connection.
Console.WriteLine("2. Get a connect");
/*
* Receive the message sent by the client and decode it
*/
string recvStr = "";
byte[] recvBytes = new byte[1024];
int bytes;
bytes = temp.Receive(recvBytes, recvBytes.Length, 0);//Receive information from client
recvStr += Encoding.UTF8.GetString(recvBytes, 0, bytes);
Console.WriteLine("3. Server Get Message:{0}", recvStr);//Display the information from the client
/*
* Returns the message of successful connection to the client
*/
string sendStr = "Ok!Client send message sucessful!";
byte[] bs = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(sendStr);
temp.Send(bs, bs.Length, 0);//Return client success information
/*
* Close port
*/
temp.Close();
Console.WriteLine("4. Completed...");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("");
//s.Close(); / / close the socket (because it is in an endless loop, there is no need to write, but if it is a single receive instance, close the socket after completing the task)
}
catch (ArgumentNullException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("ArgumentNullException: {0}", e);
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("SocketException: {0}", e);
}
}
}
}
}
function
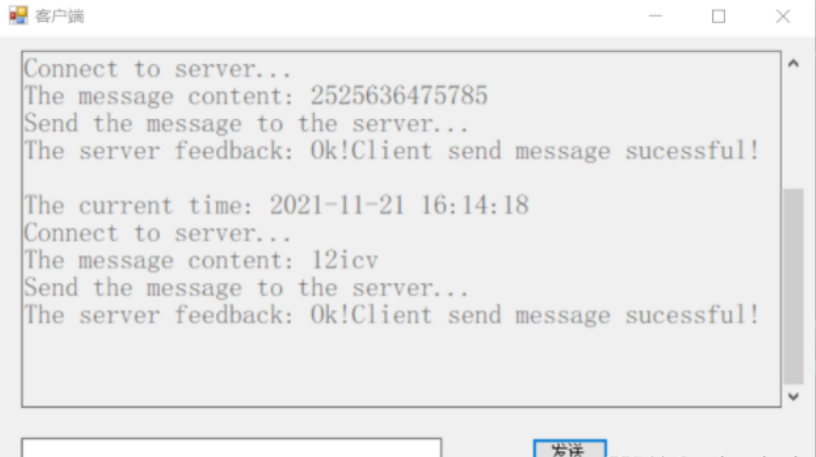
3) Write the port scanner program, and compare the effects of single process and multithreading.
7, Port scanner
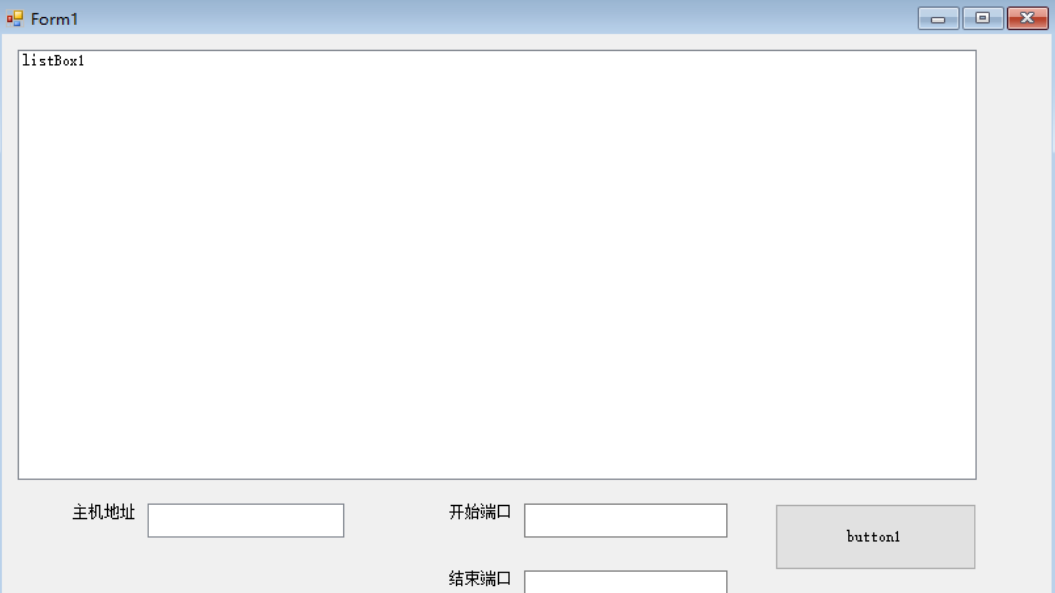
1. Single thread
The application of creating form is the same as above. Interface design:
code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Scan1
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//Custom variable
private int port;//Record the port number of the current scan
private string Address;//Record the scanned system address
private bool[] done = new bool[65536];//Record the open status of the port
private int start;//Record the starting port of the scan
private int end;//Record the end port of the scan
private bool OK;
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label4.Text = textBox2.Text;
label5.Text = textBox3.Text;
progressBar1.Minimum = Int32.Parse(textBox2.Text);
progressBar1.Maximum = Int32.Parse(textBox3.Text);
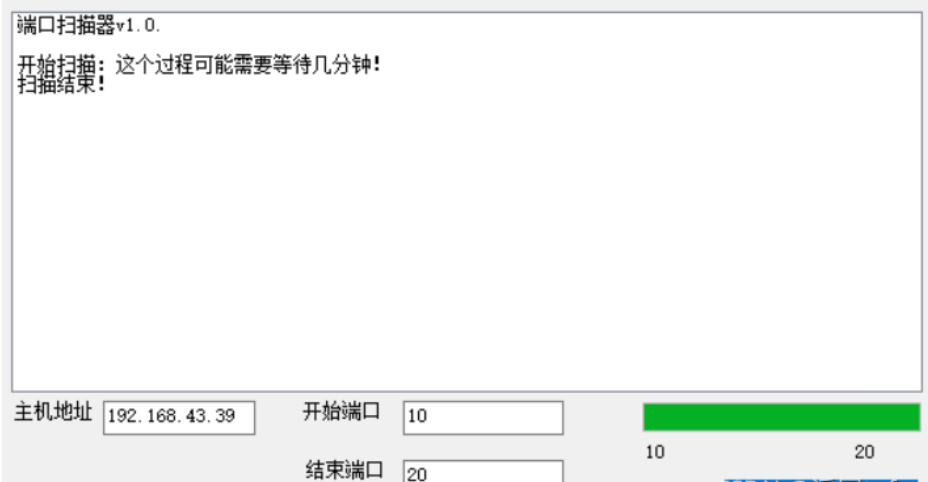
listBox1.Items.Clear();
listBox1.Items.Add("Port scanner v1.0.");
listBox1.Items.Add("");
PortScan();
}
private void PortScan()
{
start = Int32.Parse(textBox2.Text);
end = Int32.Parse(textBox3.Text);
//Determine whether the input port is legal
if ((start >= 0 && start <= 65536) && (end >= 0 && end <= 65536) && (start <= end))
{
listBox1.Items.Add("Start scanning: this process may take a few minutes!");
Address = textBox1.Text;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
{
port = i;
Scan();
progressBar1.Value = i;
label5.Text = i.ToString();
}
while (!OK)
{
OK = true;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
{
if (!done[i])
{
OK = false;
break;
}
}
}
listBox1.Items.Add("End of scan!");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Input error, port range is[0,65536]");
}
}
//Connection port
private void Scan()
{
int portnow = port;
done[portnow] = true;
TcpClient objTCP = null;
try
{
objTCP = new TcpClient(Address, portnow);
listBox1.Items.Add("port" + portnow.ToString() + "to open up");
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
2. Multithreading
code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace muti_thread_port_scan
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//Custom variable
private int port;//Record the port number of the current scan
private string Address;//Record the scanned system address
private bool[] done = new bool[65536];//Whether the record port has been scanned
private int start;//Record the starting port of the scan
private int end;//Record the end port of the scan
private bool OK;
private Thread scanThread;
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void label4_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label4.Text = textBox2.Text;//Set the start port of the progress bar
}
private void label6_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label6.Text = textBox3.Text;//Set the termination port of the progress bar
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label4_TextChanged(sender, e);
label6_TextChanged(sender, e);
//Create thread
Thread procss = new Thread(new ThreadStart(PortScan));
procss.Start();
//Set the scope of the progress bar
progressBar1.Minimum = Int32.Parse(textBox2.Text);
progressBar1.Maximum = Int32.Parse(textBox3.Text);
//Initialization of display box
listBox1.Items.Clear();
listBox1.Items.Add("Port scanner v1.0");
listBox1.Items.Add(" ");
}
private void PortScan()
{
start = Int32.Parse(textBox2.Text);
end = Int32.Parse(textBox3.Text);
//Check the validity of the port
if ((start >= 0 && start <= 65536) && (end >= 0 && end <= 65536) && (start <= end))
{
Invoke(new Action(() => {//Modify the interface in the thread
listBox1.Items.Add("Start scanning: this process may take a few minutes!");
}));
Address = textBox1.Text;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
{
port = i;
//The thread that scanned the port
scanThread = new Thread(Scan);
scanThread.Start();
//Sleep thread
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100);
Invoke(new Action(() => {//Modify the interface in the thread
progressBar1.Value = i;
label5.Text = i.ToString();
}));
}
//When not completed
while (!OK)
{
OK = true;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
{
if (!done[i])
{
OK = false;
break;
}
}
}
Invoke(new Action(() => {//Modify the interface in the thread
listBox1.Items.Add("End of scan!");
}));
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
else
{
Invoke(new Action(() => {//Modify the interface in the thread
MessageBox.Show("Input error, port range is[0,65536]");
}));
}
}
private void Scan()
{
int portnow = port;
//Create thread variable
Thread Threadnow = scanThread;
done[portnow] = true;
//Create a TcpClient object, which is used to provide client connection for TCP network service
TcpClient objTCP = null;
//Scan the port and write the information if successful
try
{
objTCP = new TcpClient(Address, portnow);
Invoke(new Action(() => {//Modify the interface in the thread
listBox1.Items.Add("port" + portnow.ToString() + "to open up!");
}));
objTCP.Close();
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
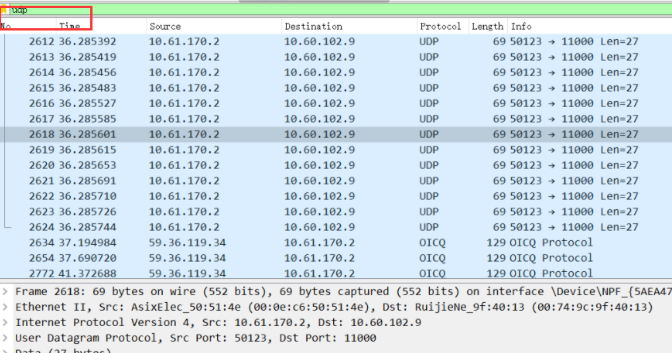
4) Install wireshark packet capturing software, capture the network packet sent by the above program, and analyze the data frame structure
8, Capture packets via wireshark
Version:
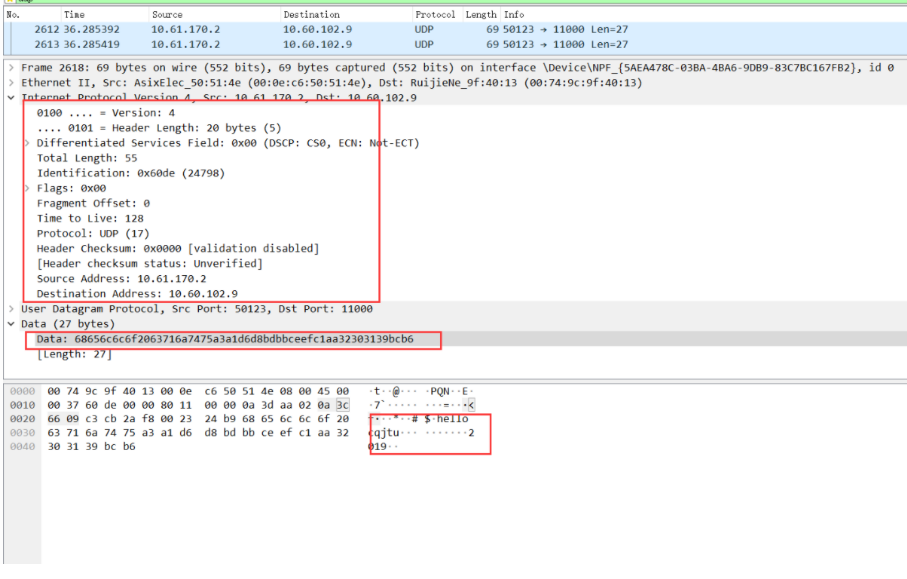
It is divided into IPv4 and IPv6, which are commonly used now, so the value is 4, 1 byte; HLen (ip header length):
Header length of 32-bit word (HLEN); TOS (level):
The service type describes how datagrams will be processed, such as priority sending. Most of them default to 0; Datagram Total Length:
Packet length identifier including header and data:
Unique IP packet value; Flags:
It indicates whether data is segmented. I send multiple data packets one by one. The data of each packet is very small and has not been segmented, so the value here is 0. Fragmentation Offset:
If the data packet is too large when it is loaded into the frame, it needs to be segmented and reorganized. There are no segments here, so the offset is 0; TTL (survival time):
The lifetime is a setting built inside the packet when it is generated. If the packet still does not reach its destination when the TTL expires, it will be discarded. This setting will prevent the IP packet from cycling in the network when looking for the destination. Its value will be reduced by one every time it passes through a router. Here, its value is 128, That is, 128 survival periods; Protocol:
The port of the upper layer protocol (TCP is port 6; UDP is port 17) also supports network layer protocols, such as ARP and ICMP. Here, the value is 17, that is, UDP protocol; Header Checksum:
Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for header only; Source Address:
The ip address of the message sender, here is 10.60.191.19; Destination Address:
The ip address of the message receiver, here is 10.60.202.32; The sixth line of the ip header:
It is used for network detection, debugging, security and more, but it defaults to 0 in most cases; Data packet:
Obviously, the length is 34 bytes, and the corresponding hexadecimal is the blue area. This is the data we want to send: line n: hello cqjtu! Heavy handed IOT class 2019
9, Summary
Learn more about the protocol through the practice of udp socket
Explanation of socket principle_ Tony Jiang's blog - CSDN blog_ socket